Prisma Access
Chromebook with Prisma Access Explicit Proxy
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma Access Docs
-
- 6.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 6.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 4.2 Preferred
- 4.1 Preferred
- 4.0 Preferred
- 3.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 2.2 Preferred
-
-
- 4.0 & Later
- Prisma Access China
-
-
Chromebook with Prisma Access Explicit Proxy
Learn how to use a Chromebook with explicit proxy.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
With the Proxy-Auto Configuration (PAC) file method, you can use a Chromebook with Prisma Access explicit proxy to access the internet. A PAC file
is JavaScript code that tells a web browser how to connect to a proxy server.
Enterprise environments employ PAC files to control web traffic and enforce Security
policy rules. You can host your PAC file in your network or you can also use a
forwarding profile to host it.
Chromebook with Prisma Access Explicit Proxy (Strata Cloud Manager)
Learn how to use a Chromebook with explicit proxy using Strata Cloud
Manager.
Complete the following steps using a PAC file.
- Enable explicit proxy.You can manage the PAC file by editing the PAC file directly or by using a forward profile.
- Edit an existing forwarding profile.
- Go to ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessConfiguration ScopePrisma AccessMobile UsersForwarding Profiles Setup and click the gear icon.
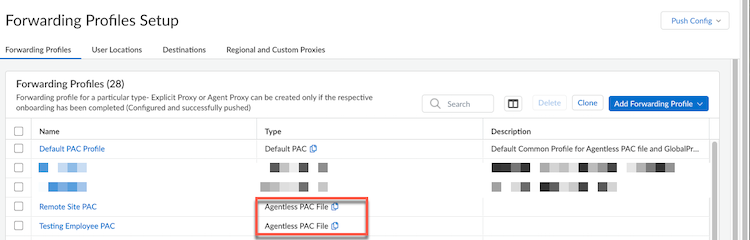
- Select a forwarding profile with Agentless PAC
file type and Edit PAC
File.
![]()
- Edit the PAC file and add the following domains as DIRECT
in the PAC file to send traffic for the hosts or domains, and
then
Save.if (shExpMatch(host, "*play.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*android.l.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*googleapis.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*googleapis.com*") || shExpMatch(host, "*android.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*android.clients.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*apps.chrome") || shExpMatch(host, "*googletagmanager.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*withgoogle.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*google-analytics.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*googleusercontent.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*dns.google") || shExpMatch(host, "*android.apis.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*safebrowsing.google") || shExpMatch(host, "*gvt1.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*gvt2.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*apps.chrome") || shExpMatch(host, "*sites.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*ogs.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*m.google.com") | shExpMatch(host, "*contacts.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*accounts.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*mail.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*www.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*appengine.google.com") ) { return "DIRECT"; }
- Select the forwarding profile that you have edited and copy the PAC file URL.
- Manage the PAC file by using a forwarding profile.
- Go to ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessConfiguration ScopePrisma AccessMobile UsersForwarding Profiles Setup and click the gear icon.
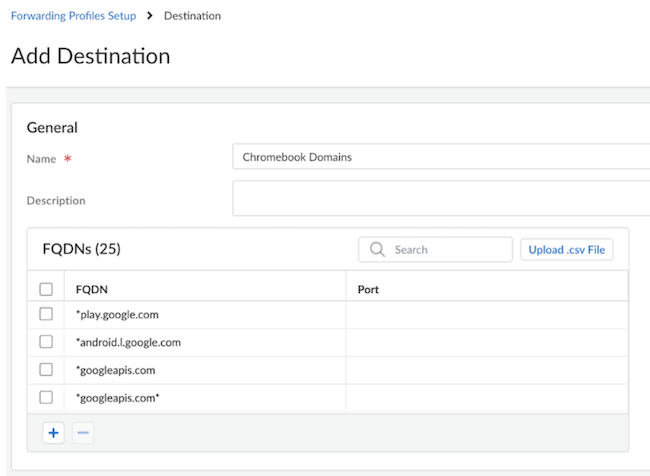
- Go to Destinations and Add
Destination. Add a Name,
Description, add the domains under
FQDNs, and
Save. Add the following domains under
FQDNs:
- *play.google.com
- *android.l.google.com
- *googleapis.com
- *android.com
- *android.clients.google.com
- *apps.chrome
- *googletagmanager.com
- *withgoogle.com
- *google-analytics.com
- *googleusercontent.com
- *dns.google
- *android.apis.google.com
- *safebrowsing.google
- *gvt1.com
- *gvt2.com
- *apps.chrome
- *sites.google.com
- *ogs.google.com
- *m.google.com
- *contacts.google.com
- *accounts.google.com
- *mail.google.com
- *www.google.com
- *appengine.google.com
![]()
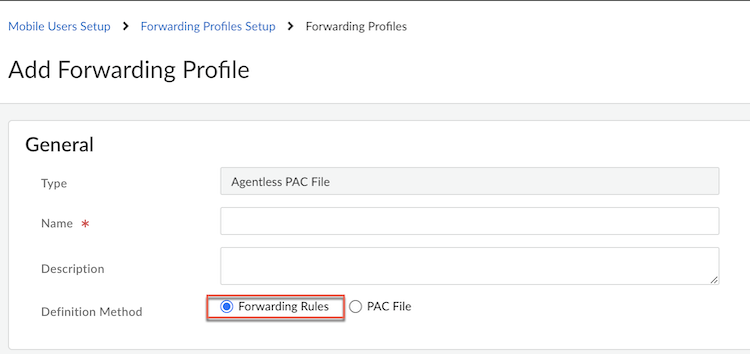
- Go to Forwarding Profiles and
Add Forwarding Profile with
Agentless PAC file type. Add a
Name,
Description and select
Forwarding Rules as a
Definition Method.
![]()
- Add Forwarding Rule for the forwarding
profile. Add a Name, User
Location, Destination and
select Proxy as Direct.
Add to save the changes.
![]()
- Save and Push Config to push the changes.
- Select the forwarding profile that you have created or edited and copy the PAC file URL.
Deploy the copied PAC file URL on the Chromebook endpoint to access the internet through Prisma Access explicit proxy.
Chromebook with Prisma Access Explicit Proxy (Panorama)
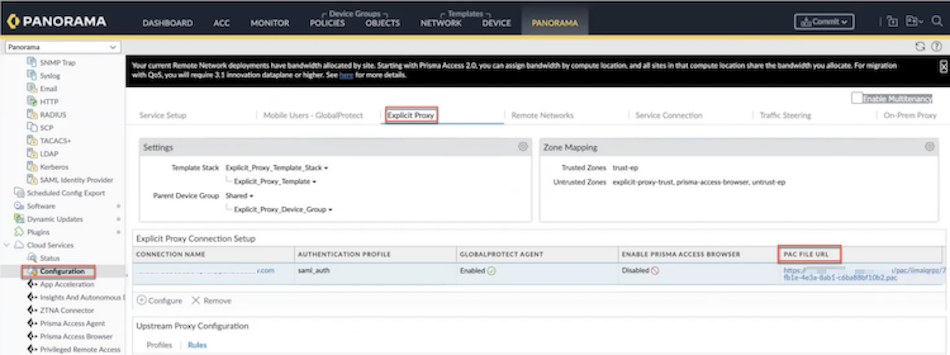
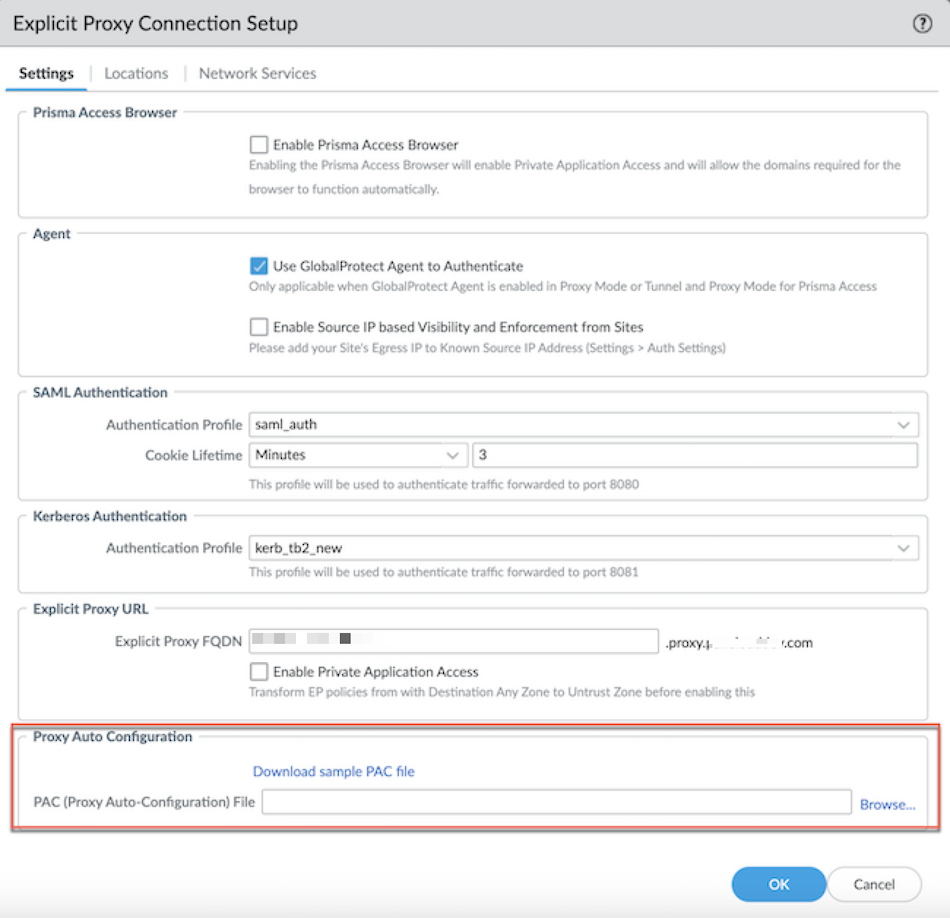
Learn how to use a Chromebook with explicit proxy using Panorama.You can manage the PAC file by editing the PAC file directly. Complete the following steps using a PAC file.- Enable explicit proxy.Go to PANORAMACloud ServicesConfigurationExplicit Proxy.Create a new PAC file or if you have an existing PAC file, select the PAC file under PAC FILE URL, and download it.
![]() Edit the PAC file and add the following URLs and set them as DIRECT.if (shExpMatch(host, "*play.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*android.l.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*googleapis.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*googleapis.com*") || shExpMatch(host, "*android.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*android.clients.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*apps.chrome") || shExpMatch(host, "*googletagmanager.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*withgoogle.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*google-analytics.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*googleusercontent.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*dns.google") || shExpMatch(host, "*android.apis.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*safebrowsing.google") || shExpMatch(host, "*gvt1.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*gvt2.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*apps.chrome") || shExpMatch(host, "*sites.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*ogs.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*m.google.com") | shExpMatch(host, "*contacts.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*accounts.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*mail.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*www.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*appengine.google.com") ) { return "DIRECT"; }Select the CONNECTION NAME. Under Proxy Auto Configuration, Browse the edited PAC file and click OK.
Edit the PAC file and add the following URLs and set them as DIRECT.if (shExpMatch(host, "*play.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*android.l.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*googleapis.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*googleapis.com*") || shExpMatch(host, "*android.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*android.clients.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*apps.chrome") || shExpMatch(host, "*googletagmanager.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*withgoogle.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*google-analytics.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*googleusercontent.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*dns.google") || shExpMatch(host, "*android.apis.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*safebrowsing.google") || shExpMatch(host, "*gvt1.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*gvt2.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*apps.chrome") || shExpMatch(host, "*sites.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*ogs.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*m.google.com") | shExpMatch(host, "*contacts.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*accounts.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*mail.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*www.google.com") || shExpMatch(host, "*appengine.google.com") ) { return "DIRECT"; }Select the CONNECTION NAME. Under Proxy Auto Configuration, Browse the edited PAC file and click OK.![]() Commit and push to Explicit_Proxy_Device_Group.
Commit and push to Explicit_Proxy_Device_Group.