Advanced URL Filtering
Configure URL Filtering
Table of Contents
Configure URL Filtering
Follow these steps to configure URL Filtering profiles
and settings that meet your organization’s business and security
needs.
| Where can I use this? | What do I need? |
|---|---|
|
Notes:
|
After you plan your URL filtering
deployment, you should have a basic understanding of the types of
websites your users are accessing. Use this information to create a URL Filtering
profile that defines how the firewall handles traffic to specific URL categories.
You can also restrict the sites to which users can submit corporate credentials or enforce strict safe search. To
activate these settings, apply the URL Filtering profile to Security policy rules that allow web
access.
Configure URL Filtering (Strata Cloud Manager)
If you’re using Panorama to manage Prisma Access:
Toggle over to the PAN-OS & Panorama tab and follow the guidance there.
If you’re using Strata Cloud Manager, continue here.
URL filtering is called URL Access Management in Strata Cloud Manager
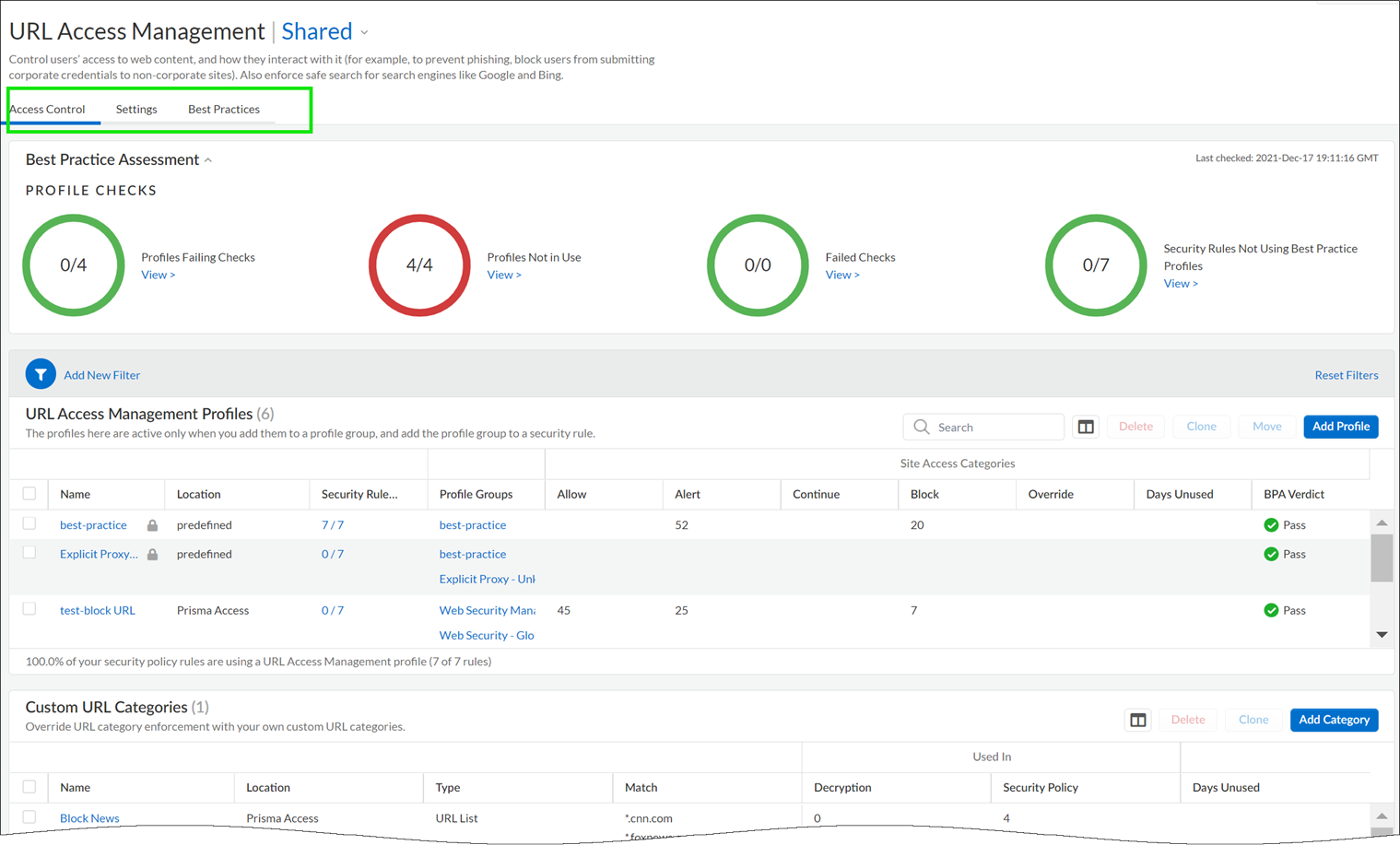
- Check that your Prisma Access subscription covers Advanced URL Filtering.Explore the URL Access Management Dashboard.Go to ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessSecurity ServicesURL Access Management.Move between the Access Control, Settings, and Best Practices tabs to explore the available URL filtering features.
![]() Review and customize General URL Filtering Settings.On the dashboard, go to Settings to see the default URL Filtering settings that apply across your Prisma Access environment, including:
Review and customize General URL Filtering Settings.On the dashboard, go to Settings to see the default URL Filtering settings that apply across your Prisma Access environment, including:- URL Filtering timeout and lookup settings
- URL Filtering overrides for certain admins
- URL Filtering response pages
Automatically append end tokens to URLs in a custom URL category or external dynamic list(PAN-OS 10.1 and earlier) If you add URLs to custom URL categories or external dynamic lists (EDLs) of URL list type and don't append a trailing slash (/), you may block or allow more URLs than intended. For example, entering example.com instead of example.com/ expands matching URLs to example.com.website.info or example.com.br. Prisma Access can automatically append a trailing slash to URLs in custom URL categories or EDLs so that, if you enter example.com, Prisma Access treats it as it would treat example.com/ and only considers that domain and its subdirectories matches. Go to SettingsGeneral Settings and enable the Append End Token to Entries option.(PAN-OS 10.2 and later)Prisma Access automatically adds a trailing slash to domain entries.You can customize these settings for each deployment type (mobile users, remote networks, or service connections).Create a URL Access Management profile.On the URL Access Management dashboard, Add Profile and continue to specify web access settings:- Access Control displays the URL categories and lists for which you can define web access and usage policy. By default, the Site Access and User Credential Submission permissions for all categories are set to Allow.
- For each URL category, configure User Credential Detection so that users can submit credentials only to sites in specified URL categories.
- Enable Safe Search Enforcement to enforce strict safe search filtering.
- Enable Log Container Page Only to log only those URLs that match the content type that is specified.
- Enabling HTTP Header Logging provides visibility into the attributes in the HTTP request sent to a server.
- Use the Advanced URL Inline Categorization to enable and configure real-time web page analysis and manage URL exceptions.
- Enable local Inline Categorization—Enables real-time analysis of URL traffic using machine learning models, to detect and prevent malicious phishing variants and JavaScript exploits from entering your network.
- Enable cloud Inline Categorization—Enables real-time analysis of URLs by forwarding suspicious web page contents to the cloud for supplemental analysis, using machine learning based detectors that complement the analysis engines used by local inline ML.
- You can define URL Exceptions for specific web sites to exclude from inline machine learning actions.
Note that:- Best practice checks are built-in to the profile to give you a live evaluation of your configuration.
- After you’ve finished enabling a profile, you can examine profile usage to see if any security policy rules are referencing the profile.
![]() Apply the URL Access Management profile to a Security policy rule.A URL Access Management profile is only active when it’s included in a profile group that a Security policy rule references.Follow the steps to activate a URL Access Management profile (and any Security profile). Be sure to Push Config
Apply the URL Access Management profile to a Security policy rule.A URL Access Management profile is only active when it’s included in a profile group that a Security policy rule references.Follow the steps to activate a URL Access Management profile (and any Security profile). Be sure to Push ConfigConfigure URL Filtering (PAN-OS & Panorama)
Follow these steps to configure URL Filtering profiles and settings that meet your organization’s business and security needs.- Create a URL Filtering profile.If you didn’t already, configure a best practice URL Filtering profile to ensure protection against URLs hosting malware or exploitive content.Select ObjectsSecurity ProfilesURL Filtering and Add or modify a URL Filtering profile.Define site access for each URL category.Select Categories, and then set Site Access:
- Select Allow to permit traffic destined for the URL category; this traffic is not logged.
- Select alert to gain visibility into sites that users are accessing. Traffic matching the category is allowed, and a URL filtering log is generated.
- Select block to deny access to traffic that matches the category and log this traffic.
- Select continue to display a response page to users that requires them to click Continue to proceed to a site in the category.
- To only allow access if users provide a configured password, select override. For more details, see Allow Password Access to Certain Sites.
Detect corporate credential submissions to websites in allowed URL categories.To ensure the best performance and a low false positive rate, the firewall automatically skips checking the credential submissions for any App-ID™ associated with sites that have never been observed hosting malware or phishing content—even if you enable checks in the corresponding category. The list of sites for which the firewall skips credential checking is automatically updated through Applications and Threats content updates.- In the URL Filtering profile, select the User Credential Detection tab.Select one of the methods to check for corporate credential submissions to web pages from the User Credential Detection drop-down:
- Use IP User Mapping—Checks for valid corporate username submissions and verifies that the username matches the user logged in to the source IP address of the session. The firewall matches the submitted username against its IP address-to-username mapping table. You can use any of the user mapping methods described in Map IP Addresses to Users.
- Use Domain Credential Filter—Checks for valid corporate usernames and password submissions and verifies that the username maps to the IP address of the logged-in user. See Configure Credential Detection with the Windows-based User-ID Agent for instructions on how to set up User-ID to enable this method.
- Use Group Mapping—Checks for valid username submissions based on the user-to-group mapping table populated when you configure the firewall to map users to groups.With group mapping, you can apply credential detection to any part of the directory or to a specific group, such as groups like IT that have access to your most sensitive applications.
This method is prone to false positives in environments that do not have uniquely structured usernames, so you should only use this method to protect your high-value user accounts.Set the Valid Username Detected Log Severity that the firewall uses to log detection of corporate credential submissions (default is medium).Detect phishing and malicious JavaScript in real-time using local inline categorization.Allow or block users from submitting corporate credentials to sites based on URL category to prevent credential phishing.To ensure the best performance and a low false positive rate, the firewall automatically skips checking the credential submissions for any App-ID associated with sites that have never been observed hosting malware or phishing content—even if you enable checks in the corresponding category. The list of sites for which the firewall skips credential checking is automatically updated through Applications and Threats content updates.- For each URL category to which you allow Site Access, select how you want to treat User Credential Submissions:
- alert—Allow users to submit credentials to the website but generate a URL filtering log each time a user submits credentials to sites in this URL category.
- allow (default)—Allow users to submit credentials to the website.
- block—Displays the anti-phishing block page to block users from submitting credentials to the website.
- continue—Present the anti-phishing continue page, which requires users to click Continue to access the site.
Configure the URL Filtering profile to detect corporate credential submissions to websites in allowed URL categories.Define URL category exceptions to specify websites that should always be blocked or allowed, regardless of URL category.For example, to reduce URL filtering logs, you may want to add your corporate websites to the allow list so that no logs are generated for those sites or, if there is a website that is being overly used and is not work-related, you can add that site to the block list.The policy actions configured for custom URL categories have priority enforcement over matching URLs in external dynamic lists.Traffic to websites in the block list is always blocked regardless of the action for the associated category and traffic to URLs in the allow list is always allowed.For more information on the proper format and wildcard usage, review the URL Category Exception Guidelines.Enable Safe Search Enforcement.Log only the page a user visits for URL filtering events.- Select URL Filtering Settings and enable Log container page only (default) so that the firewall logs only the main page that matches the category, not subsequent pages or categories that load within the container page.To enable logging for all pages and categories, disable the Log container page only option.Enable HTTP Header Logging for one or more of the supported HTTP header fields.Select URL Filtering Settings and select one or more of the following fields to log:
- User-Agent
- Referer
- X-Forwarded-For
Save the URL Filtering profile.Click OK.Apply the URL Filtering profile to Security policy rules that allow traffic from clients in the trust zone to the Internet.Make sure the Source Zone in the Security policy rules to which you add URL Filtering profiles is set to a protected internal network.- Select PoliciesSecurity. Then, select a Security policy rule to modify.On the Actions tab, edit the Profile Setting.For Profile Type, select Profiles. A list of profiles appears.For URL Filtering profile, select the profile you just created.Click OK to save your changes.Commit the configuration.Test your URL filtering configuration.(Best Practice) Enable Hold client request for category lookup to block client requests while the firewall performs URL category lookups.
- Select DeviceSetupContent-ID.Select Hold client request for category lookup.Commit your changes.Set the amount of time, in seconds, before a URL category lookup times out.
- Select DeviceSetupContent-IDgear icon.Enter a number for Category lookup timeout (sec).Click OK.Commit your changes.