5G Multi-access Edge Computing Security
Table of Contents
10.1
Expand all | Collapse all
5G Multi-access Edge Computing Security
5G Multi-access Edge Computing Security provides granular
visibility and control for Packet Forwarding Control Protocol (PFCP) traffic
by extracting information (such as subscriber ID or equipment ID)
at the mobile edge, so you can apply security policy by subscriber,
by equipment, or by network slice. It provides security at the protocol
level through stateful inspection for PFCP traffic on 4G/LTE and
5G networks, in addition to reduced latency and higher bandwidth.
By
providing context-based visibility into threats, 5G Multi-access
Edge Computing Security protects networks from potential threats
such as vulnerabilities, malware, and viruses. It secures devices
and user that connect to multi-access edge computing (MEC), as well
as applications hosted on MEC from attacks such as Denial of Service
(DoS) and spoofing.
The following platforms support 5G Multi-Edge
Security:
- PA-5200 Series
- VM-300 Series
- VM-500 Series
- VM-700 Series
- CN-Series on OpenShift
The
following log events have been added for 5G Multi-access Edge Computing
Security:
| 5G Multi-Edge Security Log Events |
|---|
| PFCP session message not matching existing PFCP association |
| PFCP association message sequence number mismatch |
| PFCP session message sequence number mismatch |
| PFCP association message is out of order |
| PFCP session message is out of order |
| PFCP association message |
| PFCP session message |
| PFCP association start |
| PFCP association end |
| PFCP session start |
| PFCP session end |
- Enable GTP Security, commit
your changes, and reboot.If you enable stateful inspection for PFCP traffic, the following options are not available:
- IMSI/APN/RAT filtering
- GTP-U tunnel limiting
- GTPv1-C stateful inspection
- GTPv2-C stateful inspection
- 5G-HTTP2 for 5G-C
- End User IP Address Spoofing for GTP-U
- Create a Mobile Network Protection Profile and enable
5G Multi-access Edge Computing Security.
- Select ObjectsSecurity ProfilesMobile Network Protection.
- Add a profile and enter a Name, such as 5G Multi-access Edge Computing Security.
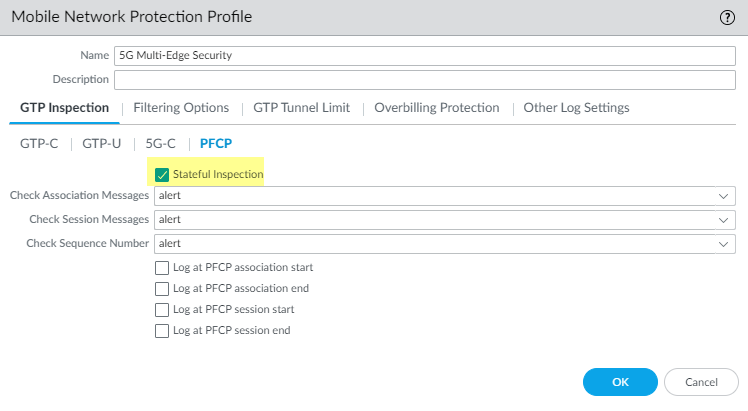
- On the PFCP tab, enable Stateful
Inspection.
![]()
- Select which state checks you want the firewall to perform
on PFCP traffic and the action you want the firewall to take if
a state check is not successful.
- Determine the state checks you want to use.
- Check Association Messages—Checks for any PFCP association messages that are out of order or that have been rejected.
- Check Session Messages—Checks for any PFCP session messages that are out of order or that have been rejected.
- Check Sequence Number—Confirms that the sequence number in the PFCP matches the sequence number in the PFCP request message.
- Select the action you want the firewall to take if
a state check is not successful.
- allow—Allow the traffic and do not generate a log entry in the GTP log.
- block—Block the traffic and generate a high-severity log entry in the GTP log.
- alert—(Default) Allow the traffic and generate a high-severity log entry in the GTP log.
- Determine the state checks you want to use.
- (Optional) Configure logging for PFCP traffic.
- Select when you want the firewall to generate a
log entry.
- Log at PFCP association start
- Log at PFCP association end
- Log at PFCP session start
- Log at PFCP session end
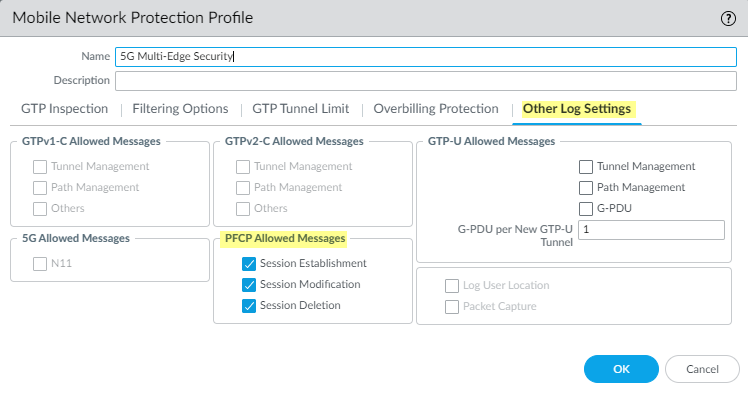
- On the Other Log Settings tab, select
the type of PFCP Allowed Messages you want to
include in the logs.
- Session Establishment—These PFCP messages set up the session, including establishing the GTP-U tunnel.
- Session Modification—These PFCP messages are sent if the session ID or PDR ID changes (for example, as a result of moving from a 4G to a 5G network). It includes messages such as PFCP Session Modification Request and PFCP Session Modification Response.
- Session Deletion—These PFCP messages terminate the PFCP session, including releasing associated resources.
![]()
- Select when you want the firewall to generate a
log entry.
- Click OK.
- Create a Security policy rule that applies your Mobile Network Protection profile to PFCP traffic by selecting the Mobile Network Protection profile you created.
- Create another Security policy rule based on equipment ID, subscriber ID, or network slice.
- Commit your changes.