Next-Generation Firewall
Configure the Palo Alto Networks Terminal Server (TS) Agent for User Mapping
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Next-Generation Firewall Docs
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- PAN-OS 12.1
- PAN-OS 11.2
- PAN-OS 11.1
- PAN-OS 11.0 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 10.2
- PAN-OS 10.1
- PAN-OS 10.0 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 9.1 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 9.0 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 8.1 (EoL)
-
- PAN-OS 12.1
- PAN-OS 11.2
- PAN-OS 11.1
- PAN-OS 10.2
- PAN-OS 10.1
Configure the Palo Alto Networks Terminal Server (TS) Agent for User Mapping
Use the following procedure to install and configure the TS agent on the
terminal server. To map all your users, you must install the TS agent on all
terminal servers to which your users log in.
If you are using TS agent 7.0
or a later version, disable any Sophos antivirus software on the TS agent host.
Otherwise, the antivirus software overwrites the source ports that the TS agent
allocates.
For information about default values, ranges, and other
specifications, refer to Configure User Mapping for Terminal Server Users. For information about the
terminal servers supported by the TS agent and the number of TS agents supported
on each firewall model, refer to the Palo Alto Networks Compatibility
Matrix.
- Download the TS agent installer.
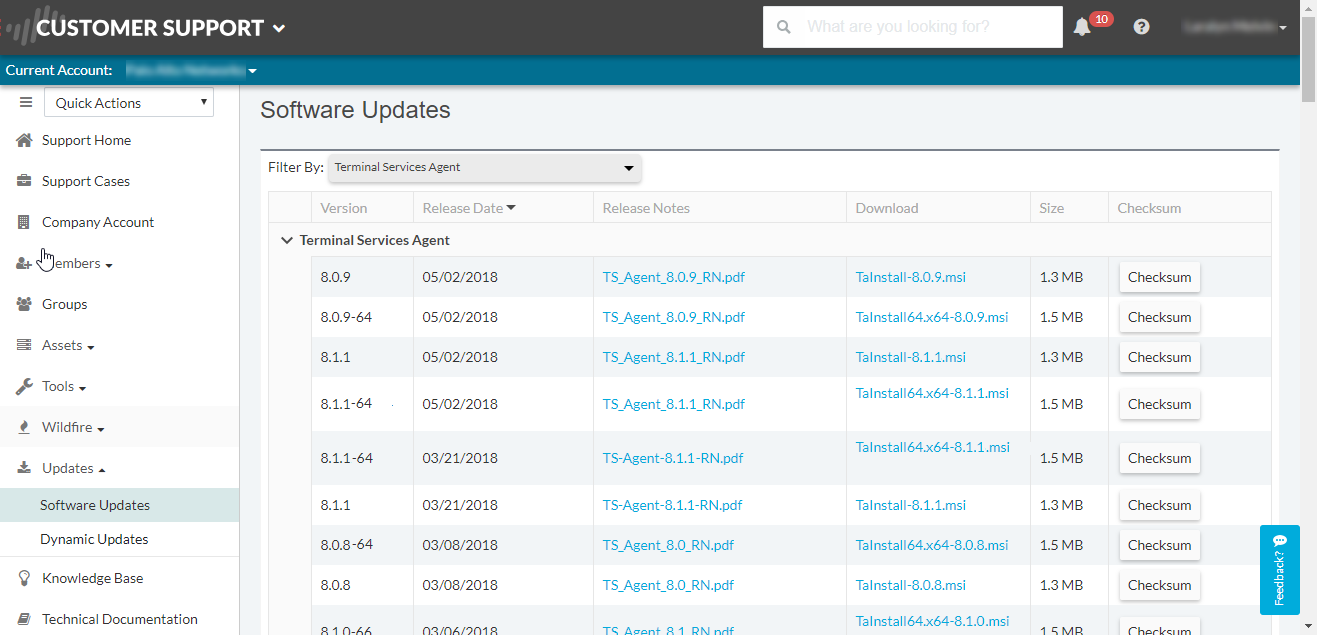
- Log in to the Palo Alto Networks Customer Support Portal.Select UpdatesSoftware Updates.Set Filter By to Terminal Services Agent and select the version of the agent you want to install from the corresponding Download column. For example, to download TS agent 9.0, select TaInstall-9.0.msi.Save the TaInstall.x64-x.x.x-xx.msi or TaInstall-x.x.x-xx.msi file on the systems where you plan to install the agent; be sure to select the appropriate version based on whether the Windows system is running a 32-bit or a 64-bit OS.
![]() Run the installer as an administrator.
Run the installer as an administrator.- Open the Windows Start menu, right-click the Command Prompt program, and Run as administrator.From the command line, run the .msi file you downloaded. For example, if you saved the TaInstall-9.0.msi file to the Desktop, then enter the following:
C:\Users\administrator.acme>cd Desktop C:\Users\administrator.acme\Desktop>TaInstall-9.0.0-1.msi
Follow the setup prompts to install the agent using the default settings. The setup installs the agent in C:\ProgramFiles\Palo Alto Networks\Terminal Server Agent.To ensure correct port allocation, you must use the default Terminal Server agent installation folder location.When the installation completes, Close the setup dialog.If you are upgrading to a TS agent version that has a newer driver than the existing installation, the installation wizard prompts you to reboot the system after you upgrade.Define the range of ports for the TS agent to allocate to end users.The System Source Port Allocation Range and System Reserved Source Ports specify the range of ports that are allocated to non-user sessions. Make sure the values in these fields do not overlap with the ports you designate for user traffic. These values can be changed only by editing the corresponding Windows registry settings. The TS agent does not allocate ports for network traffic emitted by session 0.- Open the Windows Start menu and select Terminal Server Agent to launch the Terminal Server agent application.Configure (side menu) the agent.Enter the Source Port Allocation Range (default is 20,000-39,999). This is the full range of port numbers that the TS agent will allocate for user mapping. The port range you specify cannot overlap the System Source Port Allocation Range.(Optional) If there are ports or port ranges within the source port allocation that you do not want the TS agent to allocate to user sessions, specify them as Reserved Source Ports. To include multiple ranges, use commas with no spaces (for example: 2000-3000,3500,4000-5000).Specify the number of ports to allocate to each individual user upon login to the terminal server (Port Allocation Start Size Per User); default is 200.Specify the Port Allocation Maximum Size Per User, which is the maximum number of ports the Terminal Server agent can allocate to an individual user.Specify whether to continue processing traffic from the user if the user runs out of allocated ports. The Fail port binding when available ports are used up option is enabled by default, which indicates that the application will fail to send traffic when all ports are used. To enable users to continue using applications when they run out of ports, disable (clear) this option, but if you do, this traffic may not be identified with User-ID.If the terminal server stops responding when you attempt to shut it down, enable the Detach agent driver at shutdown option.(Optional) Assign your own certificates for mutual authentication between the TS agent and the firewall.
- Obtain your certificate for the TS agent from your enterprise PKI or generate one on your firewall. The private key of the server certificate must be encrypted and the certificate must be uploaded in PEM file format. Perform one of the following tasks to upload a certificate:
- Generate a Certificate and export it.
- Export a certificate from your enterprise certificate authority (CA).
Add a server certificate to the TS agent.- On the TS agent, select Server Certificate and Add a new certificate.
- Enter the path and name of the certificate file received from the CA or browse to the certificate file.
- Enter the private key password.
- Click OK.
- Commit your changes.
The TS agent uses a self-signed certificate on port 5009 with following information:Issuer: CN=Terminal Server Agent, OU=Engineering, O=Palo Alto Networks, L=Santa Clara, S=California, C=USSubject: CN=Terminal Server Agent, OU=Engineering, O=Palo Alto Networks, L=Santa Clara, S=California, C=USConfigure and assign the certificate profile for the firewall.- Select DeviceCertificate ManagementCertificate Profile to Configure a Certificate Profile.You can assign only one certificate profile for Windows User-ID agents and TS agents. Therefore, your certificate profile must include all certificate authorities that issued certificates uploaded to connected Windows User-ID and TS agents.
- Select DeviceUser IdentificationConnection Security.
- Edit () and select the certificate profile you configured in the previous step as the User-ID Certificate Profile.
![]()
- Click OK.
- Commit your changes.
Configure the firewall to connect to the Terminal Server agent.Complete the following steps on each firewall you want to connect to the Terminal Server agent to receive user mappings:- Select DeviceUser IdentificationTerminal Server Agents and Add a new TS agent.Enter a Name for the Terminal Server agent.Enter the hostname or IP address of the Windows Host on which the Terminal Server agent is installed.The hostname or IP address must resolve to a static IP address. If you change the existing hostname, the TS agent resets when you commit the changes to resolve the new hostname. If the hostname resolves to multiple IP addresses, the TS agent uses the first address in the list.(Optional) Enter the hostname or IP address for any Alternative IP Addresses that can appear as the source IP address for the outgoing traffic.The hostname or IP address must resolve to a static IP address. You can enter up to 8 IP addresses or hostnames.Enter the Port number on which the agent will listen for user mapping requests. This value must match the value configured on the Terminal Server agent. By default, the port is set to 5009 on the firewall and on the agent. If you change it on the firewall, you must also change the Listening Port on the Terminal Server agent Configure dialog to the same port.Make sure that the configuration is Enabled and then click OK.Commit your changes.Verify that the Connected status displays as connected (a green light).Verify that the Terminal Server agent is successfully mapping IP addresses to usernames and that the firewalls can connect to the agent.
- Open the Windows Start menu and select Terminal Server Agent.Verify that the firewalls can connect by making sure the Connection Status of each firewall in the Connection List is Connected.Verify that the Terminal Server agent is successfully mapping port ranges to usernames (Monitor in the side menu) and confirm that the mapping table is populated.(Windows 2012 R2 servers only) Disable Enhanced Protected Mode in Microsoft Internet Explorer for each user who uses that browser.This task is not necessary for other browsers, such as Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox.To disable Enhanced Protected Mode for all users, use Local Security Policy.Perform these steps on the Windows Server:
- Start Internet Explorer.Select SettingsInternet optionsAdvanced and scroll to the Security section.Disable (clear) the Enable Enhanced Protected Mode option.Click OK.In Internet Explorer, Palo Alto Networks recommends that you do not disable Protected Mode, which differs from Enhanced Protected Mode.