Prisma Access
Enable and Configure IPv6 Networking and IP Pools in Your Prisma Access Infrastructure
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma Access Docs
-
- 6.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 6.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 4.2 Preferred
- 4.1 Preferred
- 4.0 Preferred
- 3.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 2.2 Preferred
-
-
- 4.0 & Later
- Prisma Access China
-
-
Enable and Configure IPv6 Networking and IP Pools in Your Prisma Access Infrastructure
Learn how to enable and configure IPv6 networking and IP pools in your Prisma Access
infrastructure.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
For any Prisma Access deployment, you need to enable IPv6 globally and specify an
IPv6 subnet in your Infrastructure Subnet so that
Prisma Access can establish an IPv6 network infrastructure between your remote
network locations, mobile users, and service connections. To do so, complete the
following steps.
Enable and Configure IPv6 Networking and IP Pools in Your Prisma Access Infrastructure (Strata Cloud Manager)
- Select ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessConfiguration ScopePrisma AccessPrisma Access Infrastructure and select the gear icon to edit the Settings.Select the check box to Enable IPv6 for Internal Traffic.Enabling or disabling IPv6 results in a brief traffic interruption (up to 120 seconds) while the dataplane prepares to accept or reject IPv6 routes on the Prisma Access backbone. We recommend that you push this configuration change during a maintenance window or during off-peak hours.If you need to delete IPv6, delete all configuration (including for mobile users, remote network, and service connections as applicable) before deselecting the Enable IPv6 for Internal Traffic check box.
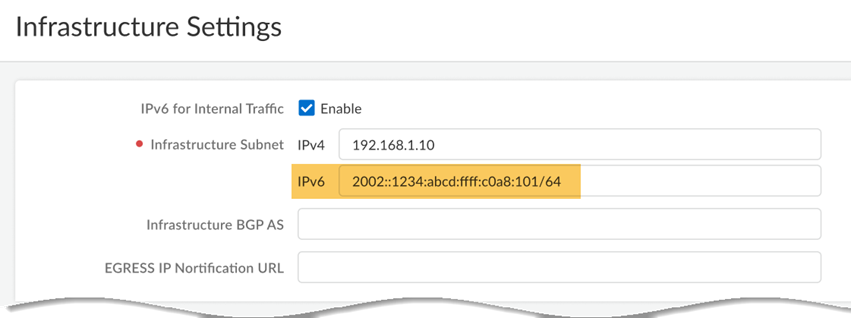
![]() Specify an IPv6 infrastructure subnet and an Infrastructure BGP AS.
Specify an IPv6 infrastructure subnet and an Infrastructure BGP AS.- Specify a minimum subnet of /96.
- You must also enter an IPv4 subnet; Prisma Access requires IPv4 and IPv6 subnets in its network infrastructure to use IPv6. See Prisma Access Infrastructure Management for details.
- Palo Alto Networks recommends that you use private (not public) IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
- Do not use IPv6 link local addresses (fe80::/10).
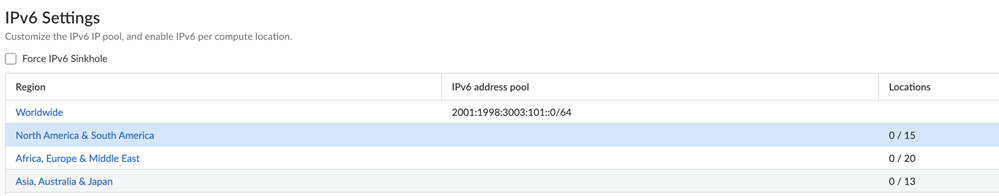
![]() Enter the Infrastructure BGP AS you want to use within the Prisma Access infrastructure.If you want to use dynamic routing to enable Prisma Access to dynamically discover routes to resources on your remote networks and HQ/data center locations, specify the autonomous system (AS) number. If you do not supply an AS number, the default AS number 65534 will be used.If you haven't done so already, consider adding Internal DNS Servers to enable Prisma Access to resolve your internal domains to access services, such as LDAP and DNS server,s on your corporate network.See Prisma Access Infrastructure Management for details.(Mobile User Deployments Only) Add IPv6 IP address pools for your Mobile Users—GlobalProtect deployment.A Mobile Users—GlobalProtect deployment requires IP address pools. Both IPv4 and IPv6 IP address pools are required to enable IPv6 functionality. You apply IPv4 addresses at a regional or Worldwide level; you apply IPv6 addresses at a Worldwide level. Specify a minimum /80 subnet.Prisma Access subdivides the Worldwide IPv6 addresses using the following method:
Enter the Infrastructure BGP AS you want to use within the Prisma Access infrastructure.If you want to use dynamic routing to enable Prisma Access to dynamically discover routes to resources on your remote networks and HQ/data center locations, specify the autonomous system (AS) number. If you do not supply an AS number, the default AS number 65534 will be used.If you haven't done so already, consider adding Internal DNS Servers to enable Prisma Access to resolve your internal domains to access services, such as LDAP and DNS server,s on your corporate network.See Prisma Access Infrastructure Management for details.(Mobile User Deployments Only) Add IPv6 IP address pools for your Mobile Users—GlobalProtect deployment.A Mobile Users—GlobalProtect deployment requires IP address pools. Both IPv4 and IPv6 IP address pools are required to enable IPv6 functionality. You apply IPv4 addresses at a regional or Worldwide level; you apply IPv6 addresses at a Worldwide level. Specify a minimum /80 subnet.Prisma Access subdivides the Worldwide IPv6 addresses using the following method:- Prisma Access assigns each location (gateway) a pool from a /112 subnet. Because each GlobalProtect connection uses one IP address from the pool, this allocation allows over 65,000 available IPv6 addresses to be assigned to users’ endpoints per location.If you experience an auto-scale event (if a large number of users log in to a single Prisma Access location), Prisma Access can add another location with another /112 subnet.
- When you enable a location to use IPv6, Prisma Access assigns an IPv6 address pool to the region to which the location belongs, and divides up the pool between the total number of regions that have IPv6 enabled.
Do not use local-link addresses (fe80::/10) in an IP address pool.- Select ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma Access Configuration ScopePrisma AccessGlobalProtect and select the gear icon to edit the Infrastructure Settings.In the Client IP Pools section, select a Region or select Add IP Portal.Enter an IPv6 Address Pool.
- You must enter both IPv4 and IPv6 IP addresses for mobile users. Prisma Access requires IPv4 and IPv6 addresses to support its internal infrastructure when using IPv6.
- Enter a minimum IPv6 subnet of /80.
- Prisma Access subdivides each subnet per region.
![]() Save and Push Config.Select ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessConfiguration ScopePrisma AccessPrisma Access Infrastructure and make a note of the following IPv6 addresses in your Infrastructure Settings:
Save and Push Config.Select ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessConfiguration ScopePrisma AccessPrisma Access Infrastructure and make a note of the following IPv6 addresses in your Infrastructure Settings:- Captive Portal Redirect IP Addresses—Used with Authentication Portal-based User-ID address mapping
- Tunnel Monitor IP Address—Used for Tunnel Monitoring
Because GlobalProtect mobile users require an IPv4 address for the VPN tunnels, loopback addresses, whose IP addresses are taken from the Infrastructure Subnet, still use IPv4 addresses.![]()
Enable and Configure IPv6 Networking and IP Pools in Your Prisma Access Infrastructure (Panorama)
- Select PanoramaCloud ServicesConfigurationService Setup and click the gear icon to edit the Settings.On the General tab, select Enable IPv6.Enabling or disabling IPv6 results in a brief traffic interruption (up to 120 seconds) while the dataplane prepares to accept or reject IPv6 routes on the Prisma Access backbone. Palo Alto Networks recommends that you commit this configuration change during a maintenance window or during off-peak hours.If you need to delete IPv6, delete all configuration (including for mobile users, remote network, and service connections as applicable) before deselecting the Enable IPv6 check box.
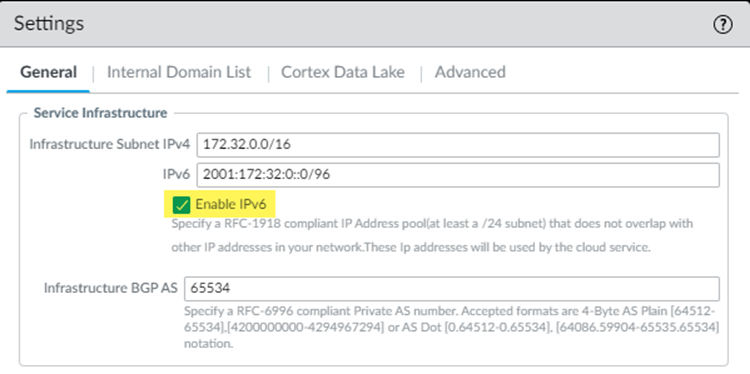
![]() Specify an IPv6 infrastructure subnet and an Infrastructure BGP AS.
Specify an IPv6 infrastructure subnet and an Infrastructure BGP AS.- Specify a minimum subnet of /96.
- You must also enter an IPv4 subnet; Prisma Access requires IPv4 and IPv6 subnets in its network infrastructure to use IPv6. See Configure the Prisma Access Service Infrastructure (Panorama) for details.
- Palo Alto Networks recommends that you use private (not public) IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
- Do not use IPv6 link local addresses (fe80::/10).
![]() Enter the Infrastructure BGP AS you want to use within the Prisma Access infrastructure.If you want to use dynamic routing to enable Prisma Access to dynamically discover routes to resources on your remote networks and HQ/data center locations, specify the autonomous system (AS) number. If you do not supply an AS number, the default AS number 65534 will be used.If you have not yet completed the service setup configuration, enter the Internal Domain List, Strata Logging Service, and Advanced settings.See Configure the Prisma Access Service Infrastructure (Panorama) for details.(Mobile User Deployments Only) Add IPv6 IP address pools for your Mobile Users—GlobalProtect deployment.A Mobile Users—GlobalProtect deployment requires IP address pools. Both IPv4 and IPv6 IP address pools are required to enable IPv6 functionality. You apply IPv4 addresses at a regional or Worldwide level; you apply IPv6 addresses at a Worldwide level. Specify a minimum /80 subnet.Prisma Access subdivides the Worldwide IPv6 addresses using the following method:
Enter the Infrastructure BGP AS you want to use within the Prisma Access infrastructure.If you want to use dynamic routing to enable Prisma Access to dynamically discover routes to resources on your remote networks and HQ/data center locations, specify the autonomous system (AS) number. If you do not supply an AS number, the default AS number 65534 will be used.If you have not yet completed the service setup configuration, enter the Internal Domain List, Strata Logging Service, and Advanced settings.See Configure the Prisma Access Service Infrastructure (Panorama) for details.(Mobile User Deployments Only) Add IPv6 IP address pools for your Mobile Users—GlobalProtect deployment.A Mobile Users—GlobalProtect deployment requires IP address pools. Both IPv4 and IPv6 IP address pools are required to enable IPv6 functionality. You apply IPv4 addresses at a regional or Worldwide level; you apply IPv6 addresses at a Worldwide level. Specify a minimum /80 subnet.Prisma Access subdivides the Worldwide IPv6 addresses using the following method:- Prisma Access assigns each location (gateway) a pool from a /112 subnet. Because each GlobalProtect connection uses one IP address from the pool, this allocation allows over 65,000 available IPv6 addresses to be assigned to users’ endpoints per location.If you experience an auto-scale event (if a large number of users log in to a single Prisma Access location), Prisma Access can add another location with another /112 subnet.
- When you enable a location to use IPv6, Prisma Access assigns an IPv6 address pool to the region to which the location belongs, and divides up the pool between the total number of regions that have IPv6 enabled.
Do not use local-link addresses (fe80::/10) in an IP address pool.- Select PanoramaCloud ServicesConfigurationMobile Users—GlobalProtect.In the Onboarding section, select the portal Hostname or select Configure.Select the IP Pools tab.Enter an IP Pool IPv6.
- You must enter both IPv4 and IPv6 IP addresses for mobile users. Prisma Access requires IPv4 and IPv6 addresses to support its internal infrastructure when using IPv6.
- Enter a minimum IPv6 subnet of /80.
- Prisma Access subdivides each subnet per region.
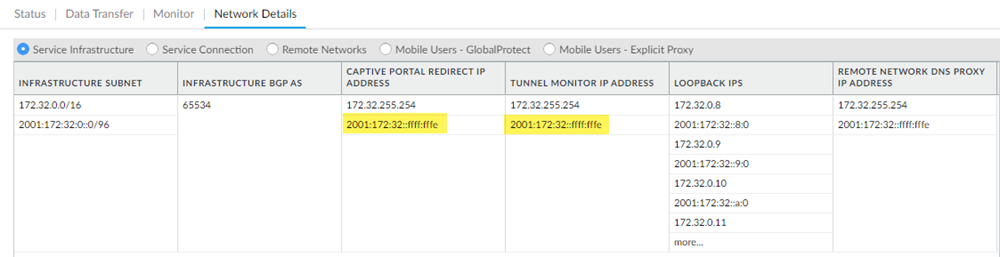
![]() Commit and Push your changes.Select PanoramaCloud ServicesStatusNetwork DetailsService Infrastructure and make a note of the following IPv6 addresses:
Commit and Push your changes.Select PanoramaCloud ServicesStatusNetwork DetailsService Infrastructure and make a note of the following IPv6 addresses:- Captive Portal Redirect IP Addresses—Used with Authentication Portal-based User-ID address mapping
- Tunnel Monitor IP Address—Used for Tunnel Monitoring
Because GlobalProtect mobile users require an IPv4 address for the VPN tunnels, loopback addresses, whose IP addresses are taken from the Infrastructure Subnet, still use IPv4 addresses.![]()