Configure 5G Subscriber ID Security
Table of Contents
10.0 (EoL)
Expand all | Collapse all
End-of-Life (EoL)
Configure 5G Subscriber ID Security
Configure 5G subscriber ID security.
After you’ve read about 5G Equipment ID and Subscriber ID Security, prepare
to configure subscriber ID security. Gather the IP addresses of
the following devices in your topology so that you can use these
addresses in Security policy rules controlling traffic to and from
these devices:
- gNodeB (gNB)
- Access and Mobility Management Function (AMF)
- Session Management Function (SMF)
- User Plane Function (UPF)
- Enable GTP security.
- Select DeviceSetupManagementGeneral Settings. Select GTP Security.
- Click OK.
- Commit the change.
- Select DeviceSetupOperations and Reboot Device.
- Enable inspection of 5G HTTP/2 control packets; create
a Mobile Network Protection profile.
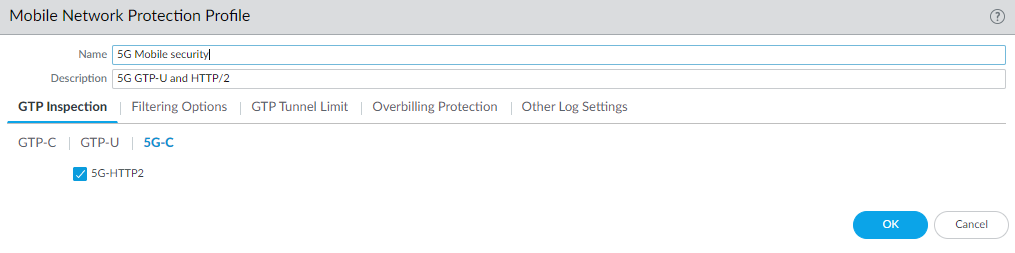
- Select ObjectsSecurity ProfilesMobile Network Protection.
- Add a profile by Name, for example, 5G Mobile security.
- Enter a Description.
- On the GTP Inspection tab, select 5G-C.
- Enable 5G-HTTP2 to enable inspection
of 5G HTTP/2 control packets.
![]()
- Select GTP-U and enable GTP-U Content Inspection to correlate context from 5G HTTP/2 control packets (Subscriber IDs and Equipment IDs) to IP user traffic inside a GTP-U tunnel.
- Select Filtering Options and RAT Filtering;
for example, you can allow NR (New Radio)
and block other RATs.
![]()
- (Optional) Select Other Log Settings and Log User Location.
- (Optional) To troubleshoot, select Other Log Settings and select 5G Allowed Messages N11 (the HTTP/2 control messages). You can also enable GTP-U Allowed Messages for Tunnel Management, Path Management, and G-PDU.
- Click OK.
- Create address objects for the IP addresses assigned to the network elements in your topology, such as the AMF on the N11 interface, the gNB on the N3 interface, the SMF on the N11 interface, and the UPF on the N3 interface.
- (Optional) Create an External Dynamic List (EDL) of Type Subscriber Identity List; the Source of the list provides access to a server that provides identifiers of IoT devices connected to the 5G network, for which you want to allow (or deny) traffic.
- Create a Security policy rule that applies your Mobile
Network Protection profile to application traffic.
- Select PoliciesSecurity and Add a Security policy rule by Name.
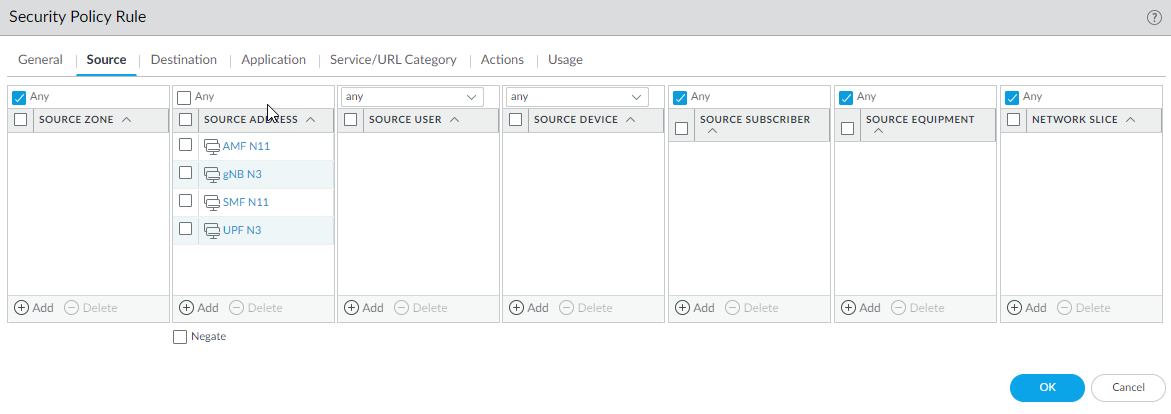
- Select Source tab and Add a Source Zone or select Any.
- For Source Address, Add the
address objects for the 5G element endpoints on the N3 and N11 interfaces
that you want to allow.
![]()
- For Destination, Add the Destination Address address objects for the 5G element endpoints on the N3 and N11 interfaces that you want to allow (the same ones you allowed for Source Address).
- Add the Applications to allow, such as the user plane, which is gtp-u and web-browsing, which has HTTP/2.
- On the Actions tab, select the Action, such as Allow.
- Select the Mobile Network Protection profile you created.
- Select other profiles you want to apply, such as Vulnerability Protection.
- Select Log Settings, such as Log at Session Start and Log at Session End.
- Click OK.
- Create another Security policy rule based on Subscriber
ID.
- Select PoliciesSecurity and Add a Security policy rule by Name, for example, Equipment ID Security.
- Select Source tab and Add a Source Zone or select Any.
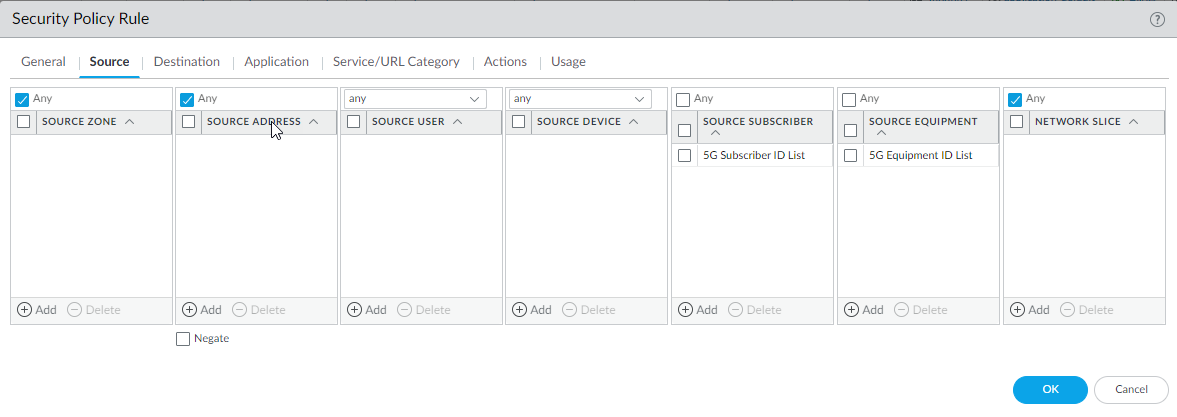
- Add one or more Source
Subscriber IDs in any of the following formats (if you
configured an EDL, specify that EDL in this step):
- 5G Subscriber Permanent Identifier (SUPI) including IMSI
- IMSI (14 or 15 digits)
- Range of IMSI values separated by a hyphen. In a range, only the 11th digit through the 15th digit of the IMSI can change from the start of the range to the end of the range; for example, 111111111111122-111111111119999.
- IMSI prefix of six digits, with an asterisk (*) as the wildcard after the prefix
- EDL that specifies IMSIs
![]()
- (Optional) You can add Source Equipment and Network Slice names to this Security policy rule to make the rule more restrictive.
- Specify Destination Zone, Destination Address, and Destination Device as Any.
- Add the Applications to allow, for example, ssh, ssl, radmin, and telnet.
- On the Actions tab, select the Action, such as Allow.
- Select profiles you want to apply, such as Antivirus, Vulnerability Protection, and Anti-Spyware.
- Select Log Settings, such as Log at Session Start and Log at Session End.
- Click OK.
- Commit.