Prisma Access
Onboard Multiple Remote Networks
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma Access Docs
-
- 6.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 6.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 4.2 Preferred
- 4.1 Preferred
- 4.0 Preferred
- 3.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 2.2 Preferred
-
-
- 4.0 & Later
- Prisma Access China
-
-
Onboard Multiple Remote Networks
Use the bulk import capability to speed up the process of onboarding remote
networks.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
To streamline the process to onboard and configure remote networks, you have the
option to onboard at least one remote network and then export those settings to a
Comma Separated Value (CSV) text file. The CSV file includes the values of IPSec
tunnel and IKE gateway settings for the network you selected for export, and you can
then edit these settings and make them unique for each new network you may want to
onboard. You can modify the CSV file to include 100 new remote networks and then
import the CSV file back to speed up the process of onboarding new remote network
locations.
The CSV file does not include keys or passwords, such as the BGP shared secret, the
IKE preshared key, Proxy ID, IKE crypto profile, IPSec crypto profile.
Therefore, any keys and passwords required for the IPSec tunnel and IKE gateway
settings are inherited from the network you select when you initiate the CSV file
import.
When using this bulk import process, you must wait for Prisma Access to deploy the
infrastructure for securing these locations.
- Select PanoramaCloud ServicesConfigurationRemote Networks (in the Onboarding section).Select a location, then Export the configuration of a remote network that you have previously onboarded.If you have not yet added any locations, you need to Add a location, then download its configuration. You must select a remote network and click Export. A CSV file that includes the settings is downloaded to your computer.(Deployments that allocate bandwidth by compute location only) Make sure that you have allocated bandwidth for the locations to onboard.Each location you onboard has a corresponding compute location for which bandwidth is allocated.
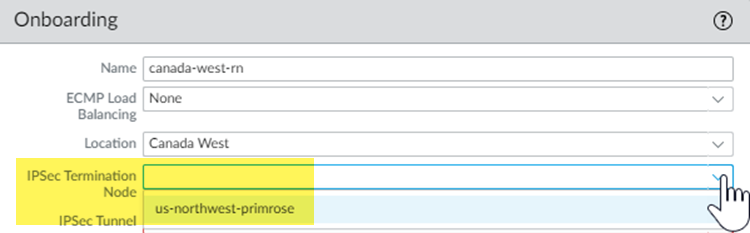
- Select PanoramaCloud ServicesConfigurationRemote Networks and click the gear in the Bandwidth Allocation area.Check the Bandwidth Allocation field in the table that displays.The table in this area shows the compute location-to-Prisma Access location mapping. You must have bandwidth allocated for the compute locations that are associated with the locations you want to onboard. For example, to onboard the Japan Central location, make sure that you have allocated bandwidth in the Asia Northeast compute location.If you have not yet allocated bandwidth for the compute locations that are associated with the locations you want to onboard, add it now.(Deployments that allocate bandwidth by compute location only) Find the IPSec Termination Node associated with the location or locations you want to onboard.You assign an IPSec Termination Node to the remote network during onboarding, and you enter this value in the spn-name column of the CSV file. Each IPSec termination node can provide up to 1,000 Mbps of bandwidth.To find the IPSec Termination Node, perform one of the following actions:
- Select PanoramaCloud ServicesConfigurationRemote Networks, Add a remote network and select the location you want to onboard, and make a note of the IPSec Termination Node choices in the onboarding area.
![]()
- Open a command-line interface (CLI) session with the Panorama that manages Prisma Access and enter the show plugins cloud_services remote-networks agg-bandwidth region compute-location-name, where compute-location-name is the compute location that is associated with the location you want to onboard. The IPSec Termination Node displays in the spn-name-list field.
Modify the CSV file to add configuration for remote networks.See Fields in Remote Networks Table for a description of the fields and the possible values in this file.You must rename the network(s) listed in the exported file. If the file has duplicate names the import will fail.Import the CSV file.The configuration from the file are displayed on screen. The remote network you selected to import the file will serve as a model configuration, and the remote networks listed in the file will inherit the keys and any missing values that do not have to be unique from there.Commit and push your changes.- CommitCommit and Push your changes.Click OK and Push.
Fields in Remote Networks Table
The following table provides a description of the fields in the remote networks table. Fields marked as Y in the Required row are required fields and fields marked as N are optional.Field Description Required?(Y/N) name The name of the remote network. Y bandwidth (Deployments that allocate bandwidth by location only) The allocated bandwidth of the remote network. Acceptable values are:- 2 Mbps
- 5 Mbps
- 10 Mbps
- 20 Mbps
- 25 Mbps
- 50 Mbps
- 100 Mbps
- 150 Mbps
- 300 Mbps
- 500 Mbps
- 1000 Mbps
The 1000 Mbps bandwidth option is in preview mode. The throughput during preview is delivered on a best-effort basis and the actual performance will vary depending upon the traffic mix.Y region The remote network’s location. Enter the locations exactly as they are in this document (for example, US West, or Japan South).Y subnets Statically routed subnets on the LAN side of the remote network. Separate multiple subnets with commas. N bgp_peer_as The BGP Autonomous System Number (ASN) of the remote network peer device. N bgp_peer_address The BGP peer address of the remote network peer device. N tunnel_name The name of the IPSec tunnel configuration. A unique value is required. Y gateway_name The name of the IKE Gateway configuration. A unique value is required. Y peer_ip_address The IP address of the Prisma Access peer device. N local_id_type The type of IKE ID that Prisma Access presents to the peer device. If you use certificates in the remote network to which you import this file, all imported types specified will refer to the Configured Certificate values. N local_id_value The value of the IKE ID that Prisma Access presents to the peer device. If you use certificates in the remote network to which you import this file, all imported types specified will refer to the Configured Certificate values. N peer_id_type The value of the IKE ID that the peer presents to Prisma Access. If you use certificates in the remote network to which you import this file, all imported types specified will refer to the Peer Certificate values. N peer_id_value The value of the IKE ID that Prisma Access presents to the peer device. If you use certificates in the remote network to which you import this file, all imported types specified will refer to the Peer Certificate values. N monitor_ip The tunnel monitoring IP address the cloud will use to determine that the IPSec tunnel is up and the peer network is reachable. You cannot export a proxy-ID value for the tunnel monitor.N proxy_ids The proxy IDs that are configured for the peer. For route-based VPNs, leave this field blank. Specify the Proxy ID in the following CSV configuration format: [{"name":"proxyidname", "local":"1.2.3.4/32", "remote":"4.3.2.1/32", "protocol":{"udp": {"local-port":123, "remote-port":234}}}, {"name":"proxyidname2", "local":"2.3.4.5/32", "remote":"3.4.5.6/32", "protocol":{"tcp": {"local-port":234,"remote-port":345}}}]N sec_wan_enabled Specifies whether or not you enable a secondary IPSec tunnel. Acceptable values are yes and no. N sec_tunnel_name The name of the secondary IPSec tunnel configuration. A unique value is required if you specify a secondary tunnel. N sec_gateway_name The name of the secondary IKE Gateway configuration. A unique value is required if you specify a secondary tunnel. N sec_peer_ip_address The IP address of the Prisma Access peer device for the secondary IPSec tunnel. N sec_local_id_type The type of IKE ID that Prisma Access presents to the peer device for the secondary IPSec tunnel. If you use certificates in the remote network to which you import this file, all imported types specified will refer to the Configured Certificate values. N sec_local_id_value The value of the IKE ID that Prisma Access presents to the peer device for the secondary IPSec tunnel. If you use certificates in the remote network to which you import this file, all imported types specified will refer to the Configured Certificate values. N sec_peer_id_type The value of the IKE ID that the peer presents to Prisma Access for the secondary IPSec tunnel. If you use certificates in the remote network to which you import this file, all imported types specified will refer to the Peer Certificate values. N sec_peer_id_value The value of the IKE ID that Prisma Access presents to the peer device for the secondary IPSec tunnel. If you use certificates in the remote network to which you import this file, all imported types specified will refer to the Peer Certificate values. N sec_monitor_ip The tunnel monitoring IP address the cloud will use for the secondary IPSec tunnel to determine that the IPSec tunnel is up and the peer network is reachable. You cannot export a proxy-ID value for the tunnel monitor.N sec_proxy_ids The proxy IDs that are configured for the peer for the secondary IPSec tunnel. For route-based VPNs, leave this field blank. Specify the Proxy ID in the following CSV configuration format: [{"name":"proxyidname", "local":"1.2.3.4/32", "remote":"4.3.2.1/32", "protocol":{"udp": {"local-port":123, "remote-port":234}}}, {"name":"proxyidname2", "local":"2.3.4.5/32", "remote":"3.4.5.6/32", "protocol":{"tcp": {"local-port":234,"remote-port":345}}}]N ecmp_link_1_tunnel_name (ECMP deployments only) The name of the IPSec tunnel configuration for ECMP tunnel 1. A unique value is required. ecmp_link_1_gateway_name (ECMP deployments only) The name of the IKE Gateway configuration for ECMP tunnel 1. A unique value is required. ecmp_link_1_peer_ip_address (ECMP deployments only) The IP address of the Prisma Access peer device for ECMP tunnel 1. ecmp_link_1_local_id_type (ECMP deployments only) The type of IKE ID that Prisma Access presents to the peer device for ECMP tunnel 1. If you use certificates in the remote network to which you import this file, all imported types specified will refer to the Configured Certificate values. ecmp_link_1_local_id_value (ECMP deployments only) The value of the IKE ID that Prisma Access presents to the peer device for ECMP tunnel 1. If you use certificates in the remote network to which you import this file, all imported types specified will refer to the Configured Certificate values. ecmp_link_1_peer_id_type (ECMP deployments only) The value of the IKE ID that the peer presents to Prisma Access for ECMP tunnel 1. If you use certificates in the remote network to which you import this file, all imported types specified will refer to the Peer Certificate values. ecmp_link_1_peer_id_value (ECMP deployments only) The value of the IKE ID that Prisma Access presents to the peer device for ECMP tunnel 1. If you use certificates in the remote network to which you import this file, all imported types specified will refer to the Peer Certificate values. ecmp_link_1_monitor_ip (ECMP deployments only) The tunnel monitoring IP address the cloud will use to determine that the IPSec tunnel is up and the peer network is reachable for ECMP tunnel 1. You cannot export a proxy-ID value for the tunnel monitor.ecmp_link_1_proxy_ids (ECMP deployments only) The proxy IDs that are configured for the peer for ECMP tunnel 1. For route-based VPNs, leave this field blank. Specify the Proxy ID in the following CSV configuration format: [{"name":"proxyidname", "local":"1.2.3.4/32", "remote":"4.3.2.1/32", "protocol":{"udp": {"local-port":123, "remote-port":234}}}, {"name":"proxyidname2", "local":"2.3.4.5/32", "remote":"3.4.5.6/32", "protocol":{"tcp": {"local-port":234,"remote-port":345}}}]ecmp_link_1_bgp_peer_as (ECMP deployments only) The BGP Autonomous System Number (ASN) of the remote network peer device for ECMP tunnel 1. ecmp_link_1_bgp_peer_address (ECMP deployments only) The BGP peer address of the remote network peer device for ECMP tunnel 1. ecmp_link_2_tunnel_name (ECMP deployments only) The name of the IPSec tunnel configuration for ECMP tunnel 2. A unique value is required. ecmp_link_2_gateway_name (ECMP deployments only) The name of the IKE Gateway configuration for ECMP tunnel 2. A unique value is required. ecmp_link_2_peer_ip_address (ECMP deployments only) The IP address of the Prisma Access peer device for ECMP tunnel 2. ecmp_link_2_local_id_type (ECMP deployments only) The type of IKE ID that Prisma Access presents to the peer device for ECMP tunnel 2. If you use certificates in the remote network to which you import this file, all imported types specified will refer to the Configured Certificate values. ecmp_link_2_local_id_value (ECMP deployments only) The value of the IKE ID that Prisma Access presents to the peer device for ECMP tunnel 2. If you use certificates in the remote network to which you import this file, all imported types specified will refer to the Configured Certificate values. ecmp_link_2_peer_id_type (ECMP deployments only) The value of the IKE ID that the peer presents to Prisma Access for ECMP tunnel 2. If you use certificates in the remote network to which you import this file, all imported types specified will refer to the Peer Certificate values. ecmp_link_2_peer_id_value (ECMP deployments only) The value of the IKE ID that Prisma Access presents to the peer device for ECMP tunnel 2. If you use certificates in the remote network to which you import this file, all imported types specified will refer to the Peer Certificate values. ecmp_link_2_monitor_ip (ECMP deployments only) The tunnel monitoring IP address the cloud will use to determine that the IPSec tunnel is up and the peer network is reachable for ECMP tunnel 2. You cannot export a proxy-ID value for the tunnel monitor.ecmp_link_2_proxy_ids (ECMP deployments only) The proxy IDs that are configured for the peer for ECMP tunnel 2. For route-based VPNs, leave this field blank. Specify the Proxy ID in the following CSV configuration format: [{"name":"proxyidname", "local":"1.2.3.4/32", "remote":"4.3.2.1/32", "protocol":{"udp": {"local-port":123, "remote-port":234}}}, {"name":"proxyidname2", "local":"2.3.4.5/32", "remote":"3.4.5.6/32", "protocol":{"tcp": {"local-port":234,"remote-port":345}}}]ecmp_link_2_bgp_peer_as (ECMP deployments only) The BGP Autonomous System Number (ASN) of the remote network peer device for ECMP tunnel 2. ecmp_link_2_bgp_peer_address (ECMP deployments only) The BGP peer address of the remote network peer device for ECMP tunnel 2. ecmp_link_3_tunnel_name (ECMP deployments only) The name of the IPSec tunnel configuration for ECMP tunnel 3. A unique value is required. ecmp_link_3_gateway_name (ECMP deployments only) The name of the IKE Gateway configuration for ECMP tunnel 3. A unique value is required. ecmp_link_3_peer_ip_address (ECMP deployments only) The IP address of the Prisma Access peer device for ECMP tunnel 3. ecmp_link_3_local_id_type (ECMP deployments only) The type of IKE ID that Prisma Access presents to the peer device for ECMP tunnel 3. If you use certificates in the remote network to which you import this file, all imported types specified will refer to the Configured Certificate values. ecmp_link_3_local_id_value (ECMP deployments only) The value of the IKE ID that Prisma Access presents to the peer device for ECMP tunnel 3. If you use certificates in the remote network to which you import this file, all imported types specified will refer to the Configured Certificate values. ecmp_link_3_peer_id_type (ECMP deployments only) The value of the IKE ID that the peer presents to Prisma Access for ECMP tunnel 3. If you use certificates in the remote network to which you import this file, all imported types specified will refer to the Peer Certificate values. ecmp_link_3_peer_id_value (ECMP deployments only) The value of the IKE ID that Prisma Access presents to the peer device for ECMP tunnel 3. If you use certificates in the remote network to which you import this file, all imported types specified will refer to the Peer Certificate values. ecmp_link_3_monitor_ip (ECMP deployments only) The tunnel monitoring IP address the cloud will use to determine that the IPSec tunnel is up and the peer network is reachable for ECMP tunnel 3. You cannot export a proxy-ID value for the tunnel monitor.ecmp_link_3_proxy_ids (ECMP deployments only) The proxy IDs that are configured for the peer for ECMP tunnel 3. For route-based VPNs, leave this field blank. Specify the Proxy ID in the following CSV configuration format: [{"name":"proxyidname", "local":"1.2.3.4/32", "remote":"4.3.2.1/32", "protocol":{"udp": {"local-port":123, "remote-port":234}}}, {"name":"proxyidname2", "local":"2.3.4.5/32", "remote":"3.4.5.6/32", "protocol":{"tcp": {"local-port":234,"remote-port":345}}}]ecmp_link_3_bgp_peer_as (ECMP deployments only) The BGP Autonomous System Number (ASN) of the remote network peer device for ECMP tunnel 3. ecmp_link_3_bgp_peer_address (ECMP deployments only) The BGP peer address of the remote network peer device for ECMP tunnel 3. ecmp_link_4_tunnel_name (ECMP deployments only) The name of the IPSec tunnel configuration for ECMP tunnel 4. A unique value is required. ecmp_link_4_gateway_name (ECMP deployments only) The name of the IKE Gateway configuration for ECMP tunnel 4. A unique value is required. ecmp_link_4_peer_ip_address (ECMP deployments only) The IP address of the Prisma Access peer device for ECMP tunnel 4. ecmp_link_4_local_id_type (ECMP deployments only) The type of IKE ID that Prisma Access presents to the peer device for ECMP tunnel 4. If you use certificates in the remote network to which you import this file, all imported types specified will refer to the Configured Certificate values. ecmp_link_4_local_id_value (ECMP deployments only) The value of the IKE ID that Prisma Access presents to the peer device for ECMP tunnel 4. If you use certificates in the remote network to which you import this file, all imported types specified will refer to the Configured Certificate values. ecmp_link_4_peer_id_type (ECMP deployments only) The value of the IKE ID that the peer presents to Prisma Access for ECMP tunnel 4. If you use certificates in the remote network to which you import this file, all imported types specified will refer to the Peer Certificate values. ecmp_link_4_peer_id_value (ECMP deployments only) The value of the IKE ID that Prisma Access presents to the peer device for ECMP tunnel 4. If you use certificates in the remote network to which you import this file, all imported types specified will refer to the Peer Certificate values. ecmp_link_4_monitor_ip (ECMP deployments only) The tunnel monitoring IP address the cloud will use to determine that the IPSec tunnel is up and the peer network is reachable for ECMP tunnel 4. You cannot export a proxy-ID value for the tunnel monitor.ecmp_link_4_proxy_ids (ECMP deployments only) The proxy IDs that are configured for the peer for ECMP tunnel 4. For route-based VPNs, leave this field blank. Specify the Proxy ID in the following CSV configuration format: [{"name":"proxyidname", "local":"1.2.3.4/32", "remote":"4.3.2.1/32", "protocol":{"udp": {"local-port":123, "remote-port":234}}}, {"name":"proxyidname2", "local":"2.3.4.5/32", "remote":"3.4.5.6/32", "protocol":{"tcp": {"local-port":234,"remote-port":345}}}]ecmp_link_4_bgp_peer_as (ECMP deployments only) The BGP Autonomous System Number (ASN) of the remote network peer device for ECMP tunnel 4. ecmp_link_4_bgp_peer_address (ECMP deployments only) The BGP peer address of the remote network peer device for ECMP tunnel 4. spn-name (Deployments that allocate bandwidth by compute location only) The name of the IPSec Termination Node. This field is required for deployments that allocate bandwidth by compute location.