Prisma Access
Identity Redistribution
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma Access Docs
-
- 6.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 6.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 4.2 Preferred
- 4.1 Preferred
- 4.0 Preferred
- 3.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 2.2 Preferred
-
-
- 4.0 & Later
- Prisma Access China
-
-
Identity Redistribution
Learn how Prisma Access redistributes User-ID mapping and how to configure it.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
So that you can enforce your security policy consistently, Prisma Access
shares identity data that GlobalProtect discovers locally across your entire Prisma
Access environment. Prisma Access can also share identity data with on-premises devices
at remote network sites or service connection sites (HQ and data centers).
For mobile users to access a resource at a remote network location or HQ/data center
that’s secured by a device with user-based policies, you must redistribute the identity
data from the Prisma Access mobile users and users at remote networks to that
on-premises device.
When the users connect to Prisma Access, Prisma Access collects the user’s identity data
and stores it.
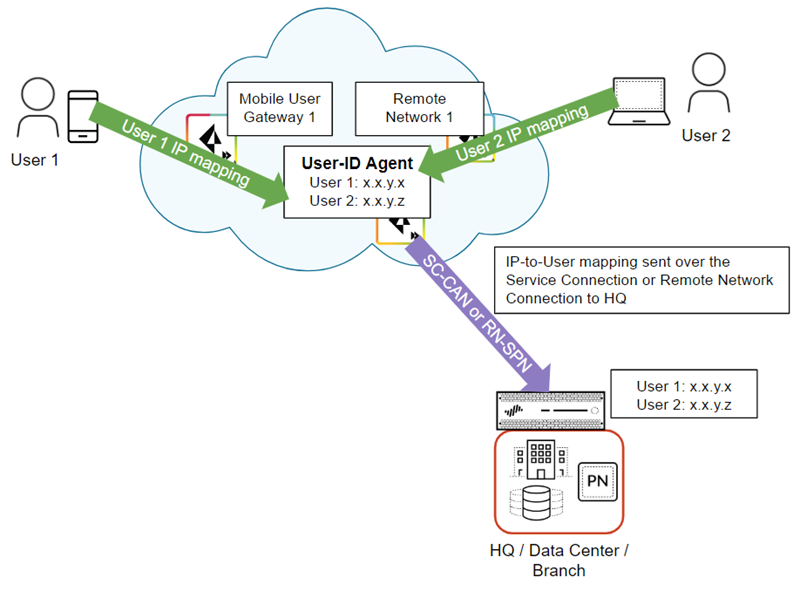
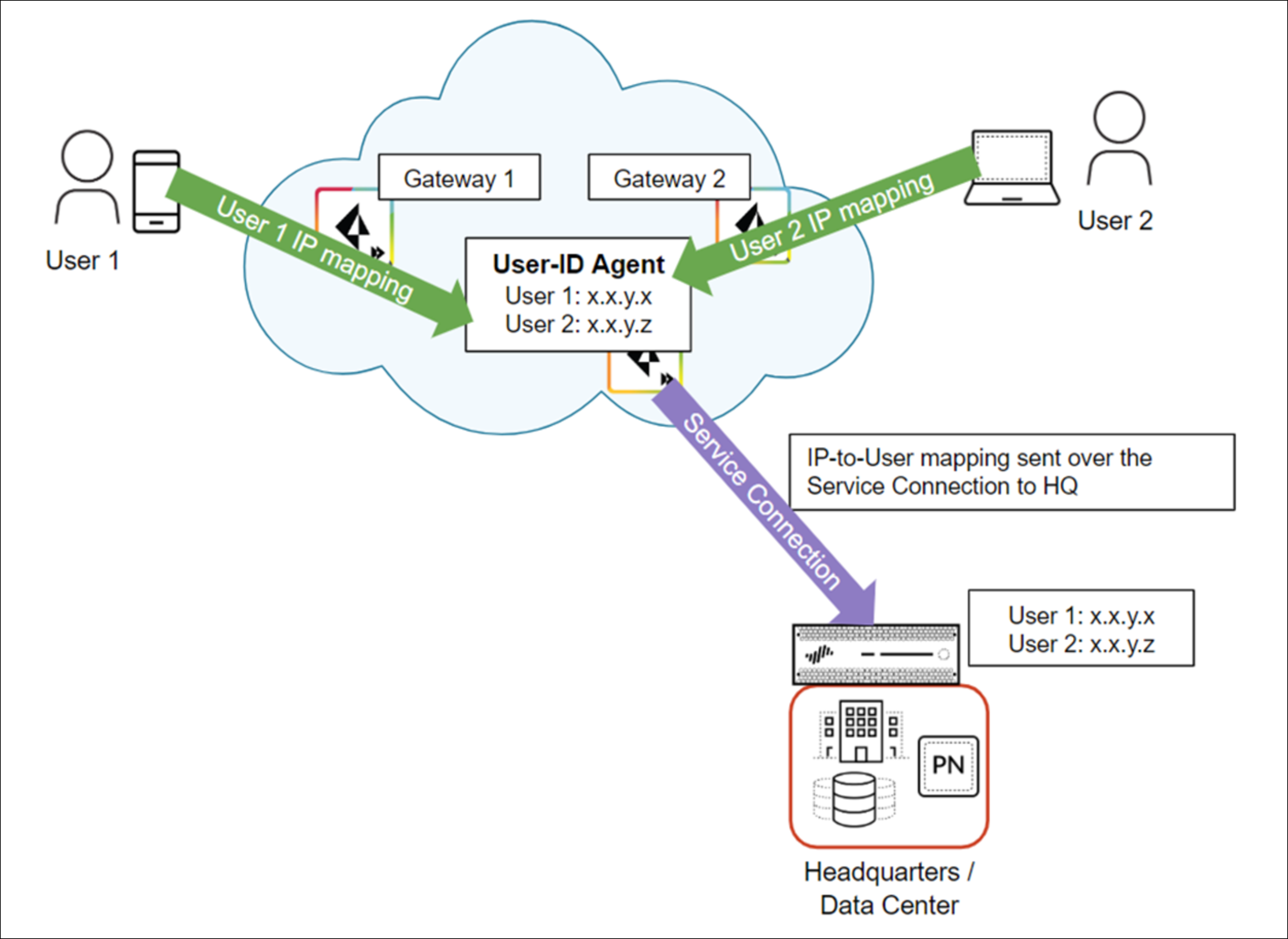
The following example shows two mobile users that have an existing IP address-to-username
mapping in Prisma Access. Prisma Access then redistributes this mapping by way of a
service connection to the on-premises devices that’s securing the HQ/data center.
Prisma Access (Managed by Strata Cloud Manager) automatically enables service connections to work as
identity redistribution agents (also called User-ID agents).
Identity Redistribution (Strata Cloud Manager)
Enable identity data redistribution in Strata Cloud Manager.
So that you can enforce your security policy consistently, Prisma Access shares
identity data that GlobalProtect discovers locally across your entire Prisma Access
environment. Prisma Access can also share identity data with on-premises devices at
remote network sites or service connection sites (HQ and data centers).
For Prisma Access (Managed by Strata Cloud Manager), we’ve enabled some identity data redistribution
by default, and for what’s left, we’ve made the configuration to enable
redistribution very simple (just select a checkbox to select what data you want to
share).
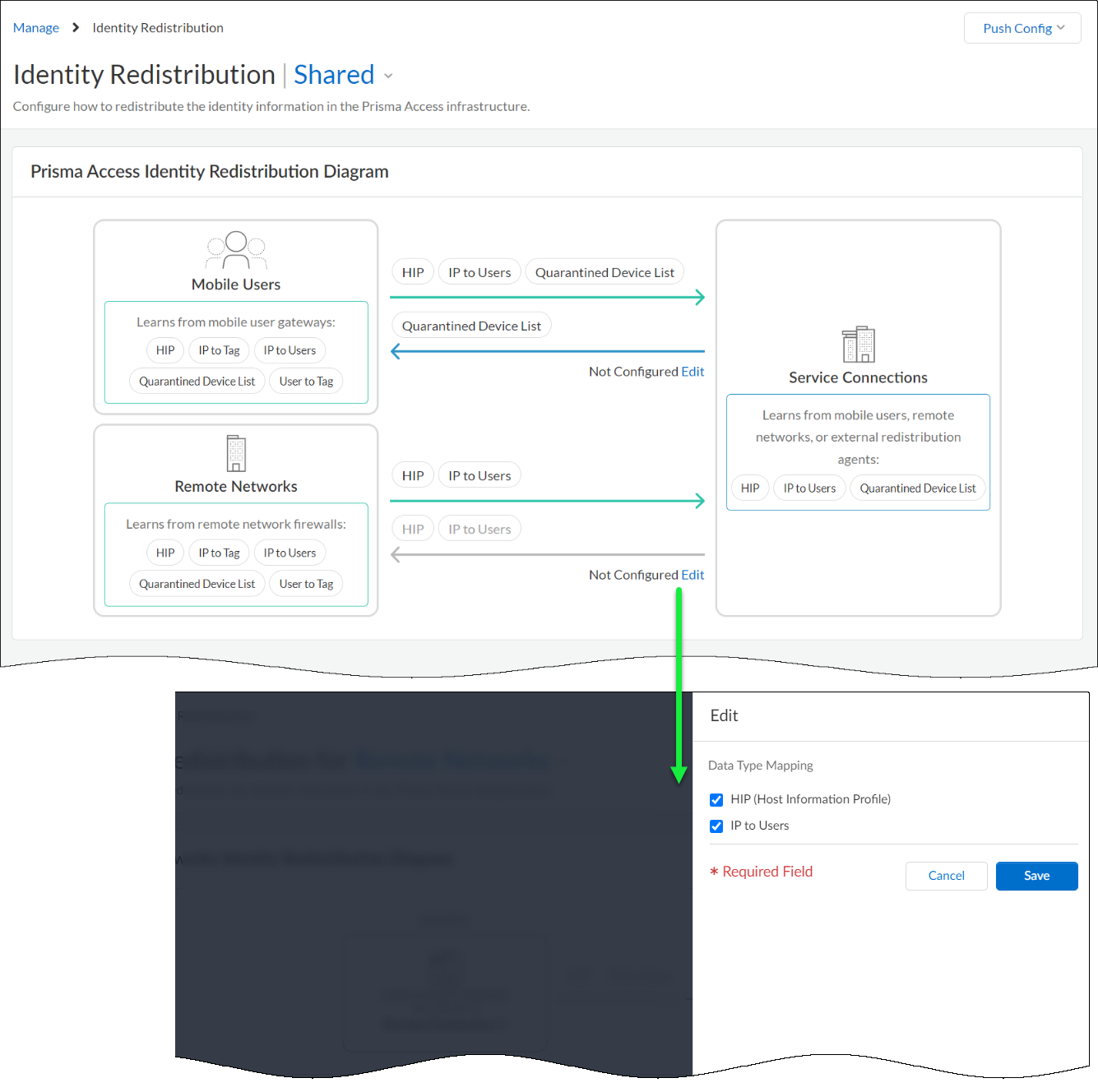
From the Identity Distribution dashboard, you can see how identity data is being
shared and manage data redistribution (ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessIdentity Services.
Identity data that you can redistribute includes:
- HIP data
- IP-address-to-tag mappings
- IP-address-to-user mappings
- User-to-tag mappings
- Quarantined devices
Get started with identity redistribution:
Set Up Identity Redistribution
Set Up Identity Redistribution
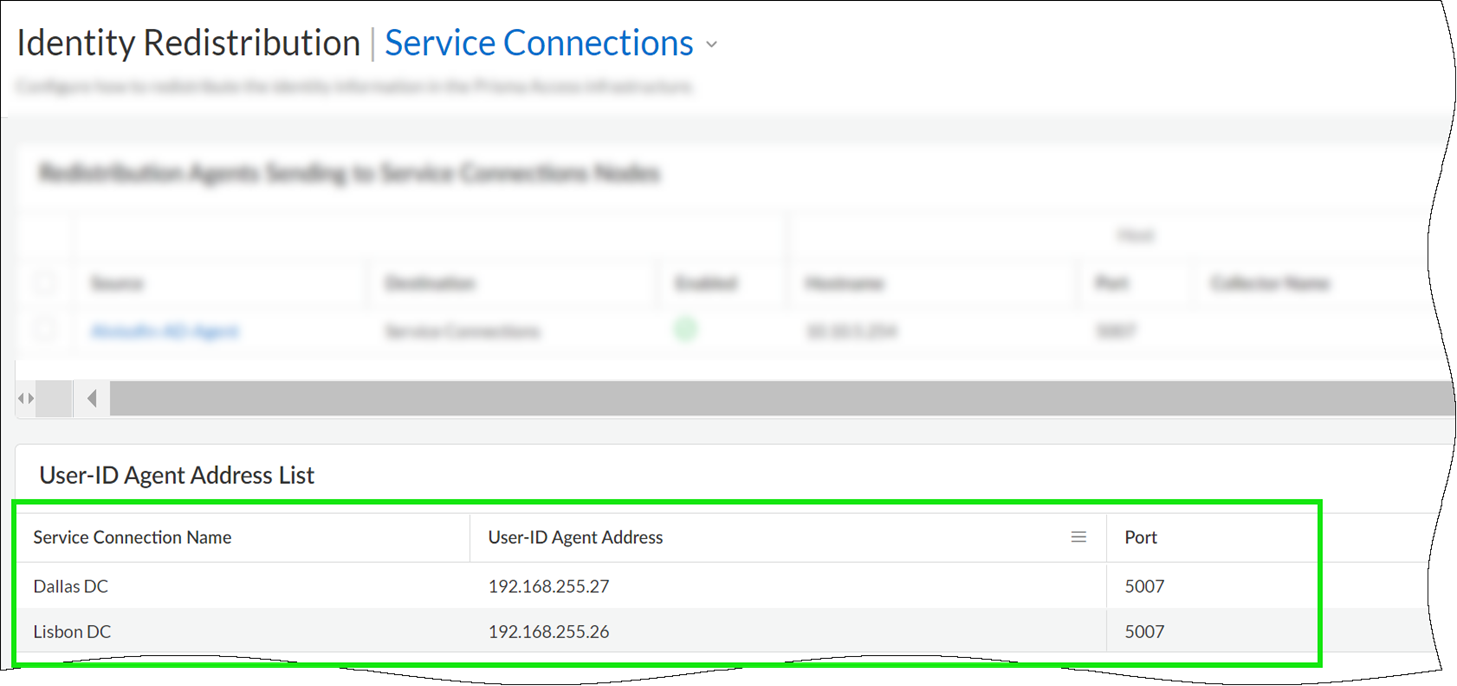
- Confirm Your Service Connection Setup.If you haven’t yet set up a service connection for your HQ or data centers, begin by configuring a service connection. A service connection is required for Prisma Access to share identity data across your environment; Prisma Access automatically enables service connections to work as redistribution agents. A newly created service connection site will be ready to be used as a redistribution agent when you see that it's been assigned a User-ID agent Address (Prisma Access does this automatically, and it'll just take a few minutes).User-ID Redistribution Management—Sometimes, granular controls are needed for user-ID redistribution in particularly large scale Prisma Access deployments. User-ID Redistribution Management lets you manually disable the default identity redistribution behavior for certain service connections by removing the check mark in the User ID column, and then select specific service connections to be used for identity redistribution. It's not necessary to do this for most configurations. Contact Palo Alto Networks support to activate this functionality.Go to ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessIdentity ServicesIdentity Redistribution and set the configuration scope to Service Connections to verify the service connection User-ID agent details.Send Identity Data from Prisma Access to on-premises Devices.The service connection’s User-ID agent information is all you need to configure Prisma Access to distribute identity data to on-premises devices.Go to ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessIdentity ServicesIdentity Redistribution and set the configuration scope to Service Connections to get the service connection User-ID agent details.Use these details to configure Prisma Access as a data redistribution agent on Panorama or a Palo Alto Networks NGFW.
![]() Send Identity Data from on-premises Devices to Prisma Access.Add on-premises devices to Prisma Access as redistribution agents; the devices you add will be able to distribute identity data to Prisma Access.
Send Identity Data from on-premises Devices to Prisma Access.Add on-premises devices to Prisma Access as redistribution agents; the devices you add will be able to distribute identity data to Prisma Access.-
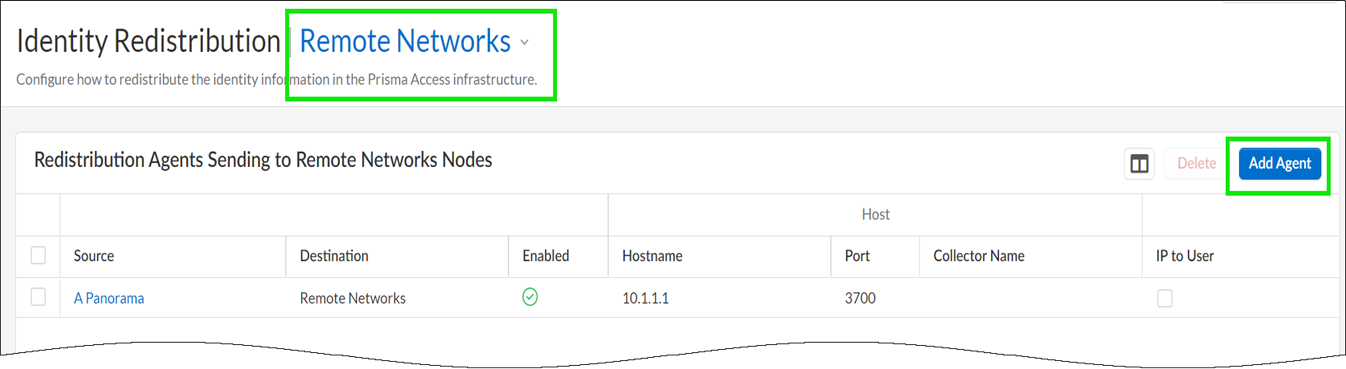
From devices at remote network sites:Go to the Identity Redistribution dashboard, set the configuration scope to Remote Networks, and Add Agent. In addition to specifying the host details, select the type of data the device shares with Prisma Access. Optional settings include the name and a pre-shared key for the device.
![]()
-
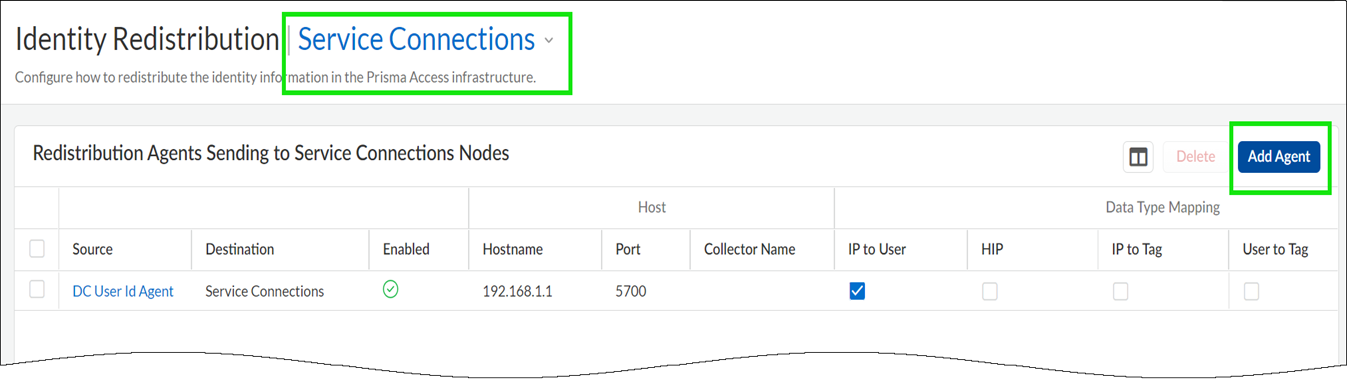
From devices at service connection sites:Go to the Identity Redistribution dashboard, set the configuration scope to Service Connections, and Add Agent. In addition to specifying the host details, select the type of data the device shares with Prisma Access. Optional settings include the name and a pre-shared key for the device.
![]()
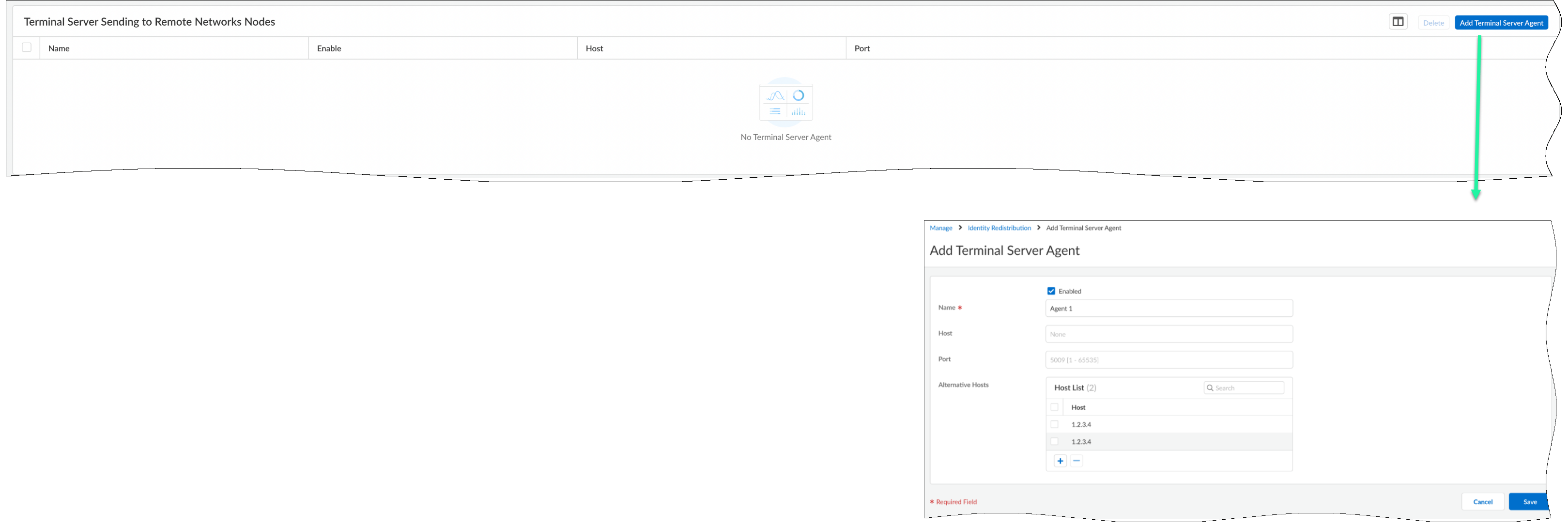
Configure the Terminal Server agent for User Mapping.The Terminal Server (TS) agent allocates a port range to each user to identify specific users on Windows-based terminal servers. The TS agent notifies Prisma Access of the allocated port ranges, so that Prisma Access can enforce policy based on users and user groups.On the Identity Redistribution dashboard, set the configuration scope to Remote Networks, and Add Terminal Server Agent under Terminal Server Sending to Remote Networks Nodes.- By default, the configuration is Enabled.
- Enter a Name for the TS agent.
- Enter the IP address of the Windows Host on which the TS agent is installed.
- Enter the Port number on which the agent listens for user mapping requests. The port is set to 5009 by default.
- Save your changes.
![]()
Distribute Identity Data Across Your Prisma Access Environment.On the Identity Redistribution dashboard, Edit the diagram to specify the identity data you want to collect from each source and share across Prisma Access.![]() To activate your changes, push the configuration to Prisma Access.
To activate your changes, push the configuration to Prisma Access.Identity Redistribution (Panorama)
Shows the steps you take to redistribute User-ID information from Prisma Access to an on-premises firewall and from an on-premises firewall to Prisma Access.After you configure User-ID, you consistently enforce user-based policy for all mobile users and users at remote network locations by redistributing the IP address-to-username mapping from Prisma Access to all next-generation firewalls that secure access to network resources. Use one of the following methods to redistribute IP address-to-username mapping to mobile users and users in remote networks from an on-premises next-generation firewall and vice versa:Redistribute User-ID Information From Prisma Access to an On-Premises Firewall
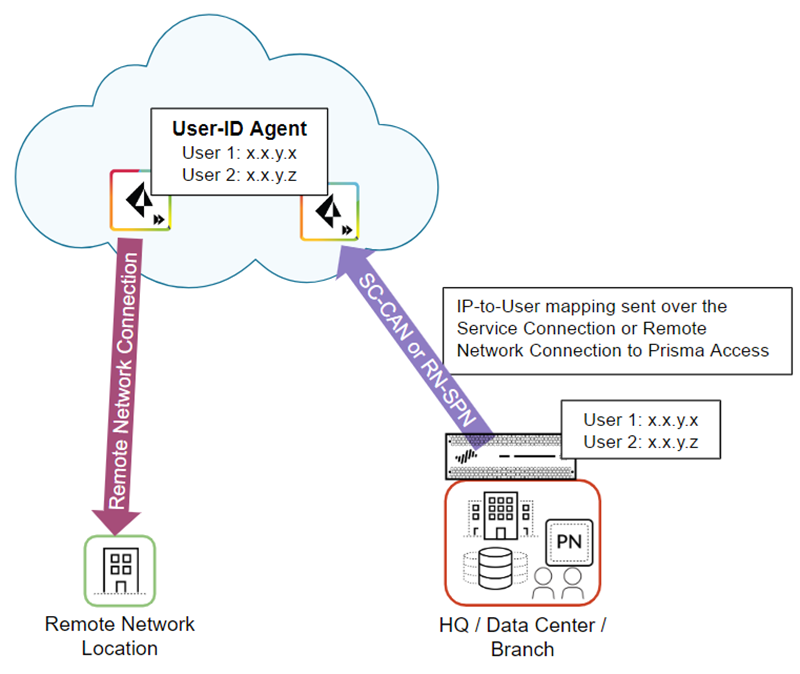
Redistribute User-ID Information From Prisma Access to an on-premises Firewall.In cases where mobile users need to access a resource on a remote network location or HQ/data center and the resource is secured by an on-premises next-generation firewall with user-based policies, you must redistribute IP address-to-username mapping from the Prisma Access mobile users and users at remote networks to the on-premises firewall. When the user connects to Prisma Access, it collects this user-to-IP address mapping and stores it.The following figure shows two mobile users who have an existing IP address-to-username mapping in Prisma Access. Prisma Access then redistributes this mapping by way of a either a service connection (SC-CAN) or remote network connection (RN-SPN) to the on-premises firewall that secures the HQ/data center.Prisma Access uses the service connection or remote network connection as an IPSec tunnel that serves as the underlay path to the Layer 3 network. You can use any route path over an IPSec trusted tunnel for privately addressed destinations to redistribute this mapping.![]() To redistribute User-ID mappings from Prisma Access to an on-premises firewall, complete the following steps.Make sure you don't apply any SSL decryption on any connection that redistributes user identity to the on-premises firewall (the SC-CAN or RN-SPN), including any firewalls that are in the redistribution path. Alternatively, you can apply a decryption exclusion to the redistribution traffic.
To redistribute User-ID mappings from Prisma Access to an on-premises firewall, complete the following steps.Make sure you don't apply any SSL decryption on any connection that redistributes user identity to the on-premises firewall (the SC-CAN or RN-SPN), including any firewalls that are in the redistribution path. Alternatively, you can apply a decryption exclusion to the redistribution traffic.- Make a note of the IP address to use when you configure the data redistribution agent.
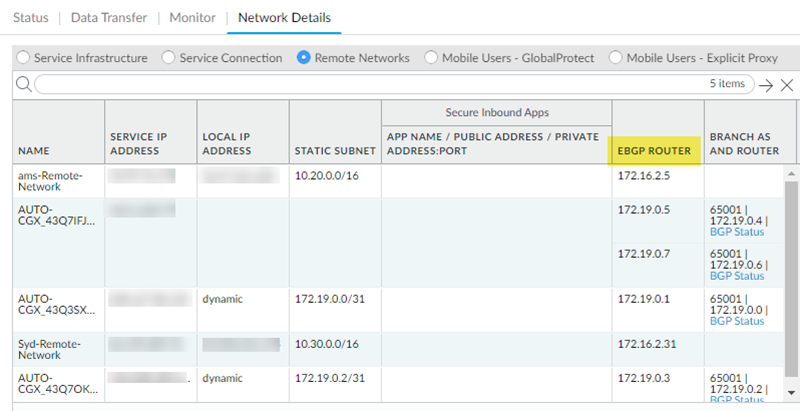
- For remote network connections, find the EBGP Router address (PanoramaCloud ServicesStatusNetwork DetailsRemote NetworksEBGP Router).
![]()
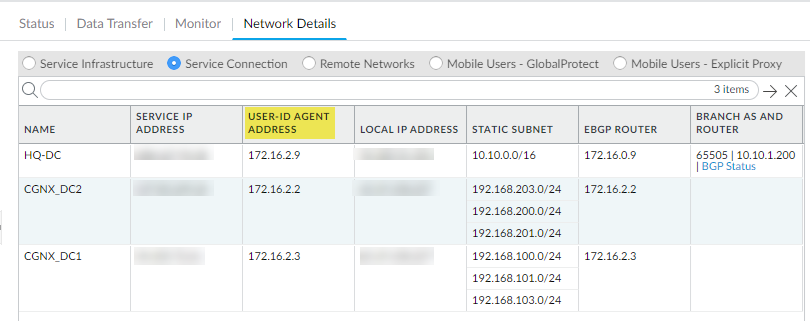
- For service connections, find the User-ID Agent Address (PanoramaCloud ServicesStatusNetwork DetailsService ConnectionUser-ID Agent Address).If you haven’t yet set up a service connection for your HQ or data centers, begin by configuring a service connection. Prisma Access uses service connections to share identity data across your environment; Prisma Access automatically enables service connections to work as redistribution agents. A newly created service connection site will be ready to be used as a redistribution agent when you see that it's been assigned a User-ID agent Address (Prisma Access does this automatically, and it'll just take a few minutes).User-ID Redistribution Management—Sometimes, granular controls are needed for user-ID redistribution in particularly large scale Prisma Access deployments. User-ID Redistribution Management lets you manually disable the default identity redistribution behavior for certain service connections by removing the check mark in the User ID column, and then select specific service connections to be used for identity redistribution. It's not necessary to do this for most configurations. Contact Palo Alto Networks support to activate this functionality.
![]()
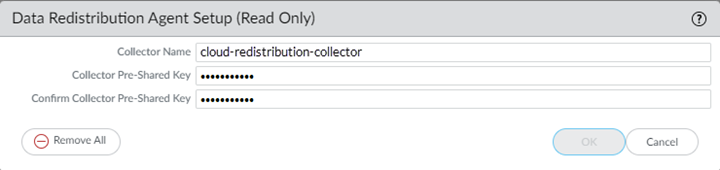
Configure Prisma Access as a User-ID agent that redistributes user mapping information.- In the Panorama that manages Prisma Access, select DeviceData RedistributionCollector Settings.To configure the collector on a service connection, select the Service_Conn_Template; to configure the collector on a remote network connection, select the Remote_Network_Template.Click the gear icon to edit the settings.Provide a Collector Name and a Collector Pre-Shared Key to identify Prisma Access as a User-ID agent.Click OK to save your changes.
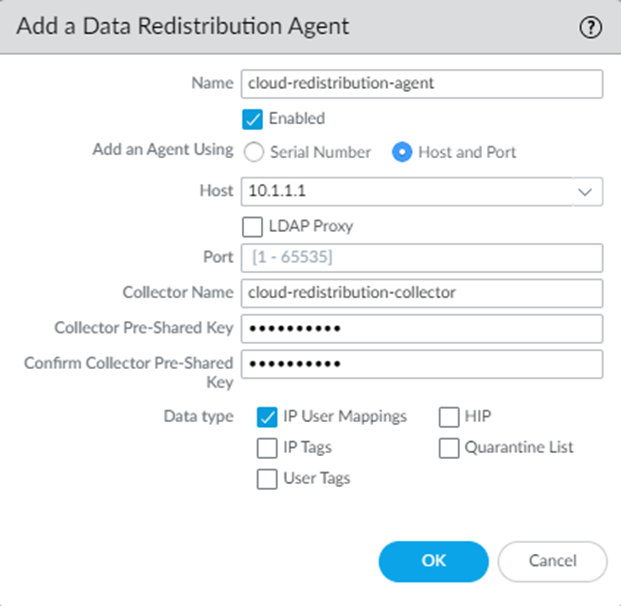
![]() Configure the on-premises firewall to collect the User-ID mapping from Prisma Access.
Configure the on-premises firewall to collect the User-ID mapping from Prisma Access.- From the on-premises firewall, select DeviceData RedistributionAgents.Add a User-ID agent and give it a Name.Select Host and Port.Enter the User-ID Agent Address (for a service connection) or EBGP Router Address (for a remote network connection) from Prisma Access in the Host field.Enter the Collector Name and Collector Pre-Shared Key for the Prisma Access collector you created earlier in the procedure.Select IP User Mappings.Click OK.Repeat these steps for each service connection or remote network connection for which you want to redistribute mappings.
![]()
Redistribute User-ID Information From an On-Premises Firewall to Prisma Access
Redistribute User-ID Information From an on-premises Firewall to Prisma Access.In cases where users are at a branch location or HQ that is secured by an on-premises next-generation firewall with user-based policies, and they need to access resources at another branch location that you have secured with Prisma Access, you must redistribute IP address-to-user name mappings from the on-premises firewall to Prisma Access.The following figure shows an HQ/Data center with an on-premises next-generation firewall with existing IP address-to-username mapping. Prisma Access connects to the firewall with either a service connection (SC-CAN) or remote network connection (RN-SPN), and the on-premises firewall redistributes the mapping to Prisma Access.The following figure shows a Prisma Access service connection or remote network connection being used to redistribute the mapping. You can use any route path over an IPSec trusted tunnel for privately addressed destinations to redistribute this mapping.![]() To redistribute User-ID mappings from an on-premises firewall to Prisma Access, complete the following steps.
To redistribute User-ID mappings from an on-premises firewall to Prisma Access, complete the following steps.- Configure the on-premises firewall to redistribute User-ID information to Prisma Access.
- From the on-premises firewall, select DeviceData RedistributionCollector Settings.Click the gear icon to edit the settings.Provide a Collector Name and a Collector Pre-Shared Key to identify the on-premises firewall as a User-ID agent.Click OK to save your changes.Configure Prisma Access to collect the User-ID mapping from the on-premises firewall.
- From the Panorama that manages Prisma Access, select DeviceData RedistributionAgents.Make sure that you have selected the Service_Conn_Template (for service connections) or the Remote_Network_Template (for remote network connections) in the Templates drop-down at the top of the page.Add a User-ID agent and give it a Name.Select Host and Port.Enter the IP address of the MGT interface or service route that the firewall uses to send user mappings in the Host field.For the MGT interface, you can enter a hostname instead of the IP address.Enter the Collector Name and Collector Pre-Shared Key, using the values for the collector you used for the on-premises firewall in Step 1.Select IP User Mappings.Click OK.