SD-WAN
Create a Full Mesh VPN Cluster with DDNS Service
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
SD-WAN Docs
-
-
-
-
- 3.4
- 3.3
- 3.2
- 3.1
- 3.0
- 2.2
- 2.1
- 2.0
- 1.0
-
Create a Full Mesh VPN Cluster with DDNS Service
Create an SD-WAN VPN cluster that is full mesh with DDNS
Service.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
Beginning with PAN-OS 10.0.3, SD-WAN supports a full mesh topology, in addition to
the hub-spoke topology. The mesh can consist of
branches with or without hubs. Use full mesh when the branches need to communicate
with each other directly. Examples of use cases for full mesh include retailers that
have branches and hubs, and enterprises that operate with or without hubs.
Some firewall interfaces use DHCP to get their IP address. Branch offices often use a
consumer-grade internet service and receive a dynamic IP address, which of course
can change. For this reason, the firewalls require Dynamic DNS (DDNS) so that a DDNS
service can detect the public-facing IP address of the firewall interface that is
running SD-WAN. When you push the DDNS setting to all firewalls, that
notifies each firewall to register its external interface IP address with the Palo
Alto Networks DDNS cloud service so that the IP address is converted to an FQDN.
DDNS is also required because the CPE device from the ISP may be performing source NAT. (The
dynamic IP address may or may not be source-NAT translated). The DDNS service allows
the firewall to register the public-facing IP address with the DDNS server. When you
have devices connect for branch-to-branch mesh, Auto VPN contacts the DDNS service
for those firewalls to pull their public IP addresses that are registered in the
DDNS cloud and uses those public IP addresses to create the IKE peering and the VPN
tunnels. If the CPE device is performing source NAT, when you add an SD-WAN branch device to be managed by Panorama, you
will enable Upstream NAT and the NAT IP Address Type will be
DDNS.
For
the CPE device or upstream routing device using source NAT, you
are responsible for creating the one-to-one destination NAT rule
(with no port translation) on that device to translate the external
IP address back to the private IP address assigned to the firewall’s
interface. This translation allows the IKE and IPSec protocols to
come back into the firewall. (Palo Alto Networks doesn’t have access
rights to the upstream CPE or upstream router that is performing source
NAT.)
SD-WAN full mesh with DDNS service requires the following:
- ZTP plugin 1.0.1 or a later 1.0 release that is downloaded, installed, and configured in order to leverage the DDNS that is associated with ZTP. Panorama must be ZTP-registered and communicating with the ZTP Service.
- Applications and Threats Content Release Version 8354 or a later version
- All firewalls participating in full mesh DDNS must be registered under the same Customer Support Portal (CSP) account.
- All firewalls participating in full mesh DDNS must have the latest device certificate installed. Properly authenticating the firewalls, Panorama, and the cloud services are important security procedures that require the device certificate, and the CSP and ZTP services.
- If you have a firewall or other network device that controls
outgoing traffic positioned in front of the Palo Alto Networks firewall,
you must change the configuration on that device to allow traffic
from the DDNS-enabled interfaces to the following FQDNs:
- https://myip.ngfw-ztp.paloaltonetworks.com/ (to reach whatsmyIP service)
- https://ngfw-ztp.paloaltonetworks.com/ (to reach DDNS registration service)
- Install the latest device certificate for Panorama and for all managed firewalls that are hubs or branches.Install ZTP Plugin 1.0.1 to set up Zero Touch Provisioning.
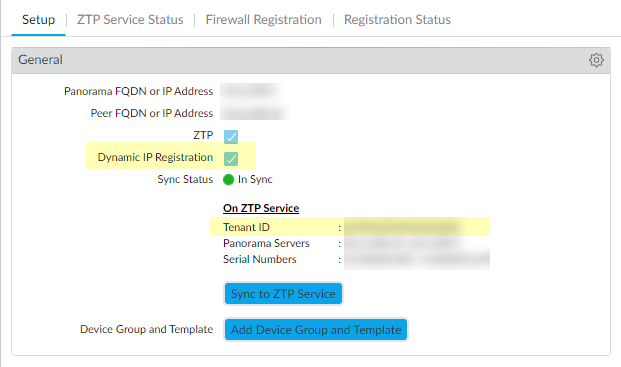
- In the Panorama Administrator’s Guide, read the ZTP Overview.Install the ZTP Plugin.Configure the ZTP Installer Administrator Account.Select PanoramaZero Touch ProvisioningSetup and edit the General settings to enable Dynamic IP Registration.Click OK. The General settings indicate On ZTP Service with a Tenant ID number.
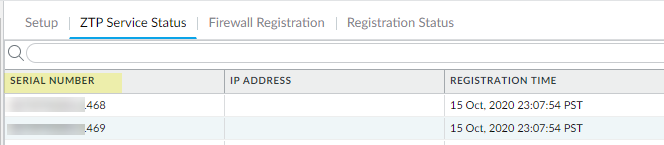
![]() Select ZTP Service Status and confirm that the firewall Serial Number is listed.
Select ZTP Service Status and confirm that the firewall Serial Number is listed.![]() If you haven’t already done so, install the SD-WAN plugin 2.0.1 or a 2.0 release.Commit on Panorama.Log in to the Panorama Web Interface.Create the VPN Address Pool while planning your topology for SD-WAN with Auto VPN.Create the full mesh VPN cluster.
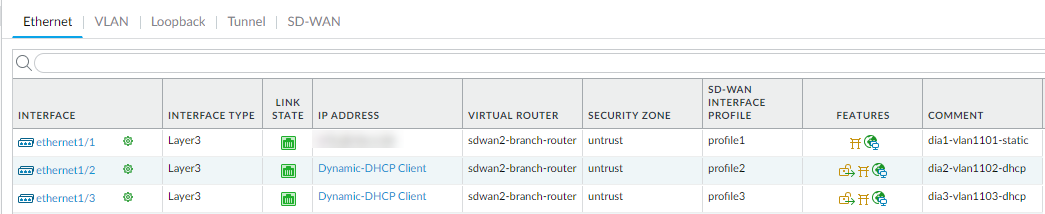
If you haven’t already done so, install the SD-WAN plugin 2.0.1 or a 2.0 release.Commit on Panorama.Log in to the Panorama Web Interface.Create the VPN Address Pool while planning your topology for SD-WAN with Auto VPN.Create the full mesh VPN cluster.- Select PanoramaSD-WANVPN Clusters.Select the Type to be Mesh.Add the Branches that need to communicate with each other.(Optional) Add one or more Hubs if you also want a hub in the mesh.Click OK.Commit and Commit to Panorama. If your firewalls have static IP addresses, you are done. If your branch or hub firewalls in a VPN mesh have DHCP or PPPoE interfaces, you must use DDNS, so continue this procedure as follows.Select NetworkInterfacesEthernet and in the Template field, select Template-stack for a particular branch.Select the interface whose IP address indicates Dynamic-DHCP Client or PPPOE, click Override on the bottom of the screen, and click OK to close.Verify on Panorama that the DDNS settings were configured.
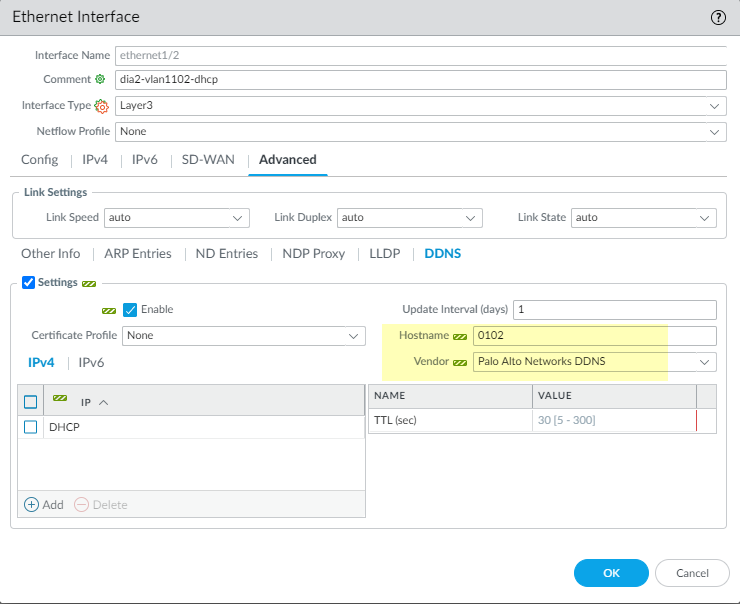
- Select NetworkInterfacesEthernet and select the same interface again.Select AdvancedDDNS.See that the DDNS settings were automatically configured with a Hostname based on the interface name, and the Vendor set to Palo Alto Networks DDNS. For example, on the Ethernet1/2 interface, the resulting Hostname is 0102.
![]() Click OK.If the VPN cluster includes any hubs that have a DHCP or PPPoE interface, repeat Steps 9 through 11, but in the Template field, select Template-stack for a particular hub.Even if your hub is not in a full mesh cluster, but is in a hub-spoke cluster, if the hub uses DHCP or PPPOE to get its IP address for an SD-WAN interface, you must perform the Override steps to enable DDNS.Commit to Panorama and Push to Devices.Verify on the branch firewall that the branch is configured with DDNS.
Click OK.If the VPN cluster includes any hubs that have a DHCP or PPPoE interface, repeat Steps 9 through 11, but in the Template field, select Template-stack for a particular hub.Even if your hub is not in a full mesh cluster, but is in a hub-spoke cluster, if the hub uses DHCP or PPPOE to get its IP address for an SD-WAN interface, you must perform the Override steps to enable DDNS.Commit to Panorama and Push to Devices.Verify on the branch firewall that the branch is configured with DDNS.- Log into the branch firewall.Select NetworkInterfacesEthernet and for the Ethernet interface that you configured, scroll over theDDNS Info icon in the Features column to see the Vendor, Hostname, IP address, and other DDNS information.
![]()
![]() On another branch in the cluster, view that the Peer Address of the interface is a system-generated FQDN for the DDNS registration.
On another branch in the cluster, view that the Peer Address of the interface is a system-generated FQDN for the DDNS registration.- Log onto another branch and select NetworkNetwork ProfilesIKE Gateways.See that the Peer Address is a secure name, not easily referenced and showing no company information; for example 0101.8ced8460fcc5177cd3665ce41b6345323a15a612b8e52ec1d9ec057a582cb4.t13855f6c9a92d6[...]e18a0d96dab45dd767a230daac94408d0.dicedns.netView FQDNs of branches and hubs and update DDNS information.
- Access the CLI.View FQDNs (generated by DDNS) for other branches and hubs: show dns-proxy fqdn allUpdate the DDNS addresses: request system fqdn refresh