Network Security
Configure Your Environment to Access an External Dynamic List
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Network Security Docs
Configure Your Environment to Access an External Dynamic List
With an active Threat Prevention license, Palo Alto Networks provides built-in IP
address EDLs that you can use to protect against malicious hosts.
Configuring your configuration to access an external dynamic list is a
critical aspect of optimizing network security and ensuring real-time threat
intelligence updates. An external dynamic list, often referred to as an external
dynamic list, allows your configuration to dynamically update its security rules based on external threat indicators. This integration ensures that your
configuration remains up-to-date with the latest threat intelligence, enhancing its
ability to detect and mitigate emerging cyberthreats effectively.
To begin the configuration process, it's essential to gather the necessary
information about the external dynamic list, such as the list URL, list type (IPv4,
IPv6, domain, etc.), and any authentication credentials required to access the list.
Once you have this information, you’ll:
- Define your external dynamic list profileNavigate to the Objects tab and select External Dynamic Lists. Here, you will create a new external dynamic list profile by providing a name, description, and the URL of the external list. Specify the refresh interval, which determines how frequently the your configuration fetches updates from the specified URL. Configure any necessary authentication parameters, if applicable.
- Incorporate your external dynamic list profile into your Security policy
rulesThis is done by referencing the external dynamic list within security rules, allowing your configuration to utilize the external list to match and enforce policies dynamically. Update the rules accordingly, considering the specific use case and security requirements of your network.
- Monitor your external dynamic list configurationRegularly monitoring and validating the external dynamic list configuration is crucial to ensure that your configuration continues to receive timely threat intelligence updates. Additionally, ongoing adjustments and fine-tuning of security rules based on the acquired threat intelligence will help maintain an effective and robust security posture against evolving cyberthreats.
Follow these steps to configure your environment to access an external dynamic list
Configure Your Environment to Access an External Dynamic List (Strata Cloud Manager)
Learn about how to configure your environment to access and EDL in Strata Cloud
Manager.
You must establish the connection between your environment and the source that hosts
the external dynamic list before you can Enforce Policy on an External Dynamic
List.
- Find an external dynamic list to use with your configuration.
- Create an external dynamic list and host it on a web server. Enter IP addresses, domains, or URLs in a blank text file. Each list entry must be on a separate line. For example:financialtimes.co.inwww.wallaby.au/joeywww.exyang.com/auto-tutorials/How-to-enter-Data-for-Success.aspxSee the Formatting Guidelines for an External Dynamic List to ensure that your environment doesn't skip list entries. To prevent commit errors and invalid entries, do not prefix http:// or https:// to any of the entries.
- Use an external dynamic list hosted by another source and verify that it follows the Formatting Guidelines for an External Dynamic List.
Select ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessObjectsExternal Dynamic Lists.Select Add External Dynamic List and enter a descriptive Name for the list.Select the list Type (for example, URL List).Ensure that the list only includes entries for the list type. See Verify whether entries in the external dynamic list were ignored or skipped.If you using a Domain List, you can optionally enable Automatically expand to include subdomains to also include the subdomains of a specified domain. For example, if your domain list includes paloaltonetworks.com, all lower level components of the domain name (e.g., *.paloaltonetworks.com) will also be included as part of the list. Keep in mind, when this setting is enabled, each domain in a given list requires an additional entry, effectively doubling the number of entries that are consumed.Enter the Source for the list you just created on the web server. The source must include the full path to access the list. For example, https://1.2.3.4/EDL_IP_2015.- If you are creating a Predefined IP external dynamic list, select a Palo Alto Networks malicious IP address feed to use as a source.
- If you are creating a Predefined URL external dynamic list, select panw-auth-portal-exclude-list as a source.
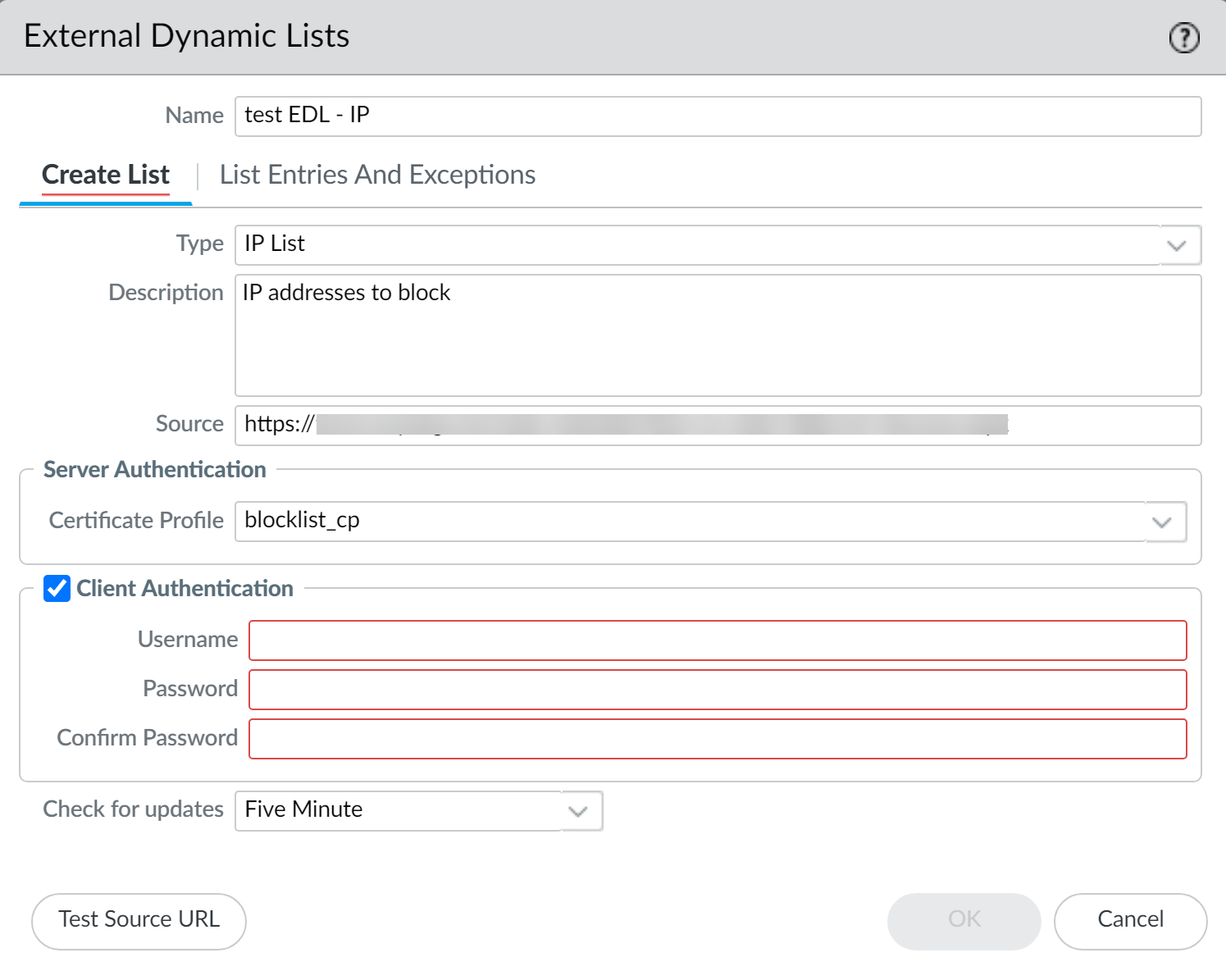
If the list source is secured with SSL (i.e. lists with an HTTPS URL), enable server authentication. Select a Certificate Profile or create a New Certificate Profile for authenticating the server that hosts the list. The certificate profile you select must have root certificate authority (CA) and intermediate CA certificates that match the certificates installed on the server you are authenticating.Maximize the number of external dynamic lists that you can use to enforce policy. Use the same certificate profile to authenticate external dynamic lists from the same source URL. If you assign different certificate profiles to external dynamic lists from the same source URL, your environment counts each list as a unique external dynamic list.Enable client authentication if the list source has an HTTPS URL and requires basic HTTP authentication for list access.- Select Client Authentication.Enter a valid Username to access the list.Enter the Password and Confirm Password.
![]() (Optional) Specify the frequency at which your environment should Check for updates to the list. By default, the list is retrieved once every hour and commits the changes.The interval is relative to the last commit. So, for the five-minute interval, the commit occurs in 5 minutes if the last commit was an hour ago. To retrieve the list immediately, see Retrieve an External Dynamic List from the Web Server.Click Save and Push Config.(Optional) EDLs are shown top to bottom, in order of evaluation. Use the directional controls at the bottom of the page to change the list order. This allows you to or order the lists to make sure the most important EDLs are committed before capacity limits are reached.Enforce Policy on an External Dynamic List.If the server or client authentication fails, your environment ceases to enforce policy based on the last successfully retrieved external dynamic list. Find External Dynamic Lists That Failed Authentication and view the reasons for authentication failure.
(Optional) Specify the frequency at which your environment should Check for updates to the list. By default, the list is retrieved once every hour and commits the changes.The interval is relative to the last commit. So, for the five-minute interval, the commit occurs in 5 minutes if the last commit was an hour ago. To retrieve the list immediately, see Retrieve an External Dynamic List from the Web Server.Click Save and Push Config.(Optional) EDLs are shown top to bottom, in order of evaluation. Use the directional controls at the bottom of the page to change the list order. This allows you to or order the lists to make sure the most important EDLs are committed before capacity limits are reached.Enforce Policy on an External Dynamic List.If the server or client authentication fails, your environment ceases to enforce policy based on the last successfully retrieved external dynamic list. Find External Dynamic Lists That Failed Authentication and view the reasons for authentication failure.Configure Your Environment to Access an External Dynamic List (PAN-OS & Panorama)
Learn how to configure your environment to access and EDL in PAN-OS and Panorama,You must establish the connection between the firewall and the source that hosts the external dynamic list before you can Enforce Policy on an External Dynamic List.- (Optional) Customize the service route that the firewall uses to retrieve external dynamic lists.Select DeviceSetupServicesService Route ConfigurationCustomize and modify the External Dynamic Lists service route.The firewall does not use the External Dynamic Lists service route to retrieve external dynamic lists; content updates modify or update the contents of those lists (active Threat Prevention license required).Find an external dynamic list to use with the firewall.
- Create an external dynamic list and host it on a web server. Enter IP addresses, domains, or URLs in a blank text file. Each list entry must be on a separate line. For example:financialtimes.co.inwww.wallaby.au/joeywww.exyang.com/auto-tutorials/How-to-enter-Data-for-Success.aspxSee the Formatting Guidelines for an External Dynamic List to ensure that the firewall does not skip list entries. To prevent commit errors and invalid entries, do not prefix http:// or https:// to any of the entries.
- Use an external dynamic list hosted by another source and verify that it follows the Formatting Guidelines for an External Dynamic List.
Select ObjectsExternal Dynamic Lists.Click Add and enter a descriptive Name for the list.(Optional) Select Shared to share the list with all virtual systems on a device that is enabled for multiple virtual systems. By default, the object is created on the virtual system that is currently selected in the Virtual Systems drop-down.As a best practice, Palo Alto Networks recommends using shared EDLs when multiple virtual systems are used. Using individual EDLs with duplicate entries for each vsys uses more memory, which might over-utilize firewall resources.(Panorama only) Select Disable override to ensure that a firewall administrator cannot override settings locally on a firewall that inherits this configuration through a Device Group commit from Panorama.Select the list Type (for example, URL List).Ensure that the list only includes entries for the list type. See Verify whether entries in the external dynamic list were ignored or skipped.If you using a Domain List, you can optionally enable Automatically expand to include subdomains to also include the subdomains of a specified domain. For example, if your domain list includes paloaltonetworks.com, all lower level components of the domain name (e.g., *.paloaltonetworks.com) will also be included as part of the list. Keep in mind, when this setting is enabled, each domain in a given list requires an additional entry, effectively doubling the number of entries that are consumed.Enter the Source for the list you just created on the web server. The source must include the full path to access the list. For example, https://1.2.3.4/EDL_IP_2015.- If you are creating a Predefined IP external dynamic list, select a Palo Alto Networks malicious IP address feed to use as a source.
- If you are creating a Predefined URL external dynamic list, select panw-auth-portal-exclude-list as a source.
If the list source is secured with SSL (i.e. lists with an HTTPS URL), enable server authentication. Select a Certificate Profile or create a New Certificate Profile for authenticating the server that hosts the list. The certificate profile you select must have root certificate authority (CA) and intermediate CA certificates that match the certificates installed on the server you are authenticating.Maximize the number of external dynamic lists that you can use to enforce policy. Use the same certificate profile to authenticate external dynamic lists from the same source URL. If you assign different certificate profiles to external dynamic lists from the same source URL, the firewall counts each list as a unique external dynamic list.Enable client authentication if the list source has an HTTPS URL and requires basic HTTP authentication for list access.- Select Client Authentication.Enter a valid Username to access the list.Enter the Password and Confirm Password.
![]() (Not available on Panorama or for Predefined URL EDLs) Click Test Source URL to verify that the firewall can connect to the web server.The Test Source URL function is not available when authentication is used for EDL access.(Optional) Specify the frequency at which the firewall should Check for updates to the list. By default, the firewall retrieves the list once every hour and commits the changes.The interval is relative to the last commit. So, for the five-minute interval, the commit occurs in 5 minutes if the last commit was an hour ago. To retrieve the list immediately, see Retrieve an External Dynamic List from the Web Server.Click OK and Commit your changes.(Optional) EDLs are shown top to bottom, in order of evaluation. Use the directional controls at the bottom of the page to change the list order. This allows you to or order the lists to make sure the most important EDLs are committed before capacity limits are reached.You can only change the EDL order when Group By Type is deselected.Enforce Policy on an External Dynamic List.If the server or client authentication fails, the firewall ceases to enforce policy based on the last successfully retrieved external dynamic list. Find External Dynamic Lists That Failed Authentication and view the reasons for authentication failure.
(Not available on Panorama or for Predefined URL EDLs) Click Test Source URL to verify that the firewall can connect to the web server.The Test Source URL function is not available when authentication is used for EDL access.(Optional) Specify the frequency at which the firewall should Check for updates to the list. By default, the firewall retrieves the list once every hour and commits the changes.The interval is relative to the last commit. So, for the five-minute interval, the commit occurs in 5 minutes if the last commit was an hour ago. To retrieve the list immediately, see Retrieve an External Dynamic List from the Web Server.Click OK and Commit your changes.(Optional) EDLs are shown top to bottom, in order of evaluation. Use the directional controls at the bottom of the page to change the list order. This allows you to or order the lists to make sure the most important EDLs are committed before capacity limits are reached.You can only change the EDL order when Group By Type is deselected.Enforce Policy on an External Dynamic List.If the server or client authentication fails, the firewall ceases to enforce policy based on the last successfully retrieved external dynamic list. Find External Dynamic Lists That Failed Authentication and view the reasons for authentication failure.