DNS Security Support for DNS Over HTTPS (DoH)
Table of Contents
11.0 (EoL)
Expand all | Collapse all
End-of-Life (EoL)
DNS Security Support for DNS Over HTTPS (DoH)
PAN-OS 11.0 and later can now analyze and categorize the DNS payload contained within encrypted
DNS traffic requests to DNS hosts using HTTPS (DoH—[DNS-over-HTTPS]). If your
organization currently blocks all DoH requests as Palo Alto Networks recommends, you
can transition away from that policy as DNS Security now enables you extract the DNS
hostname from the encrypted request and apply your organization’s existing DNS
Security policies. This allows you to safely access more websites as support for DoH
widens. DNS Security support for DoH is enabled by configuring the firewall to
decrypt the payload of DNS requests originating from a user-specified list of DNS
resolvers, providing support for a range of server options. The decrypted DNS
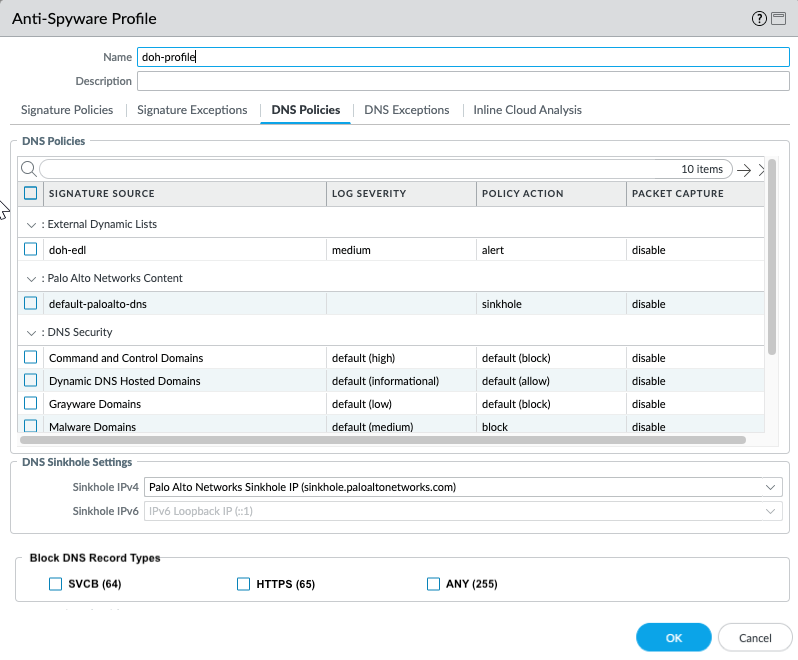
payload can then be processed using the Anti-spyware profile configuration
containing your DNS policy configuration. DNS requests that have been determined to
be DoH are labeled as dns-over-https in the traffic logs.
Palo Alto Networks also provides the option
to block ECH (Encrypted Client Hello), which is a draft state proposal
to encrypt the entire ‘client hello’ message. While that offers
some data privacy, such as ALPN and SNI, it can also prevent certain
firewall services that use the client hello from operating as intended.
To maintain optimal function of the security services of the firewall,
Palo Alto Networks recommends blocking all ECH-supporting record
types.
- Log in to the PAN-OS web interface.Create a Custom URL Category list that includes all DoH resolvers you want to enable traffic to/from (you will need the DNS server URL(s)).Create a Decryption Policy Rule that references the custom URL category list that you created in the previous step.Update or create a new anti-spyware security profile used to inspect DoH requests.
- (Optional) Block the specified DNS resource record types record types used to exchange keying information during the encryption of the client hello in the subsequent TLS connection. The following DNS RR types are available: SVCB (64), HTTPS (65), and ANY (255).
- While it is not necessary to block ECH in order to enable DNS Security over DoH, Palo Alto Networks currently recommends blocking all DNS record types used by ECH for optimum security.
- Type 64 and type 65 resource record standards are still in flux (in a draft state) and are subject to change. For more information on DNS SVCB and HTTPS RRs, refer to: Service binding and parameter specification via the DNS (DNS SVCB and HTTPS RRs) as defined by the IETF.
![]()
- Click OK to exit the anti-spyware profile configuration dialog and Commit your changes.
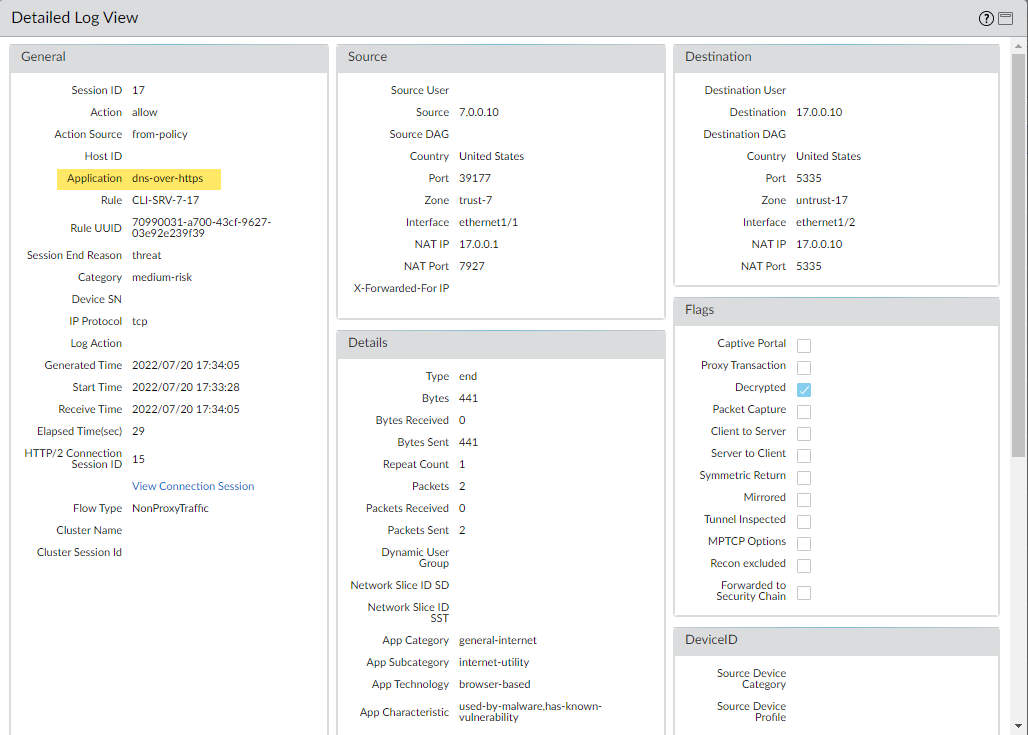
Create or update a security policy rule and reference an anti-spyware profile with the DNS Security settings and a custom URL category list (ObjectsCustom ObjectsURL Category) containing the approved list of DoH servers.Create a block policy to decrypt HTTPS traffic and block all remaining unsanctioned DoH traffic that is not explicitly allowed by the custom URL category list (referenced in step 5) by using the App-ID: dns-over-https and the following URL category: encrypted-dns.If you already have an existing block policy to block DoH traffic, verify that the rule is placed below the previous security policy rule used to match with specific DoH resolvers listed in a custom URL category list object.(Optional) Search for activity on the firewall for HTTPS-encrypted DNS queries that have been processed using DNS Security.- Select MonitorLogsTraffic and filter based on the application using dns-over-https, for example, ( app eq dns-over-https ).Select a log entry to view the details of a detected DNS threat.The Application should display dns-over-https in the General pane of the detailed log view, indicating that this is DoH traffic that has been processed using DNS Security. Other relevant details about the threat are displayed in their corresponding windows.
![]()