Advanced URL Filtering
Test URL Filtering Configuration
Table of Contents
Test URL Filtering Configuration
Follow these steps to verify that Palo Alto Networks
URL Filtering services categorize and enforce policy on URLs as
expected.
| Where can I use this? | What do I need? |
|---|---|
|
Notes:
|
To test your URL filtering policy configurations, use Palo Alto Networks URL filtering test pages. These pages have
been created for the safe testing of all predefined URL categories and Advanced URL Filtering real-time-detection categories.
Test pages are accessible through HTTP and HTTPS connections. However, you
must enable SSL decryption to view test pages over HTTPS.
You can check the classification of a specific
website using Palo Alto Networks URL category lookup tool, Test A Site.
Follow the procedure corresponding to your URL Filtering subscription.
Verify URL Filtering
If you have the legacy URL Filtering subscription,
test and verify that the firewall correctly categorizes, enforces,
and logs URLs in the categories that end users access.
- Access a website in a URL category of interest.Consider testing sites in blocked URL categories. You can use a test page (urlfiltering.paloaltonetworks.com/test-<url-category>) to avoid directly accessing a site. For example, to test your block policy for malware, visit https://urlfiltering.paloaltonetworks.com/test-malware.Review the Traffic and URL Filtering logs to verify that your firewall processes the site correctly.For example, if you configured a block page to display when someone accesses a site that violates your organization’s policy, check that one appears when you visit the test site.
Verify Advanced URL Filtering
If you have an Advanced URL Filtering subscription, test and verify that URLs submitted to the Advanced URL Filtering are properly analyzed.Palo Alto Networks recommends setting the real-time-detection (cloud inline categorization) action setting to alert for active URL Filtering profiles. This provides visibility into URLs analyzed in real-time and will block (or allow, depending on your policy settings) based on the category settings configured for specific web threats.The firewall enforces the most severe action of the actions configured for detected URL categories of a given URL. For example, suppose example.com is categorized as real-time-detection, command-and-control, and shopping—categories with an alert, block, and allow action configured, respectively. The firewall blocks the URL because block is the most severe action of the detected categories.- Visit each of the following test URLs to verify that the Advanced URL Filtering service is properly categorizing URLs:If Cloud Inline Categorization is enabled, use the following URLs to test the operation of the feature:Monitor web activity to verify that the test URLs have been properly categorized by Advanced URL Filtering:
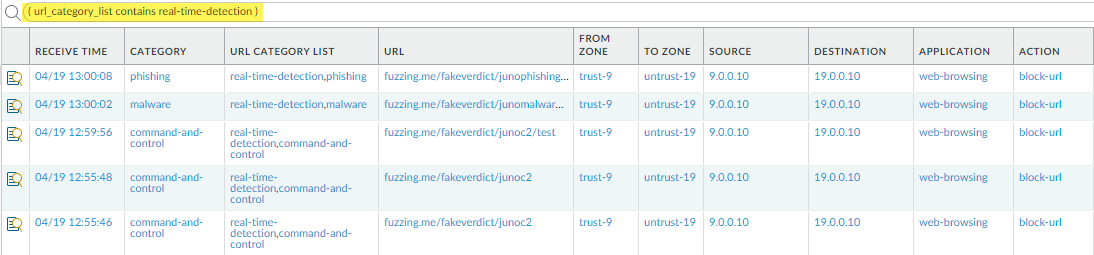
- Filter your URL Filtering logs using the following: (url_category_list contains real-time-detection).Additional web page category matches are also displayed and correspond to the categories as defined by PAN-DB.
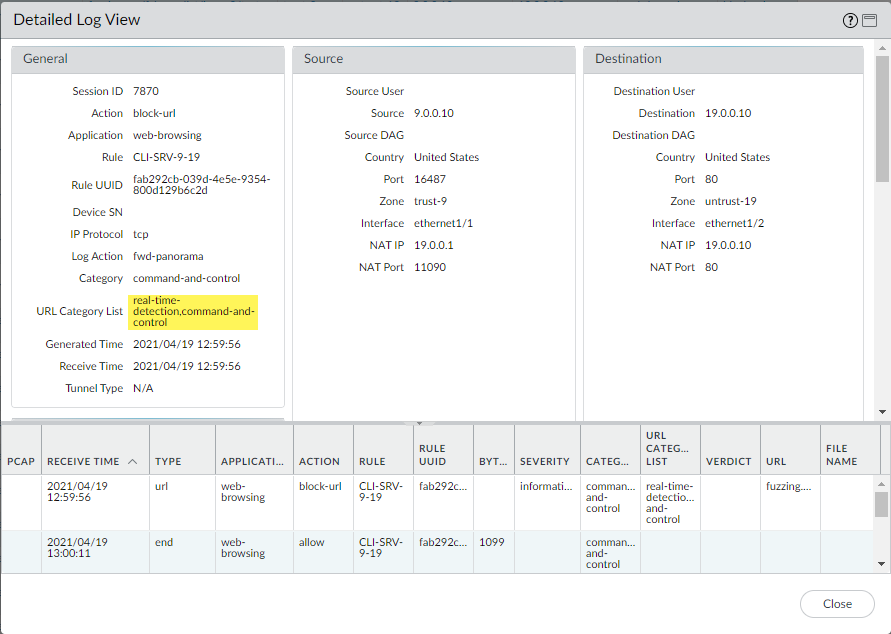
![]() Take a detailed look at the logs to verify that each type of web threat is correctly analyzed and categorized.In the next example, the URL is categorized as having been analyzed in real-time and possessing qualities that define it as command-and-control (C2). Because the C2 category has a more severe action associated with it than real-time-detection (block as opposed to alert), the URL is categorized as command-and-control and blocked.
Take a detailed look at the logs to verify that each type of web threat is correctly analyzed and categorized.In the next example, the URL is categorized as having been analyzed in real-time and possessing qualities that define it as command-and-control (C2). Because the C2 category has a more severe action associated with it than real-time-detection (block as opposed to alert), the URL is categorized as command-and-control and blocked.![]()