Prisma AIRS
Onboard AWS Cloud Account in Strata Cloud Manager
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma AIRS Docs
Onboard AWS Cloud Account in Strata Cloud Manager
Onboard your AWS cloud account in Strata Cloud Manager.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
Onboard AWS cloud account in Strata Cloud Manager. Create and download an onboarding
Terraform template. When you apply this template in your cloud environment, it
generates a service account with sufficient permissions. These permissions enable
discovery within your cloud environment, granting access to network flow logs, asset
inventory details, and other essential cloud resources.
If you are using AI Agent Discovery, you need to onboard a
new Terraform template. When you apply this template in your cloud environment, it
generates a service account with sufficient permissions. These permissions enable AI
Agent Discovery within your cloud environment, granting access to network flow logs,
asset inventory details, and other essential cloud resources. See the section Download New
Terraform for AI Agent Discovery.
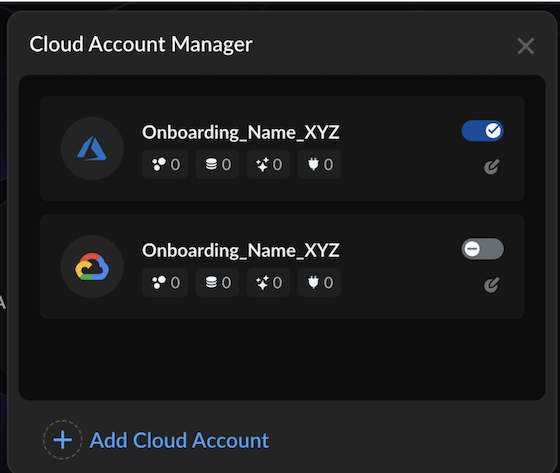
- Log in to Strata Cloud Manager.Select AI Security → AI Runtime→ AI Runtime Firewall. (If you are onboarding for the first time, click Get Started.If you have previously onboarded a cloud account; from the top right corner, click the Cloud Account Manager (cloud) icon.
![]() Select Cloud Service Provider as AWS and select Next.
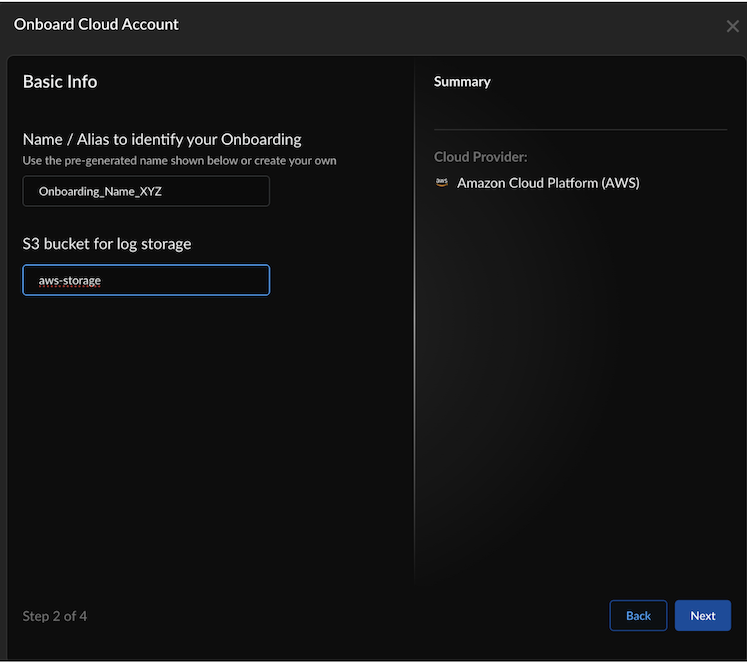
Select Cloud Service Provider as AWS and select Next.![]() Enter basic information:
Enter basic information:![]()
- A unique Name to identify your onboarded cloud account. (Limit the name to 32 characters).
- Select Next.
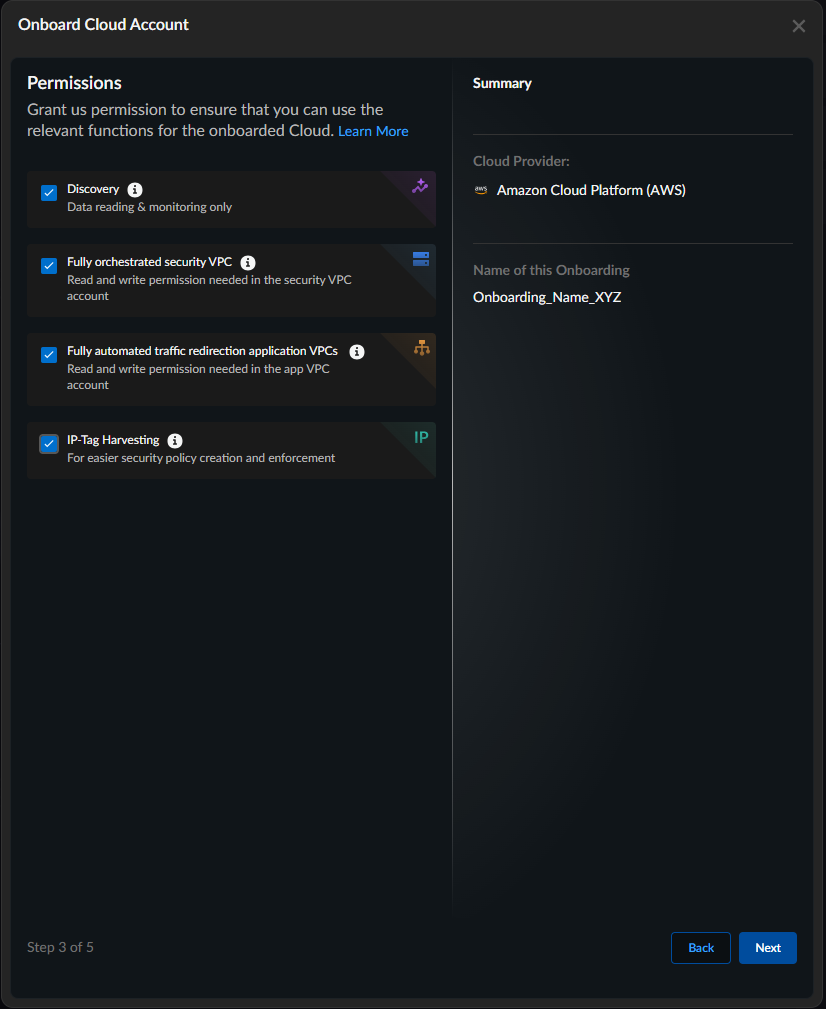
Specify the permissions to apply to this AWS account. For a list of the specific permissions enabled, see AWS Required Permissions.- Discovery—this option is pre-selected and cannot be disabled. This allows Prisma AIRS to identify and monitor assets in your AWS environment.
- Fully orchestrated security VPC—provides the necessary permissions for Prisma AIRS to read and write in your security VPC account.
- Fully automated traffic redirection application VPCs—provides the necessary permissions for Prisma AIRS to read and write in your application VPC account. Fully automated traffic redirection application VPCs requires that you enable Fully orchestrated security VPC.
- IP-Tag Harvesting—grants the necessary permissions to collect IP address-to-tag information to enforce tag-based security policy that adapts to IP address changes in your AWS environment.
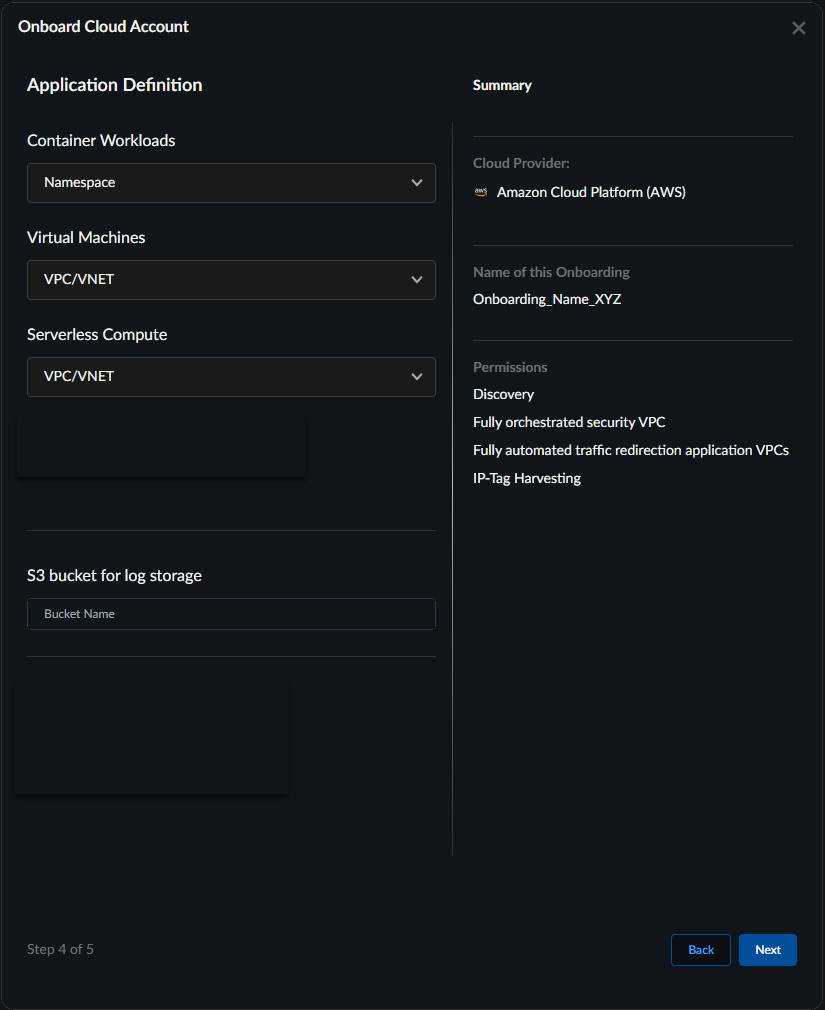
![]() In Application Definition, configure how your assets will be grouped for discovery.
In Application Definition, configure how your assets will be grouped for discovery.- Your selected application boundaries determine which applications appear in the deployment workflow. For all workload types, Prisma AIRS AI Runtime firewall maps applications to their VPCs, and the firewall protects traffic at the VPC level. The namespace shows applications from Pods/Cluster workloads, while VPC/VNETs display applications from virtual machine workloads.
- For container workloads, regardless of the application definition method you select (namespace, cluster, or tag), please annotate all pods if you want to add protection with the Palo Alto Networks-specific label "paloaltonetworks.com/firewall": "pan-fw". This annotation is needed to secure the pods, in addition to defining the application boundaries.
- Enhanced application definition options provide granular boundary criteria using workload-specific methods such as tags, subnets, and namespaces that align with your application deployment patterns and business logic.When using tag-based application boundaries, if your cloud provider allows tags with only keys (no values), you should use the application name as the tag key.
Workloads Application Definition Method Choose When Container Workloads(Default boundary: namespace)- Namespace
- Cluster Name
- Tag
- Applications are separated by Kubernetes namespaces for logical isolation.
- Applications span multiple namespaces but remain within a single cluster.
- Applications require custom grouping based on business logic, regardless of infrastructure.
Virtual Machines(Default boundary: VPC/VNET)- Subnet Name
- VPC/VNET
- Tag
- VMs are organized by network segments that align with application boundaries.
- You prefer a broader network perimeter-based application grouping (default).
- Uses key-value pairs for business-context-driven application organization.
Serverless Compute(Default boundary VPC/VNET)- Subnet Name
- VPC/VNET
- Tag
- Functions are deployed in specific subnet boundaries within the application domain.
- You want to group all functions within the same network level using VPC/VNET boundaries.
- Uses key-value pairs for flexible business requirement-based grouping.
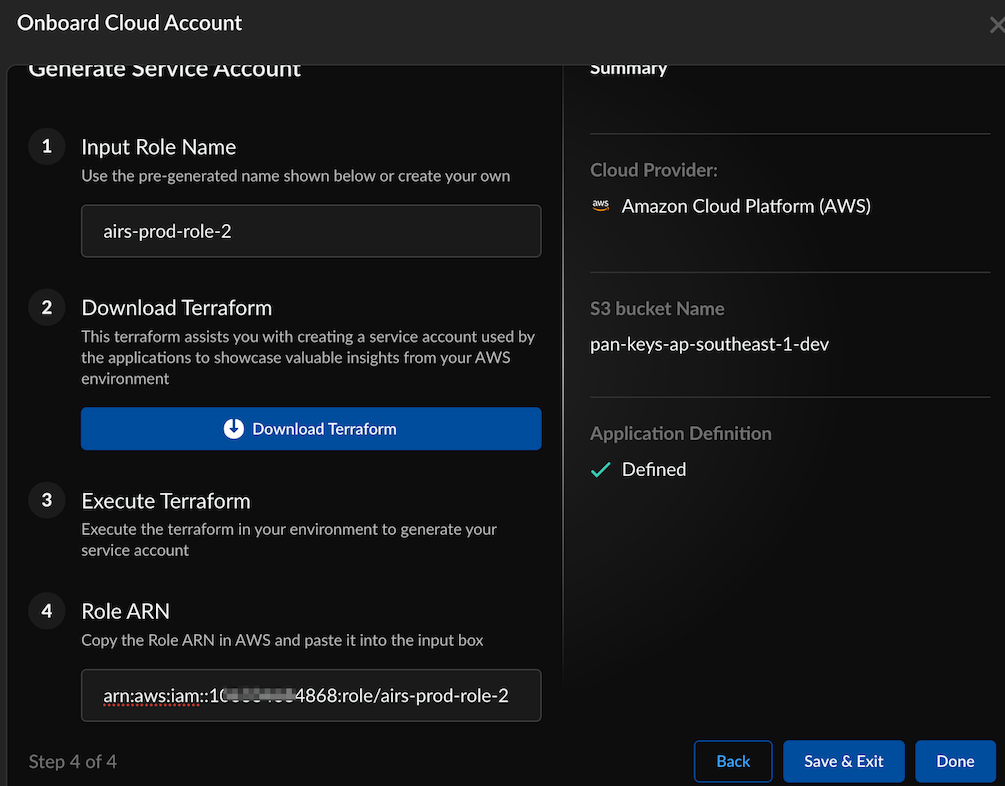
Enter the name (limit the name to 32 characters) of the S3 Bucket to use for log storage.To get the S3 bucket name, log in to AWS Management Console. Navigate to S3 bucket and copy your bucket name.Click Next.![]() Input Role Name (Use only alphanumeric characters and hyphens, avoid using a hyphen at the beginning or end, and limit the name to 19 characters).Download Terraform.
Input Role Name (Use only alphanumeric characters and hyphens, avoid using a hyphen at the beginning or end, and limit the name to 19 characters).Download Terraform.![]() Execute Terraform. Save and unzip the downloaded Terraform zip file: `aws-onboard-terraform.zip`. Navigate to `panw-discovery-10xxxx684868-onboarding/aws` and follow the `README.md` instructions to apply the Terraform in AWS to create the resources and add the role assignments.
Execute Terraform. Save and unzip the downloaded Terraform zip file: `aws-onboard-terraform.zip`. Navigate to `panw-discovery-10xxxx684868-onboarding/aws` and follow the `README.md` instructions to apply the Terraform in AWS to create the resources and add the role assignments.
Output:#Deploy the Terraform terraform init terraform plan terraform applyApply complete! Resources: 1 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed. Outputs: cross_account_role_arn = "arn:aws:iam::10xxxx684868:role/airs-prod-role-2"Copy the role ARN from the Terraform apply output in the previous step and paste it in the Role ARN field.Alternatively, you can also fetch the role ARN in the AWS Management Console. Navigate to IAM > Access Management > Roles, select the role name you entered in step 6 and copy the ARN from the summary page.Select Done.Add the following policy to enable Strata Cloud Manager to discover your Kubernetes clusters' assets:- Sign in to the Amazon EKS Console.Navigate to the EKS Console and click on your EKS cluster.In the Access tab, select the IAM access entries section. Click the Create access entry button.Find the IAM principal ARN role that was created as part of the onboarding process when you executed the onboarding Terraform.Add AmazonEKSAdminViewPolicy under Policy name.Click Create and finish the creation process.You can now view and manage the onboarded cloud accounts in Strata Cloud Manager.To discover your protected and unprotected cloud assets, see the page on discovering your cloud resources.This validates the successful creation of a service account in AWS.Initial data should populate on Strata Cloud Manager in about 30 minutes and the flow logs may have a delay of about an hour to show up on the Strata Cloud Manager dashboard.Next, protect the network traffic flow by deploying Prisma AIRS AI Runtime firewall or VM-Series firewall in AWS.
Download New Terraform for AI Agent Discovery
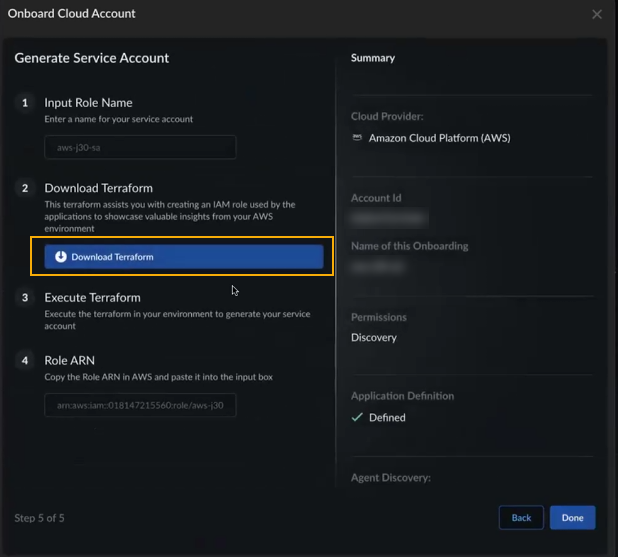
This section describes how to download an onboarding Terraform template when using AI Agent Discovery. When you apply this template in your cloud environment, it generates a service account with sufficient permissions. These permissions enable AI Agent Discovery within your cloud environment, granting access to network flow logs, asset inventory details, and other essential cloud resources.When you onboard an AWS cloud account, consider the following:- For new accounts, you'll need to onboard a cloud account if one is not present in the tenant.
- For existing accounts in an enabled state, you need to re-apply the
Terraform to provide AI Agent Discovery access for existing onboarded
accounts. This process updates the inline discovery permissions. To re-apply
the onboarding Terraform, refer to Step 12 (Download
Terraform) above:
![]()
- For existing accounts in a disabled state (that is, cloud accounts that are disabled), attempts to re-enable the account results in failed validation. To resolve this issue, download the onboarding Terraform before enabling the account again.