Strata Logging Service
Forward Logs to a Syslog Server
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Strata Logging Service Docs
Forward Logs to a Syslog Server
Learn how to forward logs from Strata Logging Service to a
syslog server.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
| One of these:
|
To meet your long-term storage, reporting
and monitoring, or legal and compliance needs, you can configure
Strata Logging Service to forward all logs or a subset of logs to a syslog
receiver.
Strata Logging Service can forward logs in multiple formats: CSV, LEEF, or CEF. For each
instance of Strata Logging Service, you can forward logs to up to 200 syslog
destinations.
If you are using the Palo Alto Networks
Splunk app, forward logs using HTTPS instead.
- (QRadar only) Add a log source in QRadar by using the TLS Syslog protocol.For details about how to do this, see the IBM documentation.Enable communication between Strata Logging Service and your syslog receiver.Ensure that your syslog receiver can connect to Strata Logging Service and can present a valid CA certificate to complete the connection request.
- Allow an inbound TLS feed to your syslog receiver from the IP address range that corresponds to your Strata Logging Service region.
- Obtain either a certificate from a well-known, public CA or a self-signed certificate and install it on your receiver. Please make sure that if you are using a certificate signed by a private CA, it contains CRL or OCSP information needed for certificate revocation checks.Because Strata Logging Service validates the server certificate to establish a connection, you must verify that the receiver is configured to properly send the TLS certificate chain to Strata Logging Service. If the app cannot verify that the certificate of the receiver and all CAs in the chain are trustworthy, the connection cannot be established. See the list of trusted certificates.
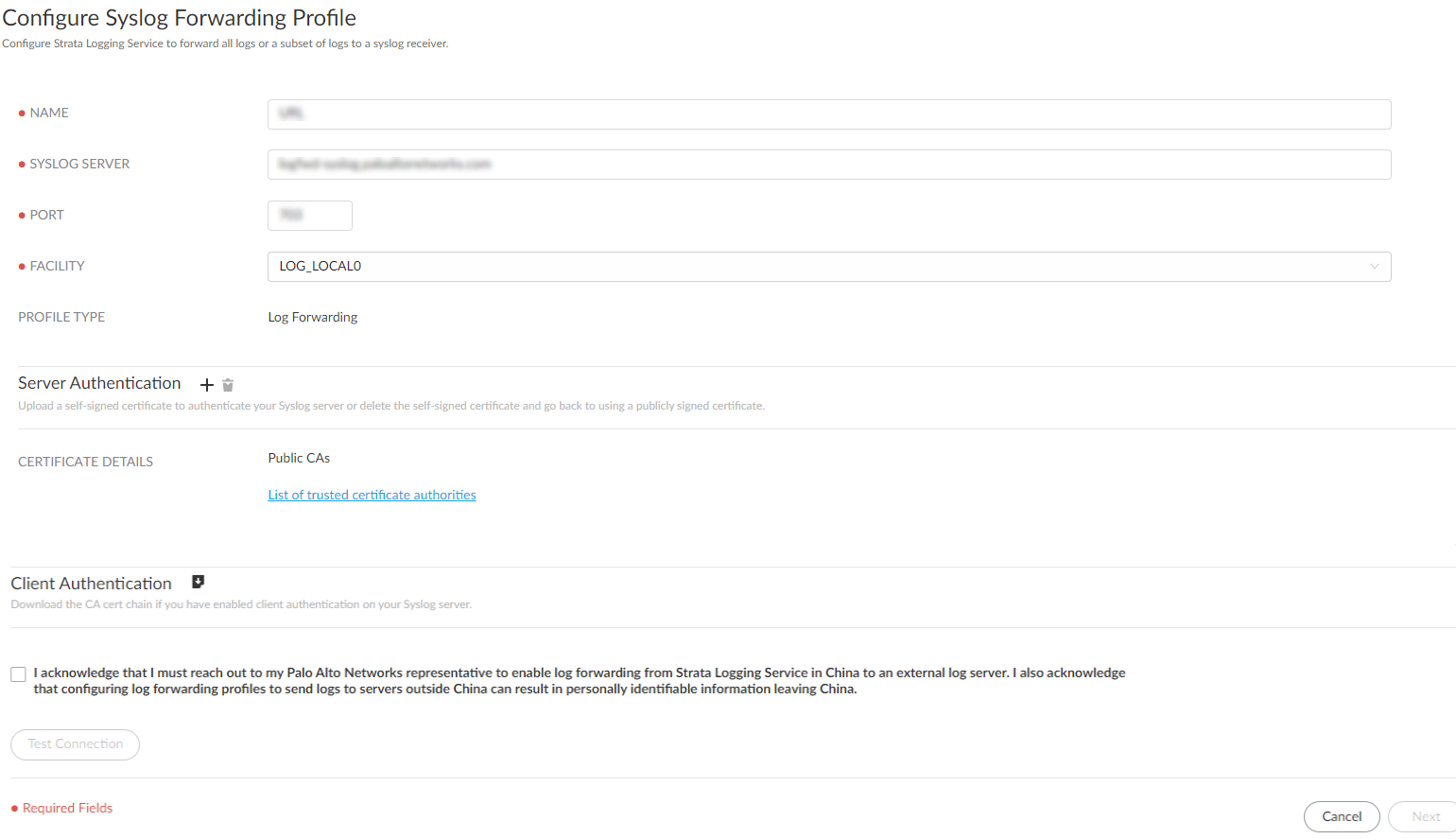
Sign In to the hub.Select the Strata Logging Service instance that you want to configure for syslog forwarding.If you have multiple Strata Logging Service instances, click the Strata Logging Service tile and select an instance from the list of those available.If you are using Strata Cloud Manager to manage Strata Logging Service, click System SettingsStrata Logging ServiceLog Forwarding to manage log forwarding from Strata Logging Service instance to an external server.Select Log ForwardingAdd to add a new Syslog forwarding profile.Enter a descriptive Name for the profile.Enter the Syslog Server IPv4 address or FQDN.Ensure that the value entered here matches the Subject Alternative Name (SAN) of the certificate installed on your syslog server.Enter the Port on which the syslog server is listening.The default port for syslog messages over TLS is 6514.Select the Facility.Choose one of the syslog standard values. The value maps to how your syslog server uses the facility field to manage messages. For details on the facility field, see the IETF standard for the log format (CSV, LEEF, or CEF) that you will choose in the next step.(Optional) Authenticate your syslog server. Click + to upload certificate. You can upload:- a self-signed certificate if you do not want to use a publicly signed certificate.
- the private Root CA and intermediate CAs (If an intermediate CA exists). Do not upload the certificate issued for the syslog server—only CA certificates are needed to verify the chain from the syslog server.
Only do this if you installed a private CA-signed, self-signed certificate on your receiver, or the public CA is not in the list of trusted CAs. The file containing the certificates must be in PEM format.![]() (Optional) Enable client authentication.Do this if company or regulatory policy requires client authentication when forwarding logs to your server.
(Optional) Enable client authentication.Do this if company or regulatory policy requires client authentication when forwarding logs to your server.- Download the certificate chain.Upload the certificate chain to your server.Refer to the documentation for your server management software to find out how to do this.Acknowledge to reach out to your Palo Alto Networks team to enable log forwarding from Strata Logging Service in China to an external log server. Be aware that configuring log forwarding profiles to send logs to servers outside China can result in personally identifiable information leaving China.Test Connection to ensure that Strata Logging Service can communicate with the receiver.This checks TLS connectivity to verify that transmission is possible.If the test fails, you can not proceed.Click Next.Specify the Format in which you would like to forward your logs.The log format (CSV, LEEF, CEF, or JSON) that you should select depends on the destination of your log data.Specify the Delimiter that you would like to separate the fields in your log messages. This option is disabled if you select JSON log format.(Optional) To receive a STATUS NOTIFICATION when Strata Logging Service is unable to connect to the syslog server, enter the email address at which you’d like to receive the notification.You will continue to receive these notifications at least once every 60 minutes until connectivity is restored. If the connectivity issue is addressed within 72 hours, no logs will be lost. However, any log older than 72 hours following the service disconnection could be lost.(Optional) Enter a PROFILE TOKEN to send logs to a cloud syslog receiver.If you use a third-party cloud-based syslog service, you can enter a token that Strata Logging Service inserts into each syslog message so that the cloud syslog provider can identify the source of the logs.
- Follow your cloud syslog provider’s instructions for generating an identifying token.Enter the Profile Token.Tokens have a maximum length of 128 characters.(Optional) Create a log filter to forward only the logs that are most critical to you.
- You can either write your own queries from scratch or use the query builder. You can also select the query field to choose from among a set of common predefined queries.Log filters function like queries in Explore, with the following differences:
- No double quotes (“”).
- No subnet masks. To return IP addresses with subnets, use the LIKE operator. Example: src_ip.value LIKE “192.1.1.%”.
If you want to forward all logs of the type you selected, do not enter a query. Instead, proceed to the next step. - Save your changes.
Save your changes.Verify that the Status of your Syslog forwarding profile is Running ().![]() Verify that you can view logs on the syslog receiver.For details about the log format, refer to the Syslog field descriptions (Select the PAN-OS Administrator’s Guide for your firewall version).(Optional) You can use the running Syslog forwarding profile to forward past logs spanning up to 3 days.When configuring event source mapping in your SIEM, be aware that the hostname value can change in the hostname field of the syslog message sent from Strata Logging Service.For example,Oct 8 15:26:51 stream-logfwd20-602226222-10061338-i2hh-harness-r9kt logforwarder LEEF:2.0|Palo Alto Networks|Next Generationmight change toOct 8 15:26:51 stream-logfwd20-602226222-10061338-i2hh-harness-a7b1 logforwarder LEEF:2.0|Palo Alto Networks|Next GenerationA change to your log forwarding configuration or a new feature/fix could change the hostname value and break event source mapping if you are using an exact match on the hostname.If hostname exact matching is required by the SIEM, consider using a middle syslog host to rewrite the log forward to a static hostname so that changes to hostname values don't affect log source mappings.
Verify that you can view logs on the syslog receiver.For details about the log format, refer to the Syslog field descriptions (Select the PAN-OS Administrator’s Guide for your firewall version).(Optional) You can use the running Syslog forwarding profile to forward past logs spanning up to 3 days.When configuring event source mapping in your SIEM, be aware that the hostname value can change in the hostname field of the syslog message sent from Strata Logging Service.For example,Oct 8 15:26:51 stream-logfwd20-602226222-10061338-i2hh-harness-r9kt logforwarder LEEF:2.0|Palo Alto Networks|Next Generationmight change toOct 8 15:26:51 stream-logfwd20-602226222-10061338-i2hh-harness-a7b1 logforwarder LEEF:2.0|Palo Alto Networks|Next GenerationA change to your log forwarding configuration or a new feature/fix could change the hostname value and break event source mapping if you are using an exact match on the hostname.If hostname exact matching is required by the SIEM, consider using a middle syslog host to rewrite the log forward to a static hostname so that changes to hostname values don't affect log source mappings.