Use the ARM Template to Deploy the VM-Series Firewall
Table of Contents
9.1 (EoL)
Expand all | Collapse all
-
- VM-Series Deployments
- VM-Series in High Availability
- Enable Jumbo Frames on the VM-Series Firewall
- Hypervisor Assigned MAC Addresses
- Custom PAN-OS Metrics Published for Monitoring
- Interface Used for Accessing External Services on the VM-Series Firewall
- PacketMMAP and DPDK Driver Support
-
- VM-Series Firewall Licensing
- Create a Support Account
- Serial Number and CPU ID Format for the VM-Series Firewall
-
- Activate Credits
- Transfer Credits
- Create a Deployment Profile
- Manage a Deployment Profile
- Provision Panorama
- Migrate Panorama to a Software NGFW License
- Renew Your Software NGFW Credits
- Amend and Extend a Credit Pool
- Deactivate License (Software NGFW Credits)
- Delicense Ungracefully Terminated Firewalls
- Create and Apply a Subscription-Only Auth Code
- Migrate to a Flexible VM-Series License
-
- Generate Your OAuth Client Credentials
- Manage Deployment Profiles Using the Licensing API
- Create a Deployment Profile Using the Licensing API
- Update a Deployment Profile Using the Licensing API
- Get Serial Numbers Associated with an Authcode Using the API
- Deactivate a VM-Series Firewall Using the API
- Use Panorama-Based Software Firewall License Management
- What Happens When Licenses Expire?
- Install a Device Certificate on the VM-Series Firewall
-
- Supported Deployments on VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi)
-
- Plan the Interfaces for the VM-Series for ESXi
- Provision the VM-Series Firewall on an ESXi Server
- Perform Initial Configuration on the VM-Series on ESXi
- Add Additional Disk Space to the VM-Series Firewall
- Use VMware Tools on the VM-Series Firewall on ESXi and vCloud Air
- Use vMotion to Move the VM-Series Firewall Between Hosts
- Use the VM-Series CLI to Swap the Management Interface on ESXi
-
-
- VM-Series Firewall for NSX-V Deployment Checklist
- Install the VMware NSX Plugin
- Apply Security Policies to the VM-Series Firewall
- Steer Traffic from Guests that are not Running VMware Tools
- Add a New Host to Your NSX-V Deployment
- Dynamically Quarantine Infected Guests
- Migrate Operations-Centric Configuration to Security-Centric Configuration
- Use Case: Shared Compute Infrastructure and Shared Security Policies
- Use Case: Shared Security Policies on Dedicated Compute Infrastructure
- Dynamic Address Groups—Information Relay from NSX-V Manager to Panorama
-
- Supported Deployments of the VM-Series Firewall on VMware NSX-T (North-South)
- Components of the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (North-South)
-
- Install the Panorama Plugin for VMware NSX
- Enable Communication Between NSX-T Manager and Panorama
- Create Template Stacks and Device Groups on Panorama
- Configure the Service Definition on Panorama
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall
- Direct Traffic to the VM-Series Firewall
- Apply Security Policy to the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T
- Use vMotion to Move the VM-Series Firewall Between Hosts
- Extend Security Policy from NSX-V to NSX-T
-
- Components of the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (East-West)
- VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (East-West) Integration
- Supported Deployments of the VM-Series Firewall on VMware NSX-T (East-West)
-
- Install the Panorama Plugin for VMware NSX
- Enable Communication Between NSX-T Manager and Panorama
- Create Template Stacks and Device Groups on Panorama
- Configure the Service Definition on Panorama
- Launch the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (East-West)
- Add a Service Chain
- Direct Traffic to the VM-Series Firewall
- Apply Security Policies to the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (East-West)
- Use vMotion to Move the VM-Series Firewall Between Hosts
- Extend Security Policy from NSX-V to NSX-T
- Use Migration Coordinator to Move Your VM-Series from NSX-V to NSX-T
-
-
- Deployments Supported on AWS
-
- Planning Worksheet for the VM-Series in the AWS VPC
- Launch the VM-Series Firewall on AWS
- Launch the VM-Series Firewall on AWS Outpost
- Create a Custom Amazon Machine Image (AMI)
- Encrypt EBS Volume for the VM-Series Firewall on AWS
- Use the VM-Series Firewall CLI to Swap the Management Interface
- Enable CloudWatch Monitoring on the VM-Series Firewall
- VM-Series Firewall Startup and Health Logs on AWS
- Use Case: Secure the EC2 Instances in the AWS Cloud
- Use Case: Use Dynamic Address Groups to Secure New EC2 Instances within the VPC
-
-
- What Components Does the VM-Series Auto Scaling Template for AWS (v2.0) Leverage?
- How Does the VM-Series Auto Scaling Template for AWS (v2.0 and v2.1) Enable Dynamic Scaling?
- Plan the VM-Series Auto Scaling Template for AWS (v2.0 and v2.1)
- Customize the Firewall Template Before Launch (v2.0 and v2.1)
- Launch the VM-Series Auto Scaling Template for AWS (v2.0)
- SQS Messaging Between the Application Template and Firewall Template
- Stack Update with VM-Series Auto Scaling Template for AWS (v2.0)
- Modify Administrative Account and Update Stack (v2.0)
-
- Launch the Firewall Template (v2.1)
- Launch the Application Template (v2.1)
- Create a Custom Amazon Machine Image (v2.1)
- VM-Series Auto Scaling Template Cleanup (v2.1)
- SQS Messaging Between the Application Template and Firewall Template (v2.1)
- Stack Update with VM-Series Auto Scaling Template for AWS (v2.1)
- Modify Administrative Account (v2.1)
- Change Scaling Parameters and CloudWatch Metrics (v2.1)
-
-
- Enable the Use of a SCSI Controller
- Verify PCI-ID for Ordering of Network Interfaces on the VM-Series Firewall
-
- Deployments Supported on Azure
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall from the Azure Marketplace (Solution Template)
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall from the Azure China Marketplace (Solution Template)
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall on Azure Stack
- Enable Azure Application Insights on the VM-Series Firewall
- Set up Active/Passive HA on Azure
- Use the ARM Template to Deploy the VM-Series Firewall
-
- About the VM-Series Firewall on Google Cloud Platform
- Supported Deployments on Google Cloud Platform
- Create a Custom VM-Series Firewall Image for Google Cloud Platform
- Prepare to Set Up VM-Series Firewalls on Google Public Cloud
-
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall from Google Cloud Platform Marketplace
- Management Interface Swap for Google Cloud Platform Load Balancing
- Use the VM-Series Firewall CLI to Swap the Management Interface
- Enable Google Stackdriver Monitoring on the VM Series Firewall
- Enable VM Monitoring to Track VM Changes on GCP
- Use Dynamic Address Groups to Secure Instances Within the VPC
- Locate VM-Series Firewall Images in the GCP Marketplace
-
- Prepare Your ACI Environment for Integration
-
-
- Create a Virtual Router and Security Zone
- Configure the Network Interfaces
- Configure a Static Default Route
- Create Address Objects for the EPGs
- Create Security Policy Rules
- Create a VLAN Pool and Domain
- Configure an Interface Policy for LLDP and LACP for East-West Traffic
- Establish the Connection Between the Firewall and ACI Fabric
- Create a VRF and Bridge Domain
- Create an L4-L7 Device
- Create a Policy-Based Redirect
- Create and Apply a Service Graph Template
-
- Create a VLAN Pool and External Routed Domain
- Configure an Interface Policy for LLDP and LACP for North-South Traffic
- Create an External Routed Network
- Configure Subnets to Advertise to the External Firewall
- Create an Outbound Contract
- Create an Inbound Web Contract
- Apply Outbound and Inbound Contracts to the EPGs
- Create a Virtual Router and Security Zone for North-South Traffic
- Configure the Network Interfaces
- Configure Route Redistribution and OSPF
- Configure NAT for External Connections
-
-
- Choose a Bootstrap Method
- VM-Series Firewall Bootstrap Workflow
- Bootstrap Package
- Bootstrap Configuration Files
- Generate the VM Auth Key on Panorama
- Create the bootstrap.xml File
- Prepare the Licenses for Bootstrapping
- Prepare the Bootstrap Package
- Bootstrap the VM-Series Firewall on AWS
- Bootstrap the VM-Series Firewall on Azure
- Bootstrap the VM-Series Firewall on Google Cloud Platform
- Verify Bootstrap Completion
- Bootstrap Errors
End-of-Life (EoL)
Use the ARM Template to Deploy the VM-Series Firewall
In addition to Marketplace based deployments,
Palo Alto Networks provides a GitHub repository which hosts sample
ARM templates that you can download and customize for your needs.
ARM templates are JSON files that describe the resources required
for individual resources such as network interfaces, a complete
virtual machine or even an entire application stack with multiple
virtual machines.
ARM templates are for advanced users, and Palo Alto Networks provides the ARM template under the
community supported policy. To learn about ARM templates, refer to the Microsoft documentation on ARM
Templates.
To
simplify the deployment of all the required resources, the two-tier
sample template (https://github.com/PaloAltoNetworks/azure/tree/master/two-tier-sample)
includes two json files:
- Template File—The azureDeploy.json is the main resources file that deploys all the components within the resource group.
- Parameters File—The azureDeploy.parameters.json is the file that includes the parameters required to successfully deploy the VM-Series firewall in the VNet. It includes details such as the virtual machine tier and size, username and password for the firewall, the name of the storage container for the firewall. You can customize this file for your Azure VNet deployment.
To
help you deploy the firewall as a gateway for Internet-facing applications,
the template provisions the VM-Series firewall, a database server,
and a web server. The VNet uses the private non-routable IP address
space 192.168.0.0/16. You can modify the template to use 172.16.0.0/12,
or 10.0.0.0/8.
The ARM template also provides the necessary user-defined rules and
IP forwarding flags to enable the VM-Series firewall to secure the Azure
resource group. For the five subnets—Trust, Untrust, Web, DB, and
NAT—included in the template, you have five route tables, one for
each subnet with user defined rules for routing traffic to the VM-Series
firewall and the NAT virtual machine.
For the four subnets—Trust,
Untrust, Web, and DB—included in the template, you have four route
tables, one for each subnet with user defined rules for routing
traffic to the VM-Series firewall.

- Download the two-tier sample ARM template from
the GitHub repository.Download and save the files to a local client: https://github.com/PaloAltoNetworks/azure/tree/master/two-tier-sample
- Create a Resource Group on Azure.
- Log in to the Azure CLI using the command: azureloginIf you need help, refer to the Azure documentation on installing the CLI, or for details on how to access the CLI on Azure Government or Azure China.
- Switch to Resource Manager mode using the command:azureconfig mode arm
- Create a resource group.
- Log in to the Azure CLI using the command: azurelogin
- Deploy the ARM template.
- Open the Parameters File with a text editor
and modify the values for your deployment:In Azure China, you must edit the path for the storage account that hosts the VHD image required to deploy the VM-Series firewall. In the variables section of the template file, find the parameter called userImageNameURI and replace the value with the location where you saved the VHD image.
- Deploy the template in the resource group you created.az deployment group create -name <YourResourceGroupName> --resource-group <YourResourceGroupName> --parameters ’@<path-to-template-parameter-azureDeploy.json>’
- Check the progress/status of the deployment from the Azure CLI:
azure group deployment show "<YourResourceGroupName>" “<YourDeploymentLabel>“When the template is successfully deployed the ProvisioningStateis Running.If the ProvisioningStateis Failed, you must check for errors on the Azure portal at Resource GroupEvents. Filter for only events in the last one hour, select the most recent events, and drill down to find the errors.- Verify that you have successfully deployed the VM-Series firewall.
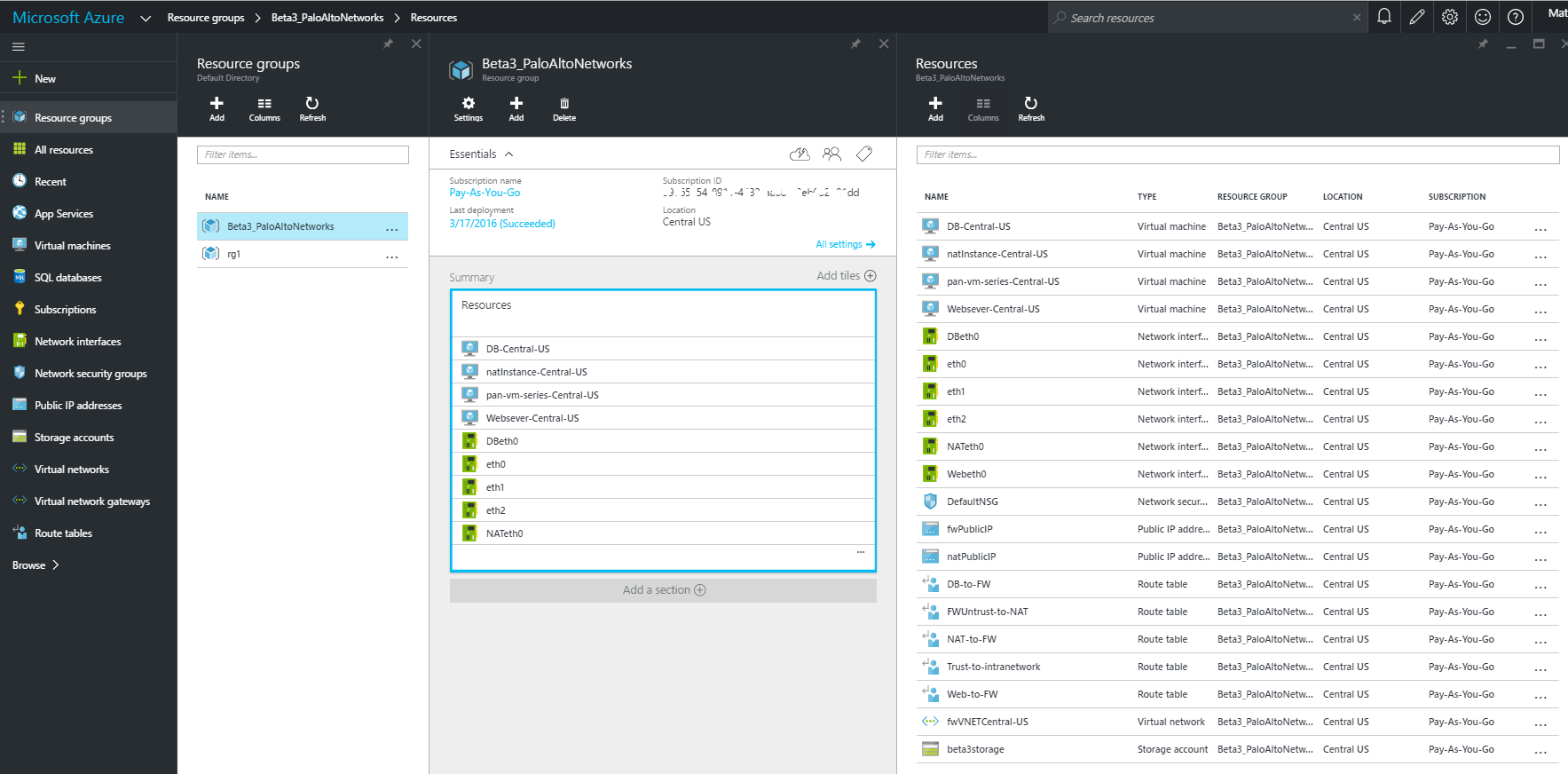
- Select DashboardResource Groups, select the resource group.
- Select All SettingsDeploymentsDeployment History for detailed status.
![]() The address space within the VNet uses the prefix 192.168, which is defined in the ARM template.
The address space within the VNet uses the prefix 192.168, which is defined in the ARM template.
- Attach a public IP address to the untrust interface on the firewall.
- Configure the firewall as a VNet gateway to protect your Internet-facing deployment.
- Log in to the management interface IP address on the firewall.
- Configure the dataplane network interfaces as Layer 3 interfaces on the firewall (NetworkInterfacesEthernet).
- Add static rules to the virtual router on the firewall.
To route traffic through the firewall in this example, you need
three static routes on the firewall (NetworkVirtual Routers, select the
router and click Static Routes):
- Route all outbound traffic through the UnTrust zone, ethernet1/1 to the Azure router at 192.168.1.1.
- Route all inbound traffic destined to the web server subnet through the Trust zone, ethernet1/2 to the Azure router at 192.168.2.1.
- Route all inbound traffic destined to the database server subnet through the Trust zone, ethernet1/2 to the Azure router at 192.168.2.1.
- Create security policy rules (PoliciesSecurity) to allow inbound and outbound traffic on the firewall. You also need security policy rules to allow appropriate traffic from the web server subnet to the database server subnet and vice versa.
- Commit the changes on the firewall.
- Verify that the VM-Series firewall is securing traffic (MonitorLogsTraffic).
- Check the progress/status of the deployment from the Azure CLI:
- Open the Parameters File with a text editor
and modify the values for your deployment: