Prisma Access
Configure Kerberos Authentication for Explicit Proxy Deployments
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma Access Docs
-
- 6.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 6.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 4.2 Preferred
- 4.1 Preferred
- 4.0 Preferred
- 3.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 2.2 Preferred
-
-
- 4.0 & Later
- Prisma Access China
-
-
Configure Kerberos Authentication for Explicit Proxy Deployments
Find out how to configure Kerberos authentication for Explicit Proxy on Prisma Access.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
Configure Kerberos Authentication for Explicit Proxy Deployments (Strata Cloud Manager)
- Set up a Kerberos authentication profile.The profile defines how Explicit Proxy connects to the Kerberos server for mobile user authentication.
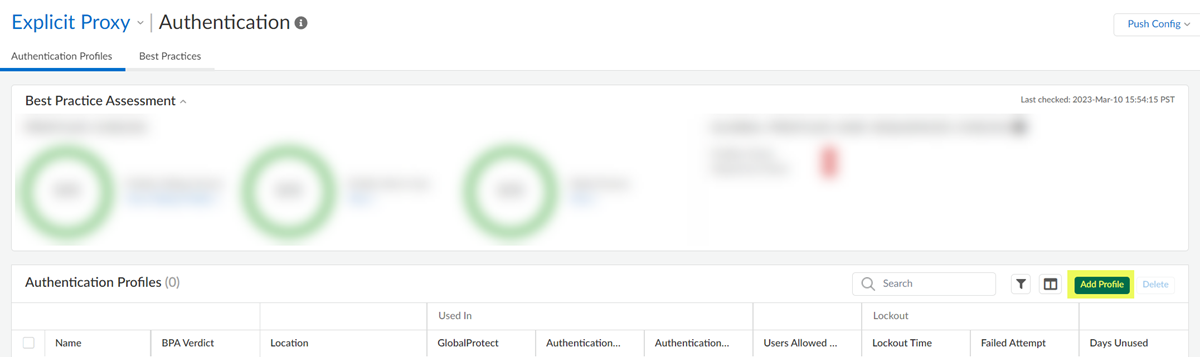
- Go to ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessIdentity ServicesAuthenticationAuthentication Profiles and Add Profile.
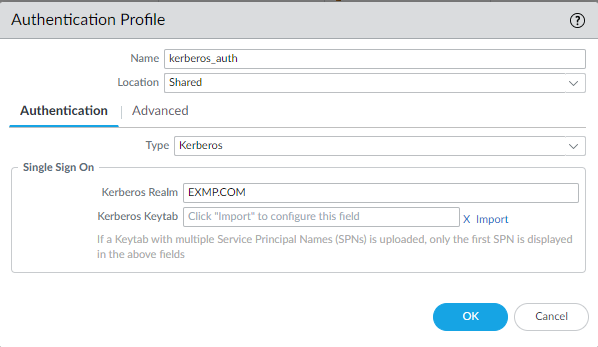
![]() Select the Authentication Method: Kerberos.
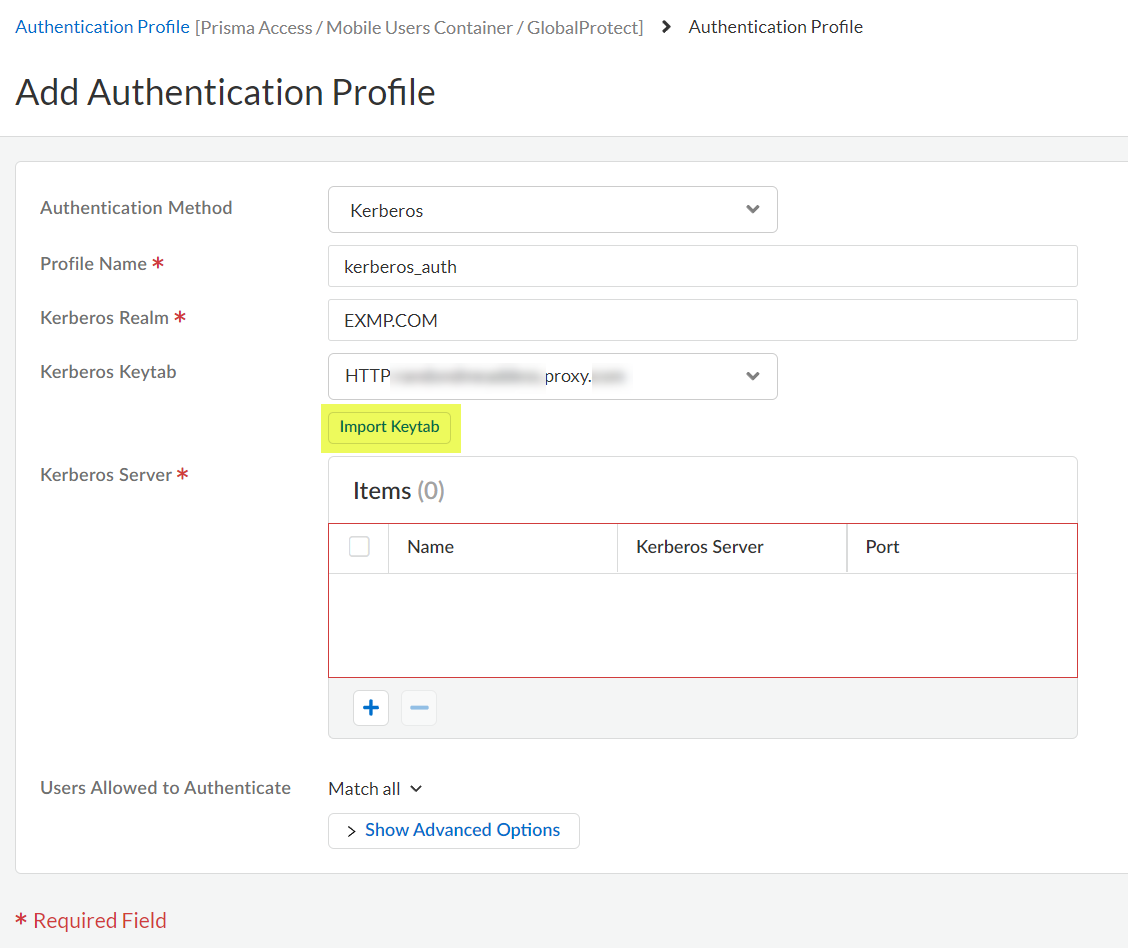
Select the Authentication Method: Kerberos.![]() Enter the Profile Name to identify the server profile.The authentication profile specifies the server profile that the portal or gateways use when they authenticate users.Enter the Kerberos Realm (up to 127 characters) to specify the hostname portion of the user login name. For example, the user account name user@EXMP.COM has the realm EXMP.COM.Import the Kerberos Keytab (Import Keytab) youcreated earlier.
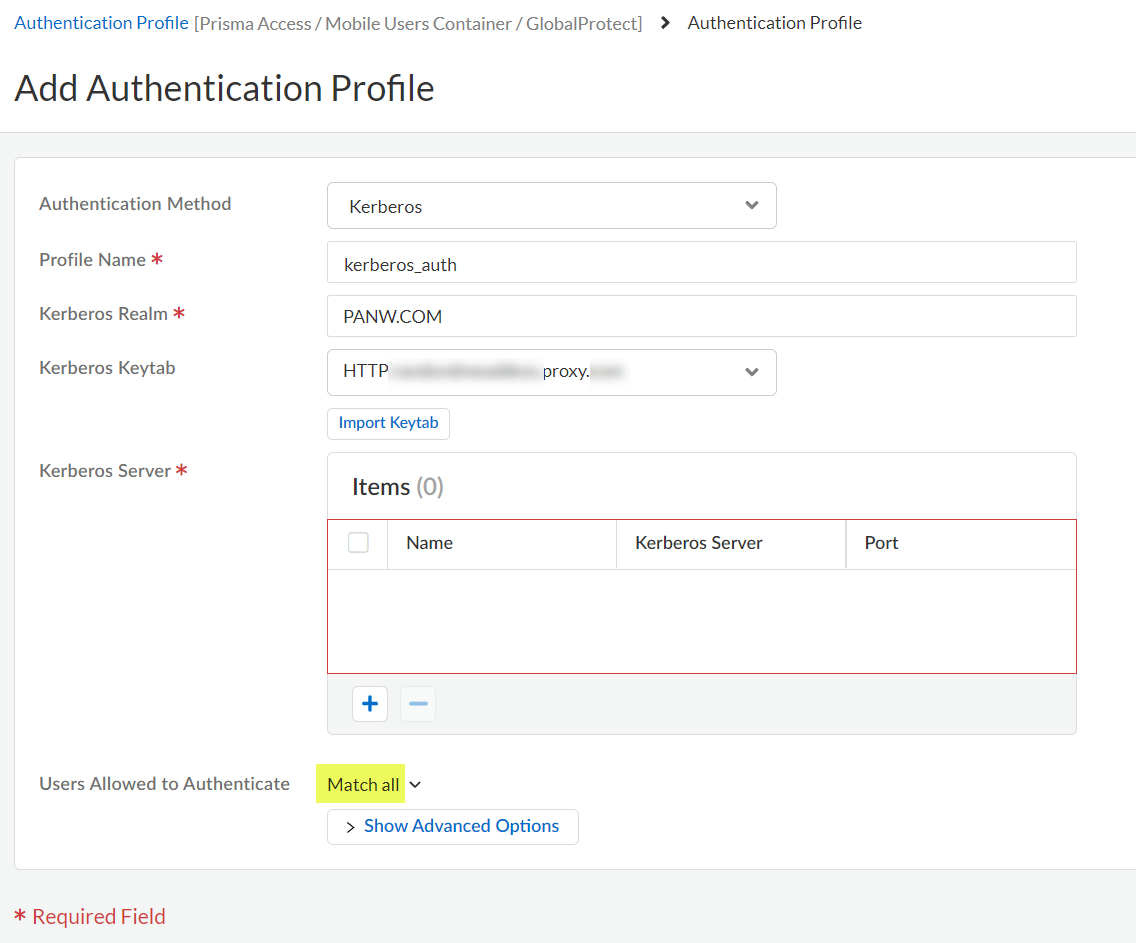
Enter the Profile Name to identify the server profile.The authentication profile specifies the server profile that the portal or gateways use when they authenticate users.Enter the Kerberos Realm (up to 127 characters) to specify the hostname portion of the user login name. For example, the user account name user@EXMP.COM has the realm EXMP.COM.Import the Kerberos Keytab (Import Keytab) youcreated earlier.![]() Add the Users Allowed to Authenticate with this profile.
Add the Users Allowed to Authenticate with this profile.- To select all users, Match all.
- If you’re using the Cloud Identity Engine to populate the list of users, select the users from a list, or select all to allow all users to authenticate.
- To add local users that can log in using Kerberos, Add Local User, add the Name, and create a Password.
- When configuring user authentication and user mapping, use a format of userPrincipalName (UPN); other formats (such as samAccountName) are not supported.
- Unicode character usernames are not supported.
![]() Save your changes.Associate the authentication profile with an authentication method.
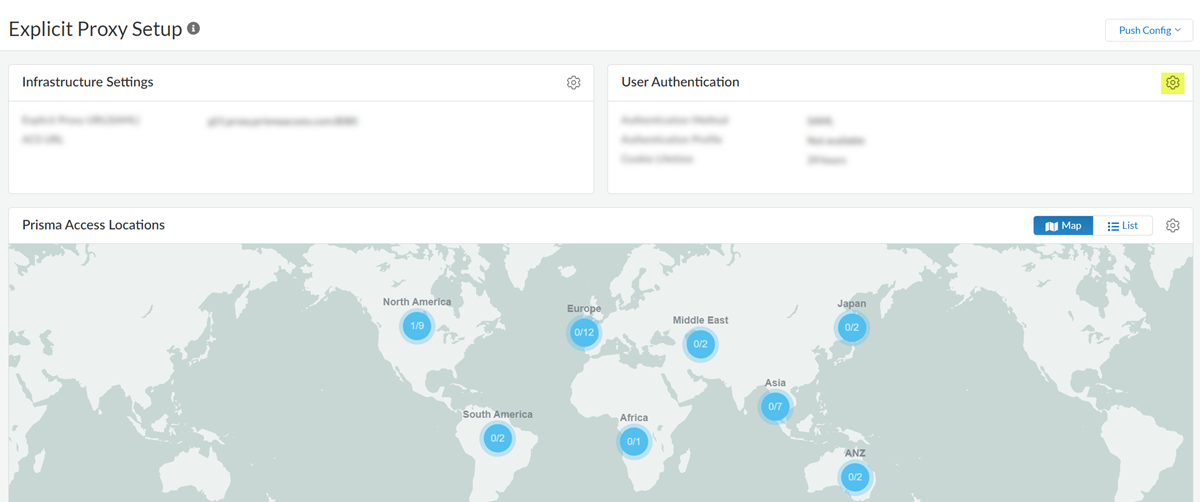
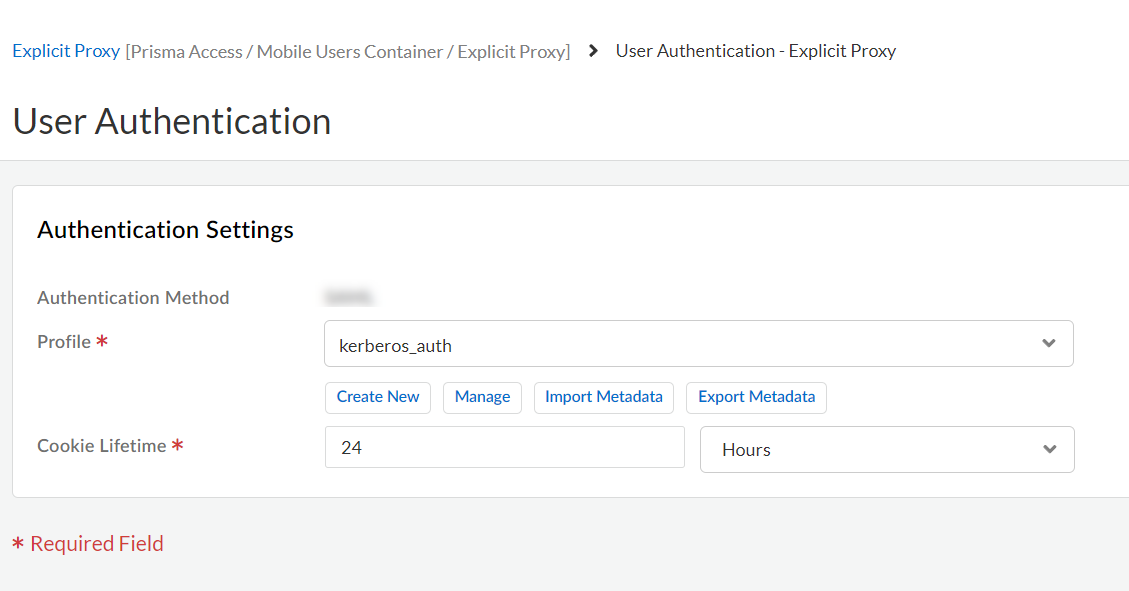
Save your changes.Associate the authentication profile with an authentication method.- Go to Configuration NGFW and Prisma Access and set Configuration Scope to Prisma Access. Select Explicit ProxyUser Authentication.
![]() Select the Connection Name.Select an Authentication Method of Kerberos and select the Kerberos Profile you created.
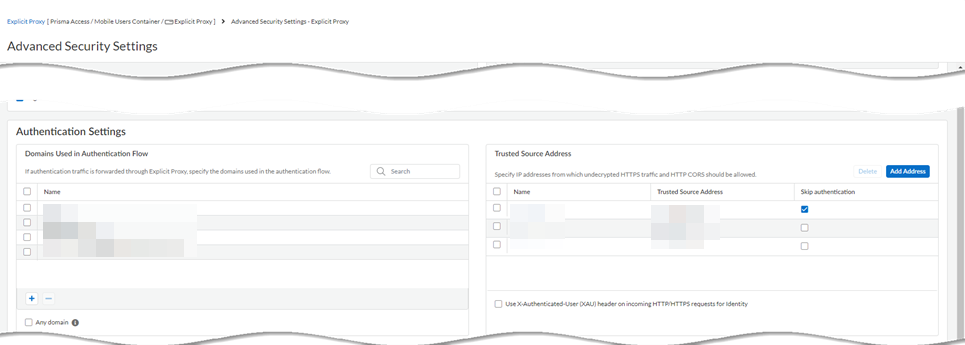
Select the Connection Name.Select an Authentication Method of Kerberos and select the Kerberos Profile you created.![]() Save your changes.(Optional) Add the egress IP addresses of the branch or campus location where your users, servers, IoT devices, or headless machines are located to the list of trusted Explicit Proxy addresses.You need to do this only if you want to Skip Authentication for specific IP addresses or Use X-Authenticated User (XAU) header on incoming HTTP/HTTPS requests for identity.
Save your changes.(Optional) Add the egress IP addresses of the branch or campus location where your users, servers, IoT devices, or headless machines are located to the list of trusted Explicit Proxy addresses.You need to do this only if you want to Skip Authentication for specific IP addresses or Use X-Authenticated User (XAU) header on incoming HTTP/HTTPS requests for identity.- Go to Configuration NGFW and Prisma Access and set Configuration Scope to Prisma Access. Select Explicit ProxyAdvanced Security Settings.
![]() Add Address (one or more) to the Trusted Source Address field.If you do not add the egress endpoint IP addresses to the trusted list, Explicit Proxy forces users and machines to authenticate with SAML as well as Kerberos.Enter a maximum of 100,000 IP addresses.
Add Address (one or more) to the Trusted Source Address field.If you do not add the egress endpoint IP addresses to the trusted list, Explicit Proxy forces users and machines to authenticate with SAML as well as Kerberos.Enter a maximum of 100,000 IP addresses.![]() Save your changes.Create an allow-all policy rule for user authentication.
Save your changes.Create an allow-all policy rule for user authentication.- Select Configuration NGFW and Prisma AccessSecurity ServicesSecurity PolicyAdd RulePre Rules..Name the rule.Set all required match criteria to Any.Set Users to KnownSet Action to Allow.Save the rule.Push your configuration changes.Verify that Kerberos authentication is working with Prisma Access by viewing the traffic and authentication logs. Logs are generated only in case of authentication failure.
- (Decrypted traffic only) Go to ActivityLog ViewerFirewall/Traffic and check that the Kerberos authentication is working.If you're using Strata Cloud Manager, go to Incidents & AlertsLog ViewerFirewall/Traffic.Decrypted traffic displays the user name in the traffic logs.(Undecrypted traffic only) Go to ActivityLog ViewerFirewall/Authentication and check that Kerberos authentication is working correctly.If you're using Strata Cloud Manager, go to Incidents & AlertsLog ViewerFirewall/Authentication.The following fields provide more information about the authentication event:
- Object—The website the user was attempting to access before being redirected to Kerberos to authenticate.
- Auth Event—The status of the authentication attempt.Authentication Success indicates that the authentication event was successful; Authentication Failure indicates that the attempt failed and generates a log.
- Authentication Description—If the authentication attempt failed, additional information about the type of failure.For example, user not allowed indicates that the user or group is not allowed to use Kerberos to authenticate, possible because it was not added to the Allow List in the authentication profile.
![]()
Configure Kerberos Authentication for Explicit Proxy Deployments (Panorama)
Find out how to configure Kerberos authentication for Explicit Proxy on Prisma Access.- Set up a Kerberos authentication profile.The profile defines how Explicit Proxy connects to the Kerberos server for mobile user authentication.
- Go to DeviceAuthentication Profile+ Add.
![]() Select the Type: Kerberos.
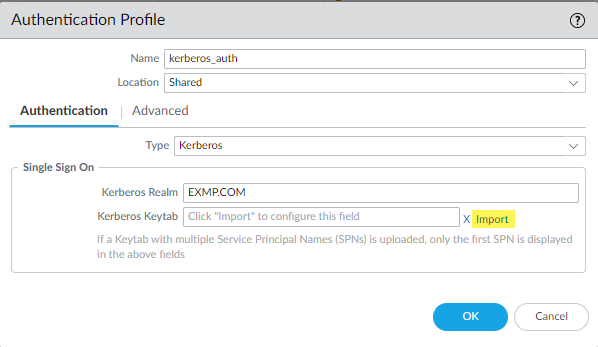
Select the Type: Kerberos.![]() Enter a Name to identify the authentication profile.Enter the Kerberos Realm (up to 127 characters) to specify the hostname portion of the user login name. For example, the user account name user@EXMP.COM has the realm EXMP.COM.Import the Kerberos Keytab you created earlier.
Enter a Name to identify the authentication profile.Enter the Kerberos Realm (up to 127 characters) to specify the hostname portion of the user login name. For example, the user account name user@EXMP.COM has the realm EXMP.COM.Import the Kerberos Keytab you created earlier.![]() Add users allowed to authenticate with this profile.
Add users allowed to authenticate with this profile.- Select Advanced+ Add
- To select all users, select all.
- If you’re using the Cloud Identity Engine to populate the list of users, select the users from a list, or select all to allow all users to authenticate.
- To add local users that can log in using Kerberos, type in their usernames.
- When configuring user authentication and user mapping, use a format of userPrincipalName (UPN); other formats (such as samAccountName) are not supported.
- Unicode character usernames are not supported.
![]() Save your changes.Associate the authentication profile with an authentication method.
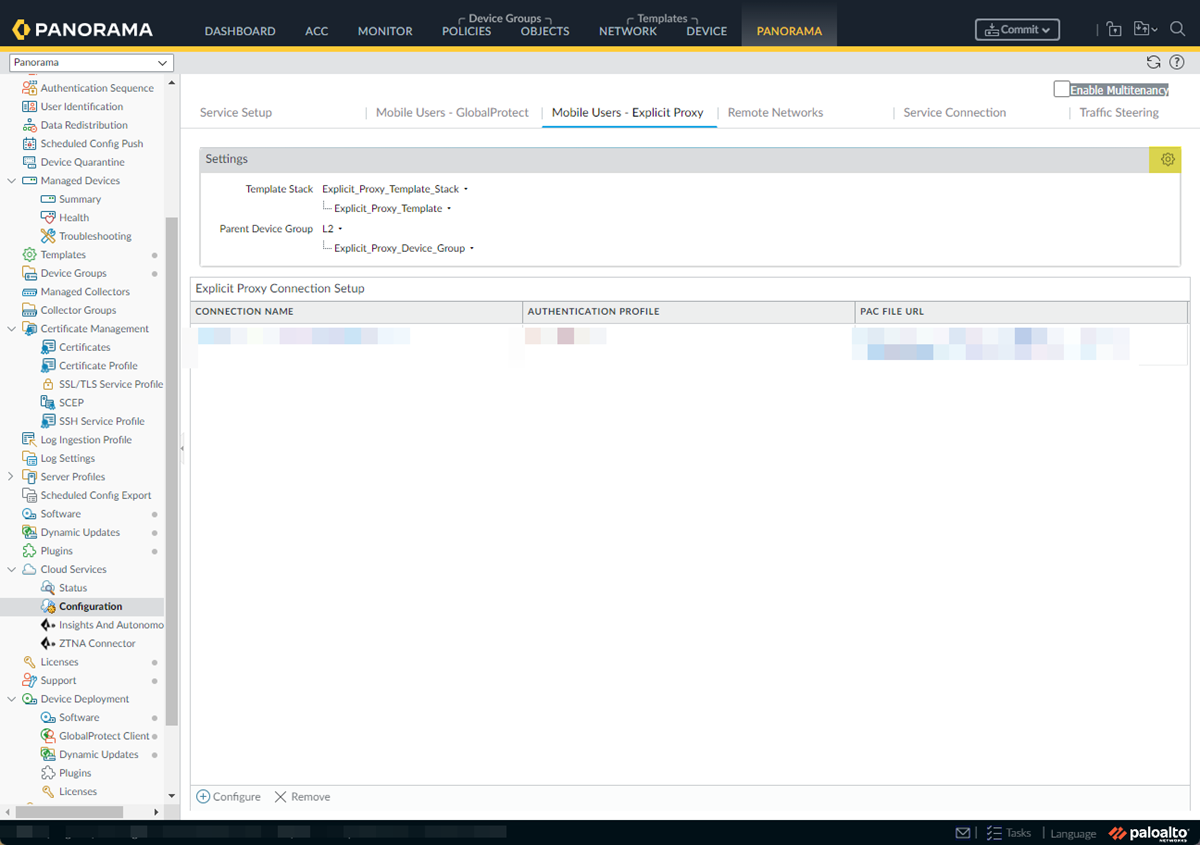
Save your changes.Associate the authentication profile with an authentication method.- Go to PanoramaCloud ServicesConfiguration+ Configure.
![]() Set the Explicity Proxy FQDN.Select the Kerberos Profile you created.Select OK to save your changes.(Optional) Add the egress IP addresses of the branch or campus location where your users, servers, IoT devices, or headless machines are located to the list of trusted Explicit Proxy addresses.You need to do this only if you want to Skip Authentication for specific IP addresses or Use X-Authenticated User (XAU) header on incoming HTTP/HTTPS requests for identity.
Set the Explicity Proxy FQDN.Select the Kerberos Profile you created.Select OK to save your changes.(Optional) Add the egress IP addresses of the branch or campus location where your users, servers, IoT devices, or headless machines are located to the list of trusted Explicit Proxy addresses.You need to do this only if you want to Skip Authentication for specific IP addresses or Use X-Authenticated User (XAU) header on incoming HTTP/HTTPS requests for identity.- Go to PanoramaCloud ServicesConfigurationSettings gearAuthentication Settings.
![]() Add addresses to the Trusted Source Address field.If you do not add the egress endpoint IP addresses to the trusted list, Explicit Proxy forces users and machines to authenticate with SAML as well as Kerberos.Enter a maximum of 100,000 IP addresses.
Add addresses to the Trusted Source Address field.If you do not add the egress endpoint IP addresses to the trusted list, Explicit Proxy forces users and machines to authenticate with SAML as well as Kerberos.Enter a maximum of 100,000 IP addresses.![]() Select OK to save your changes.Create an allow-all policy rule for user authentication.
Select OK to save your changes.Create an allow-all policy rule for user authentication.- Select PoliciesPre Rules + Add.Name the rule.Select SourceSet Source User to known-userSet all other required values to Any.Select OK to save the rule.Commit and push your configuration changes.Verify that Kerberos authentication is working with Prisma Access by viewing the traffic and authentication logs. Logs are generated only in case of authentication failure.
- (Decrypted traffic only) Go to MonitorLogsTraffic and check that the Kerberos authentication is working.Decrypted traffic displays the user name in the traffic logs.(Undecrypted traffic only) Go to MonitorLogsAuthentication and check that Kerberos authentication is working correctly.The following fields provide more information about the authentication event:
- Object—The website the user was attempting to access before being redirected to Kerberos to authenticate.
- Auth Event—The status of the authentication attempt.Authentication Success indicates that the authentication event was successful; Authentication Failure indicates that the attempt failed and generates a log.
- Authentication Description—If the authentication attempt failed, additional information about the type of failure.For example, user not allowed indicates that the user or group is not allowed to use Kerberos to authenticate, possibly because it was not added to the Allow List in the authentication profile.