Prisma Access
Dynamic Routing Considerations for Service Connections
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma Access Docs
-
- 6.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 6.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 4.2 Preferred
- 4.1 Preferred
- 4.0 Preferred
- 3.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 2.2 Preferred
-
-
- 4.0 & Later
- Prisma Access China
-
-
Dynamic Routing Considerations for Service Connections
Learn how to route data for service connection traffic.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
How It Works — Routing Service Connection Traffic
Prisma Access uses BGP for dynamic routing, and uses BGP path selection
to install routes in the route table. When Prisma Access routes traffic to your
headquarters or data center using service connections, it uses routing methods that
direct that traffic effectively. Prisma Access uses a default routing model that was
designed to fit the majority of network deployments; however, not all organization’s
networks are the same. To fit a wider range of deployments, Prisma Access allows you
choose another mode for service connection routing. The following sections describe
the BGP routing methods that Prisma Access uses, along with the factors you need to
consider in your organization’s network before changing Prisma Access’ default
method of service connection routing.
Changing the Prisma Access service connection routing method requires a thorough
understanding of your organization’s topology and routing devices, along with an
understanding of how Prisma Access routing works as described in this section.
We recommend that you read this section carefully before changing the routing
method from the default setting.
Prisma Access supports static routing and dynamic routing using BGP for service and
remote network connections; this section assumes that you use BGP routing for your
Prisma Access deployments. When you select BGP routing, your organization’s network
learns BGP information from Prisma Access.
Routing Modes for Service Connections
You can choose from the following routing modes with Prisma Access:
- Default routing—This is the current routing model that Prisma Access uses.Use this routing mode if you want Prisma Access to use BGP best path-selection mechanisms without adjusting any of the BGP attributes. In this mode, Prisma Access will honor any attribute advertised by the customer premises equipment (CPE).
- Hot Potato routing—Prisma Access hands off the traffic as quickly as it can to your organization’s network.Use this routing method if you want your organization’s network to perform the majority of routing decisions.
If you deploy a new service connection that is closer to the mobile user
gateway, Prisma Access builds a tunnel and connects the mobile user gateway
to the service connection that is the closest. You may experience routing
issues to existing service connections if they are farther away than the
newly-deployed service connection; in this case, consider adjusting the
location of the new service connection. This behavior applies to both
default and hot potato routing.
Prisma Access Default Routing
The following figure shows an example of Prisma Access routing service connection
traffic in default routing mode. The organization’s network has three separate
networks in three data centers and does not have a backbone connecting the networks.
In default routing mode, mobile user pools are advertised equally on the three
networks, as shown at the bottom of the figure.
Note that, when Prisma Access advertises mobile user routes, it divides the
routes into blocks of /24 before advertising them.
Make a note of how Prisma Access uses BGP route advertisements:
- Prisma Access does not adjust the default BGP attributes for mobile user advertised routes (Prisma Access adds its AS number to the route advertisements).
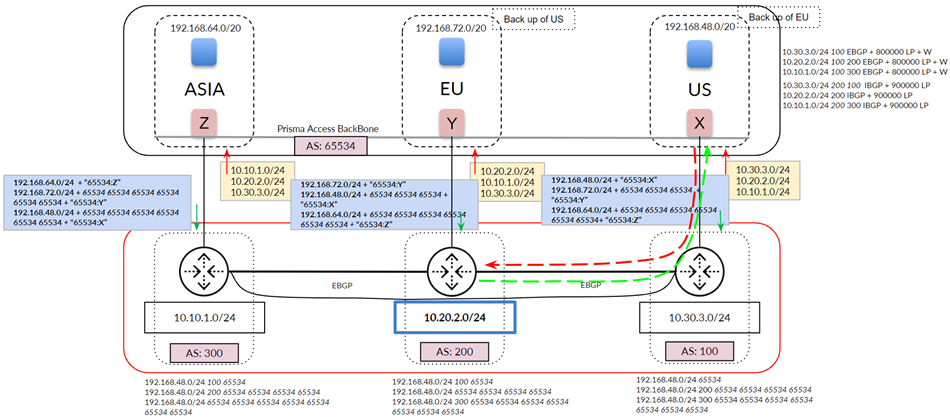
- Prisma Access advertises mobile user routes in and adds BGP community values in the routes it advertises through the service connection. The following figure shows a mobile user deployment with three service connections and three different IP address blocks specified for the : 192.168.64.0/20 for the Asia, Australia & Japan region, 192.168.72.0/20 for the Africa, Europe & Middle East region, and 192.168.48.0/20 for the North America & South America region. Prisma Access divides these routes into block of /24 and advertises them with an Prisma Access’ AS number of 65534, but also appends the BGP community values to the advertisements (Z for Asia, Y for EU, and X for US). Those routes are shown in the middle of the figure. In this way, you can differentiate service connections in your network, even though Prisma Access assigns the same AS number to them.
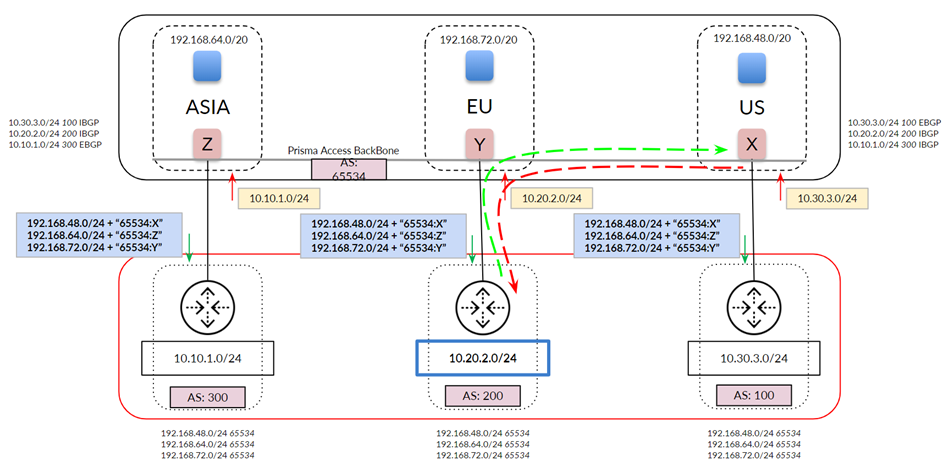
The following figure shows a more common network with a full-mesh eBGP backbone. The
figure shows the routes that Prisma Access has learned from your organization’s
network on the top right. Note the extra routes that Prisma Access has learned
through the Prisma Access backbone (iBGP) and your organization’s backbone
(eBGP).
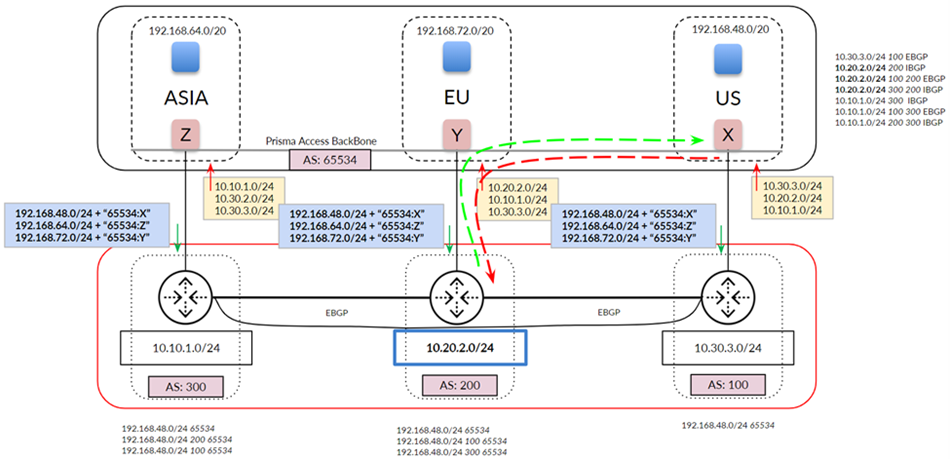
For traffic between mobile users in the North America & South
America region (US in the diagram) and the data center in your
organization’s Africa, Europe & Middle East region (EU in
the diagram), Prisma Access chooses the path through the EU service connection
because it prefers routes with a shorter AS-PATH.
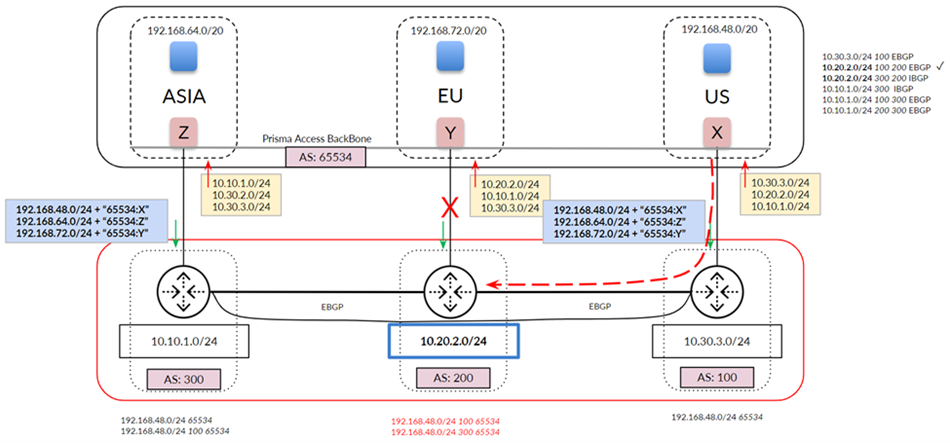
In deployments with a full-mesh eBGP backbone, asymmetry can arise when Prisma Access
cannot reach a particular data center due to an ISP/CPE failure at the customer’s
data center. The following figure shows what could happen when the link to the EU
service connection goes down. Your network detects the link failure and builds a new
route table for AS 200. Traffic from the US service connection to AS 200 uses the
path through AS 100 because the eBGP route for your backbone between AS 200 and AS
100 is preferred to the iBGP route between service connections EU and US. However,
return traffic is not guaranteed through the same path because the on-premises CPE
can choose either path (shown in red) to return the traffic.
The previous examples show a network whose routes have not been aggregated (that is,
you have not performed route summarization before you send the BGP route
advertisements to Prisma Access). The following example shows a network that
summarizes its routes to 10.0.0.0/8 before sending to Prisma Access. If you select
default routing, this configuration can lead to asymmetric routing issues, because
Prisma Access cannot determine the correct return path from the summarized
routes.
If your Prisma Access deployment has Remote Networks, Palo Alto Networks does not
recommend the use of route summarization on Service Connections. Route
summarization on service connections is for Mobile Users deployments only.

If you use route aggregation for mobile users, we strongly recommend that you enable
hot potato routing instead of default routing, where Prisma Access hands off the
traffic as quickly as possible to your organization’s network. In addition, we
recommend that you select a Backup SC as described in the
following section for each service connection to have a deterministic routing
behavior.
Hot Potato Routing
When you select Hot Potato Routing, Prisma Access egresses the
traffic bound to service connections/data centers from its internal network as
quickly as possible.
With hot potato routing, Prisma Access prepends the AS path (AS-PATH) to the BGP
prefix advertisements sent from gateways. This prepending is performed when the
prefixes are advertised out of the service connection to your organization’s
on-premises CPE. Prisma Access prepends the AS-PATHs so that your CPE gives the
correct preference to the primary and secondary tunnels, so that if the primary
tunnel goes down, your CPE chooses the secondary tunnel as the backup.
If you specified a different IP address for the secondary (backup) BGP peer, Prisma
Access adds more prepends based on the tunnel type, as shown in the following table.
| Prefix Type | Service Connection Tunnel Type | Number of As-Path Prepends | Total AS-PATHs Seen on the CPE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gateway prefixes from primary service connection | Primary or Secondary tunnel with the same BGP peer IP address | 0 | 1 |
| Gateway prefixes from backup service connection | Primary or Secondary tunnel with the same BGP peer IP address | 3 | 4 |
| Gateway prefixes from all other service connections | Primary or Secondary tunnel with the same BGP peer IP address | 6 | 7 |
| Gateway prefixes from primary service connection | Secondary tunnel with a different BGP peer IP address | 1 | 2 |
| Gateway prefixes from backup service connection | Secondary tunnel with a different BGP peer IP address | 4 | 5 |
| Gateway prefixes from all other service connections | Secondary tunnel with a different BGP peer IP address | 7 | 8 |
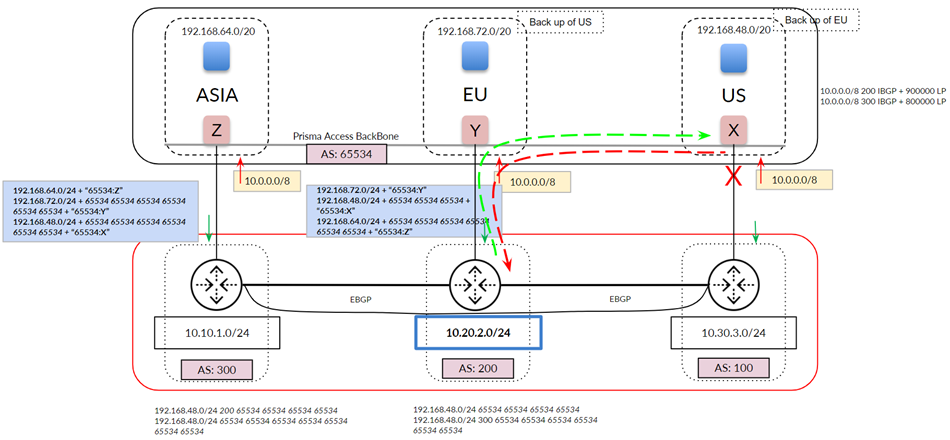
Specify a Backup Service Connection so that Prisma Access to
uses that service connection as the backup when a service connection link fails.
The following figure shows a hot potato routing configuration for traffic between the
US service connection and AS 200, with the EU service connection configured as the
Backup Service Connection of the US connection. Using hot
potato routing, Prisma Access sends the traffic from its closest exit path through
the US service connection. The return traffic takes the same path through AS100
because this path has a shorter AS-PATH to the mobile user pool in the US location.
Prisma Access prepends the AS-PATH to its prefix advertisements depending on whether
the tunnel is a primary tunnel, a backup tunnel, or not used for either primary or
backup.
Because you have set up a backup service connection, if the link to the US service
connection goes down, hot potato routing sends the traffic out using its shortest
route through the EU service connection. This routing scenario also applies to
networks that use route aggregation.
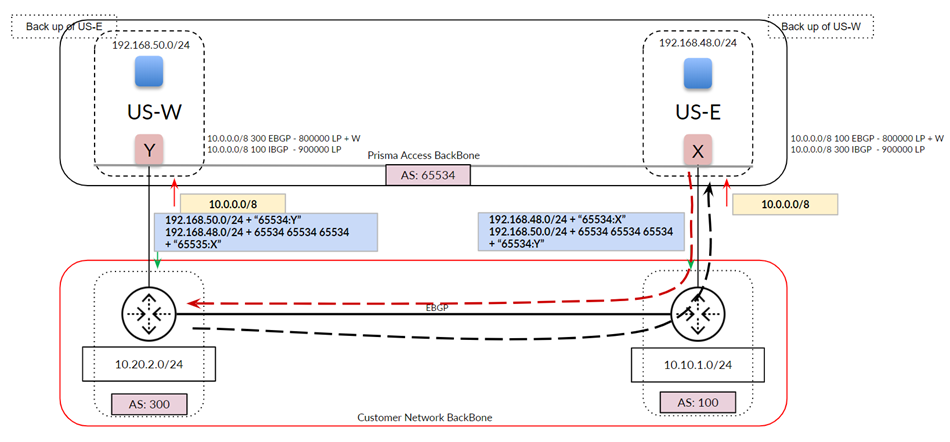
You can also use backup service connections for multiple service connections in a
single region. The following figure shows a Prisma Access deployment with two
service connections in the North America region. In this case, you specify a
Backup Service Connection of US-E for the US-W service
connection, and vice versa, to ensure symmetric routing.