Prisma Access
Monitor Colo-Connect
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma Access Docs
-
- 6.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 6.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 4.2 Preferred
- 4.1 Preferred
- 4.0 Preferred
- 3.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 2.2 Preferred
-
-
- 4.0 & Later
- Prisma Access China
-
-
Monitor Colo-Connect
View and monitor your private connectivity to hybrid cloud and on-premises data
centers over cloud interconnects.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
Prisma Access Colo-Connect leverages the cloud-native GCP interconnect
technology to provide high-bandwidth service connections to your private applications.
Colo-Connect coexists with the existing IPSec tunnel-based service connections, so if
you need to provide private app access to smaller data centers that don’t require
high-bandwidth throughput, you could also use service connections to those data centers.
Gain visibility into your Colo-Connect deployment by viewing metrics such as the number
of Colo-Connect links and status, throughput trends, and individual tunnel, connection,
and link details. By viewing data about your Colo-Connect service connections, you can
get an overall picture of the health and connectivity of your deployment.
To view and monitor your private connectivity to hybrid cloud and on-premises data
centers over cloud interconnects, go to InsightsPrisma SASEData Centers Service Connections. For more information about non-Colo-Connect service connections in this
area, see the Strata Cloud Manager Getting Started Guide.
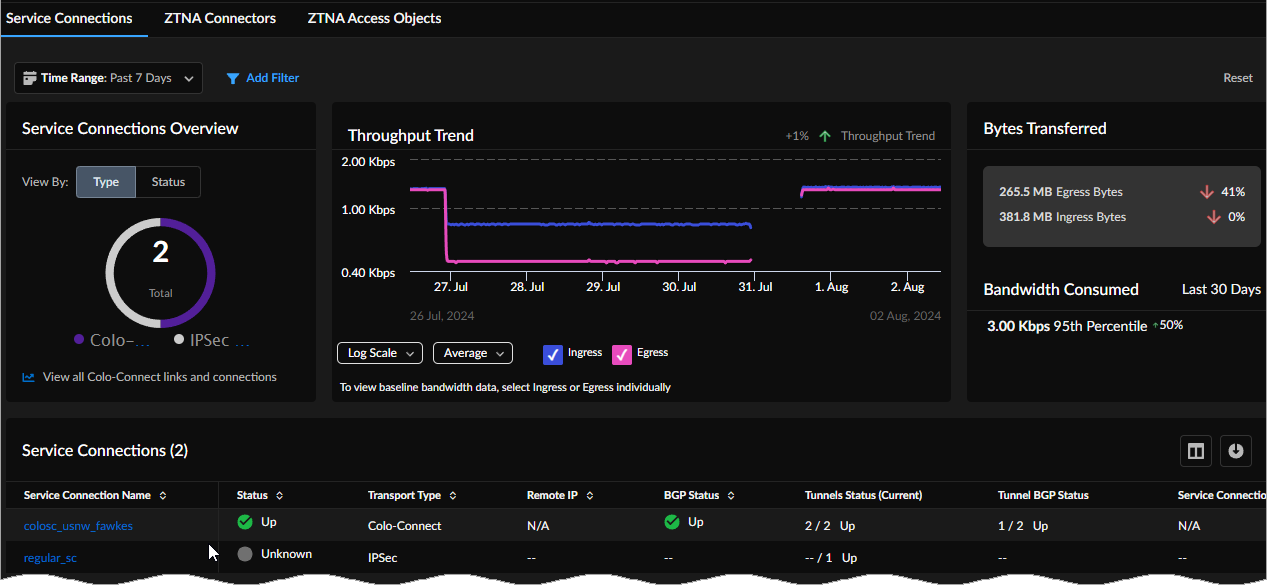
Service Connections Overview
Service Connections Overview shows the number of service connections by
transport Type.
You can see an aggregation of connected transports by Type or
their availability Status.
- IPSec
- Colo-Connect
You can view tunnel transport type by status: Up, Down,
Degraded, or Unknown.
Select View all Colo-Connect links and connections to view the
Colo-Connect details page.

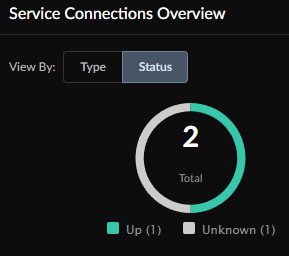
Colo-Connect Links and Connections: Throughput Trend
Throughput Trend shows the ingress and egress throughput traffic consumed
by this service connection during the time range selected.
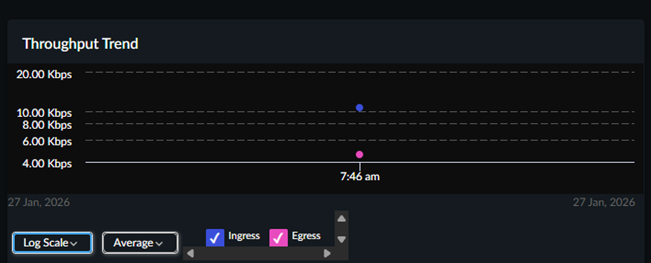
Colo-Connect Links and Connections: Bytes Transferred and Throughput
Bytes Transferred shows an aggregation of ingress and egress bytes
consumed and the difference in consumption from the time range you selected
previously. Throughput shows the 95th percentile of
bandwidth consumed in the last 30 days.
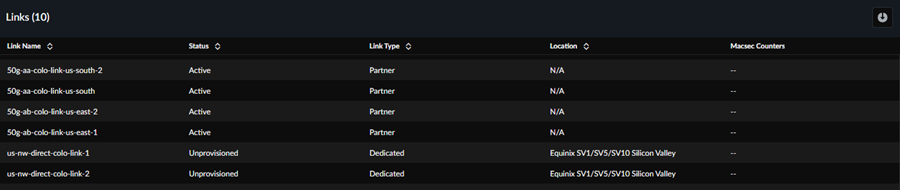
Colo-Connect Links and Connections: Links
If you have a Colo-Connect 100 Gbps license, you can view the
Links section, which shows the status of the
Colo-Connect links (also known as interconnects).
- Link Name—The name of the Colo-Connect link.
- Status—The name of the Colo-Connect link.
- Link Type—The link type (either Partner or Dedicated).
- Location—The link location. Partner links show a location of N/A; dedicated links show the location Colo to which is it connected.
- Macsec counters (Deployments that have Media Access Control (MACsec) Security Enabled Only)—Monitors the health and security of links.
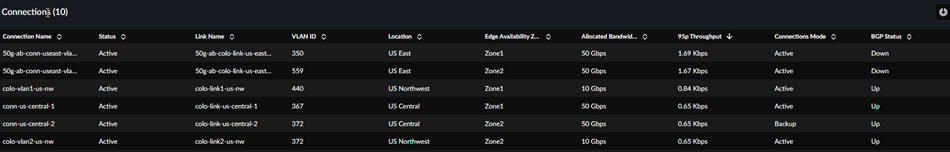
Colo-Connect Links and Connections: Connections
If you have a Colo-Connect 100 Gbps license, you can view the
Connection section, which shows the status of the
Colo-Connect links (also known as VLAN Attachments).
- Connection Name—The name of the connection.
- Status—The connection's status.
- ACTIVE—Connection is provisioned and BGP is established.
- UNPROVISIONED—Connection has not been provisioned.
- PENDING_PARTNER—Pairing key has not yet been entered on the partner interconnect.
- PARTNER_REQUEST_RECEIVED—Pairing key has been entered on the partner interconnect and is awaiting partner activation.
- PENDING_CUSTOMER—Connection is awaiting required customer configuration or approval.
- DEFUNCT—Connection is no longer valid and cannot be used.
- Link Name—The link to which the connection is attached.
- VLAN ID—The VLAN ID of the connection.
- Location—The Colo-Connect location.
- Edge Availability Zone—the zone used for this connection (either Zone1 or Zone2).
- Allocated Bandwidth—The bandwidth allocated for this connection.
- 95p Throughput—The 95th percentile of bandwidth that the connection consumed in the time provided in the filter (3 hours, 24 hours, seven days, or 30 days).
- Connections Mode—The mode of the connection (either Active or Backup).
- BGP Status—The BGP status of the connection (either Up or Down).
Service Connections
If you don't sort connections by Colo-Connect connections, the Service
Connections table displays. For more information about the Service
Connections table, see the Strata Cloud Manager Getting Started Guide
information about InsightsPrisma SASEData Centers. For Colo-Connect, the Transport Type is
Colo-Connect instead of IPSec.
For Colo-Connect:
- The Transport Type displays as Colo-Connect instead of IPSec.
- The Tunnel Status (Current) column displays a value of N/A.
Service Connection Details
For more information about the Service Connection Details table, see the Strata Cloud Manager Getting Started
Guide.
If you have a Colo-Connect 10Gbps license and you select a Transport
Type of Colo-Connect, this page displays the
details of your GRE tunnels; if you have a Colo-Connect 100Gbps license, this page
displays the Colo-Connect Links and Connections: Connections table.
Service Connection Status, Colo-Connect, and Concurrent Sessions
These areas display:
- The service connection's Access Location and, if you have a 10 Gbps license GRE Tunnels status (Up, Down, or Warning).
- The total number of Colo-Connect links and connections.
- The number of Concurrent Sessions and the number of total sessions during the past 30 days.
Bytes Transferred and Bandwidth Consumed (10 Gbps Licenses Only)
Bytes Transferred shows the aggregation of ingress and egress bytes that this
service connection consumed, as well as the difference in consumption from the
previously selected time range. You can also view the Bandwidth
Consumed, which is the 95th percentile of bandwidth that the service
connection has consumed.
GRE Tunnels (10 Gbps Licenses Only)
If you have a Colo-Connect 10 GB license, you can view details about the Colo-Connect
GRE tunnels:
- Tunnel Name—The unique tunnel name.
- Tunnel Status—Up, Down, or Unknown.
- Connection Name—The connection's unique name.
- Tunnel State—The connection status (Active or Backup).
- Remote IP—Destination IP address.
- Source IP—Local device's IP address.
- 95% Throughput—The 95th percentile of bandwidth consumed in the last 30 days.
- Peak Throughput—Peak throughput during the time range selected.
- BGP Status—Up, Down, Degraded, or Unknown.
- BGP Local IP—The BGP local IP.
- Disconnections—How many disconnections this tunnel has had.
- Disconnections Duration—How long the disconnections lasted.
- Ingress Bytes—How many ingress bytes consumed during the time range selected.
- Egress Bytes—How many egress bytes consumed during the time range selected.
- Ingress Packet Count—The ingress packet count.
- Egress Packet Count—The egress packet count.
