Prisma Access
Configure Traffic Steering in Prisma Access
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma Access Docs
-
- 6.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 6.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 4.2 Preferred
- 4.1 Preferred
- 4.0 Preferred
- 3.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 2.2 Preferred
-
-
- 4.0 & Later
- Prisma Access China
-
-
Configure Traffic Steering in Prisma Access
Configure traffic steering in the Prisma Access deployment.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
Traffic steering allows you to configure Prisma Access Access to create traffic
steering rules to specify targets for internet-bound traffic from mobile users and
remote network connections. You can specify the traffic to be redirected to a
service connection before sending to the internet, or you can specify the traffic to
directly egress to the internet. Configure traffic steering for your Prisma Access
deployment by completing the following steps.
Prisma Access traffic steering does not support Explicit
Proxy.
Configure Traffic Steering in Prisma Access (Strata Cloud Manager)
Configure traffic steering in the Prisma Access deployment.
In Prisma Access deployments, a service connection provides access to internal
network resources, such as authentication services and private apps in your
headquarters or data center. Service connections process internal traffic, where no
internet access is required. In some cases, you might want to redirect
internet-bound traffic to the data center. Traffic steering allows you to redirect
mobile user or remote network traffic to a service connection before being sent to
the internet. Configure traffic steering for your Prisma Access deployment by
completing the following steps.
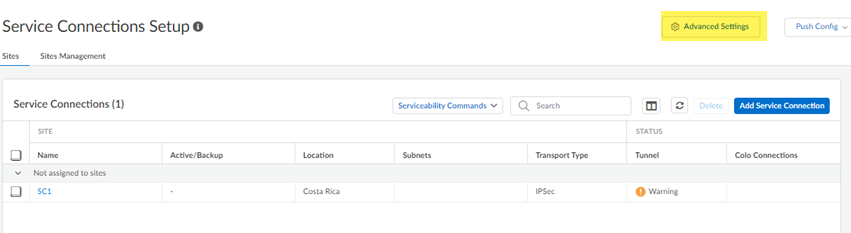
- Onboard your service connections, mobile users and remote networks, as applicable to your deployment.Go to ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessConfiguration ScopePrisma AccessService ConnectionsAdvanced Settings.
![]() Configure the Traffic Steering rules.
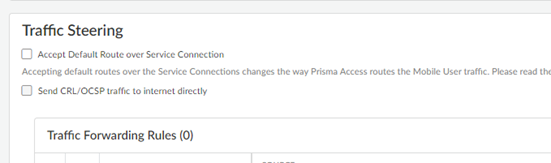
Configure the Traffic Steering rules.- (Optional, mobile user deployments only) Allow Prisma Access to accept and install the default route advertised over one or more service connections from the CPE by clicking the gear icon to open the Settings and selecting Accept Default Route over Service Connections.Default routes have guidelines that you must follow when using them; for example, default routes are supported for mobile user deployments only and have no effect on remote network deployments. Be sure to review these guidelines before implementing default routes with traffic steering.(Optional) Allow Prisma Access to send certificate revocation list (CRL) and Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) traffic directly to the internet by selecting Send CRL/OCSP traffic to internet directly.Select this choice if you have an OCSP or CRP server in the public internet and you want to send that traffic directly to the internet using the untrust zone. If you do not select this choice, Prisma Access sends this traffic to the service connection.Be sure that you have upgraded your Prisma Access deployment to a minimum version of 5.1.1 before selecting Send CRL/OCSP traffic to internet directly.
![]() Create rules for the target you created and apply them to the target.
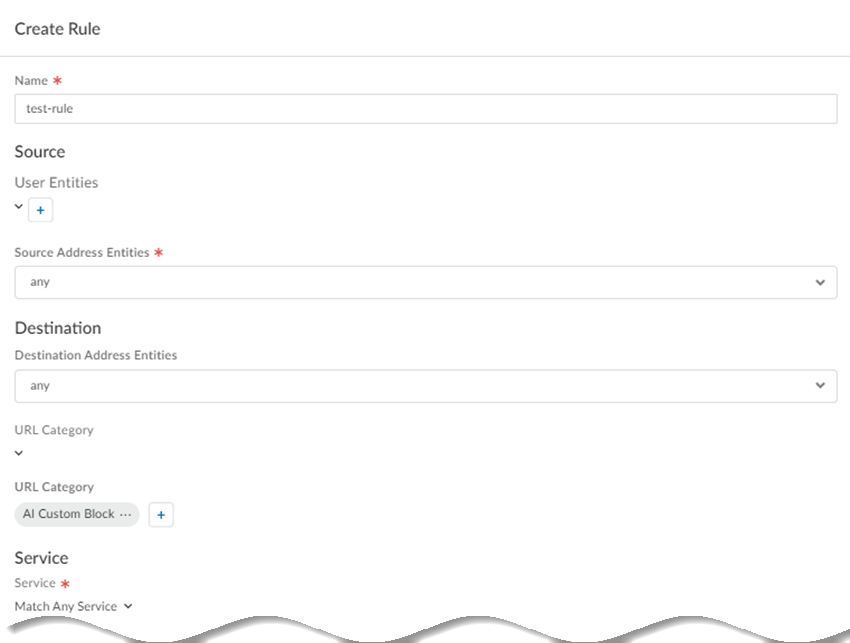
Create rules for the target you created and apply them to the target.- Add Rule.Enter a unique Name for the rule.In the Source area:
- Specify the list of users to match. You can Match Any User, Match Pre-logon, Match known-user, Match unknown, or Add Users and select the user or users to match.
- Select Source Address Entities. You can
select one or more of the following objects:
- An IP address
- An address group
- An External Dynamic List (EDL) using IP addresses or URLs
In the Destination area specify one of the following Destination Address Entities, or select Any to have traffic processed by the rules in the URL Category field:- An IP address
- An address group
- An External Dynamic List (EDL) using IP addresses or URLs
Specify a URL Category.If you create a custom URL category, enter URLs in all lower case. Traffic steering supports custom URL and predefined URL categories.You can use wildcards with the URLs in URL categories. The following wildcard formats are supported:- *.example.com
- *.fqdn.example.com
The following formats are not supported:- *
- *.*
- *example.com
- example.com/ (trailing slashes in URLs are not supported in URL categories that are used with Traffic Steering)
- example.com/path (only domain names are supported)
- *fqdn.example.com
- fqdn.example.*
Use the following guidelines when configuring destination options:- If you specify a URL category, Prisma Access only matches HTTP and HTTPS traffic, even when service is set to Any.
- Do not create a custom URL category with a type of Category Match.
Specify a Service type and Add Service.Specify service-http to forward HTTP traffic and specify service-https to specify HTTPS traffic. Select Match Any Service to forward traffic of any service type.![]() Create a service connection group and specify an Action.
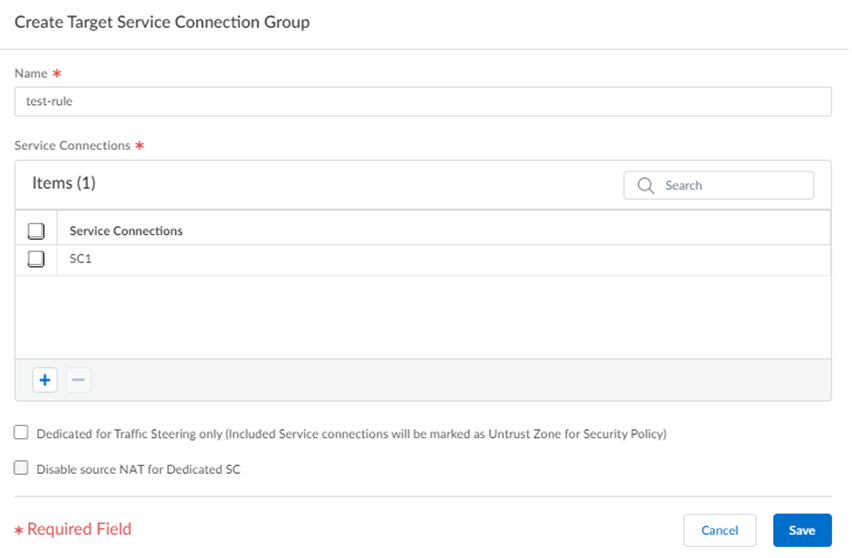
Create a service connection group and specify an Action.- Create New or Manage a group and give it a unique Name.
- Specify the Service Connection or service
connections to use with the target.Palo Alto Networks does not recommend using multiple service connections (whether dedicated or non-dedicated) in a target service connection group that is referenced in a traffic steering rule. In addition, a given service connection can only exist in one target and you cannot add a single service connection to two different targets.
- (Optional) Use a dedicated service connection to steer traffic to a third-party security stack or cloud that is not on your premises and does not need to participate in routing. To set a service connection to be used as a dedicated service connection, select Dedicated for Traffic Steering Only.Dedicated service connections change their zones and are marked as an Untrust Zone for security policy rules.Deselect Dedicated for Traffic Steering Only if you will send both normal service connection-related and traffic steering traffic through the service connection; with this choice, the zone for the service connection remains as Trust.
- Disable source NAT for Dedicated service connections by
selecting, select Disable Source NAT for Dedicated
SC. Source NAT is enabled by default (the
checkbox is deselected). If you disable source NAT, Prisma Access uses your organization’s source IP addresses for the dedicated service connection. If you enable source NAT, Prisma Access uses the EBGP Router address of the service connection (PanoramaCloud ServicesStatusNetwork DetailsService ConnectionEBGP Router) as the source IP address, even after the traffic egresses from the dedicated service connection.
- Save your changes.
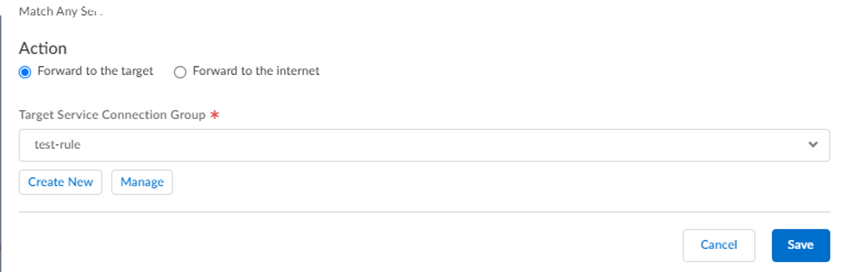
![]() Forward traffic to the specified service connection target, or send the traffic directly to the internet without going through the service connection.
Forward traffic to the specified service connection target, or send the traffic directly to the internet without going through the service connection.- To have Prisma Access forward traffic to a service connection target, select Forward to the target; then select the Target Service Connection Group.Specify this choice if you have traffic you need to send to your existing or legacy environment because of SaaS application allow list limitations, or if you want to create a traffic flow to direct specified internet traffic back to your on-premises network.
- To have Prisma Access forward traffic directly to the internet without first sending it to a service connection, select Forward to the internet.Specify this choice if you are sending a default route to Prisma Access and you want to steer some traffic directly to the internet.
![]() Push Config to save your changes.
Push Config to save your changes.Configure Traffic Steering in Prisma Access (Panorama)
Configure traffic steering in the Prisma Access deployment.- Onboard your service connections, mobile users and remote networks, as applicable to your deployment.Select PanoramaCloud ServicesConfigurationTraffic Steering.(Optional, mobile user deployments only) Allow Prisma Access to accept and install the default route advertised over one or more service connections from the CPE by clicking the gear icon to open the Settings and selecting Accept Default Route over Service Connections.Default routes have guidelines that you must follow when using them; for example, default routes are supported for mobile user deployments only and have no effect on remote network deployments. Be sure to review these guidelines before implementing default routes with traffic steering.(Optional) Allow Prisma Access to send certificate revocation list (CRL) and Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) traffic directly to the internet by selecting Send CRL/OCSP traffic to internet directly.Select this choice if you have an OCSP or CRP server in the public internet and you want to send that traffic directly to the internet using the untrust zone. If you do not select this choice, Prisma Access sends this traffic to the service connection.Be sure that you have upgraded your Prisma Access deployment to a minimum version of 5.1.1 before selecting Send CRL/OCSP traffic to internet directly.
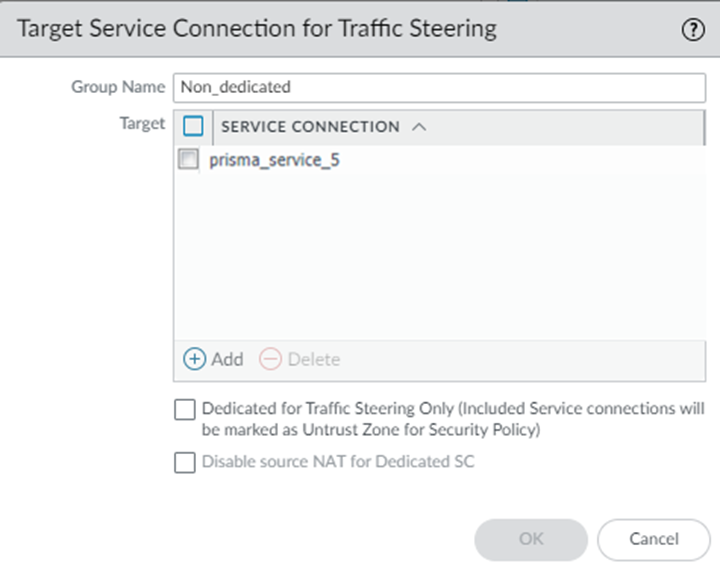
![]() (Optional) Create a target group and assign a service connection to it.
(Optional) Create a target group and assign a service connection to it.- In the Target Service Connections for Traffic Steering area, Add a group and give it a Group Name.Add a Target for the traffic, specifying the Service Connection to use with the target; then, click OK.Palo Alto Networks does not recommend using multiple service connections (whether dedicated or non-dedicated) in a target service connection group that is referenced in a traffic steering rule. In addition, a given service connection can only exist in one target and you cannot add a single service connection to two different targets.Choose whether to make the service connections associated with this target a dedicated service connection.
- You can use a dedicated service connection to steer traffic to a third-party security stack or cloud that is not on your premises and does not need to participate in routing. To set a service connection to be used as a dedicated service connection, select Dedicated for Traffic Steering Only.Dedicated service connections change their zones.
- Deselect Dedicated for Traffic Steering Only if you will send both normal service connection-related and traffic steering traffic through the service connection; with this choice, the zone for the service connection remains as Trust.
Choose whether to enable or disable source NAT.To disable source NAT for Dedicated service connections, select Disable Source NAT for Dedicated SC. Source NAT is enabled by default (the check box is deselected).If you disable source NAT, Prisma Access uses your organization’s source IP addresses for the dedicated service connection. If you enable source NAT, Prisma Access uses the EBGP Router address of the service connection (PanoramaCloud ServicesStatusNetwork DetailsService ConnectionEBGP Router) as the source IP address, even after the traffic egresses from the dedicated service connection.![]() Create rules for the target you created and apply them to the target.
Create rules for the target you created and apply them to the target.- In the Traffic Steering Rules area, Add a traffic steering rule.in the General tab, Name the traffic steering rule.In the Source tab, specify rules for source traffic.
- In the Source Address field, specify one or more of the following objects, or select Any to have traffic from any source go to this target:
- An IP address
- An address object that you created in Panorama (ObjectsAddresses)
- An External Dynamic List (EDL) using IP addresses or URLs
- In the Source User field, specify rules for source user traffic. You can specify the following user information:
- UsersEnter users in either the domain/user or the user@domain format.
- User groupsUse full distinguished names (DNs) when entering user groups.
- Users configured on Panorama (DeviceLocal User DatabaseUsers)
- User groups configured on Panorama (DeviceLocal User DatabaseUser Groups)
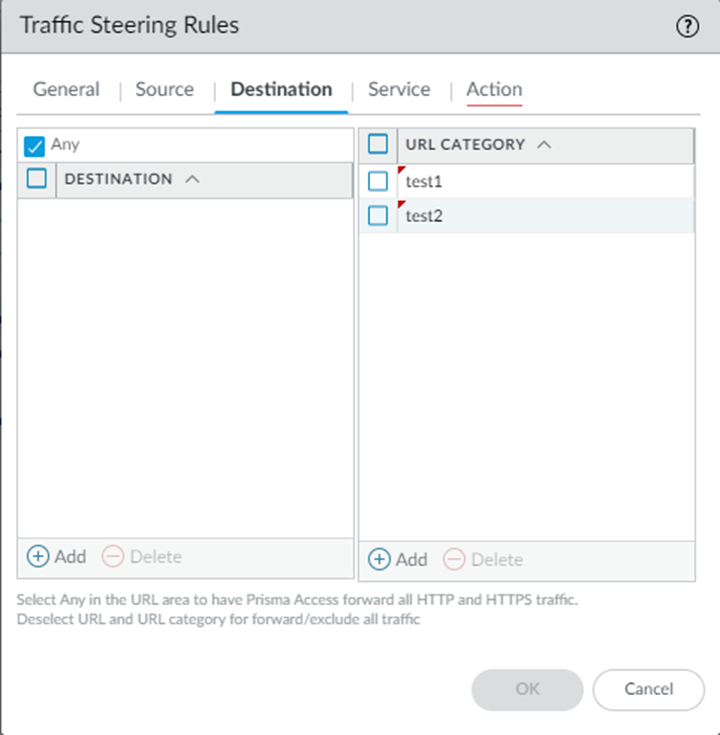
If you use address objects, DAGs, EDLs, users, or user groups, specify them as Shared to share them with all device groups in Prisma Access. In addition, do not enter 0.0.0.0/0 in address objects, DAGs, or EDLs; instead, enter 0.0.0.0/0 directly in the rule.Prisma Access automatically populates users from the mobile users device group only.In the Destination tab, specify the following values:- In the Destination area, specify one of the following criteria, or select Any to have traffic processed by the rules in the URL Category field:
- An IP address or prefix
- An address object that you created in Panorama (ObjectsAddresses)
- An IP address-based External Dynamic List (EDL)
Do not enter 0.0.0.0/0 in address objects, DAGs, or EDLs; instead, enter 0.0.0.0/0 directly in the rule.Leave Any selected to pass all traffic to be processed by the rules in the URL Category area. If you specify rules in the Destination, and URL Category areas, Prisma Access processes the rules in the Destination category first. - In the URL Category field, enter a custom URL category (ObjectsCustom ObjectsURL Category) When you create a custom URL category, enter URLs in all lower case. Traffic steering supports custom URL and predefined URL categories.You can use wildcards with the URLs in URL categories. The following wildcard formats are supported:
- *.example.com
- *.fqdn.example.com
The following formats are not supported:- *
- *.*
- *example.com
- example.com/ (trailing slashes in URLs are not supported in URL categories that are used with Traffic Steering)
- example.com/path (only domain names are supported)
- *fqdn.example.com
- fqdn.example.*
URLs in custom URL categories use the same URL pattern matching as that used by next-generation firewalls.
Use the following guidelines when configuring destination options:- If you specify a URL category, Prisma Access only matches HTTP and HTTPS traffic, even when service is set to Any.
- Do not create a custom URL category with a type of Category Match.
- Do not create a custom URL category with the name Custom_URL_Category_TFR because, for deployments that are migrated from Prisma Access 1.7 to 2.0, URLs entered in the URL area from 1.7 are moved to a custom URL category named Custom_URL_Category_TFRnumber, where number is a number appended to the custom URL category.
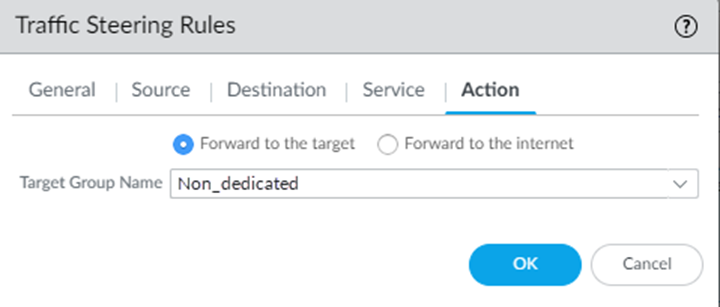
![]() In the Service tab, specify a service type.Specify service-http to forward HTTP traffic and specify service-https to specify HTTPS traffic. Select Any to forward traffic of any service type.In the Action tab, select the Target Group Name that you want to apply to the traffic steering rule.Forward traffic to the specified service connection target, or send the traffic directly to the internet without going through the service connection.
In the Service tab, specify a service type.Specify service-http to forward HTTP traffic and specify service-https to specify HTTPS traffic. Select Any to forward traffic of any service type.In the Action tab, select the Target Group Name that you want to apply to the traffic steering rule.Forward traffic to the specified service connection target, or send the traffic directly to the internet without going through the service connection.- To have Prisma Access forward traffic to a service connection target, select Forward to the target; then select the Target Group Name.
- To have Prisma Access forward traffic directly to the internet without first sending it to a service connection, select Forward to the internet.
![]() Click OK to save your changes.Optional Specify additional traffic steering rules.Prisma Access processes multiple rules in the order that you create them (from top to bottom).Commit and push your changes to make them active in Prisma Access.
Click OK to save your changes.Optional Specify additional traffic steering rules.Prisma Access processes multiple rules in the order that you create them (from top to bottom).Commit and push your changes to make them active in Prisma Access.- Select CommitCommit and Push and Edit Selections in the Push Scope.Select Prisma Access, then select Service Setup, Remote Networks, and Mobile Users.
![]() Click OK to save your changes to the Push Scope.Commit and Push your changes.
Click OK to save your changes to the Push Scope.Commit and Push your changes.