Advanced URL Filtering
Configure Inline Categorization
Table of Contents
Configure Inline Categorization
Enable inline machine learning-based URL filtering for
real-time analysis of web pages.
| Where can I use this? | What do I need? |
|---|---|
|
Notes:
|
To enable inline categorization, attach a URL
Filtering profile configured with inline categorization settings
to a Security policy rule (see Set Up a Basic Security Policy).
URL
Filtering local inline categorization is not currently supported on
the VM-50 or VM50L virtual appliance.
Configure Inline Categorization (Strata Cloud Manager)
If you’re using Panorama to manage Prisma Access:
Toggle over to the PAN-OS & Panorama tab and follow the guidance
there.
If you’re using Strata Cloud Manager, continue here.
- Update or create a URL Access Management profile.
- Go to Configuration NGFW and Prisma AccessSecurity ServicesURL Access Management.On the URL Access Management dashboard, select a URL Access Management profile or Add Profile.If you create a new profile, configure settings in the profile, such as site access for URL categories (Access Control). Configure URL Filtering (Cloud Management) describes the available settings.Under Advanced URL Inline Categorization, select an inline categorization type.Both options enable real-time web page analysis and manage URL exceptions.
- Enable cloud Inline Categorization—Enables real-time analysis of URLs by forwarding suspicious web page contents to the cloud for supplemental analysis, using machine learning based detectors that complement the analysis engines used by local inline ML.
- Enable local Inline Categorization—Enables real-time analysis of URL traffic using machine learning models, to detect and prevent malicious phishing variants and JavaScript exploits from entering your network.
- You can also define URL Exceptions to exclude specific websites from inline machine learning actions.
![]() Save the profile.Apply the URL Access Management profile to a Security policy rule.To activate a URL Access Management profile (and any Security profile), add it to profile group and reference the profile group in a Security policy rule.
Save the profile.Apply the URL Access Management profile to a Security policy rule.To activate a URL Access Management profile (and any Security profile), add it to profile group and reference the profile group in a Security policy rule.Configure Inline Categorization (PAN-OS & Panorama)
Configure inline categorization based on the PAN-OS version your management interface is running.In PAN-OS 10.2, the URL Filtering Inline ML feature was renamed to Inline Categorization. As a result, the PAN-OS 10.1 task uses the phrase URL Filtering inline ML while the PAN-OS 10.2 and Later task uses Inline Categorization. For more information, review the URL Filtering Inline ML entry in PAN-OS 10.2 Upgrade/Downgrade Considerations.Configure Inline Categorization (PAN-OS 10.1)
Configure URL Filtering Inline ML in PAN-OS 10.1.- Log in to the PAN-OS web interface.Verify that you have an active legacy URL filtering or Advanced URL Filtering subscription.Select DeviceLicenses and confirm that a URL filtering license is available and has not expired.
![]() Configure the URL Filtering Inline ML settings in a URL Filtering profile.
Configure the URL Filtering Inline ML settings in a URL Filtering profile.- Select ObjectsSecurity ProfilesURL Filtering, then Add or select a URL Filtering profile.Select Inline ML and define an Action for each inline ML model.There are two classification engines available for each type of malicious webpage content: Phishing and JavaScript Exploit.
- Block—When the firewall detects a website with phishing content, the firewall generates a URL Filtering log entry.
- Alert—The firewall allows access to the website and generates a URL Filtering log entry.
- Allow—The firewall allows access to the website but does not generate a URL Filtering log entry.
![]() Click OK to save your changes.Commit your changes.(Optional) Add URL exceptions to your URL Filtering profile if you encounter false-positives.You can add exceptions by specifying an external dynamic list in the URL Filtering profile or by adding a web page entry from the URL Filtering logs to a custom URL category.
Click OK to save your changes.Commit your changes.(Optional) Add URL exceptions to your URL Filtering profile if you encounter false-positives.You can add exceptions by specifying an external dynamic list in the URL Filtering profile or by adding a web page entry from the URL Filtering logs to a custom URL category.- Select Objects > Security Profiles > URL Filtering.Select a URL Filtering profile for which you want to exclude specific URLs, then select Inline ML.Add a pre-existing external dynamic list of URL type. If none is available, create a new external dynamic list.Click OK to save your changes.Commit your changes.Add file exceptions from URL Filtering log entries.
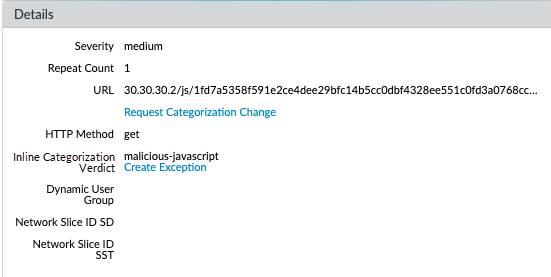
- Select Monitor > Logs > URL Filtering and filter the logs for URL entries with an Inline ML Verdict of malicious-javascript or phishing. Select a URL Filtering log for a URL that you wish to create an exception for.Go to the Detailed Log View and scroll down to the Details pane, then select Create Exception located next to the Inline ML Verdict.
![]() Select a custom category for the URL exception, then click OK.The new URL exception can be found in the list to which it was added, under Objects > Custom Objects > URL Category.(Optional) Verify the status of your firewall’s connectivity to the inline ML cloud service.Use the following CLI command on the firewall to view the connection status.
Select a custom category for the URL exception, then click OK.The new URL exception can be found in the list to which it was added, under Objects > Custom Objects > URL Category.(Optional) Verify the status of your firewall’s connectivity to the inline ML cloud service.Use the following CLI command on the firewall to view the connection status.show mlav cloud-statusFor example:show mlav cloud-status MLAV cloud Current cloud server: ml.service.paloaltonetworks.com Cloud connection: connected
If you are unable to connect to the inline ML cloud service, verify that the ML domain ml.service.paloaltonetworks.com is not blocked.Test your URL filtering deployment.To view information about web pages that have been processed using URL Filtering inline ML, filter the logs (Monitor > Logs > URL Filtering) based on Inline ML Verdict. Web pages that have been determined to contain threats are categorized with verdicts of either phishing or malicious-javascript. For example: ![]()
Configure Inline Categorization (PAN-OS 10.2 & Later)
- Log in to the PAN-OS web interface.To take advantage of inline categorization, you must have an active Advanced URL Filtering subscription.Local inline categorization can be enabled if you are a pre-existing holder of a legacy URL Filtering subscription.Verify that you have an Advanced URL Filtering subscription. To verify subscriptions for which you have currently-active licenses, select DeviceLicenses and verify that the appropriate licenses are available and have not expired.
![]() Update or create a new URL Filtering profile to enable cloud inline categorization.The policy action used by local and cloud inline categorization is dependent on the configured settings under the Categories tab.
Update or create a new URL Filtering profile to enable cloud inline categorization.The policy action used by local and cloud inline categorization is dependent on the configured settings under the Categories tab.- Select an existing URL Filtering Profile or Add a new one (ObjectsSecurity ProfilesURL Filtering).
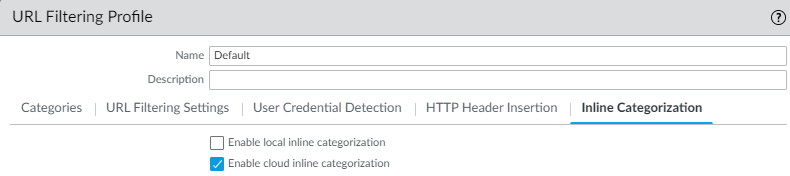
- Select your URL Filtering profile and then go to Inline Categorization and enable the inline categorization methods you want to deploy.
- Enable cloud inline categorization—A cloud-based inline deep learning engine that analyzes suspicious web page content in real-time to protect users against zero-day web attacks, including targeted phishing attacks, and other web-based attacks that use advanced evasion techniques.
- Enable local inline categorization—A firewall-based detection engine using machine learning techniques to prevent malicious variants of JavaScript exploits and phishing attacks embedded in webpages.
![]()
- Click OK and Commit your changes.
(Optional) Add URL exceptions to your URL Filtering profile if you encounter false-positives. You can add exceptions by specifying an external dynamic list or custom URL category list in the URL Filtering profile. The specified exceptions apply to both cloud and local inline categorization.URL exceptions created through other mechanisms that add entries to the custom URL category (ObjectsCustom ObjectsURL Category)can also function as exceptions for inline categorization.- Select Objects > Security Profiles > URL Filtering.
- Select a URL Filtering profile for which you want to exclude specific URLs, then select Inline Categorization.
- Click Add to select a pre-existing URL-based external dynamic list or custom URL category. If none is available, create a new external dynamic list or custom URL category, respectively.
- Click OK to save the URL Filtering profile.
- Commit your changes.
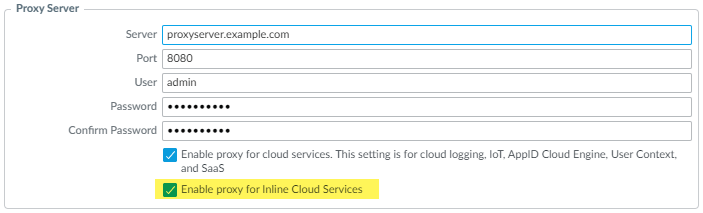
(Required when the firewall is deployed with an explicit proxy server) Configure the proxy server used to access the servers that facilitate requests generated by all configured inline cloud analysis features. A single proxy server can be specified and applies to all Palo Alto Networks update services, including all configured inline cloud and logging services.- (PAN-OS 11.2.3 and later) Configure the proxy server through PAN-OS.
- Select Device Setup Services and edit the Services details.
- Specify the Proxy Server settings and Enable proxy for Inline Cloud Services. You can provide either an IP address or FQDN in the Server field.The proxy server password must contain a minimum of seven characters.
![]()
- Click OK.
(For the following releases only: PAN-OS 10.2.11 and later and PAN-OS 11.1.5 and later) Configure the proxy server through the firewall CLI.- Configure the base proxy server settings using the following CLI commands:
set deviceconfig system secure-proxy-server <FQDN_or_IP> set deviceconfig system secure-proxy-port <1-65535> set deviceconfig system secure-proxy-user <value> set deviceconfig system secure-proxy-password <value>
The proxy server password must contain a minimum of seven characters. - Enable the proxy server to send requests to the inline cloud service servers using the following CLI command:
debug dataplane mica set inline-cloud-proxy enable
- View the current operational status of proxy support for inline cloud services using the following CLI command:
debug dataplane mica show inline-cloud-proxy
For example:debug dataplane mica show inline-cloud-proxy Proxy for Advanced Services is Disabled
(Optional) Set the Cloud Content Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) used by the firewall to handle inline categorization service requests. The default FQDN connects to hawkeye.services-edge.paloaltonetworks.com and then resolves to the closest cloud services server. You can override the automatic server selection by specifying a regional cloud content server that best meets your data residency and performance requirements.The Cloud Content FQDN is a globally used resource and affects how other services that rely on this connection sends traffic payloads.Verify that the firewall uses the correct Content Cloud FQDN (DeviceSetupContent-IDContent Cloud Setting) for your region and change the FQDN if necessary:- US—us.hawkeye.services-edge.paloaltonetworks.com
- EU—eu.hawkeye.services-edge.paloaltonetworks.com
- UK—uk.hawkeye.services-edge.paloaltonetworks.comThe UK-based cloud content FQDN provides Advanced URL Filtering inline categorization service support by connecting to the backend service located in the EU (eu.hawkeye.services-edge.paloaltonetworks.com).
- APAC—apac.hawkeye.services-edge.paloaltonetworks.com
(Optional) Verify the status of your firewall’s connectivity to the inline categorization servers.- The ml.service.paloaltonetworks.com server provides periodic updates for firewall-based components related to the operation of cloud and local inline categorization.Use the following CLI command on the firewall to view the connection status.
show mlav cloud-statusFor example:show mlav cloud-status MLAV cloud Current cloud server: ml.service.paloaltonetworks.com Cloud connection: connected
If you are unable to connect to the inline ML cloud service, verify that the following domain is not being blocked: ml.service.paloaltonetworks.com.The hawkeye.services-edge.paloaltonetworks.com server is used by cloud inline categorization to handle service requests.Use the following CLI command on the firewall to view the connection status.show ctd-agent status security-clientFor example:show ctd-agent status security-client ... Security Client AceMlc2(1) Current cloud server: hawkeye.services-edge.paloaltonetworks.com Cloud connection: connected ...
CLI output shortened for brevity.If you are unable to connect to the Advanced URL Filtering cloud service, verify that the following domain is not being blocked: hawkeye.services-edge.paloaltonetworks.com.Install an updated firewall device certificate used to authenticate to the Advanced URL Filtering cloud service. Repeat for all firewalls enabled for cloud inline categorization.