Prisma Access
Nuage Networks SD-WAN Solution Guide
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma Access Docs
-
- 6.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 6.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 4.2 Preferred
- 4.1 Preferred
- 4.0 Preferred
- 3.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 2.2 Preferred
-
-
- 4.0 & Later
- Prisma Access China
-
-
Nuage Networks SD-WAN Solution Guide
Deploy a Nuage Networks SD-WAN with Prisma Access.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
Nuage Networks Virtualized Network Services (VNS) is an SD-WAN 2.0 solution that
automates the provisioning, configuration, and management of WAN connections to provide
the optimal application performance at the lowest cost, while meeting strict business
policy and security requirements for each application. Nuage Networks VNS can provide
this policy-based automation while seamlessly connecting WAN branch sites to on-premises
data centers and private clouds, public clouds, and provider-managed VPN networks. VNS
relies on a central policy repository to define business and application specific rules
that dynamically optimize WAN links and remote branch appliances or devices.
To secure your organization’s access to resources outside the SD-WAN and to the internet,
you can deploy a Nuage Networks SD-WAN with Prisma Access, a cloud-based security
infrastructure that uses next-generation security features. Using a shared ownership
model, Palo Alto Networks manages the Prisma Access infrastructure, while you manage the
process of connecting the Nuage Networks SD-WAN to Prisma Access.
Supported Software Versions and Requirements
Nuage Networks have three types of NSGs:
- NSG-C Series
- NSG-E Series
- NSG-X Series
All of the listed NSGs work with Prisma Access. The only differences are the
resources that they have and the access and WAN interfaces that they support. For
more information, refer to the NSG series product information at http://www.nuagenetworks.net/resources/product-information/. The NSG
series consists of NSG-C (small), NSG-E (medium), and NSG-X (large).
Supported IKE and IPSec Cryptographic Profiles
You onboard your SD-WAN edge devices using a remote network connection between the
edge device at the branch site, HQ, or hub to Prisma Access. Use Prisma Access to
create a remote network connection and create IKE and IPSec Crypto profiles; then,
set up an IPSec tunnel between the SD-WAN edge device and Prisma Access.
The following table documents the IKE/IPSec crypto settings that are supported with
Prisma Access and the Nuage Networks SD-WAN. In addition, the supported architecture
types are listed at the end of the table. A check mark indicates that the profile or
architecture type is supported; a dash (—) indicates that it's not supported.
Default and Recommended settings are noted in the table.
| Crypto Profiles | Prisma Access | Nuage Networks | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tunnel Type | IPSec Tunnel |
√
|
√
|
| GRE Tunnel | — |
√
| |
| Routing | Static Routes |
√
|
√
|
| Dynamic Routing (BGP) |
√
|
√
| |
| Dynamic Routing (OSPF) | — |
√
| |
| IKE Versions | IKE v1 |
√
|
√
|
| IKE v2 |
√
|
√
| |
| IPSec Phase 1 DH-Group | Group 1 |
√
|
√
|
| Group 2 | √ (Default) | √ (Default) | |
| Group 5 |
√
|
√
| |
| Group 14 |
√
|
√
| |
| Group 19 |
√
| — | |
| Group 20 | √ (Recommended) | — | |
| IPSec Phase 1 Auth If you use
IKEv2 with certificate-based authentication, only SHA1 is
supported in IKE Crypto profiles (Phase 1). | MD5 |
√
| — |
| SHA1 | √ (Default) | √ (Default) | |
| SHA256 |
√
|
√
| |
| SHA384 |
√
| — | |
| SHA512 | √ (Recommended) | — | |
| IPSec Phase 1 Encryption | DES |
√
| — |
| 3DES | √ (Default) |
√
| |
| AES-128-CBC | √ (Default) | √ (Default) | |
| AES-192-CBC |
√
|
√
| |
| AES-256-CBC | √ (Recommended) |
√
| |
| IPSec Phase 1 Key Lifetime Default | √ (8 Hours) | √ (1 Day) | |
| IPSec Phase 1 Peer Authentication | Pre-Shared Key |
√
|
√
|
| Certificate |
√
| — | |
| IKE Peer Identification | FQDN |
√
|
√
|
| IP Address |
√
|
√
| |
| User FQDN |
√
|
√
| |
| IKE Peer | As Static Peer |
√
|
√
|
| As Dynamic Peer |
√
|
√
| |
| Options | NAT Traversal |
√
|
√
|
| Passive Mode |
√
|
√
| |
| Ability to Negotiate Tunnel | Per Subnet Pair |
√
| — |
| Per Pair of Hosts |
√
| — | |
| Per Gateway Pair |
√
| — | |
| IPSec Phase 2 DH-Group There is
no separate option on the Nuage Networks side for a Phase 2
DH-Group; however, if you enable PFS, the network can process
Phase 2 DH-Group keys. | Group 1 |
√
|
√
|
| Group 2 | √ (Default) | √ (Default) | |
| Group 5 |
√
|
√
| |
| Group 14 |
√
|
√
| |
| Group 19 |
√
| — | |
| Group 20 | √ (Recommended) | — | |
| No PFS |
√
|
√
| |
| IPSec Phase 2 Auth | MD5 |
√
|
√
|
| SHA1 | √ (Default) | √ (Default) | |
| SHA256 |
√
|
√
| |
| SHA384 |
√
| — | |
| SHA512 | √ (Recommended) |
√
| |
| None |
√
| — | |
| IPSec Phase 2 Encryption | DES |
√
| — |
| 3DES | √ (Default) |
√
| |
| AES-128-CBC | √ (Default) |
√
| |
| AES-192-CBC |
√
|
√
| |
| AES-256-CBC |
√
|
√
| |
| AES-128-CCM |
√
| — | |
| AES-128-GCM |
√
| — | |
| AES-256-GCM | √ (Recommended) | — | |
| NULL |
√
|
√
| |
| IPSec Protocol | ESP |
√
|
√
|
| AH |
√
| — | |
| IPSec Phase 2 Key Lifetime Default | √ (1 Hour) | √ (1 Hour) | |
| Tunnel Monitoring Fallback | Dead Peer Detection (DPD) |
√
|
√
|
| ICMP | — | — | |
| Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) | — | — | |
| SD-WAN Architecture Type | With Regional Hub/Gateway/Data Center | N/A | √ (Optional) |
| No Regional Hub/Gateway/Data Center | NA | √ (Optional) | |
SD-WAN Deployment Architectures Supported by Nuage Networks
Nuage Networks supports the following deployment architectures for use with Prisma
Access. A dash (—) indicates that the deployment isn't supported.
| Use Case | Architecture | Supported? |
|---|---|---|
| Securing traffic from each branch site with 1 WAN link (Type 1) |

| Yes |
| Securing branch and HQ sites with active/backup SD-WAN connections |
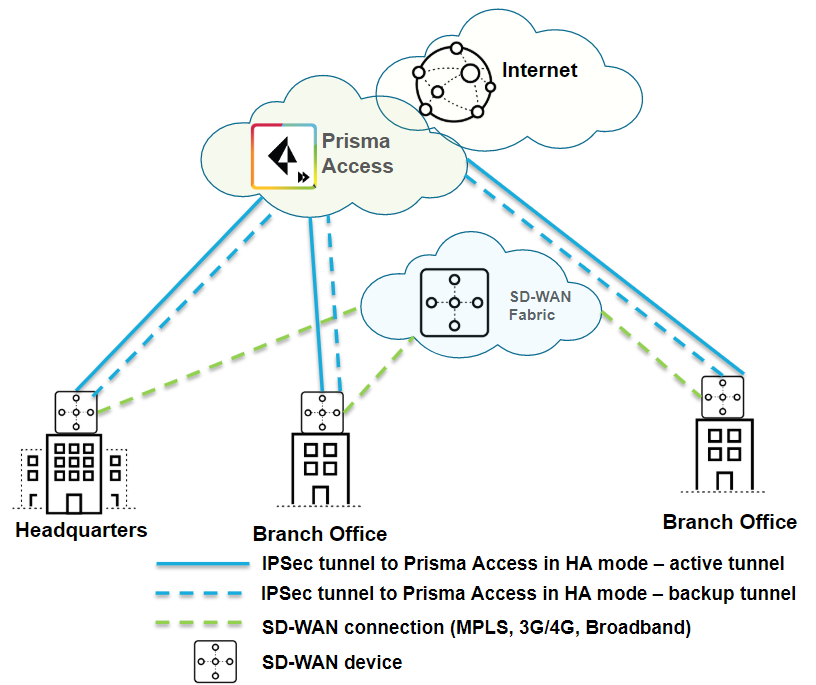
| Yes |
| Securing branch and HQ sites with active/active SD-WAN connections |
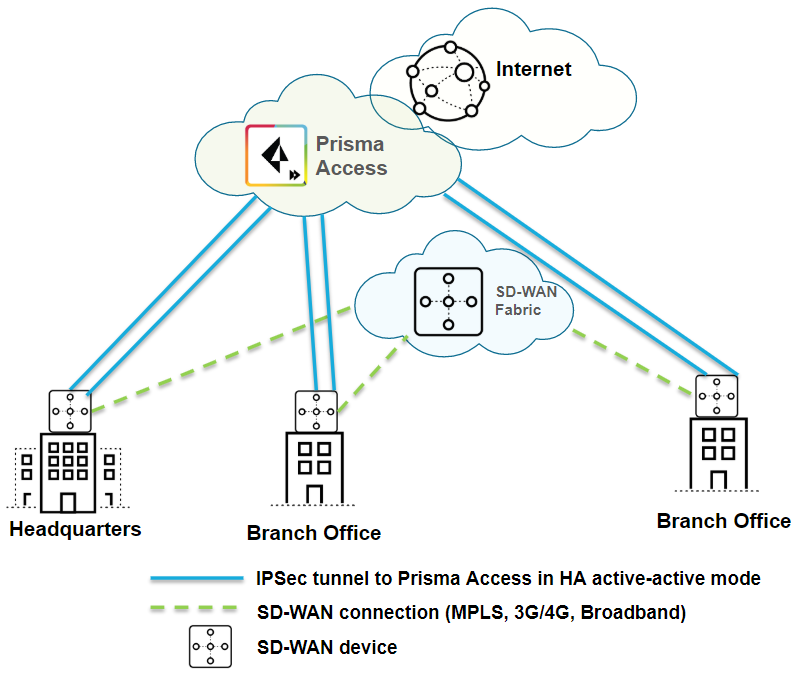
| Yes |
| Securing branch and HQ sites with SD-WAN edge devices in HA mode |
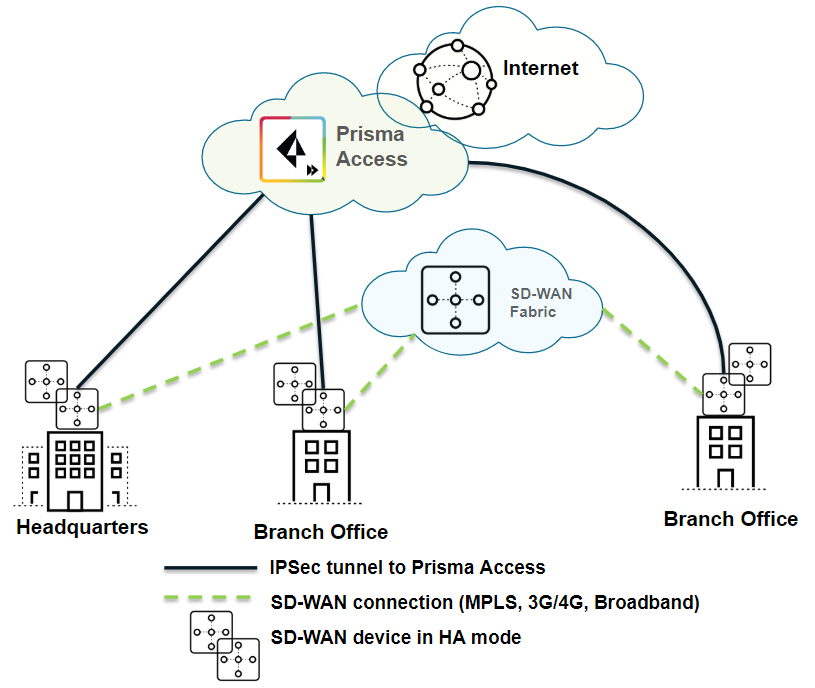
| Yes |
| Securing SD-WAN deployments with Regional Hub/POP architecture (Type 2) |
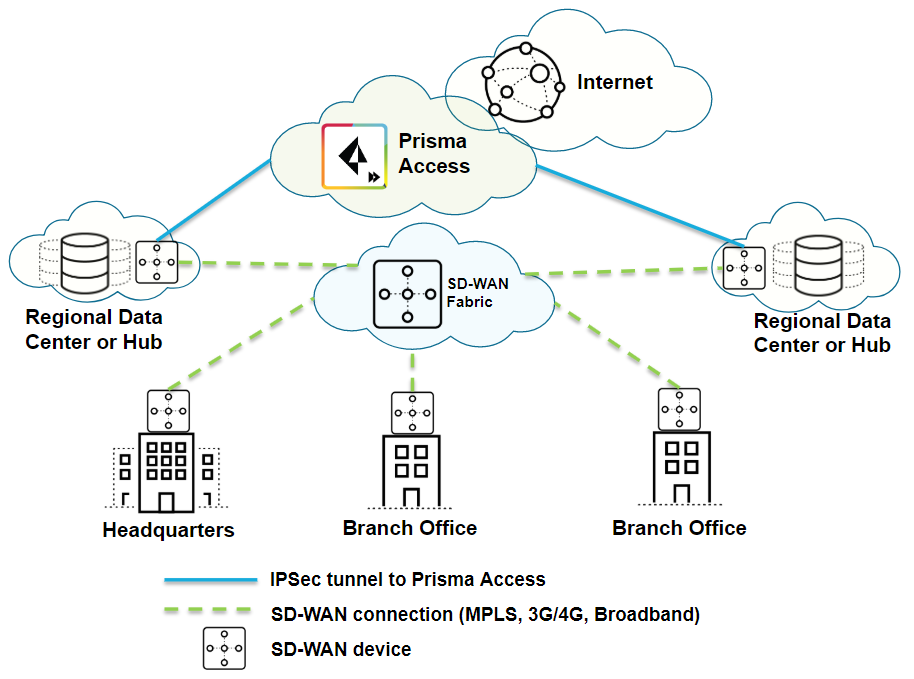
| Yes |
