Prisma Access
Remote Networks—High Performance
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma Access Docs
-
- 6.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 6.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 4.2 Preferred
- 4.1 Preferred
- 4.0 Preferred
- 3.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 2.2 Preferred
-
-
- 4.0 & Later
- Prisma Access China
-
-
Remote Networks—High Performance
Deploy branch sites to set up Remote Networks—High Performance in Prisma Access.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
As your business scales and your office locations become geographically distributed, Prisma Access remote networks allow you to quickly onboard your branch sites and
deliver best-in-class security for your users. To onboard a branch site with a high
bandwidth, Prisma Access provides you with a Remote Network—High Performance.
To onboard a Remote Network—High Performance, you specify the branch site's location, and
Prisma Access selects the location that’s closest to the site. You can
optionally set up a secondary (backup) location to the site for redundancy and
resiliency. The high-performance remote network uses a single service IP address for
every 3 Gbps of bandwidth, removing the complexity in configuring and managing multiple
IPSec devices at every remote location.
For new deployments that use site-based licensing, use the onboarding workflow for site-based remote
networks instead of this procedure.
After you have planned for your Remote Network—High
Performance, you can begin the configuration process, which includes
onboarding the high-performance remote network to Prisma Access and enabling QoS and
routing.
Remote Networks—High Performance Capabilities and Guidelines
A high-performance remote network provides you with the following core
capabilities:
- Up to 3 Gbps aggregate bandwidth per node in a compute region
- Up to 2 Gbps bandwidth per remote network tunnel from a remote site
- Up to 120 remote branches per service IP address with Prisma SD-WAN and extended (third-party) CPE deployments
- Connectivity between Prisma SD-WAN and Prisma Access (SASE) supports line conditioning features, including FEC and Packet Duplication, for enhanced reliability.
When configuring a high-performance remote network for a branch site, be aware of the
following guidelines and differences between sites and remote networks:
- Prisma Access Locations—Remote Networks—High Performance support a subset of Prisma Access locations.
- Quality of Service (QoS)—For branch sites, Prisma Access supports QoS at a per-site level, and the QoS Profile you select applies to the entire site.
- Committed Information Rate (CIR)—To secure and commit the amount of bandwidth used per site, specify a CIR. If there are multiple remote networks that share bandwidth in a compute location, the Remote Network—High Performance receives at least the bandwidth specified in the CIR when there is contention with other sites in that compute location.
- IPSec Termination Nodes No Longer Needed—Unlike traditional remote networks, you don't need to select an IPSec termination node during onboarding for Prisma Access (Managed by Strata Cloud Manager) deployments. Prisma Access automatically load-balances the remote network connections to maximize the bandwidth allocation to the sites.
- Service Endpoint Address Allocation Based on Deployment Type—The number
of Service Endpoint addresses that you receive depends on
if you have set up your site-based remote networks in a single location or if
you have set them up using two different locations in a primary and secondary
deployment. You use the Service Endpoint address as the peer IP or FQDN address on your CPE to terminate the IPSec tunnel.As a best practice, specify the FQDN instead of the IP address.
- If you have set up your site-based remote network in a single location with no secondary location, Prisma Access provides you with a single Service Endpoint address.
- If you set up compute location redundancy in a primary and secondary configuration, Prisma Access provides you with two Service Endpoint addresses (one each for the primary and secondary location).
If you set up IPSec tunnels in an Active/Passive configuration, Prisma Access provides you with a single Service Endpoint address for both tunnels (the same as a standard Prisma Access remote network configuration).Remote networks use one Service Endpoint address for every 3 Gbps of bandwidth, removing the complexity in configuring and managing multiple IPSec devices at every remote location. - Service IP Address Allocation Based on Bandwidth—Prisma Access provides you with a single IP address or FQDN for every 3 Gbps of bandwidth in a compute location.
- Bandwidth Per Compute Location—You allocate bandwidth per compute location the same as allocating bandwidth for a standard remote network. You can plan and allocate the bandwidth before you begin configuration or during high-performance remote network creation.
- User-ID Redistribution and SSL Decryption—If you configure an SSL decryption profile on your tenant, User-ID redistribution from the Remote Networks—High Performance node to service connections is not supported.
- Unsupported Configurations— The following features and configurations are not supported:
- Tunnel Modes and Circuit Settings—A site-based remote network lets you
configure both location and IPSec redundancy.
- Location redundancy (specifying a Primary
location in one compute location and
specifying a Secondary location in a separate
compute location). Configuring a secondary location is optional.
- IPSec tunnel redundancy (specifying tunnels as Active/Active or Active/Passive).
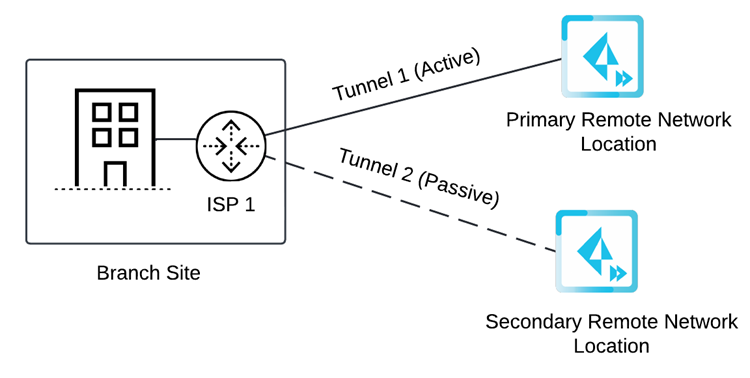
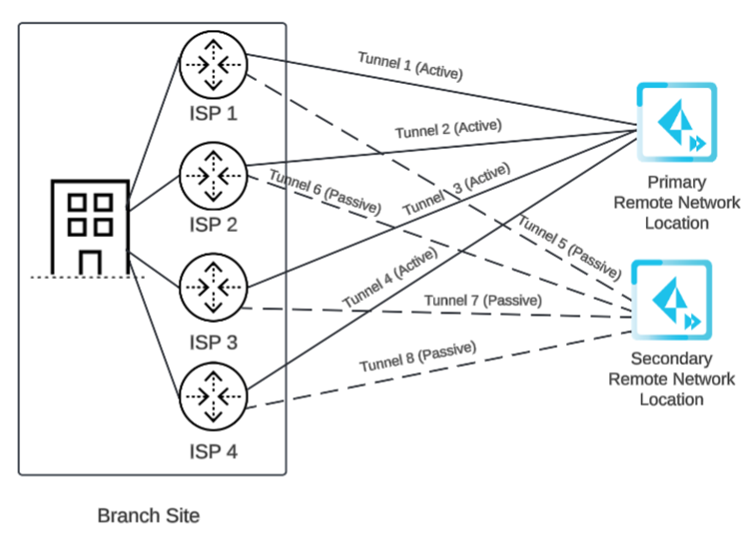
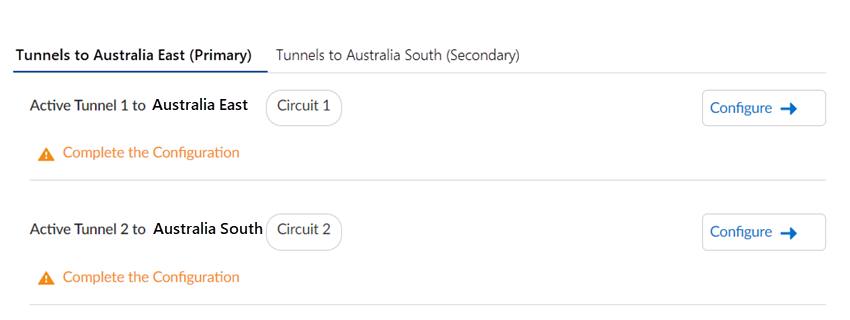
Before you begin setup, it's important to understand how you specify circuits and tunnels. Set up circuits and tunnels in the following configurations:- Active/Passive—Set up either one circuit (the
default) or two circuits. If you specify one circuit (ISP in the diagram), configure two tunnels (one for the primary remote network location and one for the secondary remote network location). Prisma Access uses this circuit for the tunnels for both the primary and secondary locations. If the primary location is unreachable (for example, if the tunnels experienced an ISP failure or CPE failure, or if the tunnels couldn't be established for any other reason), Prisma Access fails over from Tunnel 1 to Tunnel 2 and switches from the primary to the secondary remote network location.
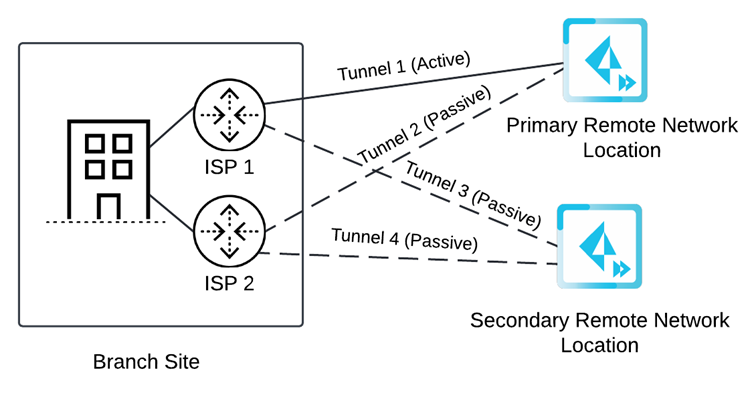
![]() If you specify two circuits, configure four tunnels (two for the primary remote network location and two for the secondary remote network location).If the primary location is unreachable by Tunnel 1, then Tunnel 2 becomes active. If both Tunnel 1 and Tunnel 2 primary tunnels go down, Prisma Access switches from the primary to the secondary location and Tunnel 3 becomes active. If Tunnel 3 to the secondary location goes down, then Tunnel 4 becomes active.
If you specify two circuits, configure four tunnels (two for the primary remote network location and two for the secondary remote network location).If the primary location is unreachable by Tunnel 1, then Tunnel 2 becomes active. If both Tunnel 1 and Tunnel 2 primary tunnels go down, Prisma Access switches from the primary to the secondary location and Tunnel 3 becomes active. If Tunnel 3 to the secondary location goes down, then Tunnel 4 becomes active.![]()
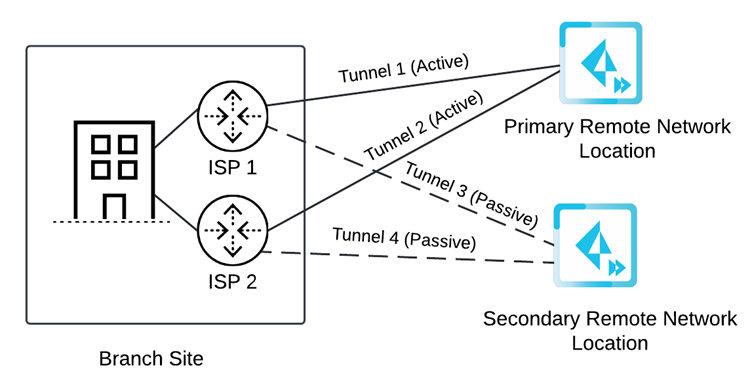
- Active/Active—Set up either two circuits (the
default), three circuits or four circuits. If you specify two circuits, configure four tunnels. If Tunnel 1 and Tunnel 2 to the primary remote network location go down, Tunnels 3 and 4 to the secondary remote network location become active. All active tunnels to the primary location must go down before Prisma Access fails over to the secondary location.
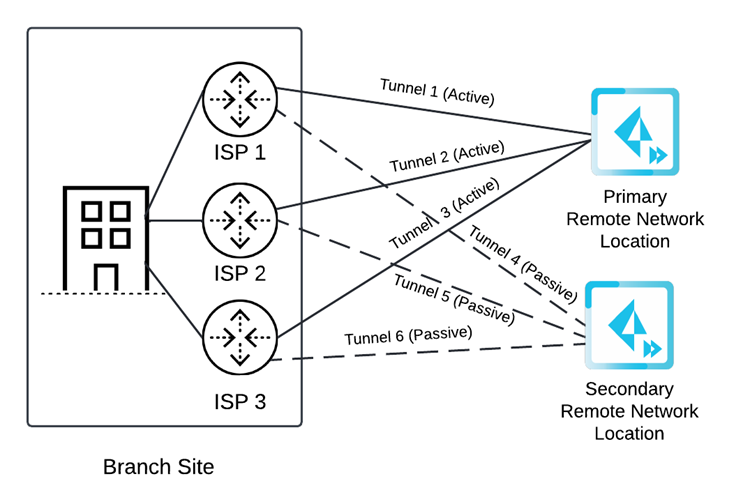
![]() If you specify three circuits, configure six tunnels. Each ISP has one active tunnel to the primary location and one passive tunnel to the secondary location. If all active tunnels to the primary location go down, the standby tunnels to the secondary location become active.
If you specify three circuits, configure six tunnels. Each ISP has one active tunnel to the primary location and one passive tunnel to the secondary location. If all active tunnels to the primary location go down, the standby tunnels to the secondary location become active.![]() If you specify four circuits, configure eight tunnels. Each ISP has one active tunnel to the primary location and one passive tunnel to the secondary location. If all active tunnels to the primary location go down, the standby tunnels to the secondary location become active.
If you specify four circuits, configure eight tunnels. Each ISP has one active tunnel to the primary location and one passive tunnel to the secondary location. If all active tunnels to the primary location go down, the standby tunnels to the secondary location become active.![]()
- Location redundancy (specifying a Primary
location in one compute location and
specifying a Secondary location in a separate
compute location).
Use one of the following procedures to onboard your remote networks depending on your
bandwidth allocation type:
Strata Cloud Manager
Add a add a Remote Network—High Performance using Strata Cloud Manager.
Here’s how to add a Remote Network—High Performance using Strata Cloud Manager.
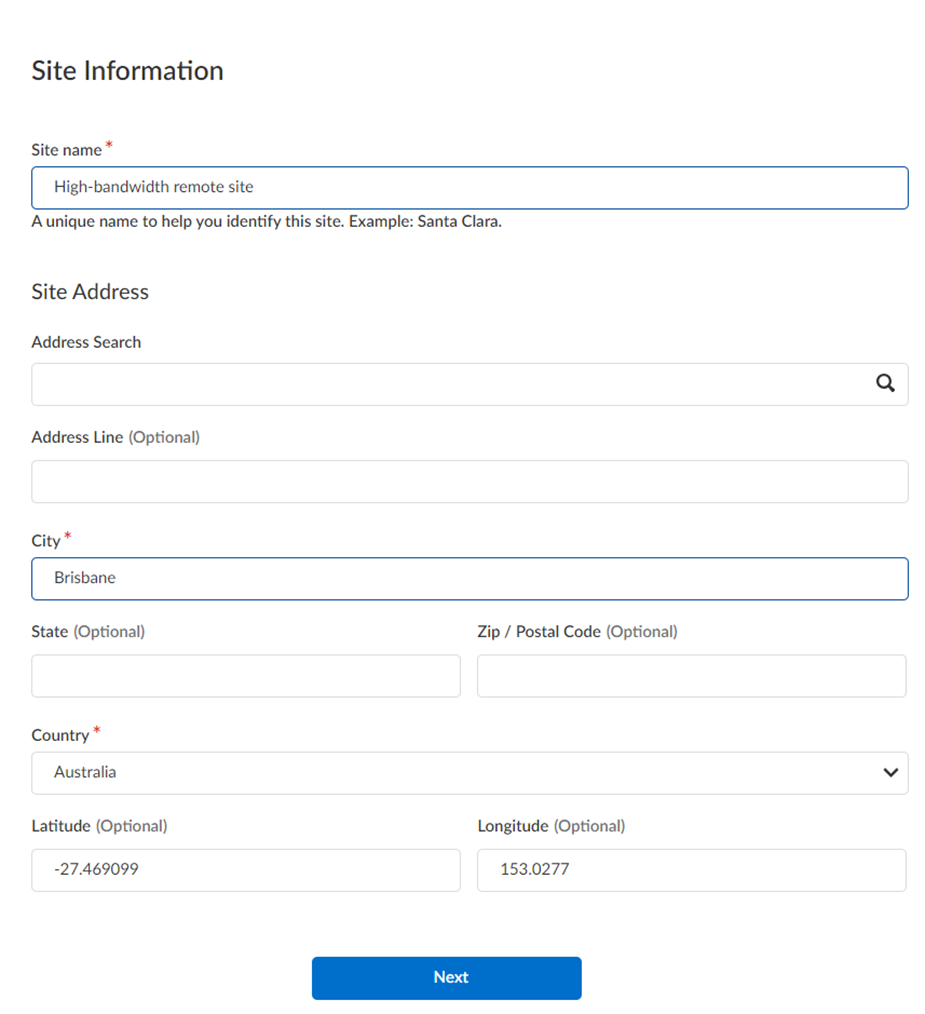
- From Strata Cloud Manager, go to InsightsBranch Sites.This choice indicates that the tunnel you create for the branch sites is terminated by your CPE (a Palo Alto Networks Next-Generation Firewall or third-party CPE).Add Site and give the remote network a descriptive Site Name.Select the City and Country of the site.For more precise searches, add an address.
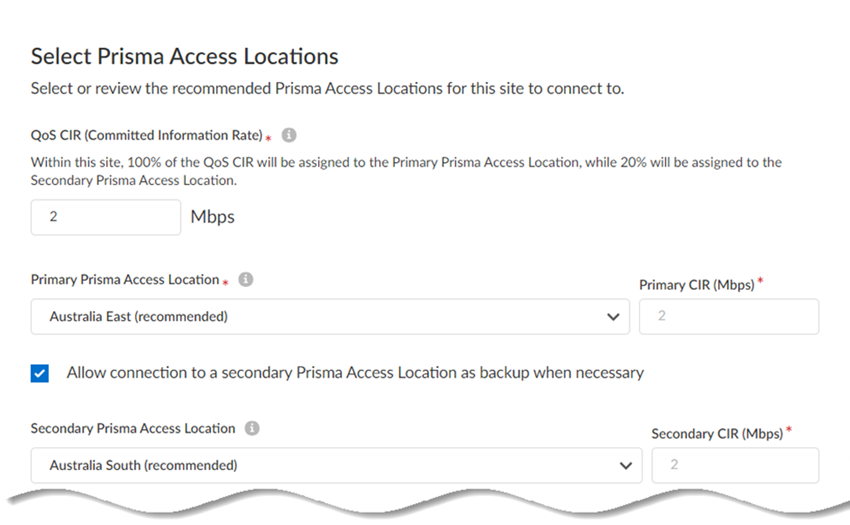
![]() Click Next.Enter the QoS CIR (Committed Information Rate) in Mbps.If you have multiple remote networks that share bandwidth in a compute location, and if there is bandwidth contention with other sites in that compute location, the Remote Network—High Performance receives at least the bandwidth specified in the CIR.If you configure primary and secondary sites, you specify different compute regions and the secondary region gets 20% of the CIR. For example, if you configure a CIR of 100 Mbps to a site, Prisma Access provides the primary site with 100 Mbps CIR and the secondary site with 20 Mbps CIR.If the CIR is 500 Mbps and if all remaining bandwidth in the compute location is used by other sites, Prisma Access drops any bandwidth in excess of 500 Mbps. However, if other sites are not using bandwidth, the bandwidth for the high-performance remote network can go above 500 Mbps up to the allocated bandwidth in the compute location.Enter a minimum CIR of 1 Mbps and a maximum of 2000 Mbps. Don't exceed the bandwidth you specify for the compute region.Select a Primary Prisma Access Location.If multiple locations are Recommended in the list; select the location that works best for your deployment.(Optional) To create a secondary (backup) site, select Allow connection to a secondary Prisma Access Location as backup when necessary and then select a Secondary Prisma Access Location.If you select this choice, Prisma Access prepopulates the best secondary location or locations that are in a different compute location than the primary location. If multiple locations are Recommended; select the location that works best for your deployment.
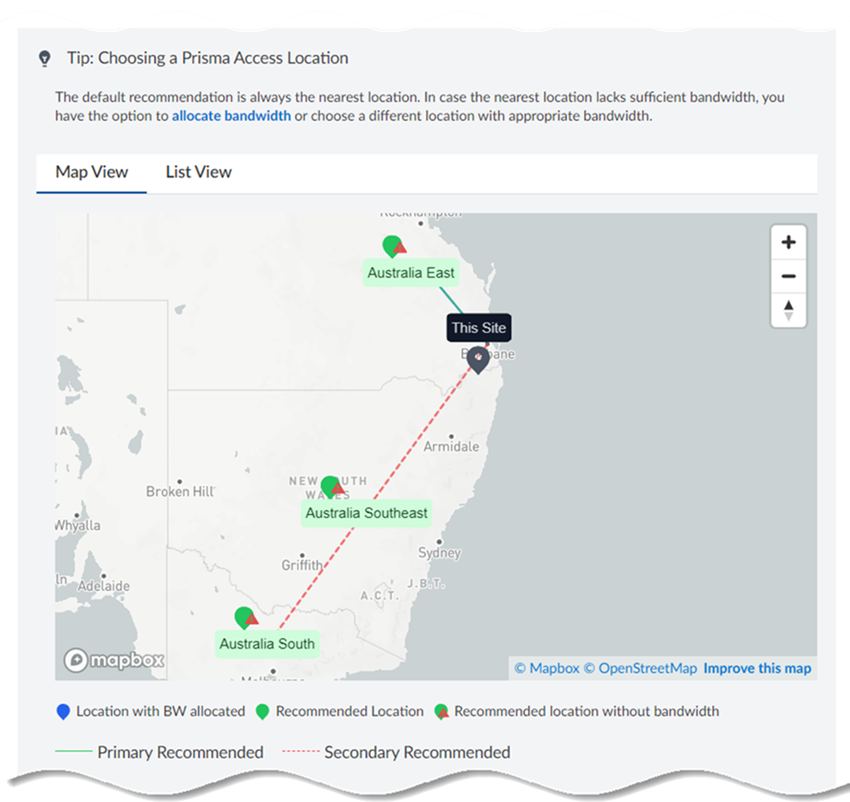
Click Next.Enter the QoS CIR (Committed Information Rate) in Mbps.If you have multiple remote networks that share bandwidth in a compute location, and if there is bandwidth contention with other sites in that compute location, the Remote Network—High Performance receives at least the bandwidth specified in the CIR.If you configure primary and secondary sites, you specify different compute regions and the secondary region gets 20% of the CIR. For example, if you configure a CIR of 100 Mbps to a site, Prisma Access provides the primary site with 100 Mbps CIR and the secondary site with 20 Mbps CIR.If the CIR is 500 Mbps and if all remaining bandwidth in the compute location is used by other sites, Prisma Access drops any bandwidth in excess of 500 Mbps. However, if other sites are not using bandwidth, the bandwidth for the high-performance remote network can go above 500 Mbps up to the allocated bandwidth in the compute location.Enter a minimum CIR of 1 Mbps and a maximum of 2000 Mbps. Don't exceed the bandwidth you specify for the compute region.Select a Primary Prisma Access Location.If multiple locations are Recommended in the list; select the location that works best for your deployment.(Optional) To create a secondary (backup) site, select Allow connection to a secondary Prisma Access Location as backup when necessary and then select a Secondary Prisma Access Location.If you select this choice, Prisma Access prepopulates the best secondary location or locations that are in a different compute location than the primary location. If multiple locations are Recommended; select the location that works best for your deployment.![]() Prisma Access provides you with a map with suggested locations to assist you with choosing one.
Prisma Access provides you with a map with suggested locations to assist you with choosing one.![]() Select a QoS Profile to use for this site.Remote Networks—High Performance use a single QoS Profile.
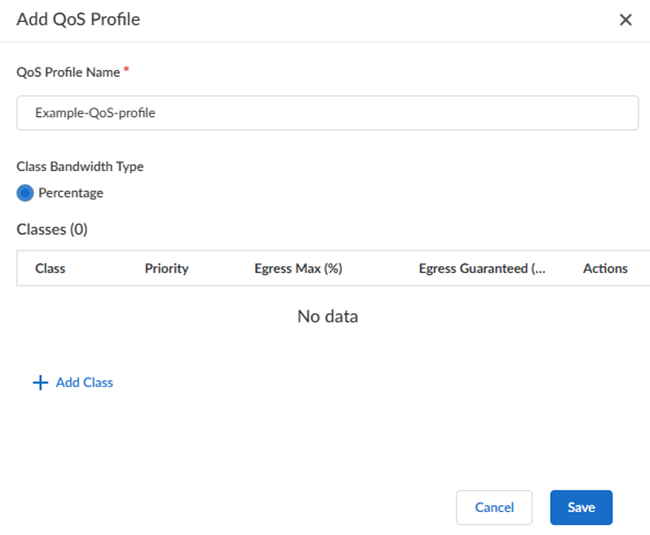
Select a QoS Profile to use for this site.Remote Networks—High Performance use a single QoS Profile.![]() If you have not yet created a QoS Profile, Add a QoS Profile, specifying the following values:
If you have not yet created a QoS Profile, Add a QoS Profile, specifying the following values:- Enter a unique QoS Profile Name.
- (Optional) Enter an Egress Max (Mbps) that represents the maximum throughput in Mbps for traffic leaving the service connection or remote network connection.
- (Optional) Enter an Egress Guaranteed (Mbps) value that represents the guaranteed bandwidth for this profile in Mbps.
- Enter a Class Bandwidth Type of either
Percentage or Mbps.
QoS for Remote Networks—High Performance does not use a guaranteed bandwidth ratio.
![]()
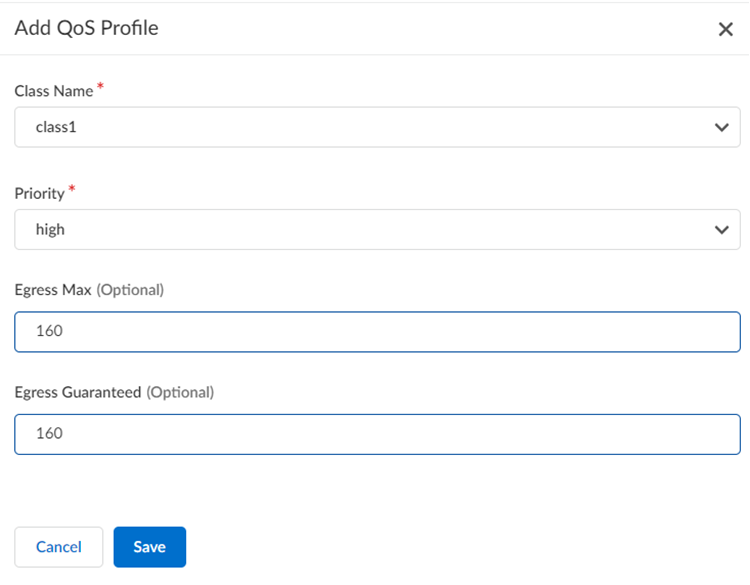
- In the Classes section, Add Class and specify how
to mark up to eight individual QoS classes.
- Enter a Class Name.
- Select the Priority for the class (either real-time, high, medium, or low).
- Enter an Egress Max that represents the maximum throughput (in Mbps) for traffic leaving the service connection or remote network connection.
- Enter an Egress Guaranteed value that represents the guaranteed bandwidth for this profile (in Mbps).
- Save your changes.
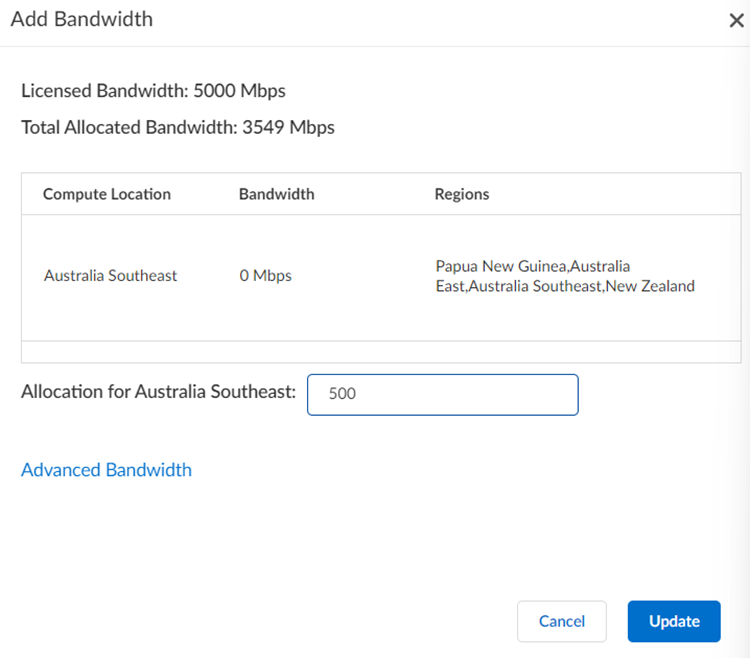
![]() If you have not yet allocated bandwidth, Prisma Access prompts you to allocate bandwidth for the compute location that's associated with the location you selected. Specify a minimum bandwidth of 50 Mbps per compute location.
If you have not yet allocated bandwidth, Prisma Access prompts you to allocate bandwidth for the compute location that's associated with the location you selected. Specify a minimum bandwidth of 50 Mbps per compute location.![]() Allocate bandwidth for the locations you selected if you have not already; then, Update your changes.
Allocate bandwidth for the locations you selected if you have not already; then, Update your changes.![]() Click Next.Define Tunnel & Circuit Settings.
Click Next.Define Tunnel & Circuit Settings.- Select a Tunnel Mode: either Active/Active or Active/Passive.The tunnel mode specifies how many of your ISP circuits you want to utilize for the remote network. Specify a minimum of one circuit and a maximum of four circuits.
- If you select Active/Passive (the default setting), Prisma Access utilizes either one or two ISP circuits to create two active tunnels. If the active tunnel goes down, the passive tunnel becomes active.
- If you select Active/Active, Prisma Access Prisma Access utilizes either two or four ISP circuits to create either two or four active tunnels, respectively.
Select the Number of circuits to use.Prisma Access assigns tunnels based on the number of circuits you specify here, and whether your deployment is Active/Active or Active/Passive, as shown in the following table.(Optional) Configure your IPSec tunnel settings.Prisma Access provides you with default IPSec tunnel settings. These settings determine the IPSec and IKE crypto settings for the remote network tunnel. If you want to change them, select the Primary Tunnel and Edit your settings.If you specify a secondary location, Prisma Access autopopulates the values from the primary tunnel to the secondary tunnel; to edit the secondary tunnel, select that tunnel and Edit the settings.![]() Make a note of these settings; you must match the settings on the CPE that terminates the IPSec tunnel at your site.
Make a note of these settings; you must match the settings on the CPE that terminates the IPSec tunnel at your site.- Give the Active tunnel a unique Tunnel Name.
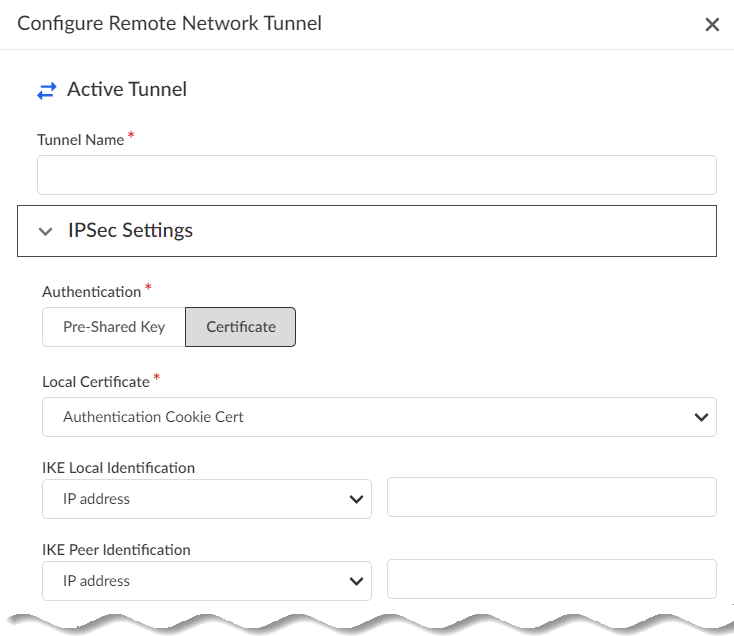
- Specify IPSec Settings.
- Specify an Authentication type
(either Pre-Shared Key or
Certificate).If you specify Pre-Shared Key, enter and confirm the Pre-Shared Key.If you specify a Certificate, enter the Local Certificate to use. This certificate must already exist in Strata Cloud Manager.
- Specify the IKE Local Identification (either IP Address, Distinguished Name (Subject), User FQDN (email address), or FQDN (hostname) .
- Specify the IKE Peer Identification (either IP Address, Distinguished Name (Subject), User FQDN (email address), or FQDN (hostname).
- Specify an Authentication type
(either Pre-Shared Key or
Certificate).
![]()
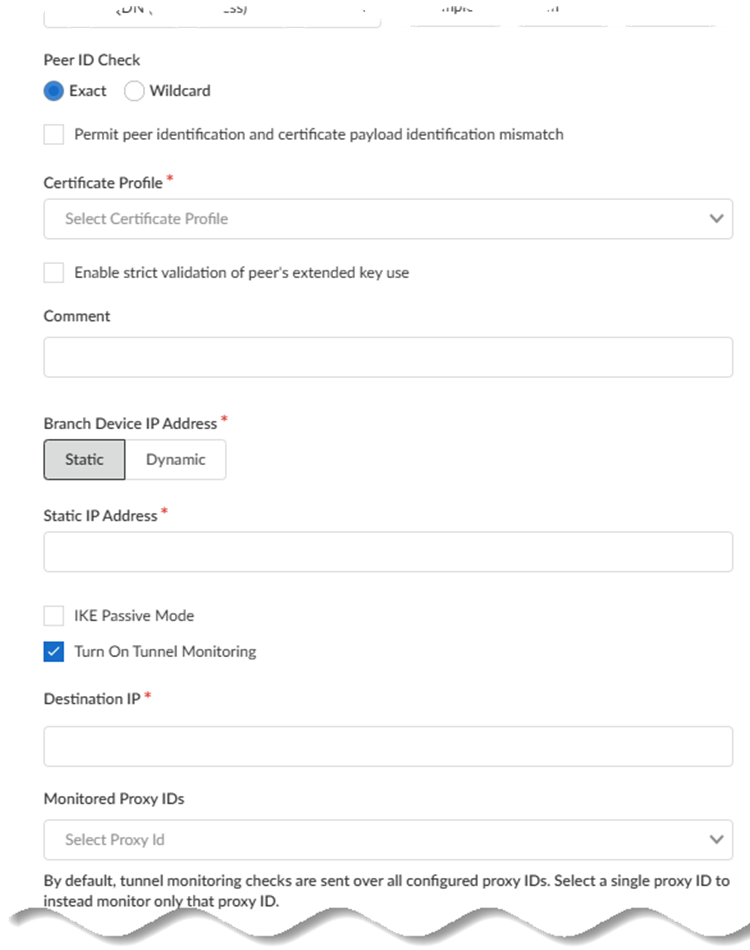
- Specify the type of Peer ID Check:
- Exact—Ensures that the local setting and peer IKE ID payload match exactly.
- Wildcard—Allows the peer identification to match as long as every character before the wildcard (*) matches. The characters after the wildcard don't need to match.
- (Optional) Permit peer identification and certificate payload identification mismatch to allow a successful IKE security association (SA) even when the peer identification does not match the peer identification in the certificate.
- Choose a Certificate Profile. A certificate profile contains information about how to authenticate the peer gateway.
- (Optional) Enable strict validation of peer’s extended key use to control strictly how the key can be used.
- Choose the Branch Device IP Address
(Static or
Dynamic).
- If you select Static, enter the Static IP Address to use for the IPSec tunnel.
- Specify Dynamic to obtain the IP address automatically.
- (Optional, Recommended) Enable IKE Passive
Mode to have Prisma Access respond to IKE
connections but not initiate them. While not required, IKE Passive Mode is the recommended setting.
- (Optional) Turn on Tunnel
Monitoring. Enter a Tunnel Monitoring Destination IP address on the remote network for Prisma Access to determine whether the tunnel is up and, if your branch IPSec device uses a policy-based VPN, enter the associated Proxy ID as the Monitored Proxy ID.
![]()
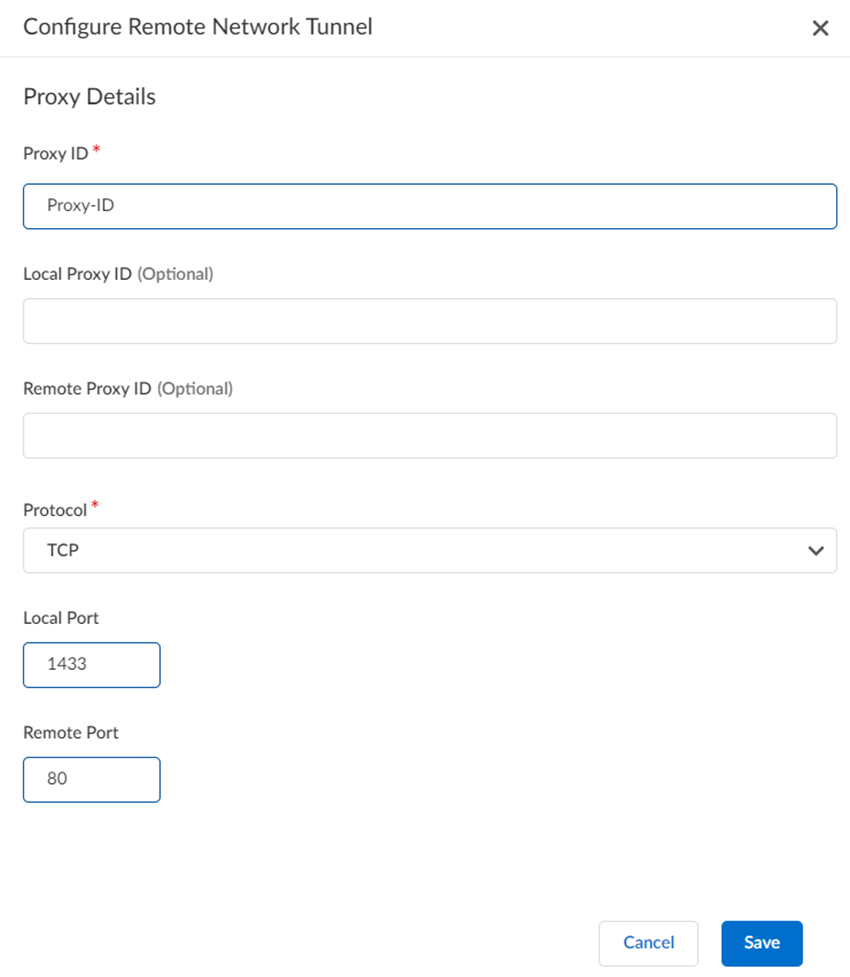
- (Optional) If you need a proxy ID:
- Add Proxy ID and enter the Proxy ID.
- Optionally, enter the Local Proxy ID and Remote Proxy ID.
- Enter the Protocol to use for the proxy ID. Enter a Number, TCP, or UDP.
- Specify a Local Port and Remote Port for TCP or UDP.
- Save your changes.
![]()
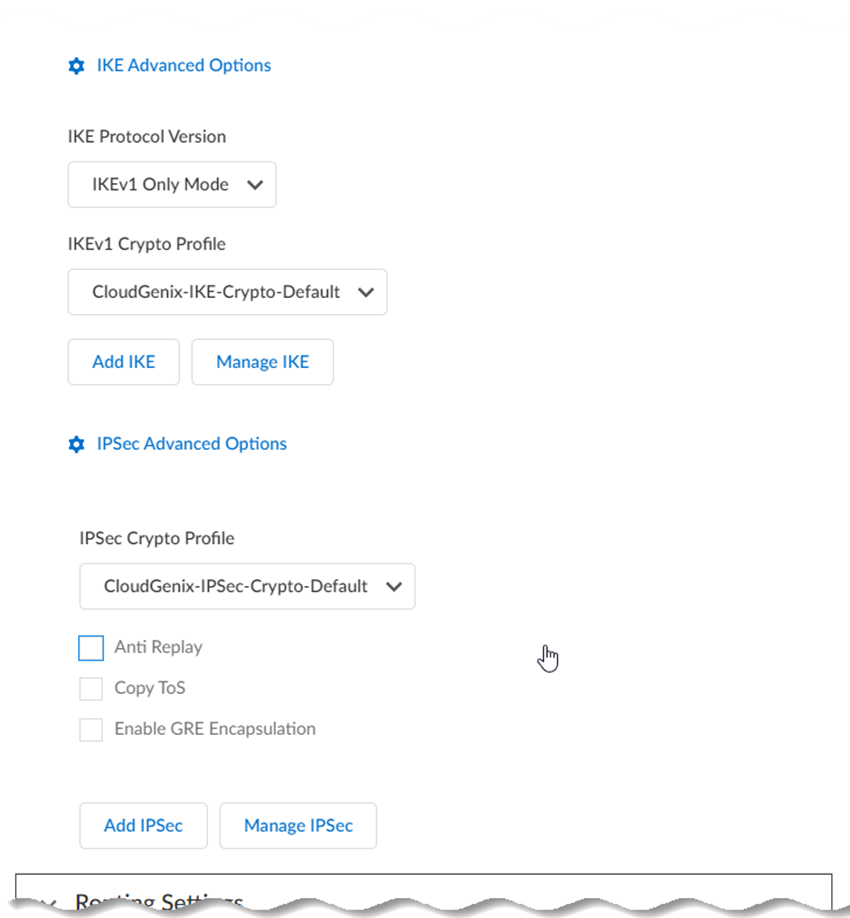
- (Optional) Specify IKE Advanced
Options.
- Select an IKE Protocol Version.
- Select an IKEv1 Crypto
Profile.To add a crypto profile, Add IKE. To manage an existing IKE profile, Manage IKE and select the profile to edit.
- Select an IKEv2 Crypto
Profile.To add a crypto profile, Add IKE. To manage an existing IKE profile, Manage IKE and select the profile to edit.
- (Optional) Specify IPSec Advanced
Options.
- Select an IPSec Crypto
Profile.To add a crypto profile, Add IPSec. To manage an existing IPSec profile, Manage IPSec and select the profile to edit.
![]()
- Select an IPSec Crypto
Profile.
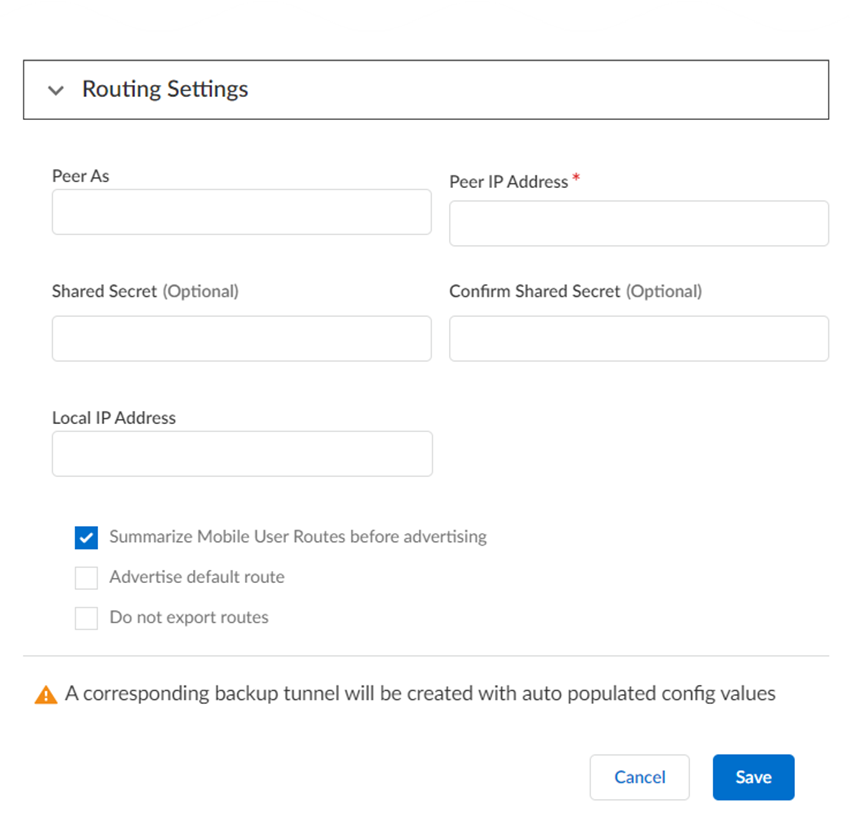
- Choose your Routing Settings.
- Select the Routing Type (either
Static or
Dynamic).If you select Static, Add the IP subnets or IP addresses that you want to secure at the site.If you select Dynamic:
- Enter the Peer As (the
autonomous system (AS) for your network). Use an RFC 6996-compliant BGP Private AS number.
- Enter the Peer IP Address assigned as the Router ID of the eBGP router on the HQ or data center network.
- (Optional) Enter a Shared Secret password to authenticate BGP peer communications.
- Enter the Local IP Address that Prisma Access uses as its Local IP address for BGP.
- (Optional) Select Summarize Mobile User Routes before advertising to reduce the number of mobile user IP subnet advertisements over BGP to your customer premises equipment (CPE) by having Prisma Access summarize the subnets before it advertises them.
- (Optional) Select Advertise Default Route to have Prisma Access originate a default route advertisement for the remote network using eBGP. Be sure that your network does not have another default route advertised by BGP, or you could introduce routing issues in your network.
- (Optional) Select Don't Export Routes to prevent Prisma Access from forwarding routes into the HQ or data center.
- Enter the Peer As (the
autonomous system (AS) for your network).
- Select the Routing Type (either
Static or
Dynamic).
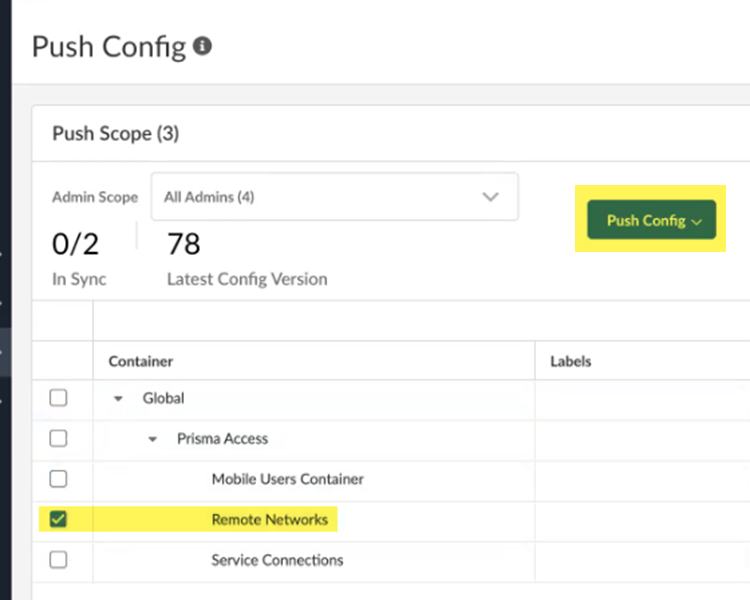
Save your IPSec tunnel changes.![]() Save & Exit.Push Configuration to save your configuration changes, making sure to select Remote Networks in the Push Scope.
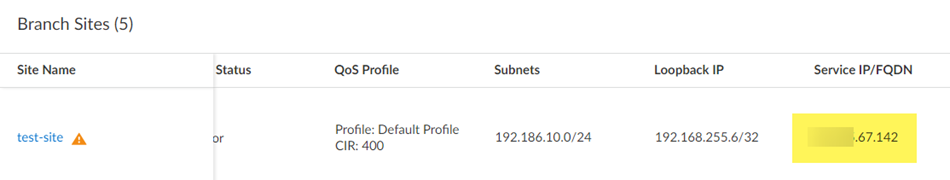
Save & Exit.Push Configuration to save your configuration changes, making sure to select Remote Networks in the Push Scope.![]() Find the Service IP address that you specify on your CPE.When you set up the remote network, use the service IP address as the peer IP address on your CPE to terminate the IPSec tunnel.
Find the Service IP address that you specify on your CPE.When you set up the remote network, use the service IP address as the peer IP address on your CPE to terminate the IPSec tunnel.- Go to InsightsBranch Sites.Find the Service IP/FQDN address.
![]()
Panorama
Configure a Prisma Access remote network deployment that allocates bandwidth by compute location.Steps to configure a Remote Network—High Performance are the same as onboarding a standard Remote Network in Prisma Access (Managed by Panorama), including choosing an IPSec Termination Node during onboarding.