SD-WAN
Define Your Custom SD-WAN Application Thresholds
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
SD-WAN Docs
-
-
-
-
- 3.4
- 3.3
- 3.2
- 3.1
- 3.0
- 2.2
- 2.1
- 2.0
- 1.0
-
Define Your Custom SD-WAN Application Thresholds
Create a path quality profile to control when the firewall replaces a deteriorating
path with a new path for packets matching the SD-WAN policy rule.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
Create a Path Quality profile for each set of business-critical and latency-sensitive
applications, application filters, application groups, services, service objects and
service group objects that has unique network quality (health) requirements based on
latency, jitter, and packet loss percentage. Applications and services can share a
Path Quality profile. Specify the maximum threshold for each parameter, above which
the firewall considers the path deteriorated enough to select a better path.
As an alternative to creating a Path Quality profile, you can use any of the
predefined Path Quality profiles, such as general-business,
voip-video, file-sharing,
audio-streaming, photo-video, and
remote-access, and more. The predefined profiles are set
up to optimize the latency, jitter, and packet loss thresholds for the type of
applications and services suggested by the name of the profile.
The predefined Path Quality profiles for a
device
group are based on the default Probe Frequency settings
in the SD-WAN Interface profile
template.
If you change the default Probe Frequency setting, you must adjust the
Packet Loss percentage threshold in the Path Quality
profile for the firewalls in a Device Group that are affected by the
template
where you changed the Interface profile.
The firewall treats the latency, jitter, and packet loss thresholds as OR conditions,
meaning if any one of the thresholds is exceeded, the firewall selects the new best
(preferred) path. Any path that has latency, jitter, and packet loss less than or
equal to all three thresholds is considered qualified and the firewall selected the
path based on the associated Traffic Distribution profile.
By default, the firewall measures latency and
jitter every 200ms and takes an average of the last three
measurements to measure path quality in a sliding window. You can modify this
behavior by selecting aggressive or relaxed path monitoring when you define your ISP connections and link types.
If a path fails over because it exceeded the configured packet
loss threshold, the firewall still sends probing packets on the
failed path and calculates its packet loss percentage as the path recovers. It can
take approximately three minutes for the packet loss percentage on a recovered path
to fall below the packet loss threshold configured in the Path Quality profile. For
example, suppose an SD-WAN policy rule for an application has a Path
Quality profile that specifies a packet loss threshold of 1% and a Traffic
Distribution profile that specifies Top Down distribution with tag 1 (applied to
tunnel.1) first on the list and tag 2 (applied to tunnel.2) next on the list. When
tunnel.1 exceeds 1% packet loss, the data packets fail over to tunnel.2. After
tunnel.1 recovers to 0% packet loss (based on probing packets), it can take up to
three minutes for the monitored packet loss rate for tunnel.1 to drop below 1%, at
which time the firewall then selects tunnel.1 as the best path again.
The sensitivity setting indicates which parameter (latency, jitter, or packet loss)
is more important (preferred) for the applications to which the profile applies.
When the firewall evaluates link quality, it considers a parameter with a
high setting first. For example, when the firewall
compares two links, suppose one link has 100ms latency and 20ms jitter; the other
link has 300ms latency and 10 ms jitter. If the sensitivity for latency is high, the
firewall chooses the first link. If the sensitivity for jitter is high, the firewall
chooses the second link. If the parameters have the same sensitivity (by default the
parameters are set to medium), the firewall evaluates packet
loss first, then latency, and jitter last.
As the SD-WAN Traffic Distribution Profiles concept states, the new path
selection occurs in less than one second if you leave path monitoring and probe frequency with default settings;
otherwise, new path selection could take more than one second. To achieve subsecond
failover based on packet loss, you must set the latency sensitivity to
high and the latency threshold to no more than 250ms.
Reference the Path Quality profile in an SD-WAN policy rule to control the threshold
at which the firewall replaces a deteriorating path with a new path for matching
application packets.
PAN-OS & Panorama
In PAN-OS, create a path quality profile to control when the firewall replaces a
deteriorating path with a new path for packets matching the SD-WAN policy
rule.
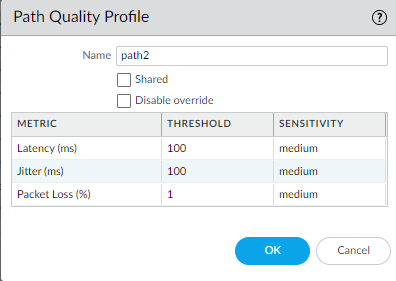
- Log in to the Panorama Web Interface.Select a Device Group.Select ObjectsSD-WAN Link ManagementPath Quality Profile.Add a Path Quality profile by Name using a maximum of 31 alphanumeric characters.
![]() For Latency, double-click the Threshold value and enter the number of milliseconds allowed for a packet to leave the firewall, arrive at the opposite end of the SD-WAN tunnel, and a response packet to return to the firewall before the threshold is exceeded (range is 10 to 2,000; default is 100).For Latency, select the Sensitivity (low, medium, or high). Default is medium.Click the arrow at the end of the Threshold column to sort thresholds in ascending or descending numerical order.For Jitter, double-click the Threshold value and enter the number of milliseconds (range is 10 to 1,000; default is 100).For Jitter, select the Sensitivity (low, medium, or high). Default is medium.For Packet Loss, double-click the Threshold value and enter the percentage of packets lost on the link before the threshold is exceeded (range is 1 to 100.0; default is 1).Setting the Sensitivity for Packet Loss has no effect, so leave the default setting.If you change the Probe Frequency in an SD-WAN Interface profile for a Panorama template, you should also adjust the Packet Loss threshold for a Panorama device group.Click OK.Commit and Commit and Push your configuration changes.Commit your changes.Repeat this task for every Device Group.
For Latency, double-click the Threshold value and enter the number of milliseconds allowed for a packet to leave the firewall, arrive at the opposite end of the SD-WAN tunnel, and a response packet to return to the firewall before the threshold is exceeded (range is 10 to 2,000; default is 100).For Latency, select the Sensitivity (low, medium, or high). Default is medium.Click the arrow at the end of the Threshold column to sort thresholds in ascending or descending numerical order.For Jitter, double-click the Threshold value and enter the number of milliseconds (range is 10 to 1,000; default is 100).For Jitter, select the Sensitivity (low, medium, or high). Default is medium.For Packet Loss, double-click the Threshold value and enter the percentage of packets lost on the link before the threshold is exceeded (range is 1 to 100.0; default is 1).Setting the Sensitivity for Packet Loss has no effect, so leave the default setting.If you change the Probe Frequency in an SD-WAN Interface profile for a Panorama template, you should also adjust the Packet Loss threshold for a Panorama device group.Click OK.Commit and Commit and Push your configuration changes.Commit your changes.Repeat this task for every Device Group.Strata Cloud Manager
In strata cloud manager, create a path quality profile to control when the firewall replaces a deteriorating path with a new path for packets matching the SD-WAN policy rule.- Log in to Strata Cloud Manager.Select ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma Access and in the Overview, select the branch folder for which you want to create your SD-WAN Link Management profiles.To make the Error Correction profile available to all SD-WAN firewalls regardless of folder association, select All Firewalls.(Optional) Create a custom Path Quality profile.Create a custom Path Quality profile for each set of business-critical and latency-sensitive applications, application filters, application groups, services, service objects and service group objects that has unique network quality (health) requirements based on latency, jitter, and packet loss percentage specific to your business needs. Applications and services can share a Path Quality profile.The firewall treats the latency, jitter, and packet loss thresholds as OR conditions, meaning if any one of the thresholds is exceeded, the firewall selects the new best (preferred) path. Any path that has latency, jitter, and packet loss less than or equal to all three thresholds is considered qualified and the firewall selected the path based on the associated Traffic Distribution profile.As an alternative to creating a Path Quality profile, you can use any of the predefined Path Quality profiles, such as general-business, voip-video, file-sharing, audio-streaming, photo-video, and remote-access, and more. The predefined profiles are set up to optimize the latency, jitter, and packet loss thresholds for the type of applications and services suggested by the name of the profile.
- Select Network PoliciesSD-WAN PolicyProfilesPath Quality and select the branch folder for which you want to create the Path Quality profile.Add Path Quality Profile.Enter a descriptive Name.Up to 31 alphanumeric characters are supported.Configure the Latency settings.The latency settings specify the number of milliseconds allowed for a packet to leave the firewall, arrive at the opposite end of the SD-WAN tunnel, and a response packet to return to the firewall before the threshold is exceeded.
- Specify the latency Threshold in milliseconds.Range is 10 to 3000. Default is 100.
- Specify the latency threshold Sensitivity.You can select Low, Medium (default), or High sensitivity.
Configure the Jitter settings.The jitter settings specify the number of milliseconds allowed for packet disruptions to impact data packet arrival. High jitter may cause packets to be received out of order or to be discarded.- Specify the jitter Threshold in milliseconds.Range is 10 to 2000. Default is 100.
- Specify the latency threshold Sensitivity.You can select Low, Medium (default), or High sensitivity.
Configure the Packet Loss settings.The packet loss settings specify the percentage of packets lost on the link before the threshold is exceeded.Range is 1 to 100. Default is 1.Save.