Prisma SD-WAN
Supported NAT Protocol Translation Types
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma SD-WAN Docs
-
-
- Prisma SD-WAN Controller
-
- CloudBlade Integrations
- CloudBlades Integration with Prisma Access
-
-
-
-
- 6.5
- 6.4
- 6.3
- 6.1
- 5.6
- Prisma SD-WAN Controller
- Prisma SD-WAN On-Premises Controller
- Prisma SD-WAN CloudBlades
- Prisma Access CloudBlade Cloud Managed
- Prisma Access CloudBlade Panorama Managed
Supported NAT Protocol Translation Types
Learn the different types of NAT Protocol Translations supported by Prisma SD-WAN.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
Prisma SD-WAN ION devices facilitate communication between different IP
address families by supporting various Network Address Translation (NAT) types. These
types are designed to handle specific translation scenarios, ensuring seamless network
interoperability.
- NAT64 – Translation between IPv6 clients and IPv4 servers
- XLAT464 – Stateful translation for IPv6-only networks accessing IPv4 resources
- NAT46 – Translation between IPv4 clients and IPv6 servers
- NAT66 – Translation between IPv6 subnets
NAT64: Connecting IPv6 Clients to IPv4 Servers
The primary purpose of NAT64 with DNS64 is to enable an IPv6-only client to
communicate with an IPv4-only server. It bridges the gap between the two distinct IP
protocols by translating addresses and facilitating DNS resolution.
The process relies on two key components: a DNS64 server and a NAT64 gateway.
- The IPv6 client sends a DNS query for a domain name to the DNS64 server.
- The DNS64 server discovers that the destination server only has an IPv4 address (an A record).
- It then synthesizes an IPv6 address (a AAAA record) by embedding the server's IPv4 address into a well-known IPv6 prefix, such as 64:ff9b::/96, and sends this back to the client.
- The IPv6 client sends its traffic to this synthesized IPv6 destination address.
- The NAT64 gateway receives this packet, removes the special prefix to recover the original IPv4 destination address, and translates the client's source IPv6 address to an IPv4 address from its NAT pool.
- The gateway then forwards the translated IPv4 packet to the IPv4 server.
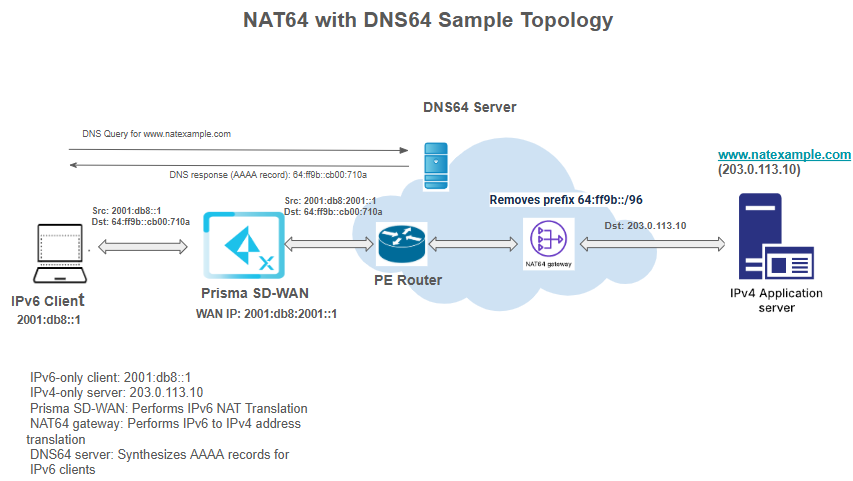
Workflow Example
- An IPv6 Client (2001:db8::1) wants to connect to www.natexample.com, which is an IPv4-only server at 203.0.113.10.
- The client queries the DNS64 server, which synthesizes and returns the AAAA record 64:ff9b::cb00:710a.
- The client sends an IPv6 packet with Source: 2001:db8::1 and Destination: 64:ff9b::cb00:710a.
- The Prisma SD-WAN device performs an initial translation, changing the source address to its WAN IP: 2001:db8:2001::1.
- The NAT64 gateway receives this packet. It removes the 64:ff9b::/96 prefix to get the destination 203.0.113.10 and translates the source address to 192.0.10.10 from its NAT pool.
- The final IPv4 packet (Source: 192.0.10.10, Destination: 203.0.113.10) is sent to the application server.
XLAT464
The XLAT464 use case allows an IPv4-only client to connect to an IPv4-only server by
traversing an IPv6-only network segment. It essentially encapsulates an IPv4
communication flow within an IPv6 transport layer.
This is a two-stage translation process involving a client-side translator and a
provider-side translator.
- The IPv4 client sends a standard IPv4 packet to the destination IPv4 server.
- A client-side translator (for example, Prisma SD-WAN) intercepts the packet. It performs source IPv4 to IPv6 translation and maps the destination IPv4 address into an IPv6 address using a well-known prefix (64:ff9b::/96).
- This newly created IPv6 packet is sent across the IPv6 network.
- A provider-side translator (a NAT64 gateway) receives the IPv6 packet. It performs the reverse operation: it removes the prefix to find the original IPv4 destination and translates the source IPv6 address back to an IPv4 address from its own NAT pool.
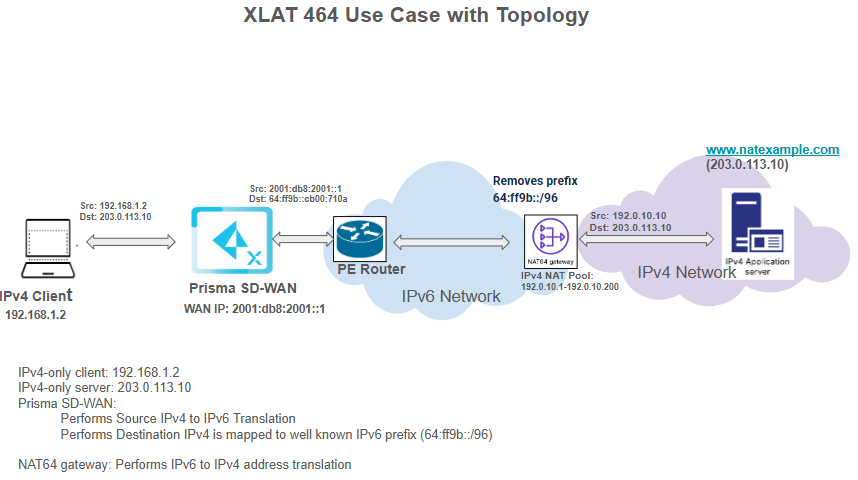
Workflow Example
- An IPv4 Client at 192.168.1.2 sends a packet to an IPv4 Application Server at 203.0.113.10.
- The Prisma SD-WAN device intercepts the IPv4 packet and translates it to IPv6. The new source is its WAN IP (2001:db8:2001::1), and the destination is the server's IPv4 mapped into the prefix (64:ff9b::cb00:710a).
- This IPv6 packet travels across the network to the NAT64 Gateway.
- The gateway translates the packet back to IPv4. The source becomes an address from its NAT pool (192.0.10.10), and the destination becomes the original server address (203.0.113.10) after stripping the prefix.
- The final IPv4 packet is delivered to the server.
NAT46: Connecting IPv4 Clients to IPv6 Servers
The goal of NAT46 with DNS64 is to allow an IPv4-only client to communicate with an
IPv6-only server.
This process is effectively the reverse of NAT64.
- The IPv4 client sends a standard DNS (A record) query for a domain.
- A device capable of DNS64 translation (like the Prisma SD-WAN) intercepts the query. It queries for the server's true AAAA record and then synthesizes an IPv4 address (A record) to send back to the client.
- The client sends an IPv4 packet to this synthesized IPv4 destination address.
- The NAT46 gateway (for example, Prisma SD-WAN) receives this packet and performs address translation: it translates the client's source IPv4 address to an IPv6 address and translates the synthesized destination IPv4 address back to the server's actual IPv6 address.
- The resulting IPv6 packet is forwarded to the IPv6 server.
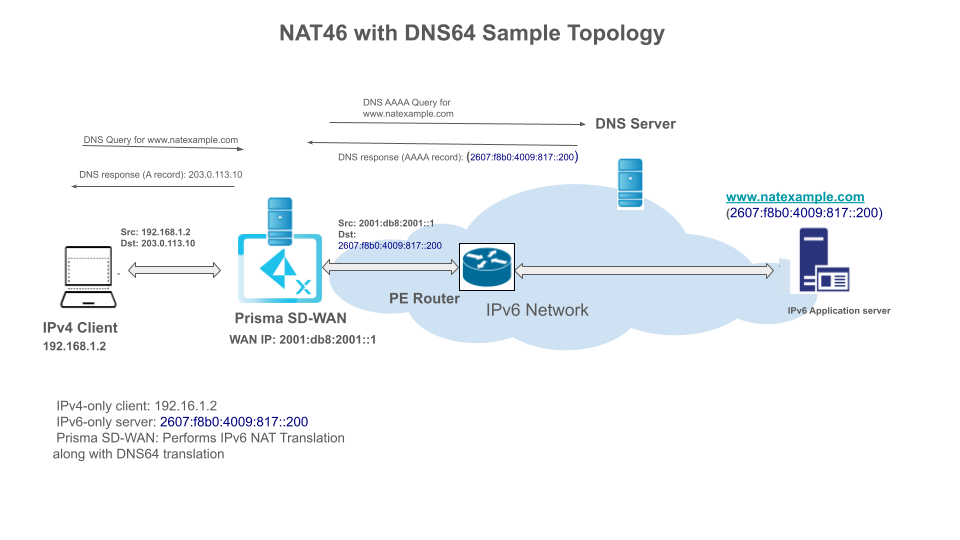
Workflow Example
- An IPv4 Client (192.16.1.2) wants to reach www.natexample.com, which is an IPv6-only server at 2607:f8b0:4009:817::200.
- The client sends a DNS query. The Prisma SD-WAN intercepts it, finds the AAAA record, and sends a synthesized A record (203.0.113.10) back to the client.
- The client sends an IPv4 packet with Source: 192.16.1.2 and Destination: 203.0.113.10.
- The Prisma SD-WAN performs NAT46 translation. The new packet has Source: 2001:db8:2001::1 (its WAN IP) and Destination: 2607:f8b0:4009:817::200.
- This translated IPv6 packet is sent to the server.
NAT66: Internal IPv6 Address Management
NAT66 is used to translate between IPv6 address spaces, enabling an IPv6-only client
to communicate with an IPv6-only server through a NAT gateway. This is often used to
map private or internal IPv6 addresses to a public-facing IPv6 address, hiding the
internal network structure.
The mechanism is a straightforward network address translation for IPv6.
- An IPv6 client sends a packet from its source address to a destination IPv6 server.
- A NAT66 gateway (for example, Prisma SD-WAN) on the edge of the network intercepts the outgoing packet.
- It translates the source IPv6 address to its own external WAN IPv6 address. The destination address of the server remains unchanged.
- The gateway forwards the packet with the new source address to the destination server. Return traffic is translated in the reverse direction.
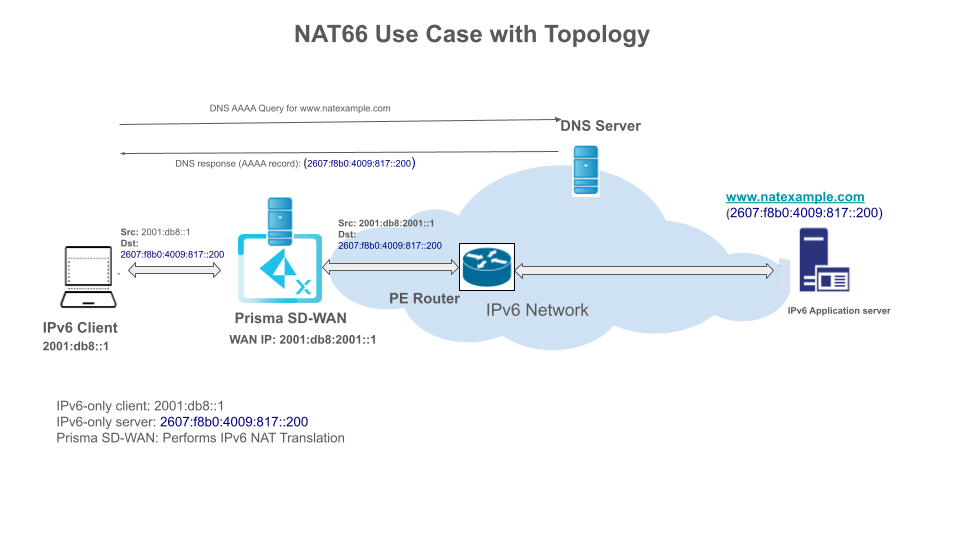
Workflow Example
- An IPv6 Client (2001:db8::1) sends a packet to an IPv6 Application Server at 2607:f8b0:4009:817::200.
- The initial packet has Source: 2001:db8::1 and Destination: 2607:f8b0:4009:817::200.
- The Prisma SD-WAN intercepts the packet and performs NAT66, changing the source address to its own WAN IP.
- The final packet sent to the server has Source: 2001:db8:2001::1 and Destination: 2607:f8b0:4009:817::200.
