Enhanced Application Logs for Palo Alto Networks Cloud Services
Table of Contents
End-of-Life (EoL)
Enhanced Application Logs for Palo Alto Networks Cloud Services
The firewall can collect data that increases
visibility into network activity for Palo Alto Networks apps and
services, like Cortex XDR and IoT Security. These enhanced application
logs are designed strictly for Palo Alto Networks apps and services
to consume and process; you cannot view enhanced application logs
on the firewall or Panorama. Only firewalls sending logs to the
logging service can generate enhanced application logs.
Follow
these procedures to enable log forwarding for enhanced application
logs for Cortex XDR and IoT Security:
Cortex XDR
Examples of the types of data that enhanced
application logs gather includes records of DNS queries, the HTTP
header User Agent field that specifies the web browser or tool used
to access a URL, and information about DHCP automatic IP address
assignment. With DHCP information, for example, Cortex XDR™ can alert
on unusual activity based on hostname instead of IP address. This
allows the security analyst using Cortex XDR to meaningfully assess
whether the user’s activity is within the scope of his or her role,
and if not, to more quickly take action to stop the activity.
To
benefit from the most comprehensive set of enhanced application
logs, you should enable User-ID; deployments for the Windows-based
User-ID agent and the PAN-OS integrated User-ID agent both collect
some data that is not reflected in the firewall User-ID logs but
that is useful towards associating network activity with specific
users.
To start forwarding enhanced application logs to Cortex
Data Lake, turn on enhanced application logging globally, and then
enable it on a per-security rule basis (using a Log Forwarding profile).
The global setting is required and captures data for traffic that
is not session-based (ARP requests, for example). The per-security
policy rule setting is strongly recommended; the majority of enhanced
application logs are gathered from the session-based traffic that
your security policy rules enforce.
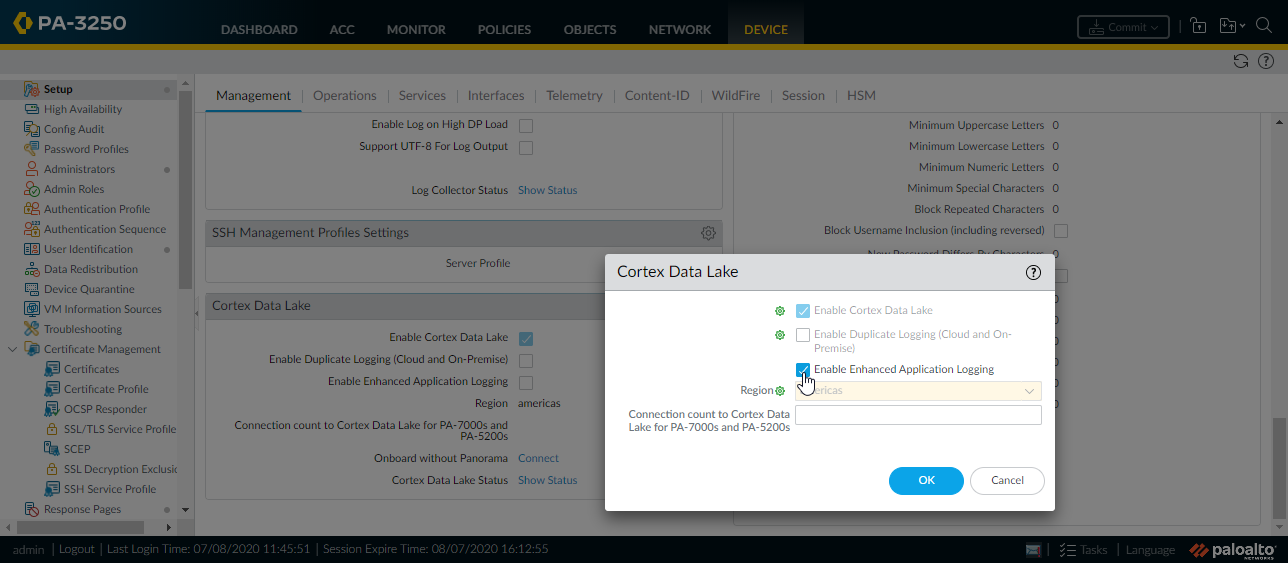
- Enhanced application logging requires a Cortex Data Lake subscription and User-ID is also recommended. Here are steps to get started with Cortex Data Lake and enable User-ID.To Enable Enhanced Application Logging on the firewall, select DeviceSetupManagementCortex Data Lake and edit Cortex Data Lake Settings.
![]() Continue to enable enhanced application logging for the security policy rules that control the traffic into which you want extended visibility.
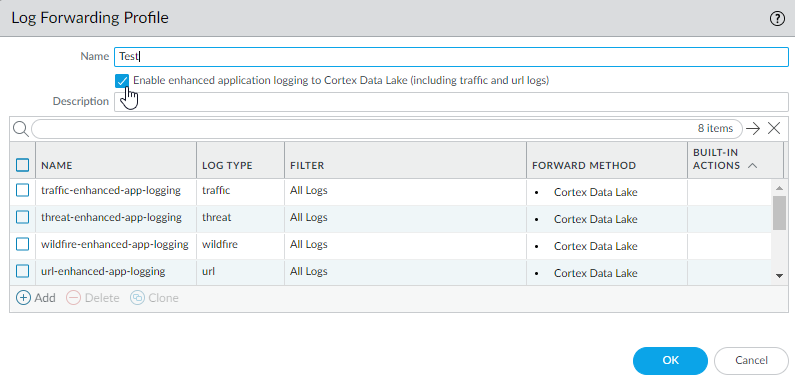
Continue to enable enhanced application logging for the security policy rules that control the traffic into which you want extended visibility.- Select ObjectsLog Forwarding and Add or modify a log forwarding profile.Update the profile to Enable enhanced application logging to Cortex Data Lake (including traffic and url logs).
![]() Notice that when you enable enhanced application logging in a Log Forwarding profile, match lists that specify the log types required for enhanced application logging are automatically added to the profile.Click OK to save the profile and continue to update as many profiles as needed.Ensure that the Log Forwarding profile that you’ve updated is attached to a security policy rule, to trigger log generation and forwarding for the traffic matched to the rule.
Notice that when you enable enhanced application logging in a Log Forwarding profile, match lists that specify the log types required for enhanced application logging are automatically added to the profile.Click OK to save the profile and continue to update as many profiles as needed.Ensure that the Log Forwarding profile that you’ve updated is attached to a security policy rule, to trigger log generation and forwarding for the traffic matched to the rule.- Select PoliciesSecurity to view the profiles attached to each security policy rule.
- To update the log forwarding profile attached to a rule, Add or edit a rule and select PoliciesSecurityActionsLog Forwarding and select the Log Forwarding profile enabled with enhanced application logging.
IoT Security
One part of the firewall setup for IoT Security involves creating a Log Forwarding profile and applying it to Security policy rules. Although you can apply a profile to each rule individually, a simpler approach is to select a predefined Log Forwarding profile and apply it to as many rules as you like in bulk. The following steps explain this approach to adding the predefined Log Forwarding profile to Security policy rules in bulk.To use this workflow, you must have already configured Security policy rules, enabled logging on the rules, and enabled logging services with enhanced application logging.- Apply a Log Forwarding profile for IoT Security to Security policy rules.
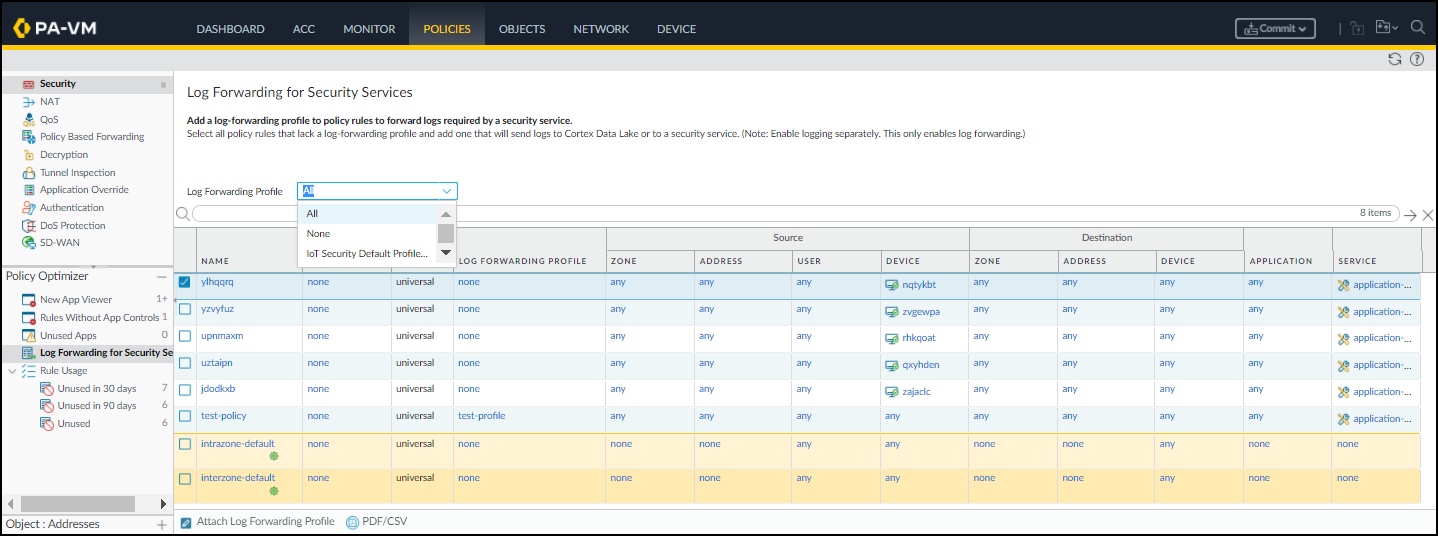
- Log in to your next-generation firewall and select PoliciesLog Forwarding for Security Services in the Policy Optimizer section.
- To view all your Security policy rules—including those with a Log Forwarding profile and those without it—choose All for Log Forwarding Profile.
![]()
- Select the rules for which you want to forward logs to the logging service.
- Attach Log Forwarding Profile at the bottom of the page.
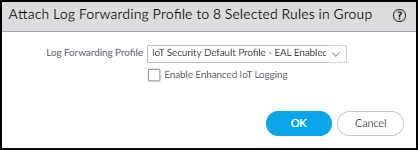
- To apply the default Log Forwarding profile to your rules, choose IoT Security Default Profile - EAL Enabled and OK.The default profile is preconfigured to provide IoT Security with all the log types it requires, including enhanced application logs (EALs).You don’t have to Enable Enhanced IoT Logging because enhanced application logging (EAL) is already enabled on IoT Security Default Profile.
![]() orTo add the forwarding of EALs to an existing Log Forwarding profile that doesn’t already have it, choose it from the Log Forwarding Profile list, select Enable Enhanced IoT Logging and then OK.When you Enable Enhanced IoT Logging, PAN-OS updates the chosen Log Forwarding profile itself and thereby enables enhanced log forwarding on all rules that use the same Log Forwarding profile.PAN-OS adds the chosen Log Forwarding profile to those rules that don’t already have one and replaces previously assigned profiles with this one.
orTo add the forwarding of EALs to an existing Log Forwarding profile that doesn’t already have it, choose it from the Log Forwarding Profile list, select Enable Enhanced IoT Logging and then OK.When you Enable Enhanced IoT Logging, PAN-OS updates the chosen Log Forwarding profile itself and thereby enables enhanced log forwarding on all rules that use the same Log Forwarding profile.PAN-OS adds the chosen Log Forwarding profile to those rules that don’t already have one and replaces previously assigned profiles with this one.
Commit your changes.