SD-WAN DIA AnyPath
Table of Contents
10.0 (EoL)
Expand all | Collapse all
-
- Automatic Content Updates Through Offline Panorama
- Enhanced Authentication for Dedicated Log Collectors and WildFire Appliances
- Syslog Forwarding Using Ethernet Interfaces
- Increased Configuration Size for Panorama
- Access Domain Enhancements for Multi-Tenancy
- Enhanced Performance for Panorama Query and Reporting
- Log Query Debugging
- Configurable Key Limits in Scheduled Reports
- Multiple Plugin Support for Panorama
End-of-Life (EoL)
SD-WAN DIA AnyPath
High-level steps to configure DIA AnyPath so that a DIA
link can fail over to VPN tunnel links.
When your SD-WAN direct internet access (DIA)
links from an ISP experience a blackout or brownout, you need those
links to fail over to another link to ensure business continuity.
DIA links can fail over to an MPLS link, but you may not have an
MPLS link. DIA links must be able to fail over to another link that
has a direct path or indirect path (through a hub or branch) to
the internet; the DIA traffic can take any path available
to get to the internet and isn’t restricted to DIA. DIA AnyPath supports
a DIA link failing over to a private VPN tunnel going to a hub firewall
to then reach the internet. Furthermore, if your topology is full
mesh (branch-to-branch) and there is no hub, the DIA traffic can
fail over to a branch firewall to reach the internet.
DIA
AnyPath requires PAN-OS 10.0.3 or a later 10.0 release and SD-WAN
Plugin 2.0.1 or a later 2.0 release.
DIA AnyPath introduces
the concept of a principal virtual interface, which can include
both DIA links and nested hub virtual interfaces and branch
virtual interfaces (VPN tunnels) that each include their own
links. The principal virtual interface can have a maximum of nine
DIA (Ethernet) interfaces, hub virtual interfaces, and branch virtual
interfaces. You assign a Link Tag to a hub when you add the hub
device to Panorama. Assuming you use the SD-WAN plugin, Auto VPN
assigns that Link Tag to the hub virtual interface, which allows
you to specify the tag in a Traffic Distribution profile to control
the failover order among virtual interfaces.
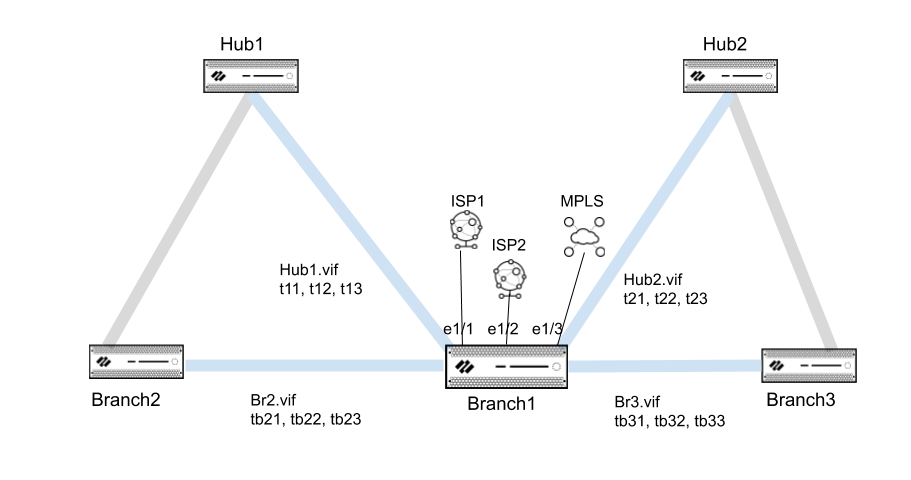
The following
topology example shows Branch1 with two ISP connections and an MPLS
link. Branch1 also has a Hub1 virtual interface with three VPN tunnels
connecting to Hub1, and a Hub2 virtual interface of three VPN tunnels
connecting to Hub2. Branch1 also has a branch2 virtual interface
with three VPN tunnels connecting to Branch2 and a branch3 virtual
interface with three VPN tunnels connecting to Branch3. The goal
of DIA AnyPath is to configure the order in which DIA can fail over
to VPN tunnels to reach the internet directly or indirectly and
thus maintain business continuity.
When you
configure a principal virtual interface, it automatically becomes
the default route so that internet traffic is routed properly to
any of the members of the principal virtual interface (both DIA
links and VPN tunnels). The path selection is based on SD-WAN Path
Quality profiles and Traffic Distribution profiles, which you would
set to use the Top Down Priority distribution method to control
the failover order. In the example topology, a Traffic Distribution
profile can list the tag for the principal virtual interface first, then
the tag for the Hub1 virtual interface, and then the tag for the
Hub2 virtual interface.
Zooming in to a deeper level of failover
priority, a hub virtual interface has multiple tunnel members, so
you need a way to prioritize the failover order of the members,
such as prioritizing that a broadband VPN tunnel be used before
an LTE VPN tunnel. You specify the priority using the VPN
Failover Metric in the SD-WAN Interface Profile that
you apply to the Ethernet interface. The lower the metric value,
the higher the priority for the tunnel to be selected upon failover.
In the topology example, in the Hub1 virtual interface, a lower
VPN Failover Metric for t11 than for t12 causes internet traffic
to fail over to t11 before t12. If multiple tunnels in a virtual
interface have the same metric, SD-WAN sends new session traffic
to the tunnels in round-robin fashion.
- Log in to the Panorama Web InterfaceSpecify the failover priority for a VPN tunnel (that is bundled in a hub virtual interface or branch virtual interface) by creating an SD-WAN Interface Profile.Configure a physical Ethernet interface for SD-WAN and on the SD-WAN tab, apply the SD-WAN Interface Profile you created.Repeat the prior two steps to configure additional SD-WAN Interface Profiles with a different VPN failover metric and apply the profiles to different Ethernet interfaces to determine the order in which failover occurs to the links.Create a Link Tag for a hub virtual interface.Add the Link Tag to a hub that you want to participate in DIA AnyPath.Repeat the prior two steps to create a Link Tag for each hub virtual interface and add the tag to each hub that will participate in DIA AnyPath. Do the same for any branch virtual interface.Create a Traffic Distribution Profile (using Top Down Priority) to implement DIA AnyPath.Create identically named SaaS Quality profiles for both the hub and branch firewalls.Allow the hubs to participate in DIA AnyPath.Create an SD-WAN policy rule for specific application(s) to use DIA AnyPath.Route new sessions that don’t match any SD-WAN policy rule and sessions that arrive during a Panorama or firewall configuration change.Commit and Push to Devices.Create a Security policy rule to allow DIA traffic to the Destination Zones named zone-internet and zone-to-hub and specify the Applications subject to the rule. Commit and push to the branches.
