Strata Logging Service
Forward Logs to Amazon Security Lake
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Strata Logging Service Docs
Forward Logs to Amazon Security Lake
Learn how to forward logs from Strata Logging Service to Amazon Security
Lake.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
| One of these:
|
You can integrate the Strata Logging Service with Amazon Security Lake to
enable forwarding of browser events and logs. These logs provide visibility into the
website access activities, along with their browser-based data handling activities.
To enable log forwarding from Strata Logging Service to Amazon Security Lake,
create a log forwarding profile in Strata Logging Service and set filters to
forward all or a subset of event logs to Amazon Security Lake. The events data sent
by the Strata Logging Service is converted to the OCSF schema, and is saved
in Parquet format in Amazon Security Lake.
You can forward only event endpoint logs from Strata Logging Service to Amazon Security Lake.
- Create an Identity and Access Management (IAM) role to permit write access to the Amazon Security Lake bucket location.
- In the AWS Management Console navigation pane of the console, click RolesCreate role.In the Select trusted entity page, select AWS accountAnother AWS account and enter the Account ID displayed in the Strata Logging Service Configure Log Forwarding Profile to Amazon Security Lake page. This allows your AWS account to assume this role, and share the logs to the desired destination.
![]() Select Require external ID and enter a password to establish connection between Amazon Security Lake and Strata Logging Service.Create policy or use an existing policy in the Add permissions page.
Select Require external ID and enter a password to establish connection between Amazon Security Lake and Strata Logging Service.Create policy or use an existing policy in the Add permissions page.- When you create a new policy, select JSON as the Policy Editor
- Edit the following code to replace DOC-EXAMPLE-BUCKET1 and
DOC-EXAMPLE-BUCKET1/* with your Amazon S3 bucket name.
⦁ { "Version":"2012-10-17", "Statement":[ { "Effect":"Allow", "Action":"s3:PutObject", "Resource": [ "arn:aws:s3:::DOC-EXAMPLE-BUCKET1", "arn:aws:s3:::DOC-EXAMPLE-BUCKET1/*" ] } ] }
- Enter a policy name and create policy.
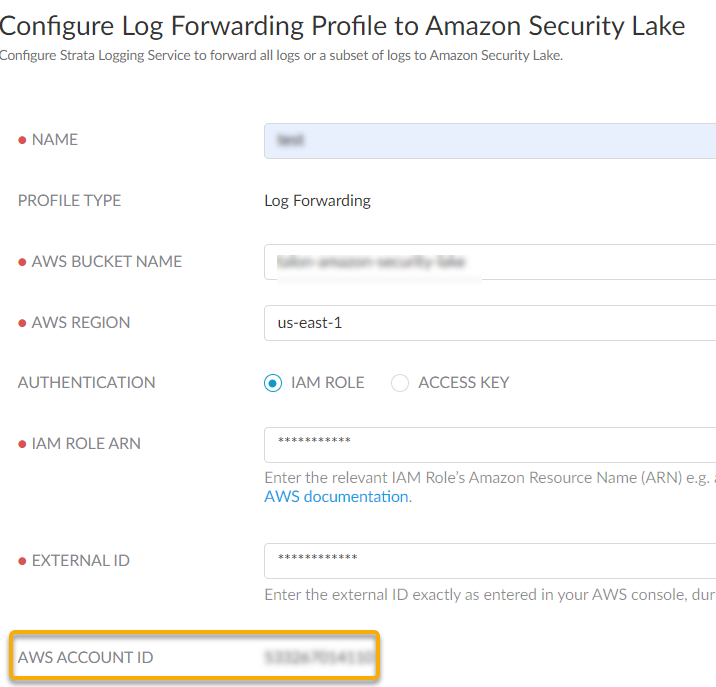
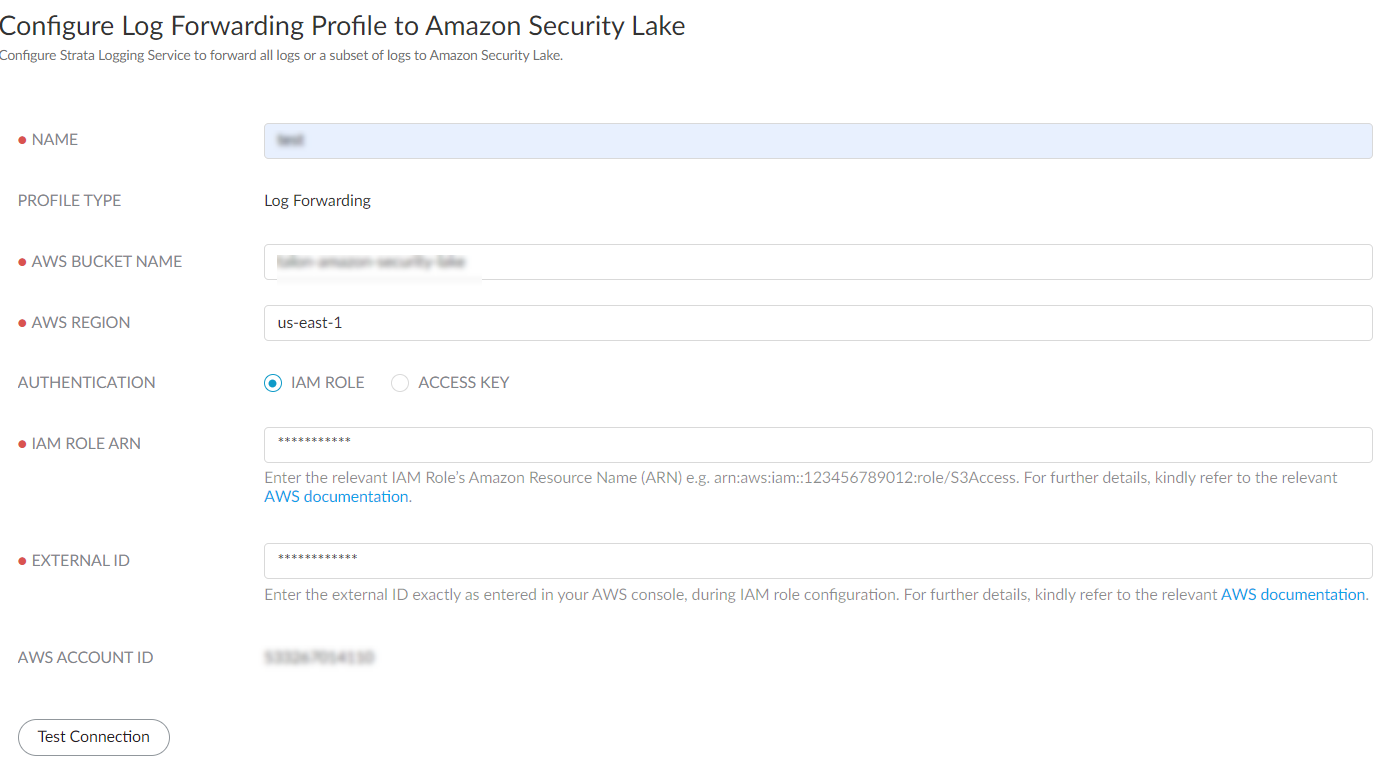
- Provide a role name and save the changes.In the Roles page, select the role you created and make a note of the IAM Role ARN. You need to use the same ARN when configuring a log forwarding profile.Sign In to the hub.Select the Strata Logging Service instance that you want to configure for log forwarding.If you have multiple Strata Logging Service instances, click the Strata Logging Service tile and select an instance from the list of those available.If you are using Strata Cloud Manager to manage Strata Logging Service, click System SettingsStrata Logging ServiceLog Forwarding forward logs to external server.Select Log ForwardingAmazon Security Lake + to add a new Amazon Security Lake profile.Configure a log forwarding profile to forward logs to Amazon Security Lake.
![]()
- Enter a descriptive Name for the profile.Enter the name of the Amazon Security Lake S3 configured bucket that is used as the storage container for your forwarded log data. You can get the name from the Amazon Console.Enter the geographic region (regional code) where the Amazon Security Lake is hosted.Select the external identification method to authenticate Amazon Security Lake.
- IAM Role
- IAM Role ARN - The Amazon Resource Names (ARN) of the role that has access to the Amazon S3 bucket. Enter the ARN you saved in step 1.f. The IAM Role ARN need to be in the following format: arn:partition:service:region:account-id:resource-type:resource-id. For example, arn:aws:iam::account:role/role-name-with-path
- External ID - The external identifier that you defined while linking the IAM role to your AWS account.
- Access Key- If you have created a long-term access key to authenticate your AWS account, enter the key and secret password here.
- To create an access key for the Amazon S3 bucket:
- Log in to AWS Management Console with your AWS account ID.
- On the Console Home page, select the IAM service.
- Select Users and then select Create user from the navigation pane.
- On the Specify user details page, enter the name for the new user.
- Do not select Provide user access to the – AWS Management Console and click Next.
- Set Permissions for the
user. Here is a sample of the JSON code to set the
permission boundaries in the
policy:{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": "s3:PutObject", "Resource": [ "arn:aws:s3:::DOC-EXAMPLE-BUCKET1", "arn:aws:s3:::DOC-EXAMPLE-BUCKET1/*" ] } ] }
- Review the selection and create the user.
- In the Summary page, select Security credentials > Create Access Key.
- Select the Third-party service option as the reason for enabling the access key and confirm the recommendation to create the access key.
- Retrieve the access key and use it while configuring the log forwarding.
- Use this AWS Account ID to connect to the Amazon Security Lake bucket.Test Connection to ensure that the Strata Logging Service can communicate with the receiver.This sends an empty log to the sls_test_events folder in the configured destination to verify that transmission is possible.If the test fails, you won't be able to proceed.Click Next.Specify the Payload Format as PARQUET - the log format in which the Strata Logging Service forwards logs.(Optional) To receive a STATUS NOTIFICATION when Strata Logging Service is unable to connect to the Amazon Security Lake, enter the email address at which you’d like to receive the notification.You will continue to receive these notifications at least once every 60 minutes until connectivity is restored. If the connectivity issue is addressed within 72 hours, no logs will be lost. However, any log older than 72 hours following the service disconnection could be lost.Add the log type as Endpoint > Events and optionally write a query to create filter to forward only the logs that are most critical to you. Save your changesIf you want to forward all logs of the type you selected, do not enter a query.You can forward only the following events endpoint log fields to Amazon Security Lake. Refer to Log Reference guide for information on the log fields
- Event Log Fields
- policy.action
- user.id
- user.name
- user.email
- user.tenant_id
- device.device_uuid
- device.hostname
- device.ip_address
- device.os.type
- network.http.method
- network.http.url
- network.http.classifications
- network.http.url
- network.http.status
- id
- batch_id
- device.browser_type
- device.browser_version
Save your changes.Verify that the Status of your forwarding profile is Running ().![]() Verify if the logs are forwarded to the destination location. This is a sample path: /Amazon S3 bucket location > folder name > logsource.logtype > year > month > date(Optional) You can use the running Amazon Security Lake forwarding profile to forward past logs spanning up to 3 days.
Verify if the logs are forwarded to the destination location. This is a sample path: /Amazon S3 bucket location > folder name > logsource.logtype > year > month > date(Optional) You can use the running Amazon Security Lake forwarding profile to forward past logs spanning up to 3 days.