Cloud NGFW for Azure
Cloud NGFW for Azure Security Features and CDSS Capabilities
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Cloud NGFW for Azure Docs
Cloud NGFW for Azure Security Features and CDSS Capabilities
Learn about Cloud-Delivered Security Services (CDSS) for Cloud NFW for
Azure.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
Palo Alto Networks suite of security features and Cloud-Delivered Security
Services (CDSS) capabilities provide access to specialized subscription-based security
solutions, designed specifically to defend against known, unknown, and advanced evasive
threats. The threat data that is generated through advanced analysis is shared across
the Palo Alto Networks security platforms to provide complete coverage across all threat
vectors.
To secure and protect your traffic, Cloud NGFW for Azure provides Palo Alto
Networks protections through granular controls and Cloud Delivered Security Services
(CDSS):
![]()
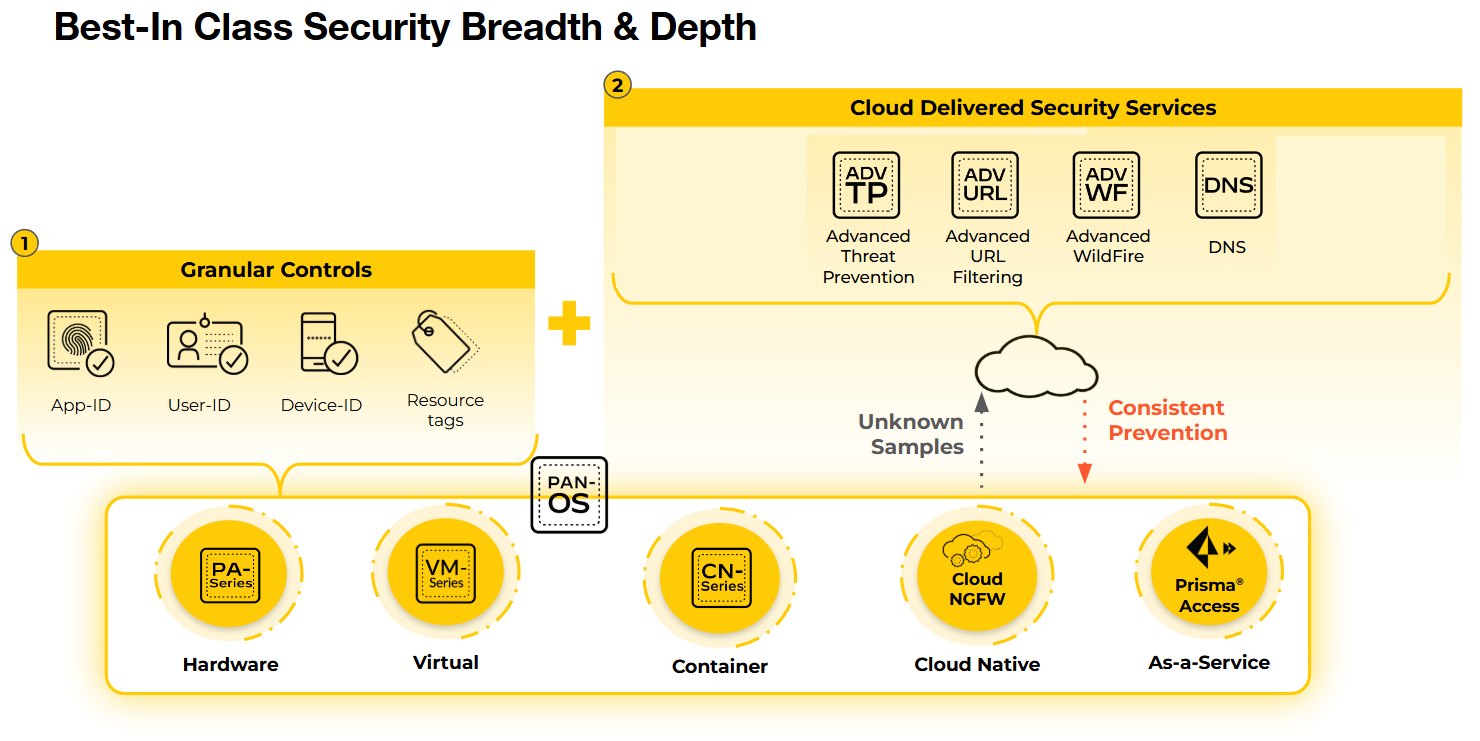
These granular controls include:
- App-ID. Based on patented Layer 7 traffic classification technology, the App-ID service allows you to see the applications on your network, learn how they work, observe their behavioral characteristics, and understand their relative risk. Cloud NGFW for Azure identifies applications and application functions via multiple techniques, including application signatures, decryption, protocol decoding, and heuristics. These capabilities determine the exact identity of applications traversing your network, including those attempting to evade detection by masquerading as legitimate traffic by hopping ports or using encryption.
- Threat Prevention. The Palo Alto Networks Threat Prevention service protects your network by providing multiple layers of prevention to confront each phase of an attack. In addition to essential intrusion prevention service (IPS) capabilities, Threat Prevention possesses the unique ability to detect and block threats on any ports—rather than simply invoking signatures based on a limited set of predefined ports.
- Advanced URL Filtering. This critical service built into Cloud NGFW for Azure stops unknown web-based attacks in real-time to prevent patient zero with the industry’s only ML-powered Advanced URL Filtering. Advanced URL Filtering combines the renowned Palo Alto Networks malicious URL database with the industry’s first real-time web protection engine so organizations can automatically and instantly detect and prevent new malicious and targeted web-based threats.
- DNS. DNS Security gives you real-time protection, applying industry-first protections to disrupt attacks that use DNS. Tight integration with a Palo Alto Networks Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW) gives you automated protections, prevents attackers from bypassing security measures, and eliminates the need for independent tools or changes to DNS routing. DNS Security gives your organization a critical new control point to stop attacks.
- WildFire. Palo Alto Networks Advanced WildFire® is the industry’s largest cloud-based malware prevention engine that protects organizations from highly evasive threats using patented machine learning detection engines, enabling automated protections across network, cloud, and endpoints. Advanced WildFire analyzes every unknown file for malicious intent and then distributes prevention in record time—60 times faster than the nearest competitor—to reduce the risk of patient zero.
Advanced Threat Protection
Advanced Threat Prevention (ATP) is an intrusion prevention system (IPS) solution
that can detect and block malware, vulnerability exploits, and command and control
(C2) across all ports and protocols, using a multilayered prevention system with
components operating on Cloud NGFW for Azure and in the cloud. The Threat Prevention
cloud operates a multitude of detection services using the combined threat data from
Palo Alto Networks services to create signatures, each possessing specific
identifiable patterns, and are used by the Cloud NGFW for Azure to enforce security
policy rules when matching threats and malicious behaviors are detected. These
signatures are categorized based on the threat type and are assigned unique
identifier numbers. To detect threats that correspond with these signatures, Cloud
NGFW for Azure operates analysis engines that inspect and classify network traffic
exhibiting anomalous traits.
After enabling Advanced
Threat Prevention, use Panorama to configure associated Advanced Threat
Prevention policies.
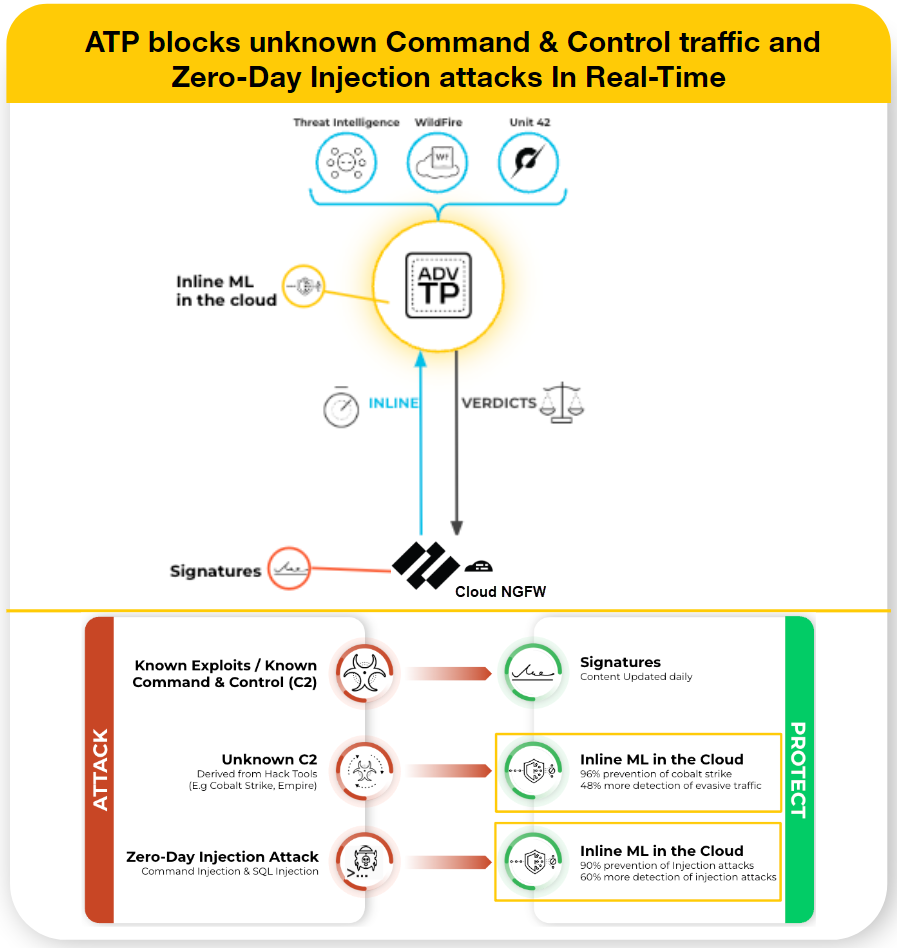
In addition to the signature-based detection mechanism, Advanced Threat Prevention
provides an inline detection system to prevent unknown and evasive C2 threats,
including those produced through the Empire framework, as well as command injection
and SQL injection vulnerabilities. The Advanced Threat Prevention cloud operates
extensible deep learning models that enable inline analysis capabilities on Cloud
NGFW for Azure, on a per-request basis to prevent zero-day threats from entering the
network as well as to distribute protections. This allows you to prevent unknown
threats using real-time traffic inspection with inline detectors. These deep
learning, ML-based detection engines in the Advanced Threat Prevention cloud analyze
traffic for unknown C2 and vulnerabilities that utilize SQL injection and command
injection to protect against zero-day threats. To provide a threat context and
comprehensive detection details, reports are generated that can include the tools
and techniques used by the attacker, the scope, and impact of the detection, as well
as the corresponding cyberattack classification as defined by the MITRE
ATT&CK® framework.
Advanced URL Filtering
Advanced URL Filtering is a comprehensive URL filtering solution that protects
your network and users from web-based threats. Combining the capabilities of
PAN-DB with a web security engine powered by machine learning, Advanced URL
Filtering categorizes and blocks malicious URLs in real-time. With an Advanced
URL Filtering license (or legacy URL filtering license), you can restrict access
to websites and control user interactions with web content. For example, you can
prevent users from accessing websites known to host malware or entering
corporate credentials into websites in specific categories.
Palo Alto Networks provides a set of predefined URL filtering categories. You can
also specify your own URL filtering categories using a customer URL category
object. For example, create a custom list of URLs that you want to use as match
criteria in a Security policy rule. This is a good way to specify exceptions to
URL categories, where you’d like to enforce specific URLs differently than the
URL category to which they belong.
For a high-level
summary of how Advanced URL Filtering provides best-in-class web protection
for the modern enterprise, review the Advanced URL Filtering
datasheet.
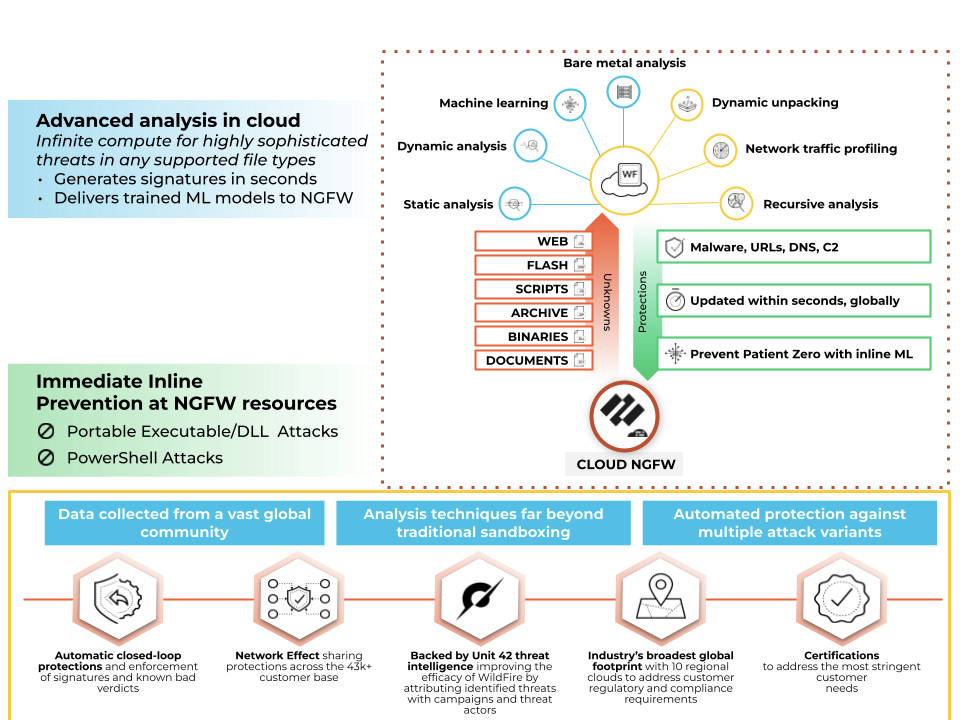
Wildfire Protection
Cloud NGFW can now detect and forward files, executables,
and malicious scripts (such as JScript and PowerShell) in your VPC traffic to
WildFire™ cloud service for analysis. WildFire then applies threat intelligence,
analytics, and correlations on these forwarded files (executables or scripts) and
delivers verdicts based on the analysis. If a threat is detected on them, WildFire
creates protections to block malware, and globally distribute these protection for
that threat in a few minutes.
WildFire goes beyond traditional sandboxing approaches and uses multiple techniques
to identify files with potential malicious behaviors. These techniques include:
- Dynamic analysis - observes files as they execute in a purpose-built, evasion-resistant virtual environment, enabling detection of previously unknown malware using hundreds of behavioral characteristics.
- Static analysis - complements dynamic analysis with effective detection of malware, providing instant identification of malware variants. Static analysis further leverages dynamic unpacking to analyze threats attempting to evade detection through the use of packing tool sets.
- Network traffic profiles - detect malicious traffic patterns based on malware variants such as backdoor creation, download of next-stage malware, access to low-reputation domains, and network reconnaissance.
- Machine learning - extracts thousands of unique features from each file, training a predictive machine learning model to identify new malware, which isn't possible with static or dynamic analysis alone.
- A custom-built hypervisor - prevents attacker evasion techniques with a robust, proprietary hypervisor that does not depend on open-source projects or proprietary software to which attackers have access.
DNS Security
Domain Name Service (DNS) is a critical and foundational Internet Protocol,
as described in the core RFCs for the protocol. Malicious actors have utilized command and control (C2)
(C2) communication channels over the DNS and, in some cases, have even used the
protocol to exfiltrate data. DNS exfiltration can happen when a bad actor
compromises an application instance in your network and then uses DNS lookup to send
data out of the network to a domain they control. Malicious actors can also
infiltrate malicious data or payloads to the network workloads over DNS. Over the
years, Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 research has described different types of DNS abuse discovered.
Cloud NGFW for Azure allows you to protect your VNet and vWAN traffic from
advanced DNS-based threats by monitoring and controlling the domains that your
network resources query. With Cloud NGFW for Azure, you can deny access to the
domains that Palo Alto Networks considers bad or suspicious and allow all other
queries to pass-through.
For this purpose, Cloud NGFW leverages the Palo Alto Networks’ DNS Security service,
which proactively detects malicious domains by
generating DNS signatures using advanced predictive analysis and machine learning,
with data from multiple sources (such as WildFire® traffic analysis, passive DNS,
active web crawling & malicious web content analysis, URL sandbox analysis,
Honeynet, DGA reverse engineering, telemetry data, whois, the Unit 42 research
organization, and Cyber Threat Alliance). The DNS security service then
distributes these DNS signatures
to your Cloud NGFW resources to
proactively defend against malware using DNS for command and control (C2)
and data theft.
With DNS Security enabled, the Cloud NGFW takes the following actions for
each DNS Security category.
| Category | Log Severity | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Ad Tracking Domains | Informational | Allow |
| Command and control (C2) Domains | High | Block |
| Dynamic DNS (DDNS) Domains | Informational | Allow |
| Grayware Domains | Low | Block |
| Malware Domains | Medium | Block |
| Newly Registered Domains | Informational | Allow |
| Parked Domains | Informational | Allow |
| Phishing Domains | Low | Block |
| Proxy Avoidance and Anonymizers | Low | Block |
