Prisma Access
Allocate Remote Network Bandwidth
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma Access Docs
-
- 6.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 6.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 4.2 Preferred
- 4.1 Preferred
- 4.0 Preferred
- 3.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 2.2 Preferred
-
-
- 4.0 & Later
- Prisma Access China
-
-
Allocate Remote Network Bandwidth
Learn how to allocate remote network bandwidth.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
Remote networks are used to secure remote network locations, such as branches, and users
in those branches.
Remote networks are metered, which means that a specific amount of bandwidth is allocated
to the compute location and there is a cost associated with this allocated
bandwidth.
As you prepare to connect remote networks to Prisma Access, you will need to know how
many sites you will onboard along with bandwidth requirements for each.
Learn how to allocate remote network bandwidth.
This procedure applies only to deployments that allocate
bandwidth by compute location (aggregate bandwidth model). For Prisma Access 6.0
and later, you can choose between allocating bandwidth per site or by compute location
(aggregate model).
Allocate Remote Network Bandwidth (Strata Cloud Manager)
Learn how Prisma Access dynamically allocates bandwidth to sites in a compute location
based on load or demand.
At least two (often more) Prisma Access locations that are geographically near each
other are grouped in to compute locations. This is the level at which
you allocate bandwidth, instead of allocating bandwidth for individual Prisma Access
locations or for specific remote network sites. It means that Prisma Access can
dynamically allocate bandwidth to sites in a compute location based on load or
demand.
For example, you need to onboard four branch offices using remote networks in the
Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam locations. All these locations map to the Asia
Southeast compute location. If you allocate 200 Mbps bandwidth to the Asia Southeast
compute location, Prisma Access divides the 200 Mbps of bandwidth between the four
branch offices you onboarded in that location. If you also add a location in Hong
Kong, you note that Hong Kong maps to the Hong Kong compute location, and you would
need to add bandwidth to that compute location. Specify a minimum bandwidth of 50
Mbps per compute location.
Prisma Access dynamically allocates the bandwidth based on load or demand per
location. Using the previous example where the four sites collectively use up to 200
Mbps, if one or more sites are not using as much bandwidth as the other sites,
Prisma Access provides more bandwidth for the locations that are more in demand,
giving you a more efficient use of allocated bandwidth. In addition, if one of the
sites goes down, Prisma Access reallocates the bandwidth between the other sites
that are still up in that compute location.
To get started, go to ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessConfiguration ScopePrisma AccessRemote NetworksBandwidth Management.

Still Consider How Much Bandwidth Each Site Needs, When You Allocate Bandwidth
Based on Location
To help you determine how much bandwidth a specific site needs, consider the
bandwidth available from your ISP at each location. When calculating the amount of
bandwidth you need at a site, consider that the bandwidth usage includes both egress
and ingress traffic for the remote network connection.
Secure inbound access for remote network sites and Quality of Service (QoS) for
remote networks is not supported when you allocate bandwidth across
locations.
Allocate Remote Network Bandwidth (Panorama)
Configure a Prisma Access remote network deployment that allocates bandwidth by compute
location.
To configure a Prisma Access remote network deployment that allocates bandwidth by
compute location, complete the following steps.
If you need to onboard many remote networks (up to 1,000), you can onboard a
remote network using the following procedure, then export the remote network configuration to a
CSV file, add the other remote networks you want to onboard to the
CSV file, then import the CSV file to save the configuration into Prisma Access.
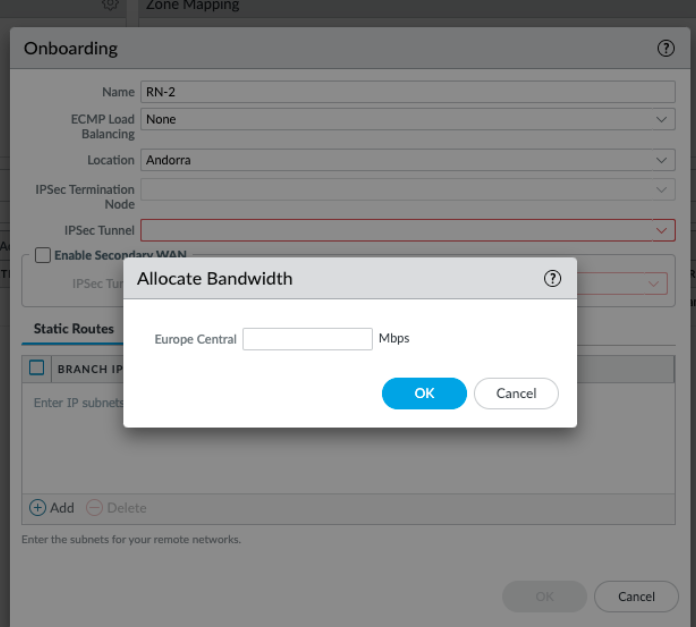
- Select PanoramaCloud ServicesConfigurationRemote Networks.Allocate bandwidth for the locations that you want to onboard by clicking the gear icon in the Bandwidth Allocation area.You allocate bandwidth at an aggregate level per compute location. See Prisma Access Remote Networks for details.If you have removed Autonomous DEM as an add-on license, or if you remove Autonomous DEM for remote networks from your license, select Disable Autonomous DEM. If you remove Autonomous DEM for remote networks and do not disable Autonomous DEM, you will receive an error upon commit.
![]() If you have an existing remote networks deployment that currently onboards remote networks by location, a pop-up window displays, asking if you want to migrate to the aggregate bandwidth model. Click Migrate to continue, or Cancel to cancel the migration.The migration to the aggregate bandwidth model is permanent and not reversible. Before you migrate, review the pre-migration checklist. You must Commit and Push your changes for them to take effect.The Service Endpoint Address (the FQDN or public IP address used on the Prisma Access side of the IPSec tunnel for the remote network connection) do not change when you migrate your deployment to the aggregate bandwidth model, and no reconfiguration of your IPSec tunnel is required.Enter the Bandwidth Allocation you want for each Compute Location that is associated with the Prisma Access Locations you want to onboard.To verify the bandwidth amount you entered, select the check mark next to the bandwidth amount; to cancel the amount, select x.Specify a minimum bandwidth of 50 Mbps and a maximum bandwidth of the maximum remaining licensed bandwidth.(Optional, Deployments with Autonomous DEM for Remote Networks Licenses Only) Enable Autonomous DEM Allocation for the compute location for which you allocated bandwidth.If you enable Autonomous DEM for the compute location, the amount of bandwidth used by the Autonomous DEM license is the same as the bandwidth you specify for the compute location. The Autonomous DEM Allocated Total shows you how much bandwidth is used by Autonomous DEM and how much is remaining. See the Autonomous DEM guide for more information.Wait for the bandwidth to be reflected in the Allocated Total field at the top of the page; then, click OK.
If you have an existing remote networks deployment that currently onboards remote networks by location, a pop-up window displays, asking if you want to migrate to the aggregate bandwidth model. Click Migrate to continue, or Cancel to cancel the migration.The migration to the aggregate bandwidth model is permanent and not reversible. Before you migrate, review the pre-migration checklist. You must Commit and Push your changes for them to take effect.The Service Endpoint Address (the FQDN or public IP address used on the Prisma Access side of the IPSec tunnel for the remote network connection) do not change when you migrate your deployment to the aggregate bandwidth model, and no reconfiguration of your IPSec tunnel is required.Enter the Bandwidth Allocation you want for each Compute Location that is associated with the Prisma Access Locations you want to onboard.To verify the bandwidth amount you entered, select the check mark next to the bandwidth amount; to cancel the amount, select x.Specify a minimum bandwidth of 50 Mbps and a maximum bandwidth of the maximum remaining licensed bandwidth.(Optional, Deployments with Autonomous DEM for Remote Networks Licenses Only) Enable Autonomous DEM Allocation for the compute location for which you allocated bandwidth.If you enable Autonomous DEM for the compute location, the amount of bandwidth used by the Autonomous DEM license is the same as the bandwidth you specify for the compute location. The Autonomous DEM Allocated Total shows you how much bandwidth is used by Autonomous DEM and how much is remaining. See the Autonomous DEM guide for more information.Wait for the bandwidth to be reflected in the Allocated Total field at the top of the page; then, click OK.![]() (Optional) If you want to configure your remote network to provide secure inbound access to remote network locations, click the Inbound Access Remote Networks tab and follow the workflow to configure secure inbound access for a remote network.Add a remote network and specify a Name.You cannot change the name of the remote network location after you enter it. Make sure you know your naming scheme for your remote networks before you begin onboarding.(Optional, BGP deployments only) Create a configuration so that your remote network connection can use up to four IPSec tunnels for its traffic (ECMP Load Balancing).Static routes are not supported (BGP is required), and, if you have QoS configured, you cannot change the Allocation Ratio for ECMP links. If your deployment uses one IPSec tunnel for its remote network connection or uses static routes, select None for ECMP Load Balancing and continue to Step 11.
(Optional) If you want to configure your remote network to provide secure inbound access to remote network locations, click the Inbound Access Remote Networks tab and follow the workflow to configure secure inbound access for a remote network.Add a remote network and specify a Name.You cannot change the name of the remote network location after you enter it. Make sure you know your naming scheme for your remote networks before you begin onboarding.(Optional, BGP deployments only) Create a configuration so that your remote network connection can use up to four IPSec tunnels for its traffic (ECMP Load Balancing).Static routes are not supported (BGP is required), and, if you have QoS configured, you cannot change the Allocation Ratio for ECMP links. If your deployment uses one IPSec tunnel for its remote network connection or uses static routes, select None for ECMP Load Balancing and continue to Step 11.- Select one of the choices to enable or disable ECMP load balancing.
- None—Do not use ECMP load balancing (use a single remote network tunnel for this remote network connection). This is the only choice you can make for static routes; BGP is required for ECMP load balancing.
- Enabled with Symmetric Return—Specify up to four IPSec tunnels for this remote network connection and force Prisma Access to use the same link for the return traffic as it used to send the traffic.Select this option if you use one or more tunnels as a backup tunnel to be used only if one of the primary tunnels go down. If a link fails, Prisma Access uses one of the other tunnels to send and receive traffic symmetrically.
![]() Add an IPSec tunnel for the remote network connection and specify the following values:
Add an IPSec tunnel for the remote network connection and specify the following values:- Enable—Enables BGP for the IPSec tunnel.This selection is not configurable; you must enable BGP to configure ECMP.
- Summarize Mobile User Routes before advertising—Reduces the number of mobile user IP subnet advertisements over BGP to your customer premises equipment (CPE) by summarizing them.By default, Prisma Access advertises the mobile users IP address pools in blocks of /24 subnets; if you summarize them, Prisma Access advertises the pool based on the subnet you specified. For example, Prisma Access advertises a public user mobile IP pool of 10.8.0.0/20 using the /20 subnet, rather than dividing the pool into subnets of 10.8.1.0/24, 10.8.2.0/24, 10.8.3.0/24, and so on before advertising them. Summarizing these advertisements can reduce the number of routes stored in CPE routing tables. For example, you can use IP pool summarization with cloud VPN gateways (Virtual Private Gateways (VGWs) or Transit Gateways (TGWs)) that can accept a limited number of routes.If you enable route summarization for a location that uses ECMP, you must enable route summarization on all links to that location, or you will receive an error during commit.Prisma Access sets the community string for aggregated mobile user routes to 0xFFFE:0xFFF0.
- Advertise Default Route—Prisma Access originates a default route advertisement for the remote network using eBGP.Be sure that your network does not have another default route being advertised by BGP, or you could introduce routing issues in your network.
- Don’t Advertise Prisma Access Routes—Prevents the Prisma Access BGP peer from forwarding routes into your organization’s network.By default, Prisma Access advertises all BGP routing information, including local routes and all prefixes it receives from other service connections, remote networks, and mobile user subnets. Select this check box to prevent Prisma Access from sending any BGP advertisements, but still use the BGP information it receives to learn routes from other BGP neighbors.Since Prisma Access does not send BGP advertisements if you select this option, you must configure static routes on the on-premises equipment to establish routes back to Prisma Access.
![]()
- Peer AS—Specify the autonomous system (AS) to which the firewall, virtual router, or BGP router at your remote network belongs.
- Peer IP Address—Enter the IP address assigned as the Router ID of the eBGP router on the remote network for which you are configuring this connection.
- Local IP Address (Optional)—Enter an address that Prisma Access uses as its Local IP address for BGP.Specify the IP address to use on the Prisma Access side of the tunnel.Specifying a Local Address is useful where the device on the other side of the connection (such as an Amazon Web Service (AWS) Virtual Private Gateway) requires a specific local IP address for BGP peering to be successful. Make sure that the address you specify does not conflict or overlap with IP addresses in the Infrastructure Subnet or subnets in the remote network.
- Secret and Confirm Secret (Optional)—Enter and confirm a passphrase to authenticate BGP peer communications.
Repeat the previous step to add up to four tunnels to use with the remote network connection.![]() Select the Location in which Prisma Access will deploy the infrastructure required to secure your remote network location. This region should be geographically located close to your remote network location.If you have not yet allocated bandwidth for the compute location to which the location maps, Prisma Access prompts you to enter bandwidth for that compute location.
Select the Location in which Prisma Access will deploy the infrastructure required to secure your remote network location. This region should be geographically located close to your remote network location.If you have not yet allocated bandwidth for the compute location to which the location maps, Prisma Access prompts you to enter bandwidth for that compute location.![]() Select the IPSec Termination Node that you want to use for this remote network.Prisma Access uses this node to associate remote network locations with compute locations.(Static routing or single-tunnel deployments only) Select or add a new IPSec Tunnel configuration to access the firewall, router, or SD-WAN device at the corporate location:
Select the IPSec Termination Node that you want to use for this remote network.Prisma Access uses this node to associate remote network locations with compute locations.(Static routing or single-tunnel deployments only) Select or add a new IPSec Tunnel configuration to access the firewall, router, or SD-WAN device at the corporate location:- Select one of the predefined IPSec templates in the Remote_Network_Template, or, if you have added a template to the Remote_Network_Template_Stack (or modified the predefined Remote_Network_Template) that includes an IPSec Tunnel configuration, select that IPSec Tunnel from the drop-down. Note that the tunnel you are creating for each remote network connection connects Prisma Access to the IPSec-capable device at each branch location.Use the following guidelines when configuring an IPSec tunnel:
- The peer addresses in the IKE Gateway configuration must be unique for each tunnel. You can, however, re-use some of the other common configuration elements, such as crypto profiles.
- The IPSec Tunnel you select from a template must use Auto Key exchange and IPv4 only.
- The IPSec tunnel, IKE gateway, and crypto profile names cannot be longer than 31 characters.
- If you onboard multiple remote networks to the same location with dynamic IKE peers, you must use the same IKE crypto profile for all remote network configurations.
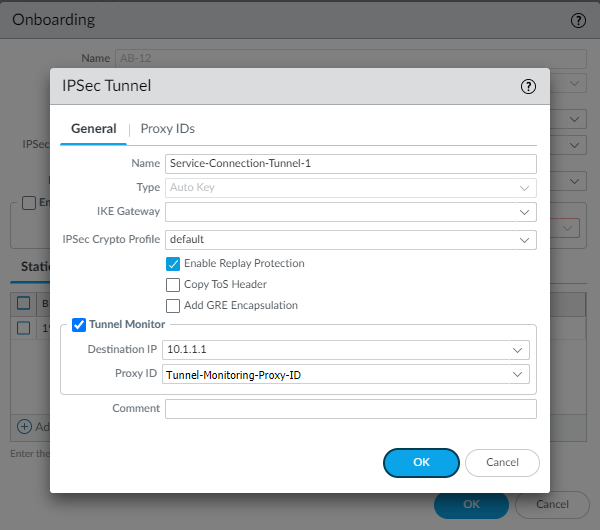
- To create a new IPSec Tunnel
configuration, click New IPSec Tunnel, give it a
Name and configure the IKE Gateway, IPSec Crypto Profile, and
Tunnel Monitoring settings.
- If the IPSec-capable device at your branch location uses policy-based VPN, on the Proxy IDs tab, Add a proxy ID that matches the settings configured on your local IPSec device to ensure that Prisma Access can successfully establish an IPSec tunnel with your local device.
- Leave Enable Replay Protection selected to detect and neutralize against replay attacks.
- Select Copy TOS Header to copy the Type of Service (TOS) header from the inner IP header to the outer IP header of the encapsulated packets in order to preserve the original TOS information.
- To enable tunnel monitoring for the service connection, select Tunnel Monitor.
- Enter a Destination IP address.Specify an IP address at your branch location to which Prisma Access can send ICMP ping requests for IPSec tunnel monitoring. Make sure that this address is reachable by ICMP from the entire Prisma Access infrastructure subnet.
- If you use tunnel monitoring with a peer device that uses multiple proxy IDs, specify a Proxy ID or add a New Proxy ID that allows access from the infrastructure subnet to your branch location.The following figure shows a proxy ID with the service infrastructure subnet (172.16.55.0/24 in this example) as the Local IP subnet and the branch location’s subnet (10.1.1.0/24 in this example) as the Remote subnet.
![]() The following figure shows the Proxy ID you created being applied to the tunnel monitor configuration by specifying it in the Proxy ID field.
The following figure shows the Proxy ID you created being applied to the tunnel monitor configuration by specifying it in the Proxy ID field.
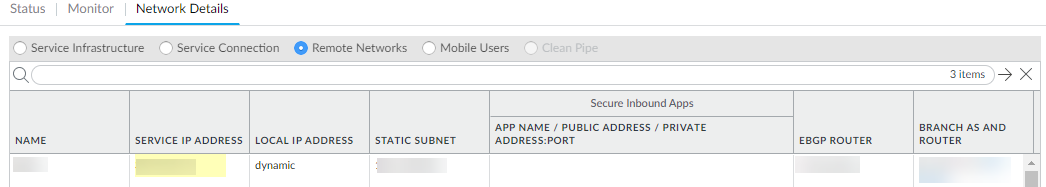
![]() You must configure a static route on your CPE to the Tunnel Monitor IP Address for tunnel monitoring to function. To find the destination IP address to use for tunnel monitoring from your branch location to Prisma Access, select PanoramaCloud ServicesStatusNetwork Details, click the Service Infrastructure radio button, and find the Tunnel Monitor IP Address.
You must configure a static route on your CPE to the Tunnel Monitor IP Address for tunnel monitoring to function. To find the destination IP address to use for tunnel monitoring from your branch location to Prisma Access, select PanoramaCloud ServicesStatusNetwork Details, click the Service Infrastructure radio button, and find the Tunnel Monitor IP Address.
If you have a secondary WAN link at this location, select Enable Secondary WAN.Be sure to create a unique IPSec tunnel for each remote network’s secondary WAN; Prisma Access does not support reusing the same IPSec tunnel for secondary WANs in multiple remote networks.Configuring a Secondary WAN is not supported in the following deployments:- If your secondary WAN is set up in active-active mode with the Primary IPSec tunnel.
- If your customer premises equipment (CPE) is set up in an Equal Cost Multipath (ECMP) configuration with the Primary and Secondary IPSec tunnel.
If you use static routes, tunnel failover time is less than 15 seconds from the time of detection, depending on your WAN provider.If you configure BGP routing and have enabled tunnel monitoring, the shortest default hold time to determine that a security parameter index (SPI) is failing is the tunnel monitor, which removes all routes to a peer when it detects a tunnel failure for 15 consecutive seconds. In this way, the tunnel monitor determines the behavior of the BGP routes. If you do not configure tunnel monitoring, the hold timer determines the amount of time that the tunnel is down before removing the route. Prisma Access uses the default BGP HoldTime value of 90 seconds as defined by RFC 4271, which is the maximum wait time before Prisma Access removes a route for an inactive SPI. If the peer BGP device has a shorter configured hold time, the BGP hold timer uses the lower value.When the secondary tunnel is successfully installed, the secondary route takes precedence until the primary tunnel comes back up. If the primary and secondary are both up, the primary route takes priority.If you use a different BGP peer for the secondary (backup) connection, Prisma Access does not honor the Multi-Exit Discriminator (MED) attributes advertised by the CPE. This caveat applies if you use multiple BGP peers on either remote network connections or service connections.Enable routing to the subnetworks or individual IP addresses at the remote network site that your users will need access to.Prisma Access uses this information to route requests to the appropriate site. The networks at each site cannot overlap with each other or with IP address pools that you designated for the service infrastructure or for the Prisma Access for users IP pools. You can configure Static Routes, BGP, or a combination of both.- To configure Static Routes:
- On the Static Routes tab, click Add and enter the subnetwork address (for example, 172.168.10.0/24) or individual IP address of a resource, such as a DNS server (for example, 10.32.5.1/32) that your remote users will need access to.
- Repeat for all subnets or IP addresses that Prisma Access will need access to at this location.
![]()
- To configure BGP:
- Select the BGP tab.
- (Optional) Select the ECMP Load Balancing choices. See Step 8.
- If you select None for ECMP Load Balancing, enter the BGP choices.
![]()
- To enable BGP for the remote network connection, select Enable.When you enable BGP, Prisma Access sets the time to live (TTL) value for external BGP (eBGP) to 8 to accommodate any extra hops that might occur between the Prisma Access infrastructure and your customer premises equipment (CPE) that terminates the eBGP connection.
- To reduce the number of mobile user IP subnet advertisements over BGP to your customer premises equipment (CPE) by summarizing them, select Summarize Mobile User Routes before advertising.By default, Prisma Access advertises the mobile users IP address pools in blocks of /24 subnets; if you summarize them, Prisma Access advertises the pool based on the subnet you specified. For example, Prisma Access advertises a public user mobile IP pool of 10.8.0.0/20 using the /20 subnet, rather than dividing the pool into subnets of 10.8.1.0/24, 10.8.2.0/24, 10.8.3.0/24, and so on before advertising them. Summarizing these advertisements can reduce the number of routes stored in CPE routing tables. For example, you can use IP pool summarization with cloud VPN gateways (Virtual Private Gateways (VGWs) or Transit Gateways (TGWs)) that can accept a limited number of routes.Prisma Access sets the community string for aggregated mobile user routes to 0xFFFE:0xFFF0.
- To allow Prisma Access to advertise a default route for the remote network using eBGP, select Advertise Default Route.If you select Advertise Default Route, be sure that your network does not have another default route being advertised by BGP, or you could introduce routing issues in your network.You must publish your default routes before you make this selection to advertise them. In addition, be sure that your network does not have another default route being advertised by BGP, or you could introduce routing issues in your network.
- To prevent the BGP peer on the Prisma Access firewall from forwarding routes into your organization’s network, select Don’t Advertise Prisma Access Routes.By default, Prisma Access advertises all BGP routing information, including local routes and all prefixes it receives from other service connections, remote networks, and mobile user subnets. Select this check box to prevent Prisma Access from sending any BGP advertisements, but still use the BGP information it receives to learn routes from other BGP neighbors.Since Prisma Access does not send BGP advertisements if you select this option, you must configure static routes on the on-premises equipment to establish routes back to Prisma Access.
- Enter the Peer AS, which is the autonomous system (AS) to which the firewall, virtual router, or BGP router at your remote network belongs.
- Enter the IP address assigned as the Router ID of the eBGP router on the remote network for which you are configuring this connection as the Peer Address.
- (Optional) Enter an address that Prisma Access uses as its Local IP address for BGP.Specifying a Local Address is useful where the device on the other side of the connection (such as an Amazon Web Service (AWS) Virtual Private Gateway) requires a specific local IP address for BGP peering to be successful. Make sure that the address you specify does not conflict or overlap with IP addresses in the Infrastructure Subnet or subnets in the remote network.You must configure a static route on your CPE to the BGP Local Address.
- (Optional) Enter and confirm a passphrase to authenticate BGP peer communications.
- (Optional) If you configured a Secondary WAN and you need to change the Peer Address or Local Address for the secondary (backup) BGP peer, deselect Same as Primary WAN and enter a unique Peer and, optionally, Local IP address for the secondary WAN.If you use IPv6 networking in your remote network deployment, you can configure IPv6 addresses as well as IPv4 addresses. You also need to enable IPv6 networking globally in your Prisma Access infrastructure before you can use IPv6 addressing.In some deployments (for example, when using BGP to peer with an AWS VPN gateway), the BGP peer for the primary and secondary WAN might be different. In those scenarios, you can choose to set a different BGP peer for the secondary WAN.For BGP deployments with secondary WANs, Prisma Access sets both the primary and secondary tunnels in an UP state, but follows normal BGP active-backup behavior for network traffic. Prisma Access sets the primary tunnel as active and sends and receives traffic through that tunnel only; if the primary tunnel fails, Prisma Access detects the failure using BGP rules, sets the secondary tunnel as active, and uses only the secondary tunnel to send and receive traffic.
(Optional) Enable QoS for the location and specify a QoS Profile.You specify QoS options and overall settings on a per-compute location basis in the Settings; however, you can enable or disable QoS or change the QoS profile on a per-location basis here.Commit the configuration changes to Panorama and push the configuration out to Prisma Access for networks.- Click CommitCommit to Panorama.Click CommitCommit and Push. Click Edit SelectionsPrisma Access, and select both Prisma Access for networks and Prisma Access for service setup to push the configuration out to the service.
![]() Click OK and Push.Configure the IPSec-capable device at the remote network location to set up an IPSec connection with Prisma Access for networks.
Click OK and Push.Configure the IPSec-capable device at the remote network location to set up an IPSec connection with Prisma Access for networks.- Find the Service Endpoint Address for this remote network connection by selecting PanoramaCloud ServicesStatusNetwork Details, clicking the Remote Networks radio button, and viewing the Service Endpoint Address field. Prisma Access for networks infrastructure has assigned this FQDN or IP address for the Prisma Access remote network connection, and you must configure this as the peer IP address to set up the IPSec tunnel between the remote network location and Prisma Access for networks.
![]() Check the Local IP address for the device at the remote network location on the PanoramaCloud ServicesStatusNetwork DetailsRemote Networks page. If you are performing NAT at the remote network location, the Local IP address displays the IP address of the device after NAT.To secure traffic at the remote network location you must create security policy rules.
Check the Local IP address for the device at the remote network location on the PanoramaCloud ServicesStatusNetwork DetailsRemote Networks page. If you are performing NAT at the remote network location, the Local IP address displays the IP address of the device after NAT.To secure traffic at the remote network location you must create security policy rules.- Select Policies.Select the Device Group in which to add policy rules. You can select the Remote_Network_Device_Group or the parent device group that you selected for defining policies to secure the remote network location.Create security policy rules. Make sure that you do not define security policy rules to allow traffic from any zone to any zone. In the security policy rules, use the zones that you defined in your template.If a user on your network is denied access to a website, report website access issues before you open a ticket with Palo Alto Networks.Enable logging to Strata Logging Service. You must create and attach a log forwarding profile to each policy rule for which you want to forward logs.
- Select Objects > Log Forwarding.Select the Device Group in which you added the policy rules, for example, Remote_Network_Device_Group.Add a Log Forwarding profile. In the log forwarding profile match list, Add each Log Type that you want to forward.Select Panorama/Strata Logging Service as the Forward Method to enable Prisma Access to forward the logs to Strata Logging Service. You will be able to monitor the logs and generate reports from Panorama. Strata Logging Service provides a seamless integration to store logs without backhauling them to your Panorama at the corporate headquarters, and Panorama can query Strata Logging Service as needed.The following example enables forwarding of Traffic, Threat Prevention, WildFire Submission, URL Filtering, Data Filtering, and Authentication logs to Strata Logging Service.
![]() Select Policies > Security and edit the policy rule. In Actions, select the Log Forwarding profile you created.Commit all your changes to Panorama and push the configuration changes to Prisma Access.
Select Policies > Security and edit the policy rule. In Actions, select the Log Forwarding profile you created.Commit all your changes to Panorama and push the configuration changes to Prisma Access.- Click CommitCommit and Push.Edit Selections and, in the Prisma Access tab, make sure Prisma Access for networks is selected in the Push Scope, then click OK.Commit and Push your changes.Check the remote network status.See Verify If Remote Network Is Connected to Prisma Access for details.