Prisma Access
ZTNA Connector Requirements and Guidelines
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma Access Docs
-
- 6.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 6.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 4.2 Preferred
- 4.1 Preferred
- 4.0 Preferred
- 3.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 2.2 Preferred
-
-
- 4.0 & Later
- Prisma Access China
-
-
ZTNA Connector Requirements and Guidelines
Learn about the requirements and guidelines for using ZTNA Connector.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
Before you configure ZTNA Connector, be sure that you understand the Connector
requirements and limits, as well as the guidelines you should follow when deploying
it.
Supported Prisma Access Versions and Requirements
- Upgrade any Prisma Access release earlier than 5.0, including any Innovation releases, to a minimum version of 5.0.
- For Prisma Access (Managed by Panorama), upgrade the Cloud Services plugin version to a minimum version of 4.0. Upgrade to the latest Cloud Services plugin to unlock the latest features.
Scale and Throughput Considerations
| Connector and Application Metrics | Maximum Value |
|---|---|
| Applications per tenant across all Connector Groups |
20,000
|
| Applications per Connector Group | 1000 |
| Connectors per tenant | 200 |
| Bandwidth per Connector | 2 Gbps* |
| Bandwidth per Connector Group (with 4 Connectors) | 6 Gbps* |
| Connector per Connector Group | 4 |
| Concurrent sessions per Connector | 100,000 Each Connector can support
100,000 concurrent connections. A Connector Group can have a
maximum of 4 connectors for up to 400,000 concurrent
connections per Connector Group. |
| Concurrent sessions per Connector Group | 400,000 |
| Maximum IP subnets per tenant | 1024 |
* Performance metrics are based on internal testing. The observed
performance might vary and is dependent on customer-specific equipment, ISP
performance, and environmental network factors that are external to the Prisma
Access service.
App Support
ZTNA Connector provides access to all of your private app traffic, with the
following exceptions:
- ZTNA Connector does not support the following:
- Traffic originating from the data center (such as SCCM or remote help desk traffic)
- Panorama managed multitenant
- Clientless VPN
- Resolving CNAME FQDNs
- Applications that perform port hopping (such as VoIP or Active Mode FTP)
- Application-level gateway (ALG) apps such as Active Mode FTP and SIP
- Dynamic address group with FQDN based addresses
- Windows-integrated authentication for applications (such as NTLM or Kerberos) is only supported if you onboard the data center domain controllers and resources as FQDN applications with Use DC IP Address enabled or as IP address subnets.
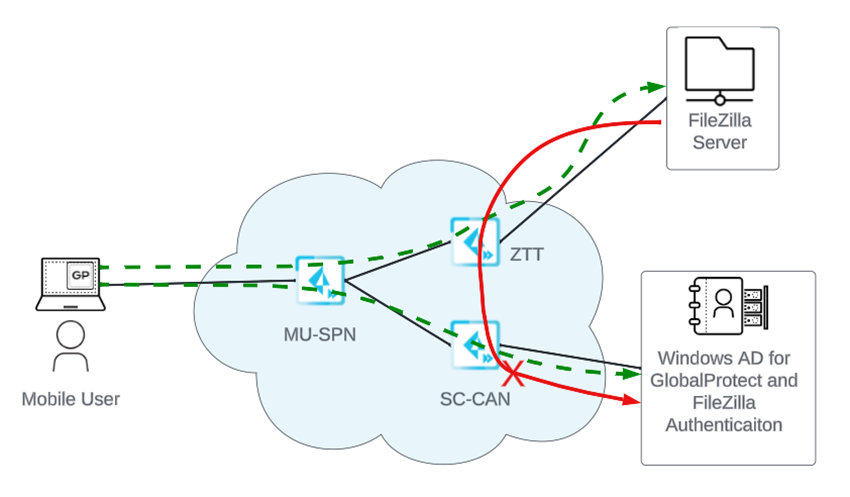
- Communication between apps behind a service connection and apps
behind a ZTNA Connector. For example, you host a Windows Active Directory (AD) server behind a service connection, and host an FTP (Filezilla) server behind a ZTNA Connector. If the FTP server requires authentication to the Windows AD server, authentication fails, because you can't use Prisma Access as a backbone between the Service Connection Corporate Access Node (SC-CAN) and the ZTNA Connector Tunnel Terminator (ZTT).
![]()
Feature and Functionality Restrictions
Keep in mind the following restrictions when setting up and configuring a ZTNA
Connector deployment:
- Don't use special characters, including < > ! @ # $ % ^ & and Chinese, Japanese, or Korean characters, in ZTNA object names.
- Interoperability with Service Connections—You can use service connections and ZTNA Connector in the same tenant; however, make sure that subnets advertised from the data center to the service connection do not overlap with any subnets used by ZTNA Connector for the same purpose. For example, make sure that subnets advertised from a data center to Prisma Access service connections using static routes or BGP do not overlap with subnets used in ZTNA Connector IP subnet-based application targets.
- The following functionalities are not supported with the default Prisma
Access deployment; reach out to your Palo Alto Networks team to activate
them:
- Using RFC 6598 Addresses for your with ZTNA Connector
- Connector Group Guidelines—When adding connector groups, use the
following recommendations:
- All apps in a single Connector Group should use the same DNS server for DNS resolution.
- If you're accessing apps from a data center or headquarters location, all apps in the Connector Group should be from the same data center or headquarters location.
- Don't add connectors in two or more regions in a single Connector Group . All connectors in a Connector Group should be in the same region.
- You can specify up to a four connector groups per FQDN target or
wildcard target. Be sure that, when you assign connector groups per
FQDN target or wildcard target, you don't assign the same app to
more than four connectors per region. For example, you have assigned the same app (either an FQDN target or a wildcard target) to four connector groups, each group has a single connector, and all connectors are in the same region. This configuration is acceptable because you're not assigning more than four connectors per app in a single region.However, if you assign the same app (either an FQDN target or a wildcard target) to three connector groups, each group has two connectors, and all connectors are in the same region, that is an invalid configuration, because you're assigning six connectors to the same app in a single region.
- Some ZTNA Connectors such as AWS-based connectors or Azure-based connectors support autoscaling, where AWS or Azure monitors network bandwidth utilization on the connectors and automatically adjusts capacity to maintain app performance. When network bandwidth utilization on connectors drops, AWS or Azure triggers auto scale-in. If scale-in occurs in a ZTNA Connector, existing long-lived sessions handled by the ZTNA Connector marked for scale-in terminate prematurely. This behavior does not impact new traffic sessions initiated after scale-in. For long-lived sessions, such as SSH or RDP, ZTNA Connector terminates the session during scale-in, and you must reconnect that session.
Supported Application Hosting Environments
You can deploy your ZTNA Connector VMs in the following data center environments
with the specified minimum requirements:
| Cloud Provider | Instance Size | CPU Size | Memory Size | Disk Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon AWS | m5.xlarge per region | 4 vCPUs | 16 GB | 40 GB |
| Google Cloud Platform (GCP) | n2-standard-4 per region | 4 vCPUs | 16 GB | 40 GB |
| Microsoft Azure | Standard_D4_v3 per region | 4 vCPUs | 16 GB | 40 GB |
| Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) | VM.Standard.E5.Flex | 2 OCPUs (4 vCPUs) | 16 GB | |
| KVM | Uses qcow image | 4 vCPUs | 16 GB | 40 GB |
| Hyper-V | Uses vhd image | 4 vCPUs | 8 GB memory per VM | 40 GB |
| VMware ESXi | Uses OVA image. Supported on vSphere and directly on ESXi Hosts | 4 vCPUs per VM | 8 GB memory per VM | 40 GB disk (Thick Provisioned) |
|
For VMware ESXi, vMotion, VM snapshots, or migrations are not
supported for Connector VMs.
For KVM, Live Migrations and snapshots are not supported on
Connector VMs.
| ||||
It's your responsibility to host the VMs and ensure that
they can connect to the internet.
AWS, GCP, and Azure have ZTNA Connectors you can acquire in their respective
Marketplaces. You can download the VMware ESXi Open Virtualization Application
(OVA) file and the KVM qcow file from the Palo Alto Customer Support Portal.
Network Requirements
The following networking requirements enable connectivity between ZTNA Connector
and Prisma Access:
- After you enable ZTNA Connector Prisma Access sets up a DNS proxy for DNS requests using the DNS rules set up for Remote Networks and Mobile Users—GlobalProtect.
- Allow outbound TCP port 443 from the WAN interface (port 1) IP address HTTPS connectivity to the ZTNA Connector Controllers.
- Allow outbound UDP port 123 to any destination address for NTP time synchronization.
- Allow outbound UDP port 500 and UDP 4500 from the WAN interface (port 1)
IP address for IPSec and IKE connectivity to the Prisma Access
Service IP address (es). Since a Connector Group might include multiple
Connectors, the data center security policy
allows the traffic from the WAN interface IP address of each Connector
in the group to all regional Prisma Access Service IP addresses. As
additional Connectors are added to a Connector Group, more PA Service
nodes will be deployed and these new Service IP addresses must be
whitelisted in the data center security policy. This configuration
ensures the required full mesh connectivity.
![]()
- If ZTNA Connector uses a public IP address for its internet interface, you must allow a IP/50 Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP).
- ZTNA Connector autoconfigures both the Prisma Access ZTT side of the IPSec tunnel and the ZTNA Connector side. The algorithms configured for DH Group/Encryption/Hash for both IKE and ESP are: ecp384/aes256/sha512.
- (Mobile Users—GlobalProtect deployments only) When you first onboard an application in ZTNA Connector, you must refresh the GlobalProtect app so mobile users receive the updated DNS server configuration. If you removed an application from ZTNA Connector, you must refresh the GlobalProtect app so mobile users can receive the updated DNS server configuration.
- If there is a firewall between the ZTNA Connector and the private app,
the firewall must allow access to the app from the ZTNA Connector (that
is, you must allow access to the app server's resolved IP addresses,
protocols, and ports for the private app). In addition, you need to allow the protocol (either TCP or ICMP) that you configured for the application target health probes to the app. The connector application probes the app server to determine if it can provide access to the app, and you can configure the Probing Type for the Application Target to be tcp ping, icmp ping, or none (no probing). If you specify tcp ping, the firewall must allow TCP access to the app; if you specify icmp ping, the firewall must allow ICMP echo request and reply for the app.
- Be sure that you allow ICMP in your data center before using the ping and traceroute diagnostic tools (ping uses
ICMP and traceroute uses UDP ports). Some cloud environments have ICMP
disallowed for security concerns; in this case, these tools don't
display any activity.The traceroute diagnostic tool also uses random UDP ports, so you must allow all UDP and ICMP error replies for the traceroute tool to function.
- Make sure you have configured DNS entries on the local interfaces to allow ZTNA Connector to resolve the app FQDNs, and that ZTNA Connector and access the DNS server at UDP port 53 (the port used for DNS resolution).
- (ZTNA Connector versions 5.0 and later) Make sure that you have configured security rules in your network to permit ZTNA Connectors to perform application probes into your data center. ZTNA Connectors use their data center interface IP address as the source IP address of the application probing to the application servers. If the application probing is successful, the Application Status is Up and user sessions to ZTNA Connector have the same data center interface IP address as the source IP address. If the application probing is unsuccessful, the Application Status is Down; in this case, you can use the ping and tcp ping diagnostic tools to test connections to the application.
- UDP payload size, including headers, should not exceed an MTU size of 1,300 bytes on the path to the ZTNA application server. Palo Alto Networks recommends keeping packets at or below this MTU size.
- If you use RFC 6598 shared addresses within your network, you must specify blocks of IP addresses that ZTNA Connector can use for routing between Prisma Access and your connectors and between Prisma Access and your private apps.
- If you need to restrict the list of IP addresses and FQDNs that you add
to your organization's allow lists, add the ones listed in IP Addresses and FQDNs to Allow for ZTNA Connector.For example, if you're setting up a ZTNA Connector in the United States, add the following URLs to your organization's allow lists:
- https://controller.cgnx.net
- https://locator.cgnx.net
- https://controller.hood.cgnx.net
- https://vmfg.hood.cgnx.net
- https://sdwan-stats-hood-us.cgnx.net
- time.nist.gov (for NTP)
- 0.cloudgenix.pool.ntp.org (for NTP)
- 1.cloudgenix.pool.ntp.org (for NTP)
- 2.cloudgenix.pool.ntp.org (for NTP)
- 3.cloudgenix.pool.ntp.org (for NTP)
Limit DNS resolution of the previous FQDNs to IPv4 resolution. ZTNA Connector does not support establishing connection to the controller FQDNs using IPv6. - Disable the SSL decryption for sessions to the Controllers.
- If you are setting up a ZTNA Connector in the mainland China, add the URLs to your organization's allow lists.
IP Addresses and FQDNs to Allow for ZTNA Connector
To ensure smooth functioning of ZTNA Connector, add the following URLs and IP
addresses to your allow lists.
| Service Name | Port | Direction | Source Interface Internet Protocol | Destination and IP Addresses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZTNA Connector access to Prisma Access | 443 | Outbound |
ZTNA Connector WAN port
| https://controller.cgnx.net Address:
52.8.93.87 Address:
52.8.25.40 https://locator.cgnx.net Address:
18.223.78.55 Address:
52.15.45.235 hood: 52.40.98.31 34.218.98.185 sugarloaf: 18.200.102.82 18.200.135.33 faber: 18.139.242.53 54.255.61.109 https://vmfg.cgnx.net Address:
52.53.122.104 Address:
52.53.102.7 https://controller.elcapitan.cgnx.net Address:
52.8.93.87 Address:
52.8.25.40 https://vmfg.elcapitan.cgnx.net Address:
52.53.122.104 Address:
52.53.102.7 https://controller.hood.cgnx.net Address:
52.32.167.5 Address:
54.70.168.33 https://vmfg.hood.cgnx.net Address:
50.112.136.184 Address:
34.210.34.87 https://controller.sugarloaf.cgnx.net Address:
108.128.176.192 Address:
18.200.144.58 https://vmfg.sugarloaf.cgnx.net Address:
99.81.179.99 Address:
99.80.52.255 https://sdwan-stats-hood-us.cgnx.net https://sdwan-stats-elcapitan-us.cgnx.net https://sdwan-stats-hood-jp.cgnx.net https://sdwan-stats-elcapitan-jp.cgnx.net https://sdwan-stats-hood-sg.cgnx.net https://sdwan-stats-elcapitan-sg.cgnx.net https://sdwan-stats-hood-au.cgnx.net https://sdwan-stats-elcapitan-au.cgnx.net https://sdwan-stats-hood-in.cgnx.net https://sdwan-stats-elcapitan-in.cgnx.net https://sdwan-stats-hood-ca.cgnx.net https://sdwan-stats-elcapitan-ca.cgnx.net https://sdwan-stats-sugarloaf-eu.cgnx.net https://sdwan-stats-sugarloaf-de.cgnx.net https://sdwan-stats-sugarloaf-uk.cgnx.net https://controller.bowfell.cgnx.net Address:
13.41.243.90 Address:
18.171.17.23 https://vmfg.bowfell.cgnx.net Address:
52.56.35.36 Address:
52.56.224.242 https://controller.faber.cgnx.net Address:
52.74.47.220 Address:
13.251.109.27 https://vmfg.faber.cgnx.net Address:
18.142.153.59 Address:
52.74.58.219 https://controller.townsend.cgnx.net Address:
13.55.31.41 Address:
3.106.168.215 https://vmfg.townsend.cgnx.net Address:
52.64.177.240 Address:
13.55.164.51 https://sdwan-stats-faber-sg.cgnx.net https://sdwan-stats-bowfell-uk.cgnx.net https://sdwan-stats-townsend-au.cgnx.net |
| NTP | 123 | Outbound |
ZTNA Connector WAN and LAN ports
|
time.nist.gov
0.cloudgenix.pool.ntp.org
1.cloudgenix.pool.ntp.org
2.cloudgenix.pool.ntp.org
3.cloudgenix.pool.ntp.org
|
| DNS | 53 | Outbound |
ZTNA Connector WAN and LAN ports
| Customer or Provider DNS servers |