Example Admin Role Profile Construction
Table of Contents
Example Admin Role Profile Construction
This example shows an Admin Role profile for a Security Operations Center (SOC)
manager who needs access to investigate potential issues. The SOC Manager needs read
access to many areas of the firewall, but generally doesn’t need write access. The
example covers all four of the Admin Role Profile’s tabs and each step describes why
the profile enables or disables a particular area of access to the SOC manager.
This is an example profile for a fictional SOC manager. Configure Admin Role
profiles for your administrators based on the functions they manage and the
access required to do their job. Do not enable unnecessary access. Create
separate profiles for each administrative group that shares the same duties and
for administrators who have unique duties. Each administrator should have the
exact level of access required to perform their duties and no access beyond
that.
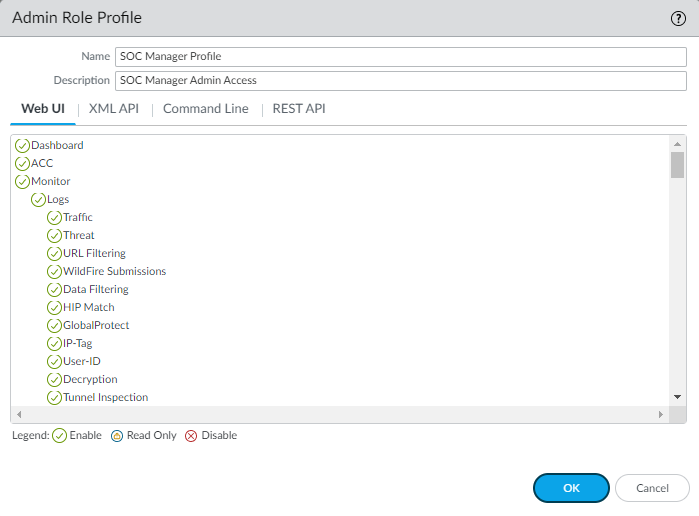
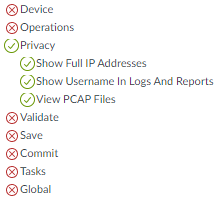
- Configure Web UI access permissions. Each snip of the Web UI screen shows a different area of Web UI permissions. Permissions are listed by firewall tab, in the order you see the tabs in the Web UI, followed by permissions for other actions.The Dashboard, ACC, and MonitorLogs areas of the firewall don’t contain configuration elements—all of the objects are informational (you can only toggle them between enable and disable because they are already read only). Because the SOC Manager needs to investigate potential issues, the SOC Manager needs access to the information on these tabs.The profile name and description make it easy to understand the profile’s objective. This snip doesn’t show all of the Logs permissions, but all of them are enabled for this profile.
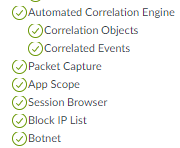
![]() The next snip shows permissions for more informational objects on the Monitor tab. The SOC Manager uses these tools to investigate potential issues and therefore requires access.
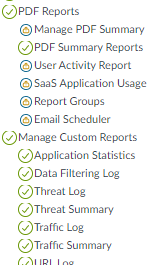
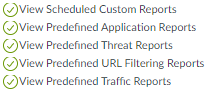
The next snip shows permissions for more informational objects on the Monitor tab. The SOC Manager uses these tools to investigate potential issues and therefore requires access.![]() The next two snips show permissions for PDF Reports, Custom Reports, and predefined reports on the Monitor tab. While the SOC Manager needs access to PDF reports to gather information, in this example, the SOC Manager does not need to configure reports, so access is set to read-only (summary reports are not configurable). However, the SOC Manager needs to manage custom reports to investigate specific potential issues, so full access permissions are granted for all custom reports (including those not shown in the snip). Finally the SOC Manager requires access to predefined reports for investigating potential issues.
The next two snips show permissions for PDF Reports, Custom Reports, and predefined reports on the Monitor tab. While the SOC Manager needs access to PDF reports to gather information, in this example, the SOC Manager does not need to configure reports, so access is set to read-only (summary reports are not configurable). However, the SOC Manager needs to manage custom reports to investigate specific potential issues, so full access permissions are granted for all custom reports (including those not shown in the snip). Finally the SOC Manager requires access to predefined reports for investigating potential issues.![]()
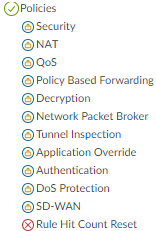
![]() Because the SOC Manager is an investigator and not an administrator who configures the firewall, permissions for the Policies tab are read-only, with the exception of resetting the rule hit count. Resetting the rule hit count is not one of the SOC Manager’s duties (and changing the hit count could adversely affect or confuse other administrators), so access is disabled. Read access enables the SOC Manager to investigate the construction of a policy that the SOC Manager suspects may have caused an issue.
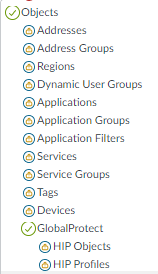
Because the SOC Manager is an investigator and not an administrator who configures the firewall, permissions for the Policies tab are read-only, with the exception of resetting the rule hit count. Resetting the rule hit count is not one of the SOC Manager’s duties (and changing the hit count could adversely affect or confuse other administrators), so access is disabled. Read access enables the SOC Manager to investigate the construction of a policy that the SOC Manager suspects may have caused an issue.![]() Permissions for the Objects tab are also read-only for the same reason—the SOC Manager’s job doesn’t require configuration, so no configuration permissions are assigned. For areas that aren’t included in the SOC Manager’s duties, access is disabled. In this example, the SOC Manager has read-only access to investigate objects configurations for all objects except URL Filtering, SD-WAN Link Management and Schedules, which are under the control of different administrators in this example.
Permissions for the Objects tab are also read-only for the same reason—the SOC Manager’s job doesn’t require configuration, so no configuration permissions are assigned. For areas that aren’t included in the SOC Manager’s duties, access is disabled. In this example, the SOC Manager has read-only access to investigate objects configurations for all objects except URL Filtering, SD-WAN Link Management and Schedules, which are under the control of different administrators in this example.![]()
![]()
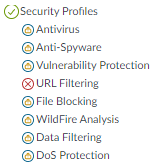
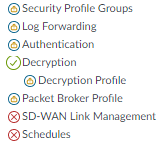
![]() For Network tab permissions, the scenario is similar: the SOC Manager doesn’t need to configure any of the objects, but may need information to investigate issues, so read-only access is assigned to the areas that the SOC Manager may need to investigate. In this example, access is disabled for QoS, LLDP, Network Profiles, or SD-WAN Interface profiles because these items are not part of the SOC Manager’s duties.
For Network tab permissions, the scenario is similar: the SOC Manager doesn’t need to configure any of the objects, but may need information to investigate issues, so read-only access is assigned to the areas that the SOC Manager may need to investigate. In this example, access is disabled for QoS, LLDP, Network Profiles, or SD-WAN Interface profiles because these items are not part of the SOC Manager’s duties.![]()
![]() In this example, the SOC Manager needs no access to the Device tab capabilities for investigative purposes, so all Device tab permissions are blocked. In addition, investigation doesn’t require commit actions or access to any of the remaining actions, so those permissions are also blocked.
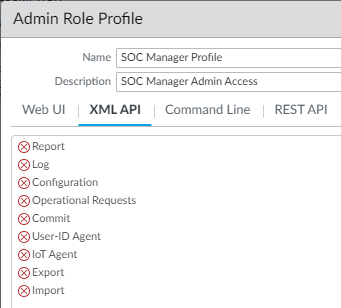
In this example, the SOC Manager needs no access to the Device tab capabilities for investigative purposes, so all Device tab permissions are blocked. In addition, investigation doesn’t require commit actions or access to any of the remaining actions, so those permissions are also blocked.![]() Configure XML API access permissions.The following snip shows that all XML API permissions are disabled for the SOC Manager because the SOC Manager doesn’t access the firewall using XML API commands.
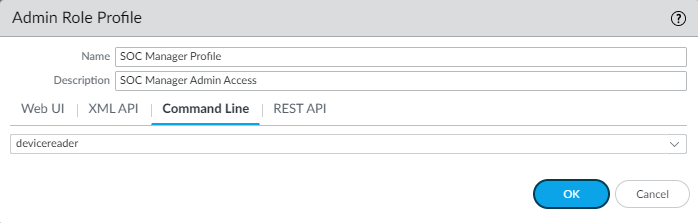
Configure XML API access permissions.The following snip shows that all XML API permissions are disabled for the SOC Manager because the SOC Manager doesn’t access the firewall using XML API commands.![]() Configure Command Line (CLI) access permissions.CLI access permissions are read-only for the SOC Manager because the SOC Manager needs access to logs and other monitoring tools and also needs to be able to see certain configurations in order to investigate potential issues. However, the SOC Manager doesn’t configure the firewall, so no configuration permissions are assigned. The access level is set to devicereader instead of to superreader because the SOC Manager doesn’t need access to password profiles or to other administrative accounts.
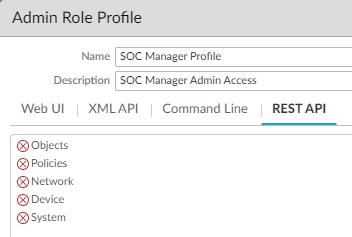
Configure Command Line (CLI) access permissions.CLI access permissions are read-only for the SOC Manager because the SOC Manager needs access to logs and other monitoring tools and also needs to be able to see certain configurations in order to investigate potential issues. However, the SOC Manager doesn’t configure the firewall, so no configuration permissions are assigned. The access level is set to devicereader instead of to superreader because the SOC Manager doesn’t need access to password profiles or to other administrative accounts.![]() Configure REST API access permissions.The SOC Manager doesn’t access the firewall using REST API commands, so all REST API access is disabled.
Configure REST API access permissions.The SOC Manager doesn’t access the firewall using REST API commands, so all REST API access is disabled.![]()