Prisma SD-WAN
Configure VLAN on Switch Ports
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma SD-WAN Docs
-
-
- Prisma SD-WAN Controller
-
- CloudBlade Integrations
- CloudBlades Integration with Prisma Access
-
-
-
-
- 6.5
- 6.4
- 6.3
- 6.1
- 5.6
- Prisma SD-WAN Controller
- Prisma SD-WAN On-Premises Controller
- Prisma SD-WAN CloudBlades
- Prisma Access CloudBlade Cloud Managed
- Prisma Access CloudBlade Panorama Managed
Configure VLAN on Switch Ports
Lets learn how to configure a VLAN on switch ports in Prisma SD-WAN.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
After adding the VLAN, configure the VLAN
on the switch ports.
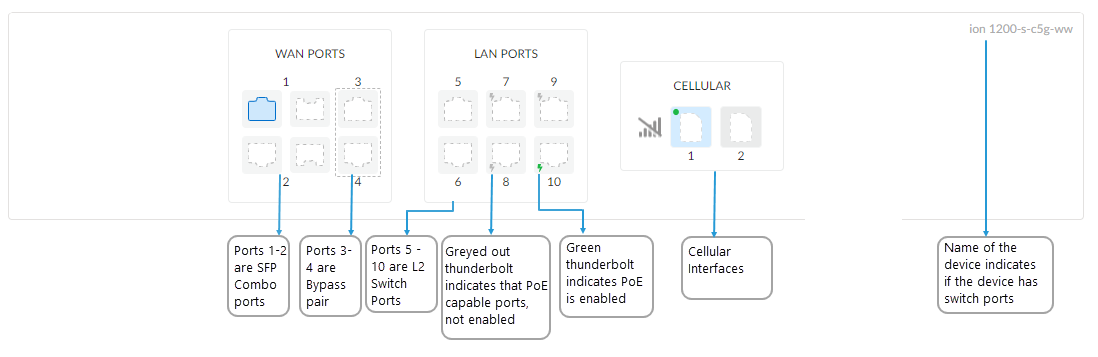
- Select a port from the LAN ports.
![]() In the General section,
In the General section,- Enter a Name and (Optional) Description, and add Tags for the port channel interface.For Admin Up, select Up or Down.In the Network Setting section,
- Interface type and Use Interface for are system-populated.If the port is a switch port, Interface Type and Use Interface for are auto populated.Toggle Scope as Global or Local for Internet and Private WAN.Select the VLAN Type as Data or Voice.Select the Interface Mode.
- Access is used for endpoint access. Select the Access VLAN and Voice VLAN. If you need a Voice VLAN, you need to first create the Voice VLAN when creating Switch Virtual Interface.
- Use Trunk to use multiple VLANs. Select all VLANs or select a VLAN IDs.Trunk ports carry only VLAN tagged packets. If Native VLAN is configured, select Native VLAN for untagged packets.
Control access to your network by using a different Authentication mode, it's Disabled by default:- 802.1X only - Select Reauthentication Timeout, select a value between 30-86400 seconds, default is 1800 seconds.802.1X authentication is a client-server model facilitating network access only to authorized clients. It defines authentication controls for any user or device trying to access a LAN or WLAN. The user's identity is determined based on their credentials or certificate, which is confirmed by the RADIUS server. Before services can be provided to a client by the ION device, the client connected to the switch port has to be authenticated by the RADIUS authentication server.802.1X is supported only on switch ports.Prisma SD-WAN supports the following IEEE 8021X-PAE-MIB values. It supports SNMP get and walk requests.
- ieee8021XEapolStatsTable
- ieee8021XAuthenticatorTable
- ieee8021XPaePortSessionTable
- ieee8021XPaePortLogonTable
- ieee8021XPaePortTable
- MAC Auth Only - Select Reauthentication Timeout, select a value between 30-86400 seconds, default is 1800 seconds.Media Access Control (MAC) authentication is used to authenticate devices based on their physical MAC addresses. You can authorize an endpoint using MAC Authentication. The authenticator uses the MAC address of the connecting device to determine what kind of network access to provide.MAC Auth is supported only on switch ports.
- 802.1X to MAC Auth Fallback - Select the fallback option to fall back to MAC Auth if the client isn't using 802.1X authentication.
Enable PoE for the port.By default, PoE is disabled.Enter the Port Power Usage Alarm Threshold value for the selected port between 50-100%.If the port power usage exceeds the alarm threshold, an incident is generated.Select the option for LLDP/LLDP-MED.Receive Only option is the default option. Select Receive and Transmit, only if you want the ION device to respond to the powered device (PD) when it receives LLDP-MED packets.Starting with release 6.4.1, voice VLANs will be advertised as part of LLDP-MED to support dynamic detection for VoIP phones on ION 1200-S device.Advanced settings- Physical indicates the speed of the interface, it's disabled by default. Select from the available options.Interface speed, displayed in Mbps, is the speed of each interface. Interfaces can have ethernet speed rates of 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, and 1000 Mbps.
- Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is enabled by default. By default, the STP type is RSTP.The Spanning Tree Protocol (mSTP), used in case of multiple switches, provides connectivity to a VLAN throughout a Bridged local area network. These LANs are connected into a single Common Spanning Tree (CST).
- Root/BPDU Guard is used to protect the Layer 2 STP topology from BPDU-related attacks.Root Guard is enabled on a port-by-port basis, it prevents a configured port from becoming a root port. Root Guard prevents a downstream switch (often mis-configured or rogue) from becoming a root bridge in a topology.BPDU Guard must be enabled on ports that should never receive a BPDU from its connected devices. When a BPDU Guard enabled port receives BPDU from a connected device, BPDU Guard disables the port.
- Spanning tree Portfast is enabled by default.
- Enter STP Port priority between 0-240. The default value is 128, STP port priority is in multiples of 16.
- Enter STP port cost between 1-65535. The STP port cost depends on the speed of the port.
Select Storm Control. Set a threshold for traffic rate limit, the traffic is rate limited for the set threshold value.By default, the broadcast threshold is set to 1000 Kbps. Enter a value between 64-1000000 Kbps.- Unknown Unicast threshold (Opt)- enter a value between 64-1000000 Kbps.
- Broadcast threshold (Opt)- enter a value between 64-1000000 Kbps.
- Multicast threshold (Opt)- enter a value between 64-1000000 Kbps.
Save to update the changes.To edit an existing VLAN, Edit the VLAN by selecting it from the ellipsis menu.You can delete an existing VLAN only after deleting the VLAN from all the associated access or trunk ports. To delete an existing VLAN, delete the VLAN by selecting it from the ellipsis menu.