Download PDF
Cloud NGFW for Azure
Cloud NGFW for Azure Hub-and-Spoke Virtual Networks
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Cloud NGFW for Azure Docs
Cloud NGFW for Azure Hub-and-Spoke Virtual Networks
Learn about Cloud NGFW for Azure hub-and-spoke virtual networks.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
This architecture connects Azure virtual networks to the hub Virtual networks by
using peering connections that are
non-transitive, low-latency connections between virtual networks. Peered virtual
networks can exchange traffic over the Azure backbone without a router. In this
model, Cloud NGFW is deployed into the centralized hub VNet to secure traffic from
multiple spoke VNets in multiple Azure subscriptions. The deployed Cloud NGFW can
protect inbound, outbound, and lateral traffic that traverses a hub virtual network.
To implement Cloud NGFW into a Hub virtual network, you create two subnets—private
and public. Both subnets should have subnet delegation enabled. Cloud NGFW
private and public interfaces will reside in these two subnets.
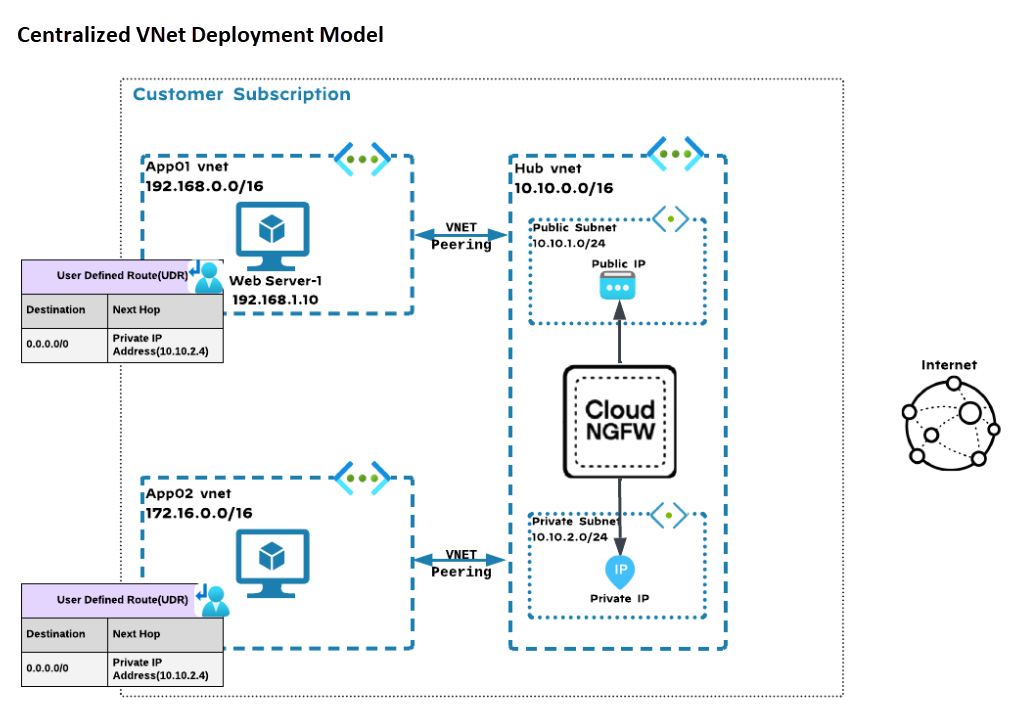
Centralized VNet Deployment Model: Internet Egress Traffic Inspection via Application Gateway VNET
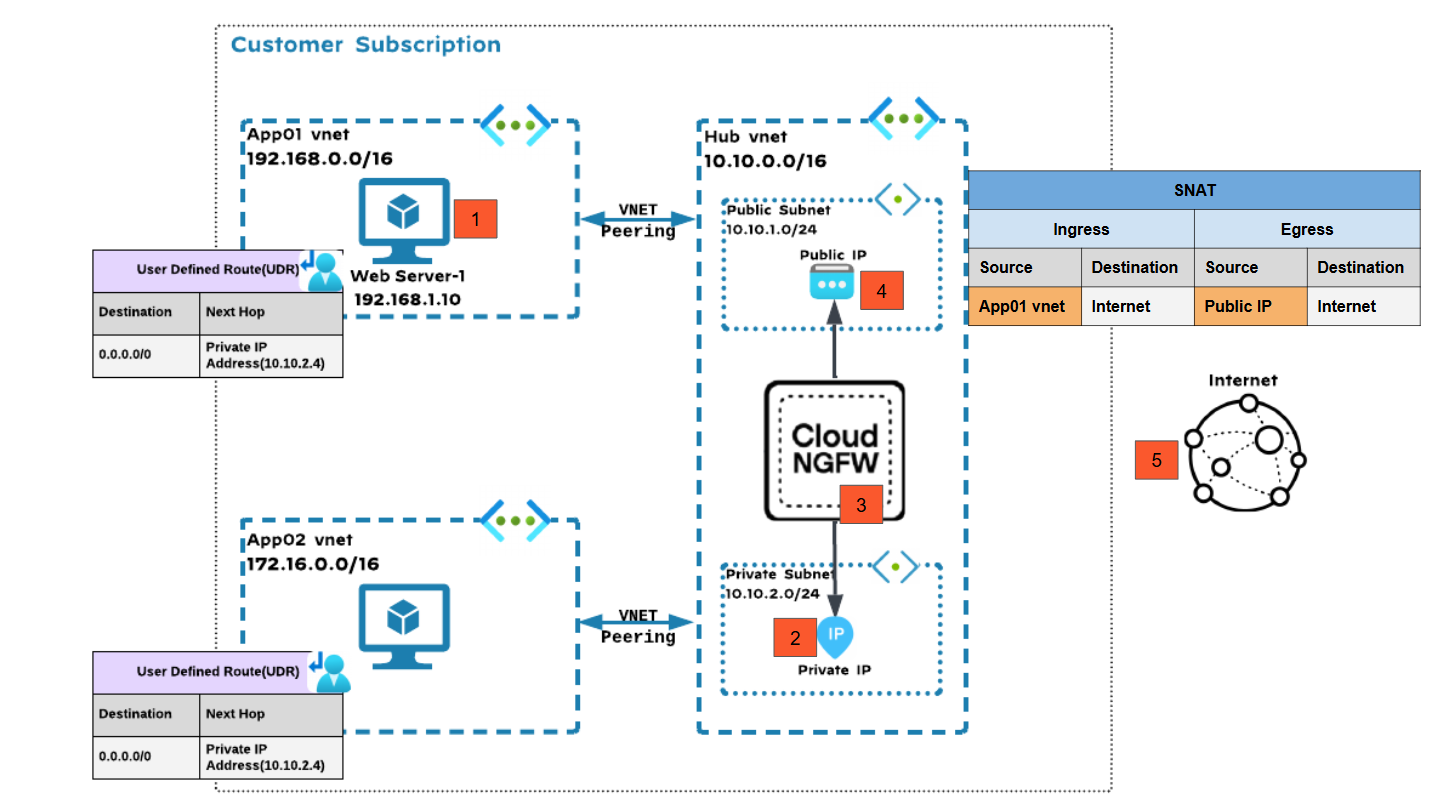
In this deployment model:
- Traffic from a App01 VNet workload VM is destined for the internet.Traffic from the spoke VM is forwarded to the private IP address of the Cloud NGFW using the User-Defined Route (UDR) associated with the workload subnet.Since the private IP address was internally associated with the Cloud NGFW, the packet arrives at the Cloud NGFW for inspection.After inspection, Cloud NGFW performs source NAT by changing the private IP address to the public IP address of the Cloud NGFW.After performing SNAT, the traffic is sent to the actual internet destination.
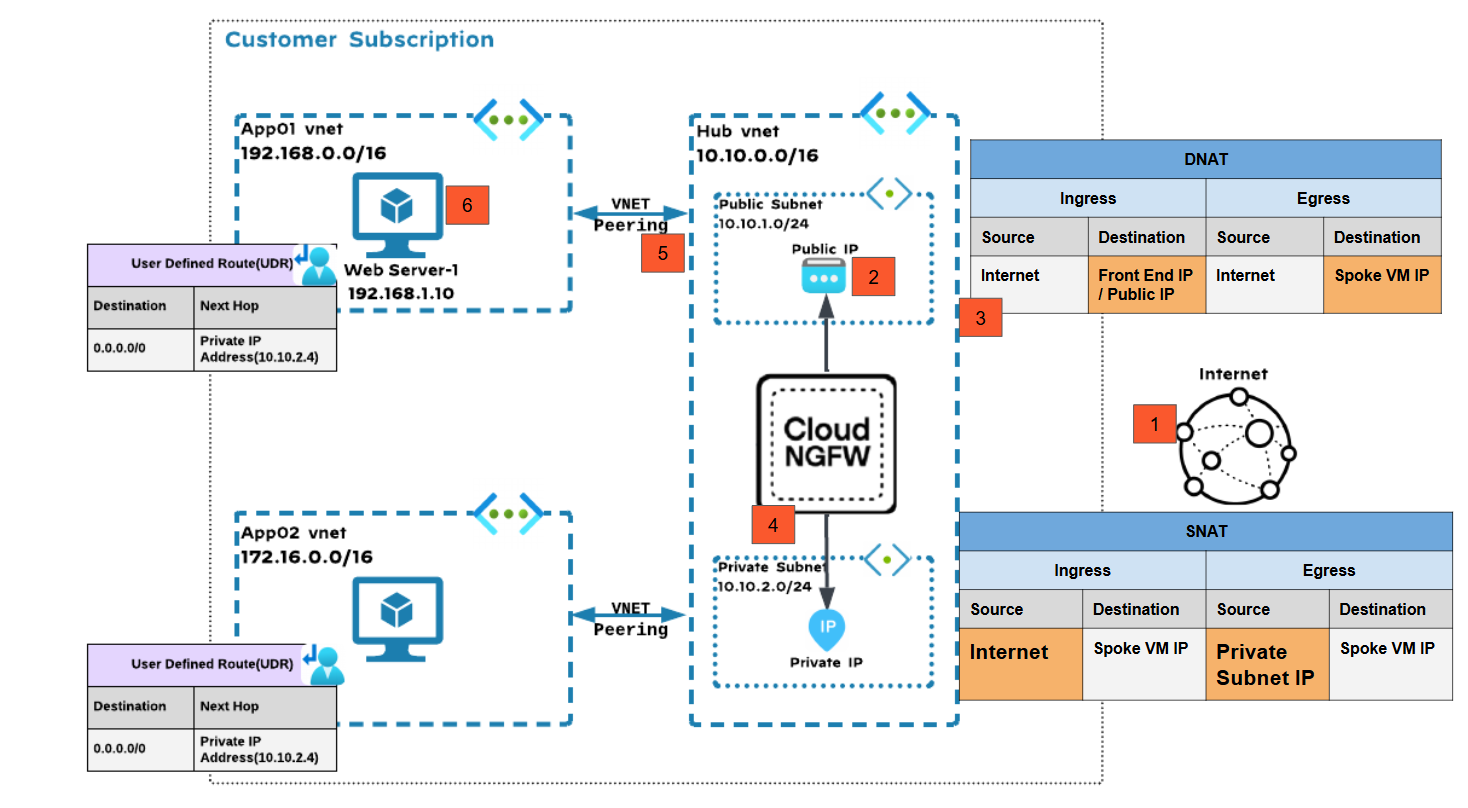
Centralized VNet Deployment Model: Internet Ingress Traffic Inspection via Application Gateway Subnet
![]() In this deployment model:
In this deployment model:- Traffic is destined from the internet to Web server-1 in App01 VNet.Traffic from the internet lands on the front-end or public IP address of the Cloud NGFW.The Cloud NGFW performs destination NAT is changed from the public IP address to the actual spoke VM IP address.After inspecting the traffic, the Cloud NGFW performs source NAT using the private IP address subnet.Traffic is sent to the actual destination across the VNet peering connection.Traffic with the source IP address as one of the IP addresses from within the private subnet and the destination IP address as the spoke VM IP arrives at the web server.
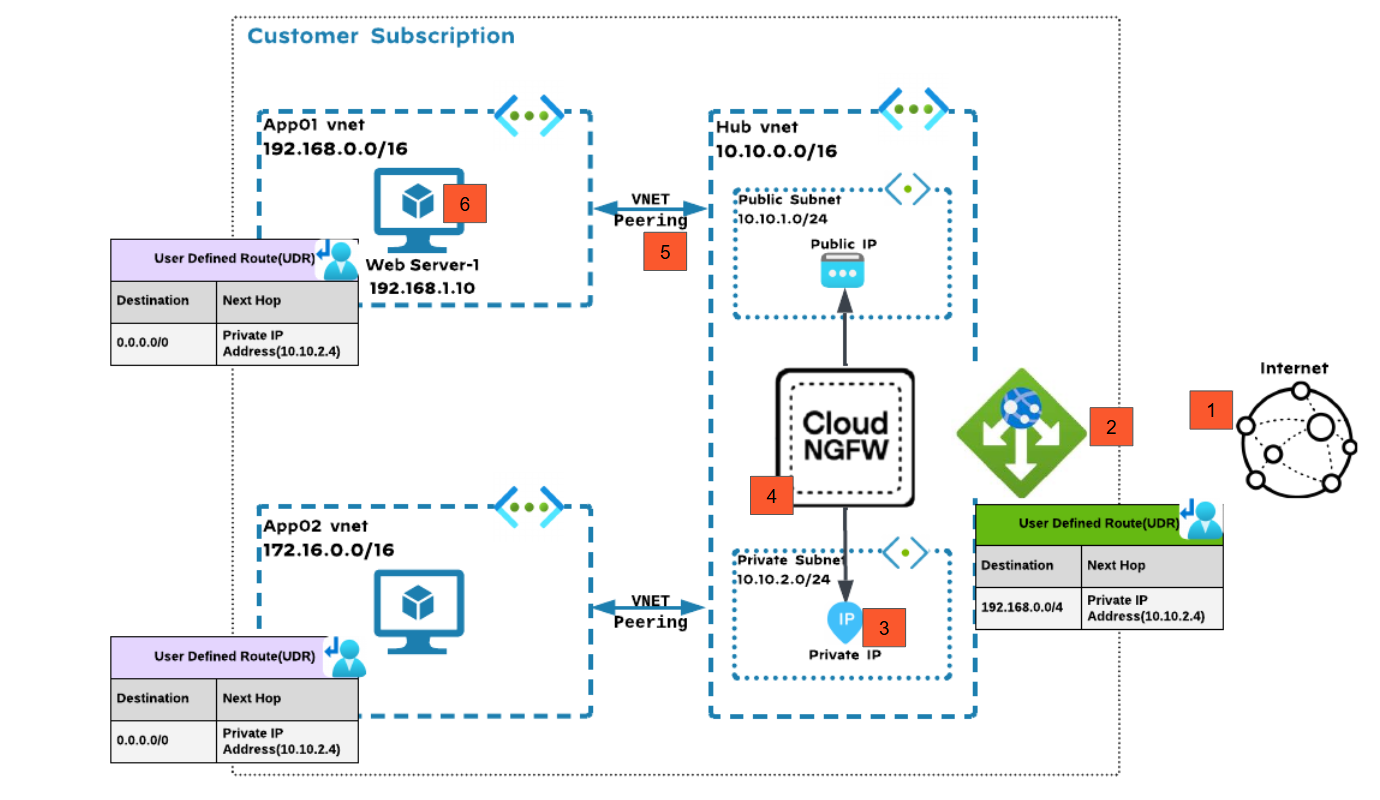
Centralized VNet Deployment Model: Internet Ingress via Application Gateway
![]() In this deployment model:
In this deployment model:- Internet inbound web traffic is routed to the App-01 web server through an App Gateway and the Cloud NGFW to achieve zero trust security.Traffic from the internet lands on the front-end IP of the Application Gateway for which the App-01 Web server acts as the backend pool.Configure UDR on the App Gateway subnet with the next hop as the Cloud NGFW private IP address.The packet arrives at the Cloud NGFW for inspection.After inspection, Cloud NGFW sends the allowed traffic to the web server using VNet peering.The web server and it uses UDR to redirect the response traffic to the Cloud NGFW for inspection.
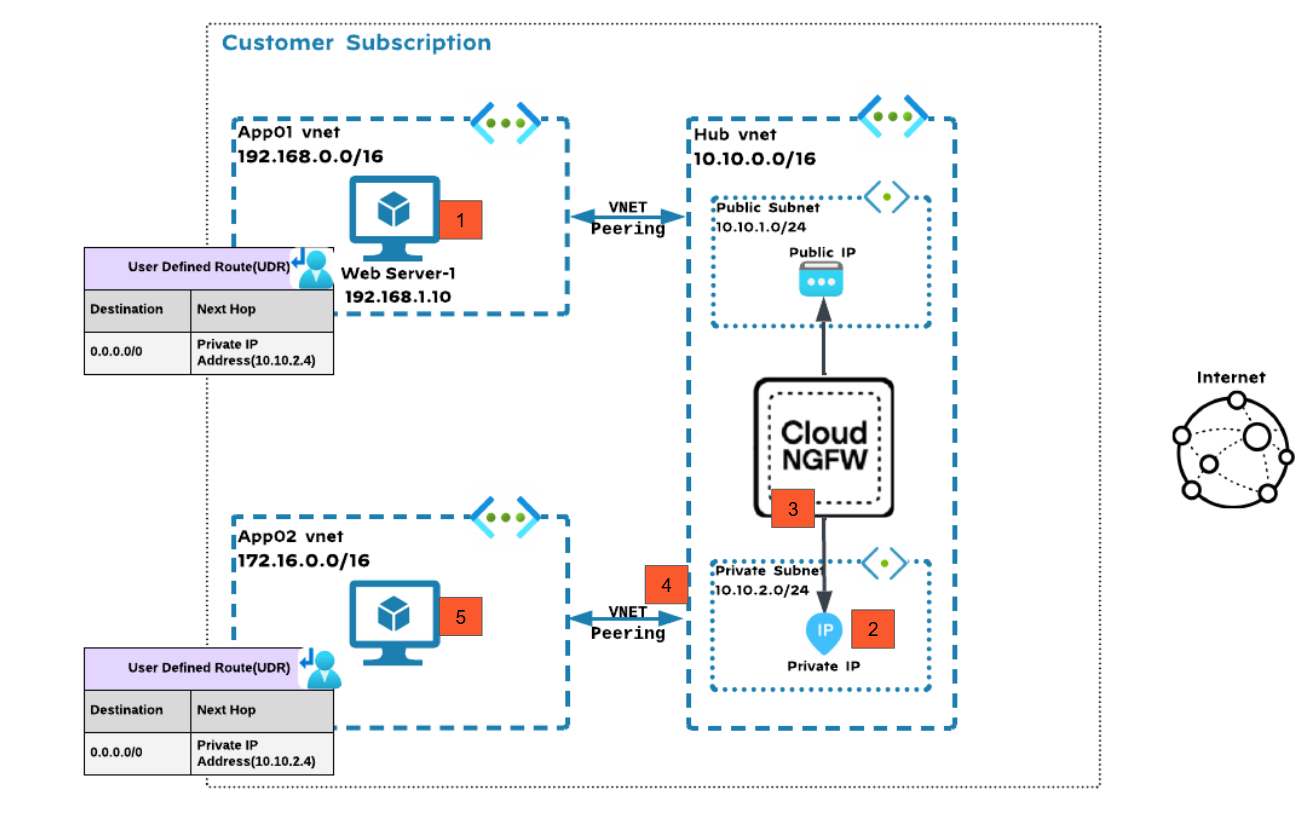
Centralized VNet Deployment Model: East-West Traffic Inspection
![]() In this deployment model:
In this deployment model:- Traffic from the App01 VNet workload VM is destined for the App02 VNet workload VM.Traffic from the App01 VM is forwarded to the private IP address of the Cloud NGFW based on the User-Defined Route (UDR) associated with the workload subnet.Since the private IP address was internally associated with the Cloud NGFW, the packet arrives at the Cloud NGFW for inspection.After inspection, Cloud NGFW forwards the traffic to App02.There is no source NAT performed on east-west traffic.