SD-WAN
Segment SD-WAN Traffic using VLAN Tags
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
SD-WAN Docs
-
- SD-WAN Deployment Workflow
-
- Add SD-WAN Branch or Hub Firewall
- Configure Certificate-based Authentication for Strong Security
- Quickly Add Multiple SD-WAN Devices with Bulk Import
- Configure SD-WAN Devices in HA Mode
- Onboard PAN-OS Firewalls to Prisma Access for Cloud-based Security
- Plan Your Topology for SD-WAN with Auto VPN
- Create a Full Mesh VPN Cluster with DDNS Service
- Create a Static Route for SD-WAN
- Configure Advanced Routing for SD-WAN
Segment SD-WAN Traffic using VLAN Tags
Configure Layer 3 subinterfaces for SD-WAN.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
SD-WAN
supports
Layer 3 subinterfaces so that the firewall can segment traffic
using VLAN tags. The following task shows how to create a Layer3 subinterface that
uses a static IP address and how to create one that uses DHCP to get its address. It
shows how to assign a VLAN tag to the subinterface and enable SD-WAN
on the subinterface. Create an SD-WAN interface profile to define
each ISP connection and assign the profile to the corresponding subinterface (a
virtual SD-WAN interface).
If you configure SD-WAN Layer 3 subinterfaces on VM-Series firewalls, the
VMware configuration must have respective portgroups attached to those interfaces
that allow all VLANs.
PPPoE is not supported on subinterfaces.
- Configure an SD-WAN interface profile for each ISP connection (subinterface) to define its link attributes.
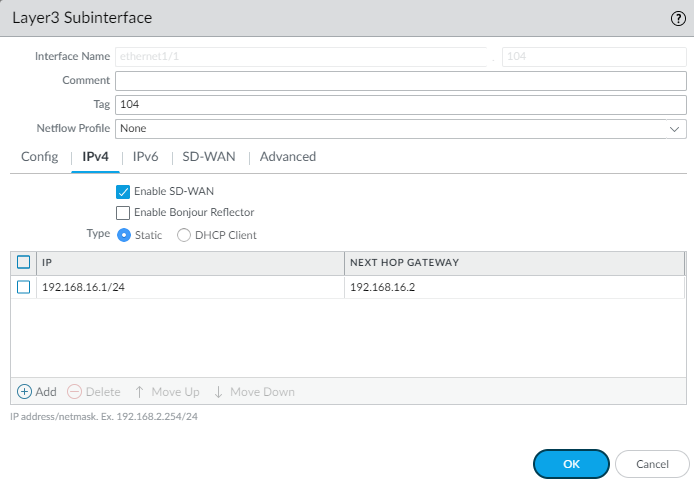
- Create a Layer 3 subinterface that uses a static IPv4 address.
- Select NetworkInterfacesEthernet and in the Template field select a template.
- Select an interface.
- For Interface Type, select Layer3 and click OK.
- Highlight the interface and click Add Subinterface at the bottom of the screen.
- After the Interface Name and period, enter the subinterface number.
- Enter a Tag for the subinterface (range is 1 to 4,094). For ease of use, make the tag the same number as the subinterface ID.
- On the IPv4 tab, Enable SD-WAN.
- Select the Type of address: Static.
- Add the IP address and subnet mask.
- Enter the IP address of the Next Hop Gateway.
- Click OK.

- (SD-WAN plugin 3.2.0 and later versions) Create a Layer 3 subinterface that uses a static IPv6 address.
- Perform the first six substeps of the step to create a Layer 3 subinterface that uses a static IPv4 address, because they are the same for an IPv6 address.
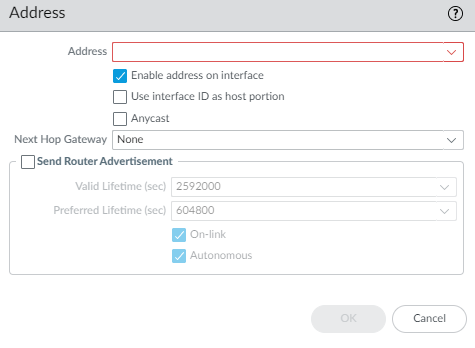
- On the IPv6 tab, Enable IPv6 on the interface and Enable SD-WAN.
- In the EUI-64 (default 64-bit Extended Unique Identifier) field, enter the 64-bit EUI in hexadecimal format. If you leave this field blank, the firewall uses the EUI-64 generated from the MAC address of the physical interface. If you enable the Use interface ID as host portion option when adding an address, the firewall uses the Interface ID as the host portion of that address.
- Select the Type of address: Static.
- Select Address Assignment.

- Add an IPv6 Address for the interface or select New Variable to create the variable. SD-WAN supports one IPv6 address per physical interface.
- Enable address on interface.

- Use interface ID as host portion—.See the third substep above for explanation.
- Anycast—Select to make the IPv6 address (route) an Anycast address (route), which means multiple locations can advertise the same prefix, and IPv6 sends the anycast traffic to the node it considers the nearest, based on routing protocol costs and other factors.
- Next Hop Gateway—Enter the IPv6 address of the Next Hop Gateway (the next hop from the IPv6 address you entered). The Next Hop Gateway must be on the same subnet as the IPv6 address. The Next Hop Gateway is the IP address of the ISP’s default router that the ISP gave you when you bought the service. It is the next hop IP address to which the firewall sends traffic to reach the ISP’s network, and ultimately, the internet and the hub.
- Send Router Advertisement—Select to enable the firewall to send this address in Router Advertisements (RAs), in which case you must also enable the global Enable Router Advertisement option for the interface (on the Router Advertisement tab).
- Valid Lifetime (sec)—Enter the valid lifetime (in seconds) that the firewall considers the address valid. The valid lifetime must equal or exceed the Preferred Lifetime (sec) (default is 2,592,000).
- Preferred Lifetime (sec)—Enter the preferred lifetime (in seconds) that the valid address is preferred, which means the firewall can use it to send and receive traffic. After the preferred lifetime expires, the firewall can't use the address to establish new connections, but any existing connections are valid until the valid lifetime expires (default is 604,800).
- On-link—Select if systems that have addresses within the prefix are reachable without a router.
- Autonomous—Select if systems can independently create an IP address by combining the advertised prefix with an Interface ID.
- Click OK.
- As an alternative to a static address, create a Layer 3 subinterface that uses DHCP to get its IPv4 address.
- Select NetworkInterfacesEthernet and in the Template field, select a template stack (not a template).
- Select an interface.
- For Interface Type, select Layer3 and click OK.
- Highlight the interface and click Add Subinterfaces at the bottom of the screen.
- Highlight the subinterface and click Override.
- Highlight the subinterface and after the Interface Name and period, enter the subinterface number.
- Enter a Tag for the subinterface (range is 1 to 4,094). For ease of use, make the tag the same number as the subinterface ID.
- On the IPv4 tab, Enable SD-WAN.
- Select Type of address: DHCP Client and Enable.
- Uncheck (do not select) Automatically create default route pointing to default gateway provided by server.
- Select the Advanced tab and then the DDNS tab.
- Select Settings and Enable. The Hostname is automatically generated by the Panorama SD-WAN plugin.
- Select the Vendor as Palo Alto Networks DDNS.
- Click OK.

- Apply an SD-WAN Interface Profile to the subinterface.
- Highlight the subinterface you created and select the SD-WAN tab.
- Select the SD-WAN Interface Profile you created for this link or create a new profile.
- Click OK.
- Repeat the prior steps to add more subinterfaces to the interface.
- Commit.