Prisma Access
New Features in Prisma Access 4.2
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma Access Docs
-
- 6.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 6.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 4.2 Preferred
- 4.1 Preferred
- 4.0 Preferred
- 3.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 2.2 Preferred
-
-
- 4.0 & Later
- Prisma Access China
-
-
New Features in Prisma Access 4.2
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
The following table describes the new features that will be available with Prisma Access 4.2 Preferred.
Prisma Access Application Name Update
|
November 18, 2023
The application tile name on the hub for Prisma Access is now
changed to Strata Cloud Manager.
|
The application tile names on the hub for Prisma Access, Prisma SD-WAN, and
AIOps for NGFW (the premium app only) are now changed to Strata Cloud
Manager. With this update, the application URL has also changed to stratacloudmanager.paloaltonetworks.com, and
you’ll also now see the Strata Cloud Manager logo on the left navigation
pane.
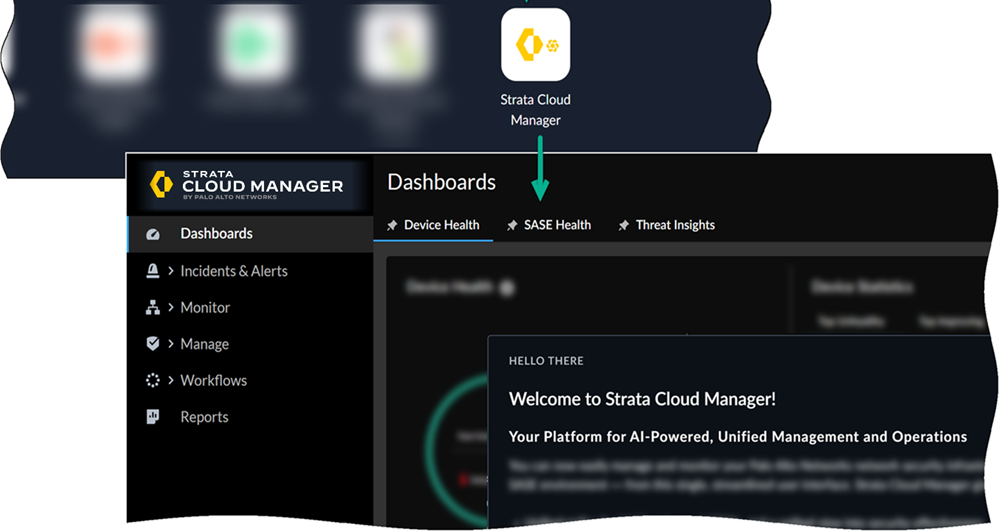
Moving forward, continue using the Strata Cloud Manager app to manage and
monitor your deployments.
Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN Integration
|
Supported in:
|
Previously, to secure Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN, formerly known as Viptela SD-WAN, you
should create remote networks and IPSec tunnels manually. Now, you can onboard a
remote network using IPSec tunnels between Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN and Prisma Access
automatically. Contact your Palo Alto Networks Account representative to enable this
functionality. After you enable this functionality, configure the settings to
establish the connection between Prisma Access and Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN. View the
discovered sites that are eligible for the integration, and enable them accordingly.
This creates remote networks and establishes IPSec tunnels. Ensure to follow all the
requirements and prerequisites before you enable this functionality. See Integrate Prisma Access with Cisco Catalyst
SD-WAN for more information.
Credential Phishing Prevention Support
|
Supported in:
|
You can configure credential phishing prevention
to restrict the websites user can submit corporate credentials to and prevent
successful phishing attacks. This task involves selecting the credential detection method that the
firewall uses and specifying the actions the firewall takes when it detects
corporate credential submissions to allowed URL categories. The firewall enforces
the following actions: alert, allow, block, or continue. The continue option results
in the display of an anti-phishing response page that warns users against supplying
their credentials to certain websites and requires them to click "continue" before
they proceed to the requested website.
Each credential detection method requires a different User-ID™
configuration and varies in detection ability. For example, the domain credential filter method requires
installation of the Windows User-ID agent and User-ID credential service add-on on a
read-only domain controller (RODC). These tools enable the firewall to detect valid
corporate username and password pairs and verify that the IP address associated with
a login attempt matches an IP address-to-username mapping. The other methods focus
on username detection.
Prisma Access PAC File Endpoint for Explicit Proxy
|
Supported in:
|
Palo Alto Networks will begin rolling out a new endpoint for the Proxy
Auto-Configuration (PAC) file used for Explicit Proxy to make it easier for you to
enable access to PAC files. This new endpoint is hosted by Palo Alto Networks
instead of the current AWS S3 endpoint. When you modify the PAC file after September
1, 2023, you will see the PAC File URL with the updated endpoint.
No immediate action is required if you are using PAC file directly, as you
can continue to use the current AWS S3-based PAC File URL until Mar 31, 2024. We
suggest migrating to use the PAC file URL with updated endpoint before March 31,
2024 at your convenience.
If you are using GlobalProtect in proxy Mode or tunnel and proxy mode and you don’t allow
your devices to access all domains under prismaaccess.com (for example, because of
a third-party VPN split tunnel or firewall rule), please allow your devices to
access the PAC file endpoint (store.swg.prismaaccess.com) to avoid
interruptions. Alternatively, you can override the PAC File URL in the Global
Protect App Settings to use the S3-based PAC file URL until you are able to make
changes to allow access to the new endpoint. Please migrate to new endpoint before
March 31, 2024.
Please refer to the PAC file guidelines for additional
information, including IP addresses that you need to allow on your endpoints so that
they can reach the PAC file at the new URL.
After the PAC file updates, if you want to refer to the previous URL, you
can replace the FQDN of the new URL with the previous one. The exact FQDN that you
use depends on whether you have changed your PAC file after Prisma Access 4.1. For
example:
| New URL | Previous URL |
| https://pac-files-us-west-2-prod.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/<tenant-id>/<uuid>.pac OR https://pac-files-prod.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/<tenant-id>/<uuid>.pac |
<tenant-id> and <uuid> remain the same across URLs.
User-Based Enforcement for Explicit Proxy Kerberos Authentication
|
Supported in:
|
You can now implement user identity-based visibility and control using
security policies for undecrypted HTTPS traffic when a user or system authenticates using Kerberos. In addition,
administrators no longer need to configure Trusted Source Addresses when configuring
Kerberos authentication for undecrypted HTTPS traffic. This ensures consistent user
visibility and policy enforcement for all HTTP(S) traffic even in cases when client
IP addresses change, such as if your branch employs dynamic egress IP addresses.
Formerly, you could authenticate decrypted and undecrypted traffic, but
could only enforce user-based controls for decrypted HTTPS traffic. With this new
feature, all HTTP-based traffic (undecrypted HTTPS, decrypted HTTPS, and HTTP
traffic) can authenticate and undergo user-based controls.
Additionally, to allow undecrypted HTTPS traffic, users or systems had to
come from static IP addresses configured as Trusted Source Addresses. With this
feature, that is no longer necessary, which simplifies initial configuration and
supports the use case in which your branch locations have dynamic IP addresses.
Local Zone Additions
|
Supported in:
|
Local zones place compute, storage,
database, and other services close to large population and industry centers. These
locations have their own compute locations.
Keep in mind the following guidelines when deploying local zones:
- Local zone locations do not support IPv6.
- Local zone locations do not use Palo Alto Networks registered IP addresses.
- 1 Gbps support for remote networks is not supported.
- Remote network and service connection node redundancy across availability zones is not available if you deploy them in the same local zone, as both nodes are provisioned in a single zone.
- These local zones do not use Palo Alto Networks registered IPs. If you have problems accessing URLs, report the website issue using https://reportasite.gpcloudservice.com/ or reach out to Palo Alto Networks support.
- Some SaaS applications might experience a higher latency in local zones when compared with non-local zone locations.
Enterprise DLP Support for AI Applications
|
Supported in:
|
ChatGPT is the fastest growing consumer application in history, with 100 million
monthly active users just two months after launch. Many organizations may be
surprised to learn that their employees are already using AI-based tools to
streamline their daily workflows, potentially putting sensitive company data at
risk. Software developers can upload proprietary code to help find and fix bugs,
while corporate communications teams can ask for help in crafting sensitive press
releases.
To safeguard against the growing risk of sensitive data leakage to AI apps and APIs,
we are excited to announce a new set of capabilities to secure ChatGPT and other AI
apps as part of our Next-Generation CASB solution that includes: Comprehensive app
usage visibility for complete monitoring of all SaaS usage activity, including
employee use of new and emerging generative AI apps that can put data at risk.
Granular SaaS application controls that safely enable employee access to
business-critical applications, while limiting or blocking access to high risk
apps—including generative AI apps—that have no legitimate business purpose.
While AI apps can significantly boost productivity and creative output, they also
pose a serious data security risk to modern enterprises. Enterprise Data Loss
Prevention (E-DLP) provides advanced data security that provides ML-based data
classification and data loss prevention to detect and stop company secrets,
personally identifiable information (PII), and other sensitive data from being
leaked to generative AI apps by well-intentioned employees.
New Prisma Access Location
|
Supported in:
|
- Sweden
- Kazakhstan
- Qatar
- Senegal
