Prisma Access
App Acceleration in Prisma Access
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma Access Docs
-
- 6.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 6.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 4.2 Preferred
- 4.1 Preferred
- 4.0 Preferred
- 3.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 2.2 Preferred
-
-
- 4.0 & Later
- Prisma Access China
-
-
App Acceleration in Prisma Access
Learn how Prisma Access can speed up app performance using App
Acceleration.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
App Acceleration directly addresses the causes of poor app performance and
acts in real-time to mitigate them, dramatically improving the user experience for
Prisma Access GlobalProtect and Remote Network users.
The primary causes of poor user experience when accessing apps are dynamic content
(content that must be processed for each user individually, on-demand) and network
connectivity issues.
App Acceleration provides you with the following functionality:
Acceleration for top SaaS apps—App
Acceleration for Prisma SASE accelerates dynamic content to improve the response
time of top SaaS apps. It securely and intelligently prepares the dynamic content
that each user needs, before the user requests it.
As a result, App Acceleration dramatically
reduces the response time of applications and the APIs powering them to improve the
user experience and boost productivity.
Accelerated applications are
listed in the Supported Apps section.
Network Acceleration—When your users access apps, they can experience poor app
performance that is caused by decreased throughput, which could be caused by packet
loss, degraded wireless connectivity, network congestion, and other factors. These
networking issues can adversely affect the employee experience and reduce their
productivity.
When the internet was conceived, networks were homogenous and wireless
connectivity was in its infancy. Fundamental protocols like TCP were originally
created for these networks. Today, networks are no longer homogenous and wireless
connectivity creates a highly variable user experience. When users experience
degraded network conditions, TCP can't differentiate if the problem occurred because
of device limitations, network limitations, or physical constraints.
Without requiring any changes to your client configuration or applications, App
Acceleration securely builds an understanding of the:
- Device capability—The type of client endpoint
- Network capability—The type of network
- App Context— The type of app being used
Using its understanding of device, network and application context, App
Acceleration maximizes throughput and adjusts in real-time to account for changing
network conditions.
When compared to direct internet access, App Acceleration offers a marked throughput
improvement for TCP traffic when connecting through Prisma Access.
You can view throughput improvements from App Acceleration in Prisma SASE
Incidents and Alerts. AI-powered Autonomous DEM (ADEM)
integrates with App Acceleration and provides you with metrics such as the number of
applications that were accelerated and the performance boost gained overall.
App Acceleration Requirements and Guidelines
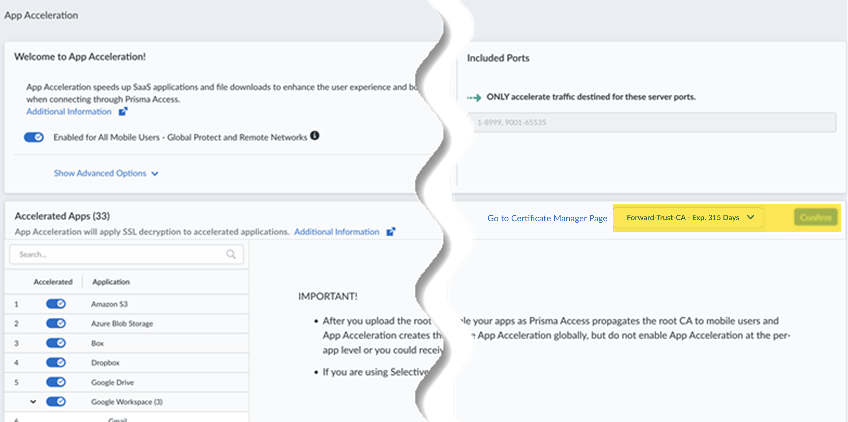
- Supported Apps—App Acceleration supports the following apps:
- Amazon S3
- Azure Blob Storage
- Box
- Dropbox
- Google Workspace:
- Gmail
- Google Sheets
- Google Docs
- Google Drive
- Microsoft 365:
- Excel
- Forms
- My Content
- OneDrive
- OneNote
- PowerPoint
- Word
- Teams (file downloads)
- To Do
- Microsoft 365 China:
- Excel
- OneDrive
- Outlook
- OneNote
- PowerPoint
- Teams (file downloads)
- Word
- SAP Ariba
- SAP Concur
- SAP S/4 Hana Cloud Public Edition
- SFDC (Salesforce.com)
- ServiceNow
- Slack (file downloads)
- Workday
- Zoom:
- Cloud recording downloads
- Zoom Team Chat
- Supported Locations—App Acceleration supports a subset of Prisma Access locations.
- Trusted Root CA Upload—You need to set up a trusted Root CA and perform a commit and push operation and then select it during App Acceleration setup, as shown in the following procedures. If using Strata Cloud Manager to configure App Acceleration, set up the Root CA in the Prisma Access scope. If you change the certificate you use, you must also commit and push the changed certificate before you select it.
- Forward Trust Certificate and Trusted Root CA—Enable the CA/certificate you uploaded as a forward trust certificate and trusted root CA, as shown in the following procedures. If SSL decryption is applied to any accelerated apps, you must mark the certificate as a forward trust certificate and trusted root CA, or users will encounter SSL errors when trying to access those apps.
- Unsupported Prisma Access Functionality—The following
functionality does not support App Acceleration and Prisma Access
deployments with these features enabled won't be accelerated:
- IPv6App Acceleration coexists with IPv6 networking when IPv6 is configured; however, only IPv4 TCP traffic is accelerated. IPv6 traffic is not accelerated, but functions normally.
- Remote Networks that use Overlapped Subnets (supported by default in Prisma Access (Managed by Strata Cloud Manager) deployments, configurable in Prisma Access (Managed by Panorama) deployments.
- IPv6
- App Acceleration Guidelines:
- QUIC Protocol Support—Some browsers (such as Google Chrome) might use the Quick UDP Internet Connections (QUIC) protocol by default. Layer 7 App Acceleration can't be used on traffic using QUIC. As a workaround, disable the QUIC protocol when you configure App Acceleration.
- SaaS Apps and Zy-* Response Headers—Users connecting to Prisma Access deployments that have App Acceleration enabled for top SaaS apps can expect to see response headers with a name of Zy-*, such as Zy-Server and Zy-Accelerated, and a zy_sid session cookie.If the response header is Zy-Accelerated, a value of 1 indicates that the response was accelerated and a value of 0 indicates the response wasn't accelerated.
- Content Localization—If an accelerated SaaS app localizes content based solely on the user's IP address or user ID, when acceleration is enabled for that app, its content won't be localized.
- Change to Default Behavior for Security Policy Rules with an Action set to Deny—If you have a Security policy rule with an action set to Deny that is applied to traffic going through App Acceleration using a rule based on source or destination address, application, or service, the traffic will complete a three-way handshake but Prisma Access will block it, and the Deny policy functions as configured.
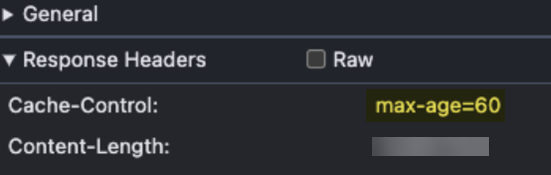
- Amazon S3 and Azure Blob Storage
cache-control—Amazon S3 and
Azure Blob Storage buckets and files have a series of HTTP response
headers associated with them. One of these values is
cache-control. Files are not
accelerated if the cache-control value
is:
- Unset
- Set to a value of max-age=0
- Set to a value of max-age=no-cache
To gain the benefit of App Acceleration for Amazon S3 and Azure Blob Storage, set the cache-control max-age value to one that’s greater than zero.![]()
- Apps with Shared Domain in Activity Insights—When using App Acceleration, Layer 7 acceleration is based on the domain. Under certain conditions, if two apps share the same domain, the app reporting in Activity Insights might attribute one app's Layer 7 traffic to another app. For example, if some traffic from MS Teams and OneDrive app share the same domain, the MS Teams app reporting will display under OneDrive.
- Long-Lived Connections and System Logs—App Acceleration's writes
Layer 4 logs when an individual TCP connection ends. For short-lived
connections, this behavior is transparent, because short-lived connections
are frequently created by applications.App Acceleration collects metrics for the entire period that the connection is active. For long-lived connections such as those used by mounted SMB network drives, this behavior can make it seem as if metrics are collected only during the end of the connection.
Configure App Acceleration
To configure App Acceleration in Prisma Access, select one of the following tabs
depending on your deployment (Prisma Access (Managed by Strata Cloud Manager) or Prisma Access (Managed by Panorama)).
Configure App Acceleration in Prisma Access (Strata Cloud Manager)
Configure App Acceleration in a Prisma Access (Managed by Strata Cloud Manager) deployment.
To configure App Acceleration in a Prisma Access (Managed by Strata Cloud Manager) deployment, complete this
task.
- (Optional) Disable the Quick UDP Internet Connections (QUIC) protocol.App Acceleration can’t accelerate apps at Layer 7 without disabling QUIC.
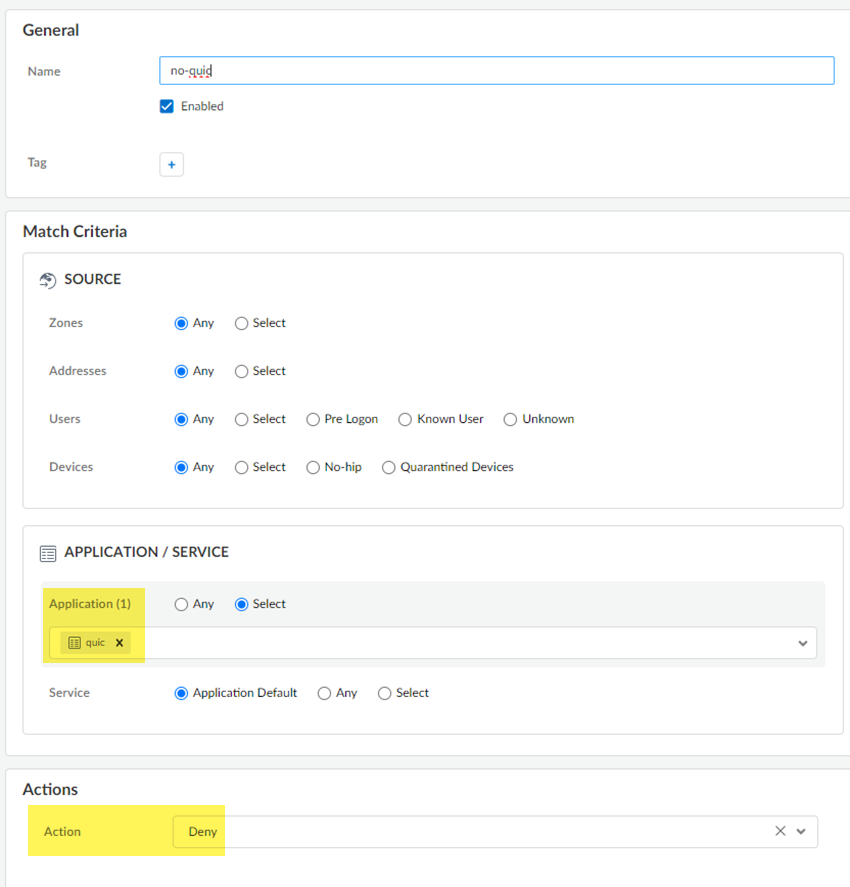
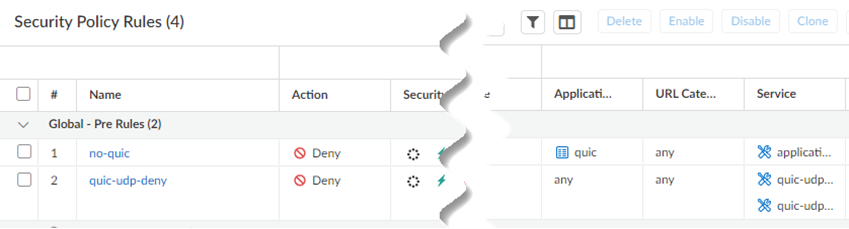
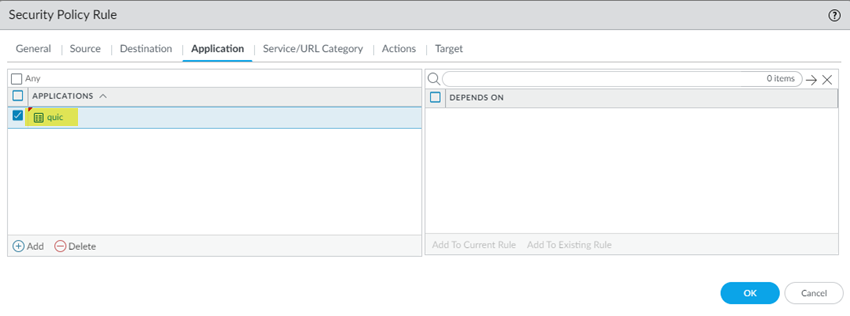
- Go to ConfigurationNGFW & Prisma AccessSecurity ServicesSecurity Policy and Add RulePre Rules.Create this Security policy rule in the Global configuration scope.Select an Application/Service of quic and an Actions of Deny.
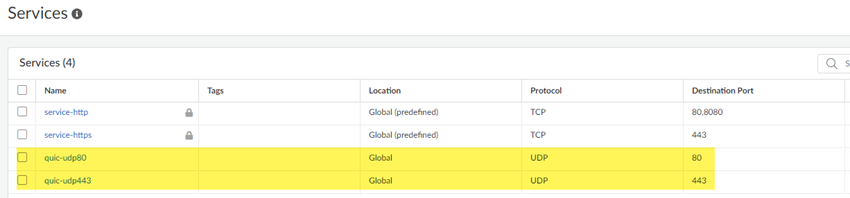
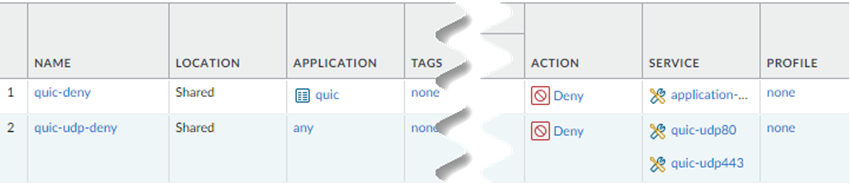
![]() Save your changes.Go to ConfigurationNGFW & Prisma AccessObjectsServiceServices and Add services for UDP port 80 and UDP port 443.Palo Alto Networks recommends adding services for UDP port 80 and UDP port 443 and creating an additional security policy to block UDP traffic on those ports, because newer versions of QUIC might be misidentified as unknown-udp.
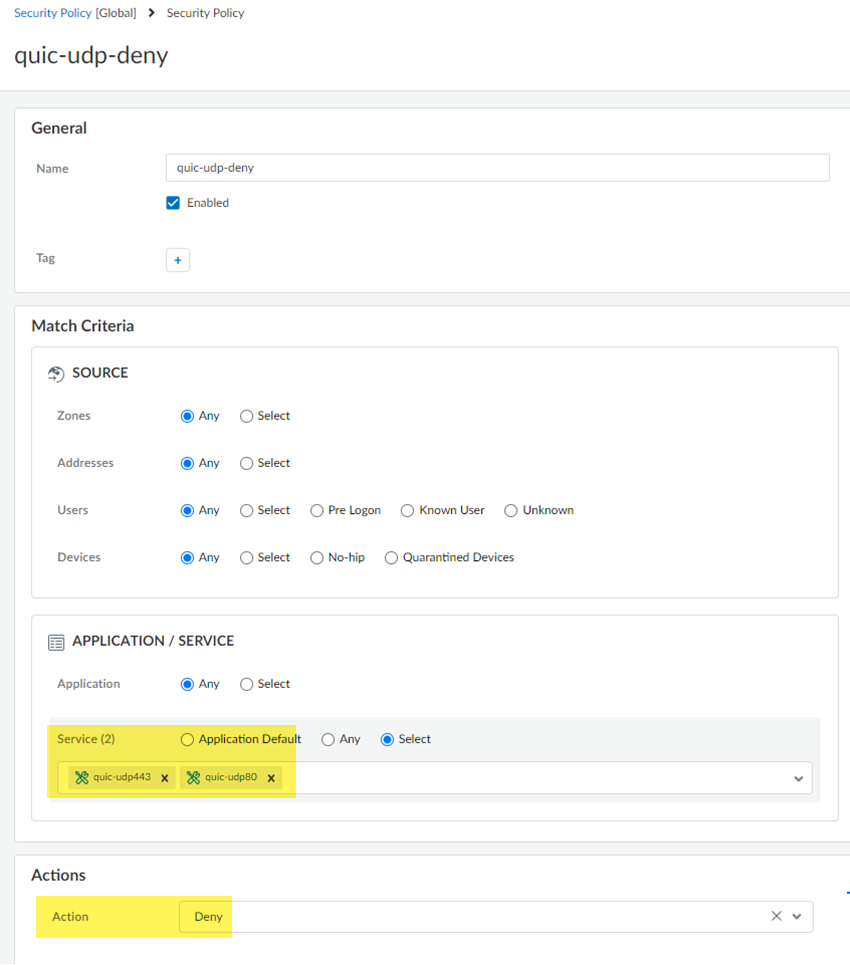
Save your changes.Go to ConfigurationNGFW & Prisma AccessObjectsServiceServices and Add services for UDP port 80 and UDP port 443.Palo Alto Networks recommends adding services for UDP port 80 and UDP port 443 and creating an additional security policy to block UDP traffic on those ports, because newer versions of QUIC might be misidentified as unknown-udp.![]() Return to ConfigurationNGFW & Prisma AccessSecurity ServicesSecurity Policy and Add Rule for a second security policy, specifying the services under Application/Service and an Action of Deny.
Return to ConfigurationNGFW & Prisma AccessSecurity ServicesSecurity Policy and Add Rule for a second security policy, specifying the services under Application/Service and an Action of Deny.![]() When completed, you will have two Security policy rules: One that blocks the QUIC protocol and one that blocks traffic on UDP ports 80 and 443.
When completed, you will have two Security policy rules: One that blocks the QUIC protocol and one that blocks traffic on UDP ports 80 and 443.![]() Import a root certificate authority (CA) certificate and private key in Strata Cloud Manager in the Prisma Access scope to use with App Acceleration and push your changes.A self-signed root CA/certificate is the top-most certificate in a certificate chain. App Acceleration uses the root CA/certificates to create certificates for the accelerated apps. Push the root CA/certificate in Prisma Access so that App Acceleration can begin creation of the app-specific certificates.The root CA/certificate must have these characteristics: :
Import a root certificate authority (CA) certificate and private key in Strata Cloud Manager in the Prisma Access scope to use with App Acceleration and push your changes.A self-signed root CA/certificate is the top-most certificate in a certificate chain. App Acceleration uses the root CA/certificates to create certificates for the accelerated apps. Push the root CA/certificate in Prisma Access so that App Acceleration can begin creation of the app-specific certificates.The root CA/certificate must have these characteristics: :- The CA must be a trusted CA.You can use an intermediate certificate; however be sure that you mark it as a forward trust certificate and a trusted root CA as shown in this procedure.
- (Recommended) The CA should be unique and used for App Acceleration only.
- The CA can't be expired. Make a note of the CA expiration date, and renew the certificate before it expires. If a CA/certificate in use by App Acceleration expires, users will receive an SSL error when trying to access accelerated apps. It's critical to ensure that the CA is valid when App Acceleration is in use by your organization.
- It must include a key.
- It must use a passphrase.
- It must be in the Prisma Access scope.
- (Mobile Users—GlobalProtect™ Deployments Only) It must be
installed in the local root certificate store. You can perform this installation by adding it to the list of trusted certificates as described in this procedure or, if you're using Active Directory (AD), you can distribute the root CA from AD using an AD Group Policy Object (GPO).
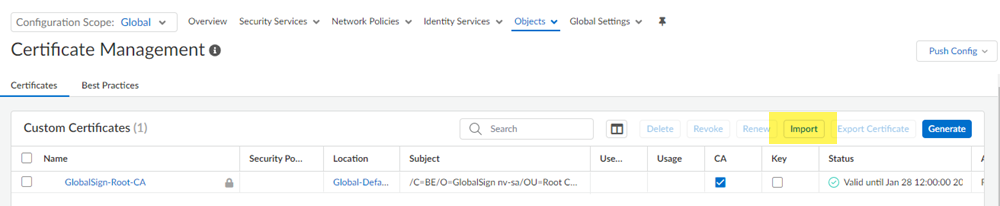
If you ever need to change the root CA/certificate, you must upload it and commit your changes before you can use the changed certificate.- Go to ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessObjectsCertificate Management.Import a certificate.
![]() Select the following parameters:
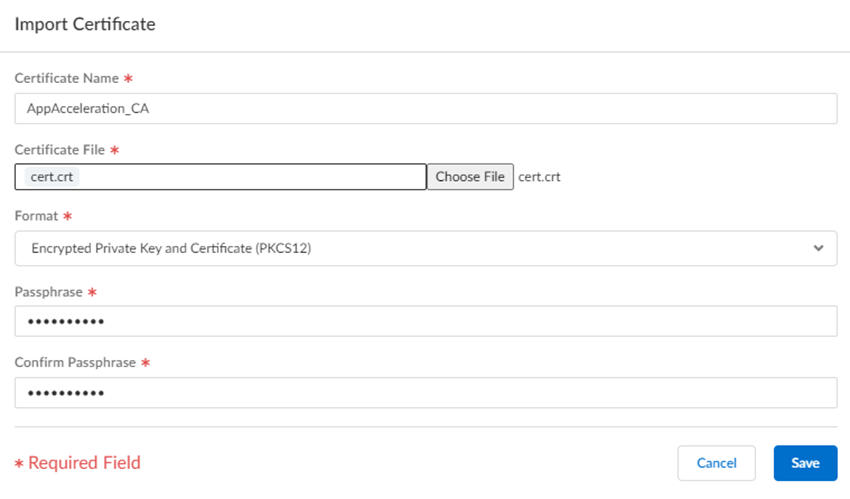
Select the following parameters:- Enter a unique Certificate Name for the
certificate, such as
AppAcceleration_CA.The name is case-sensitive and can be up to 31 characters long. Use only letters, numbers, hyphens, and underscores in the name.
- Choose File and browse for the Certificate File received from the CA and Open it.
- Select a Format:
- Encrypted Private Key and Certificate (PKCS12)—This is the default and most common format, in which the key and certificate are in a single container (Certificate File).
- Base64 Encoded Certificate (PEM)—You must import the key separately from the certificate. You're required to select a Key File if you select this format.
- Enter a Passphrase and Confirm Passphrase.
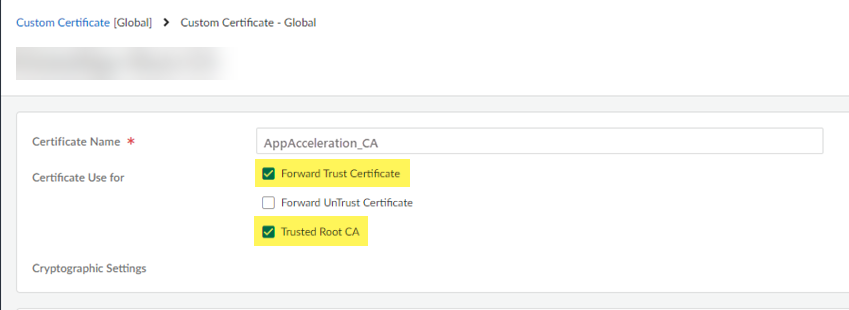
Save your changes.![]() Mark the root CA/certificate you added as a forward trust certificate and a trusted root CA.If you don't specify the certificate as a forward trust certificate and trusted root CA, users will encounter SSL errors when trying to access accelerated apps when using SSL decryption.
Mark the root CA/certificate you added as a forward trust certificate and a trusted root CA.If you don't specify the certificate as a forward trust certificate and trusted root CA, users will encounter SSL errors when trying to access accelerated apps when using SSL decryption.- Select the root CA/certificate you added.Select the certificate as a Forward Trust Certificate and Trusted Root CA.
![]() Update the certificate.
Update the certificate.![]() Push your changes.
Push your changes.![]() (Mobile Users—GlobalProtect Deployments Only) Add the root CA/certificate you added to the list of GlobalProtect trusted certificates and install it in the local root certificate store.Alternatively, if you're using Active Directory, you can distribute the root CA from AD using an Active Directory GPO.
(Mobile Users—GlobalProtect Deployments Only) Add the root CA/certificate you added to the list of GlobalProtect trusted certificates and install it in the local root certificate store.Alternatively, if you're using Active Directory, you can distribute the root CA from AD using an Active Directory GPO.- Go to ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessConfiguration ScopePrisma AccessGlobalProtectGlobalProtect AppGlobal App Settings.Click the gear to edit the Settings.
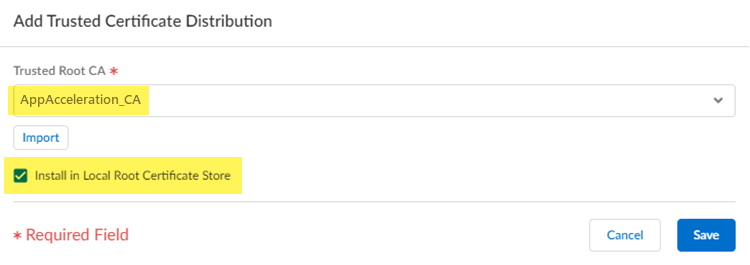
![]() Add Trusted Certificate Distribution.
Add Trusted Certificate Distribution.![]() Select the Trusted Root CA you created in a previous step and select Install in Local Root Certificate Store.
Select the Trusted Root CA you created in a previous step and select Install in Local Root Certificate Store.![]() Save your changes.Push your changes.Enable App Acceleration and choose the certificate file you created.
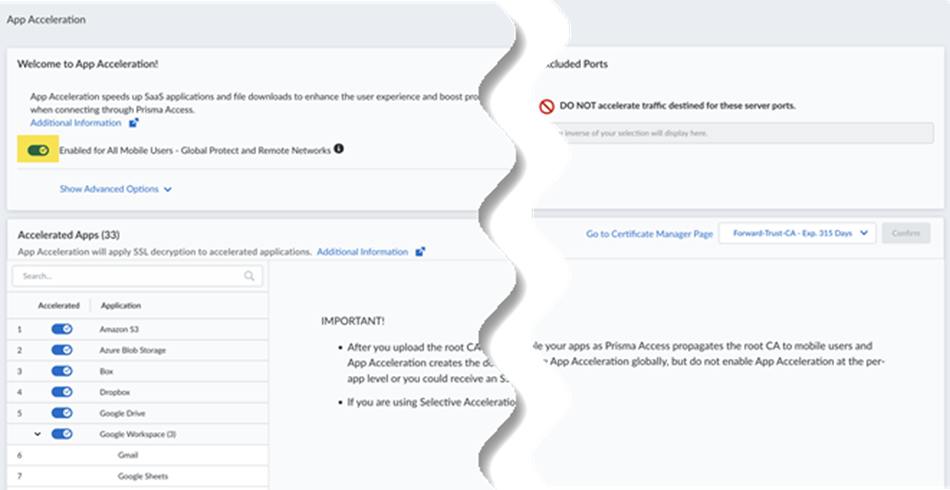
Save your changes.Push your changes.Enable App Acceleration and choose the certificate file you created.- Go to ConfigurationApp Acceleration.Move the slider to the right to have App Acceleration be Enabled for all Mobile Users—GlobalProtect and Remote Networks.If commits are ongoing, App Acceleration settings will take effect after all commits are complete.
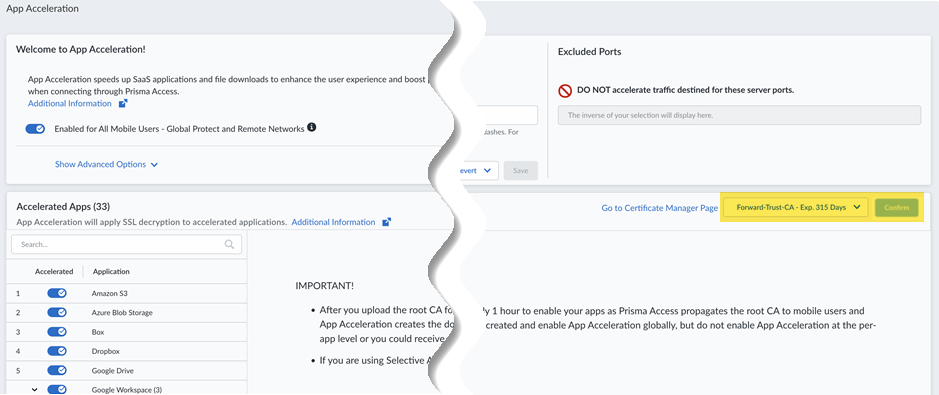
![]() App Acceleration will be enabled for all TCP traffic. If you wish to accelerate SaaS apps, you will need to select a root CA/certificate, as shown in the next step.Select the certificate you created in a previous step and Confirm your change.If you need to change the certificate from an existing one, make sure you have committed and pushed the certificate to your firewalls and users, then select it here. Commit the new certificate before you select it.
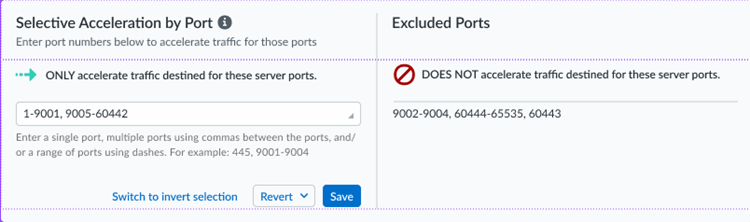
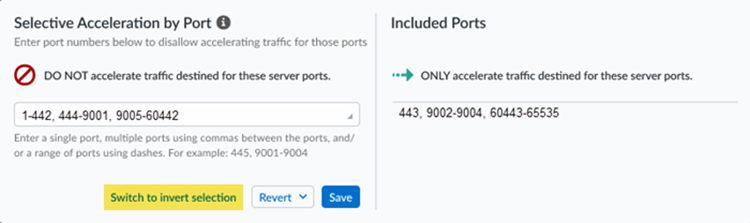
App Acceleration will be enabled for all TCP traffic. If you wish to accelerate SaaS apps, you will need to select a root CA/certificate, as shown in the next step.Select the certificate you created in a previous step and Confirm your change.If you need to change the certificate from an existing one, make sure you have committed and pushed the certificate to your firewalls and users, then select it here. Commit the new certificate before you select it.![]() After you import the certificate, you must wait until App Acceleration generates domain-specific certificates for each app. This process can take up to 1 hour. In the meantime, you can move the slider for the Accelerated Apps to the left to temporarily disable App Acceleration and access the apps until the certificates are generated; if you don't, you might receive an SSL error until the certificates are generated.Allow up to 10 minutes for acceleration to be active after you have turned it on for a given application.(Optional) Specify the ports to include or exclude for App Acceleration .Selective Acceleration by Port lets you specify which network traffic receives acceleration based on destination server ports. This granular control lets you boost application performance while leaving other traffic unaffected. By default, all ports are accelerated.When you use Selective Acceleration by port, make a note of the following guidelines:
After you import the certificate, you must wait until App Acceleration generates domain-specific certificates for each app. This process can take up to 1 hour. In the meantime, you can move the slider for the Accelerated Apps to the left to temporarily disable App Acceleration and access the apps until the certificates are generated; if you don't, you might receive an SSL error until the certificates are generated.Allow up to 10 minutes for acceleration to be active after you have turned it on for a given application.(Optional) Specify the ports to include or exclude for App Acceleration .Selective Acceleration by Port lets you specify which network traffic receives acceleration based on destination server ports. This granular control lets you boost application performance while leaving other traffic unaffected. By default, all ports are accelerated.When you use Selective Acceleration by port, make a note of the following guidelines:- If accelerating SaaS apps with App Acceleration, you must include port 443 in the accelerated ports in order to boost SaaS apps.
- If you are using App Security with App Acceleration, and have defined an app with custom ports, you must include those ports for the defined app traffic to be secured. Excluding the ports from App Acceleration prevents App Security traffic inspection.
- To select the ports to accelerate, enter a single port, multiple ports
using commas between the ports, a range of ports using dashes, or any
combination of the preceding entries. App Acceleration accelerates the
traffic for those ports. The ports that App Acceleration excludes
display in the Excluded Ports area.
![]()
- To select the ports to exclude from acceleration, Switch to
invert selection and enter the ports to exclude. App
Acceleration accelerates every port you do not select.
![]()
- To revert your changes to the last saved setting or the original default setting, select Revert.
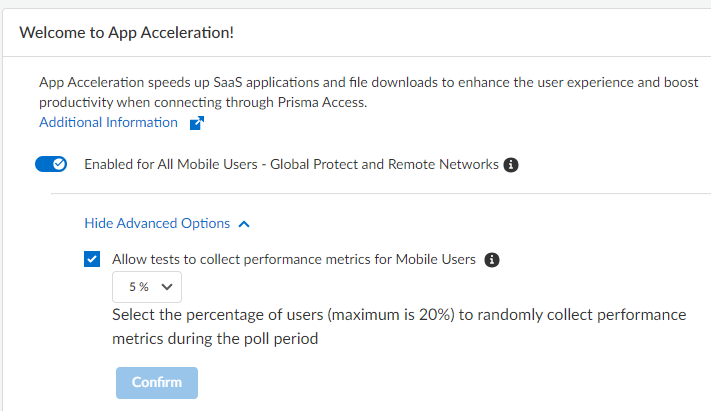
(Optional) Show Advanced Options and change the metric testing parameters.- (Optional) To disable the collection of metrics to obtain
performance information, deselect Allow tests to collect
performance metrics for Mobile Users.Palo Alto Networks recommends that you enable metric collection to view the app performance improvements when using App Acceleration.
- (Optional) To change the percentage of users for which predictive tests are processed from the default of 5%, select another percentage in the drop-down and Confirm the changes.
![]()
(Optional) To view details about the applications that have been accelerated in your environment, go to InsightsOperationalApp Acceleration.Configure App Acceleration in Prisma Access (Panorama)
Configure App Acceleration in a Prisma Access (Managed by Panorama) deployment.To configure App Acceleration in a Prisma Access (Managed by Panorama) deployment, complete this task.- (Optional) Disable the Quick UDP Internet Connections (QUIC) protocol.App Acceleration can’t accelerate apps at Layer 7 without disabling QUIC.
- Go to PoliciesSecurityPre Rules and Add a security policy.Create this Security policy rule in the Shared device group.Select an Application of quic and an action of Deny.
![]() Add a second security policy.Newer versions of QUIC might be misidentified as unknown-udp. For this reason, Palo Alto Networks recommends adding services for UDP port 80 and UDP port 443 and creating an additional security policy to block UDP traffic on those ports.Under Service/URL Category, Add new services for UDP port 80 and UDP port 443 and an Action of Deny.When completed, you will have two security policy rules: One that blocks the QUIC protocol and one that blocks traffic on UDP ports 80 and 443.
Add a second security policy.Newer versions of QUIC might be misidentified as unknown-udp. For this reason, Palo Alto Networks recommends adding services for UDP port 80 and UDP port 443 and creating an additional security policy to block UDP traffic on those ports.Under Service/URL Category, Add new services for UDP port 80 and UDP port 443 and an Action of Deny.When completed, you will have two security policy rules: One that blocks the QUIC protocol and one that blocks traffic on UDP ports 80 and 443.![]() Import a root certificate authority (CA) certificate and private key in Panorama to use with App Acceleration and commit and push your changes.A self-signed root CA/certificate is the top-most certificate in a certificate chain. App Acceleration uses the root CA/certificates to create certificates for the accelerated apps. Push the root CA/certificate in Prisma Access so that App Acceleration can begin creation of the app-specific certificates.The root CA/certificate must have these characteristics:
Import a root certificate authority (CA) certificate and private key in Panorama to use with App Acceleration and commit and push your changes.A self-signed root CA/certificate is the top-most certificate in a certificate chain. App Acceleration uses the root CA/certificates to create certificates for the accelerated apps. Push the root CA/certificate in Prisma Access so that App Acceleration can begin creation of the app-specific certificates.The root CA/certificate must have these characteristics:- The CA must be a trusted CA.You can use an intermediate certificate; however be sure that you mark it as a forward trust certificate and a trusted root CA as shown in this procedure.
- (Recommended) The CA should be unique and used for App Acceleration only.
- The CA can't be expired. Make a note of the CA expiration date, and renew the certificate before it expires. If a CA/certificate in use by App Acceleration expires, users will receive an SSL error when trying to access accelerated apps. It's critical to ensure that the CA is valid when App Acceleration is in use by your organization.
- It must include a key.
- It must use a passphrase.
- (Mobile Users—GlobalProtect™ Deployments Only) It must be
installed in the local root certificate store. You can perform this installation by adding it to the list of trusted certificates as described in this procedure or, if you're using Active Directory (AD), you can distribute the root CA from AD using an AD Group Policy Object (GPO).
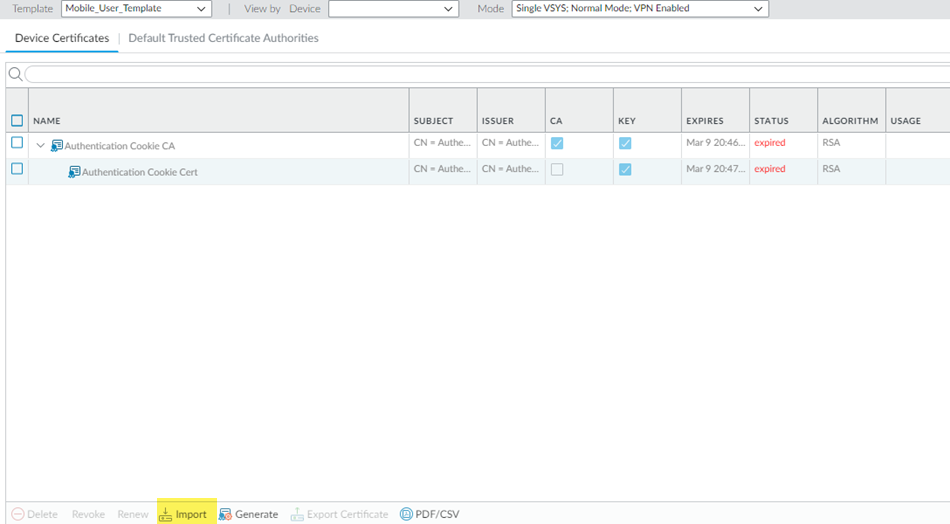
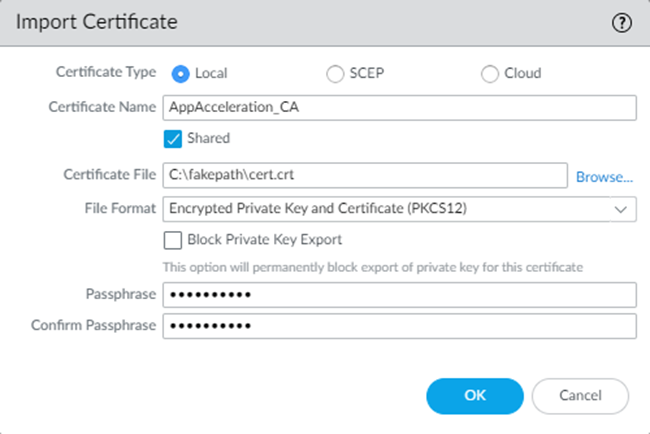
If you ever need to change the root CA/certificate, you must upload it and commit and push your changes before you can use the changed certificate.- Go to DeviceCertificatesCertificate Management.Be sure that you're in the Mobile_User_Template.Import a certificate.
![]() Select the following parameters:
Select the following parameters:- Enter a unique Certificate Name for the
certificate, such as
AppAcceleration_CA.The name is case-sensitive and can be up to 31 characters long. Use only letters, numbers, hyphens, and underscores in the name.
- Browse for the Certificate File received from the CA and Open it.
- Select a Format:
- Encrypted Private Key and Certificate (PKCS12)—This is the default and most common format, in which the key and certificate are in a single container (Certificate File).
- Base64 Encoded Certificate (PEM)—You must import the key separately from the certificate. You're required to Import Private Key and select a Key File if you select this format.
- Enter a Passphrase and Confirm Passphrase.
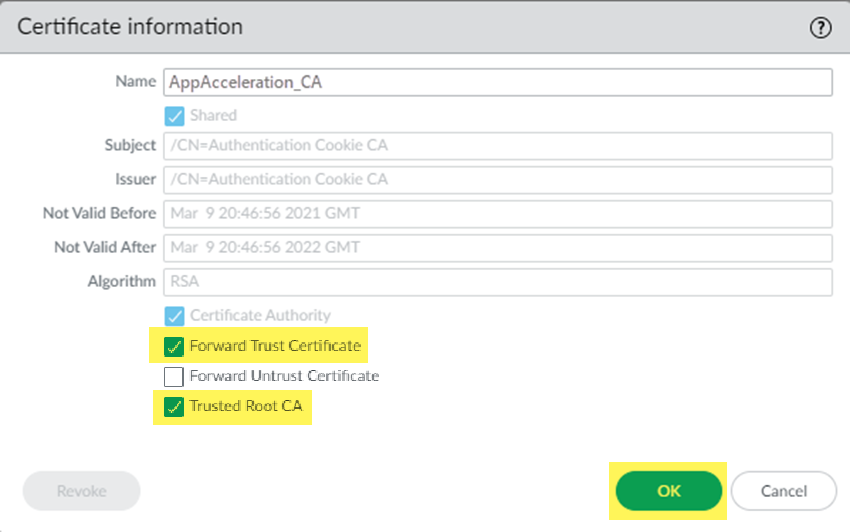
Click OK.![]() Repeat these steps, substituting the Remote_Network_Template for the Mobile_User_Template.Import these certificates in both the Mobile_User_Template and Remote_Network_Template to accelerate apps for your mobile users and users at remote network sites.Mark the root CA/certificate you added as a forward trust certificate and a trusted root CA.If you don't specify the certificate as a forward trust certificate and trusted root CA, users will encounter SSL errors when trying to access accelerated apps when using SSL decryption. If you have certificates in the Mobile_User_Template and Remote_Network_Template, perform this step in both templates.
Repeat these steps, substituting the Remote_Network_Template for the Mobile_User_Template.Import these certificates in both the Mobile_User_Template and Remote_Network_Template to accelerate apps for your mobile users and users at remote network sites.Mark the root CA/certificate you added as a forward trust certificate and a trusted root CA.If you don't specify the certificate as a forward trust certificate and trusted root CA, users will encounter SSL errors when trying to access accelerated apps when using SSL decryption. If you have certificates in the Mobile_User_Template and Remote_Network_Template, perform this step in both templates.- Select the root CA/certificate you added.Select the certificate as a Forward Trust Certificate and Trusted Root CA and click OK.
![]() Commit and Push your changes.(Mobile Users—GlobalProtect Deployments Only) Add the root CA/certificate you added to the list of GlobalProtect trusted certificates in the GlobalProtect portal configuration.Alternatively, if you're using AD, you can distribute the root CA from AD using an AD GPO.
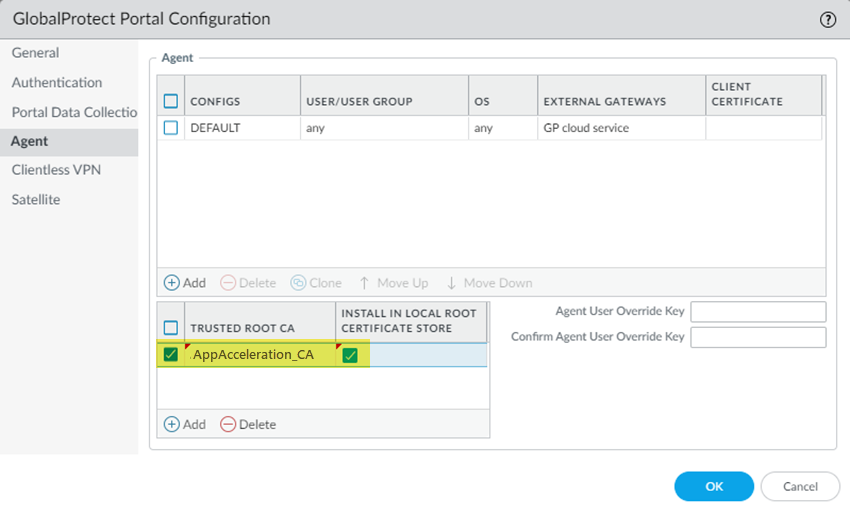
Commit and Push your changes.(Mobile Users—GlobalProtect Deployments Only) Add the root CA/certificate you added to the list of GlobalProtect trusted certificates in the GlobalProtect portal configuration.Alternatively, if you're using AD, you can distribute the root CA from AD using an AD GPO.- Go to NetworkGlobalProtectPortalsGlobalProtect_PortalAgent.Be sure that you're in the Mobile_User_Template.Add the trusted root CA you created in a previous step.Select Install in Local Root Certificate Store.Click OK.
![]() Commit and Push your changes.Enable App Acceleration and choose the certificate file you created.
Commit and Push your changes.Enable App Acceleration and choose the certificate file you created.- Go to PanoramaCloud ServicesApp Acceleration and Get Started with App Acceleration.
![]() From Strata Cloud Manager, go to ConfigurationApp Acceleration from the left navigation bar.Move the slider to the right to have App Acceleration be Enabled for all Mobile Users—GlobalProtect and Remote Networks.If commits are ongoing, App Acceleration settings will take effect after all commits are complete.
From Strata Cloud Manager, go to ConfigurationApp Acceleration from the left navigation bar.Move the slider to the right to have App Acceleration be Enabled for all Mobile Users—GlobalProtect and Remote Networks.If commits are ongoing, App Acceleration settings will take effect after all commits are complete.![]() App Acceleration will be enabled for all TCP traffic. If you wish to accelerate SaaS apps, you will need to select a root CA/certificate, as shown in the next step.In the App Acceleration configuration, type the name of the certificate you created in an earlier step exactly as it's listed in Panorama.Be sure that you have committed and pushed the certificate before typing it.If you need to change the certificate from an existing one, type the new name. Type in the name (you can’t select it from a list), and you must commit and push the new certificate before you enter the name.
App Acceleration will be enabled for all TCP traffic. If you wish to accelerate SaaS apps, you will need to select a root CA/certificate, as shown in the next step.In the App Acceleration configuration, type the name of the certificate you created in an earlier step exactly as it's listed in Panorama.Be sure that you have committed and pushed the certificate before typing it.If you need to change the certificate from an existing one, type the new name. Type in the name (you can’t select it from a list), and you must commit and push the new certificate before you enter the name.![]() After you import the certificate, you must wait until App Acceleration generates domain-specific certificates for each app. This process can take up to 1 hour. In the meantime, you can move the slider for the Accelerated Apps to the left to temporarily disable App Acceleration and access the apps until the certificates are generated; if you don't, you might receive an SSL error until the certificates are generated.Allow up to 10 minutes for acceleration to be active after you have turned it on for a given application.(Optional) Specify the ports to include or exclude for App Acceleration.Selective Acceleration by Port lets you specify which network traffic receives acceleration based on destination server ports. This granular control lets you boost application performance while leaving other traffic unaffected. By default, all ports are accelerated.When you use Selective Acceleration by port, make a note of the following guidelines:
After you import the certificate, you must wait until App Acceleration generates domain-specific certificates for each app. This process can take up to 1 hour. In the meantime, you can move the slider for the Accelerated Apps to the left to temporarily disable App Acceleration and access the apps until the certificates are generated; if you don't, you might receive an SSL error until the certificates are generated.Allow up to 10 minutes for acceleration to be active after you have turned it on for a given application.(Optional) Specify the ports to include or exclude for App Acceleration.Selective Acceleration by Port lets you specify which network traffic receives acceleration based on destination server ports. This granular control lets you boost application performance while leaving other traffic unaffected. By default, all ports are accelerated.When you use Selective Acceleration by port, make a note of the following guidelines:- If accelerating SaaS apps with App Acceleration, you must include port 443 in the accelerated ports in order to boost SaaS apps.
- If you are using App Security with App Acceleration, and have defined an app with custom ports, you must include those ports for the defined app traffic to be secured. Excluding the ports from App Acceleration prevents App Security traffic inspection.
- To select the ports to accelerate, enter a single port, multiple ports
using commas between the ports, a range of ports using dashes, or any
combination of the preceding entries. App Acceleration accelerates the
traffic for those ports. The ports that App Acceleration excludes
display in the Excluded Ports area.
![]()
- To select the ports to exclude from acceleration, Switch to
invert selection and enter the ports to exclude. App
Acceleration accelerates every port you don’t select.
![]()
- To revert your changes to the last saved setting or the original default setting, select Revert.
(Optional) Show Advanced Options and change the metric testing parameters.- (Optional) To disable the collection of metrics to obtain
performance information, deselect Allow tests to collect
performance metrics for Mobile Users.Palo Alto Networks recommends that you enable metric collection to view the app performance improvements when using App Acceleration.
- (Optional) To change the percentage of users for which predictive tests are processed from the default of 5%, select another percentage in the drop-down and Confirm the changes.
![]()
(Optional) To view details about the applications that have been accelerated in your environment, go to InsightsOperationalApp Acceleration.