Next-Generation Firewall
Enable NDP Monitoring
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Next-Generation Firewall Docs
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- PAN-OS 12.1
- PAN-OS 11.2
- PAN-OS 11.1
- PAN-OS 11.0 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 10.2
- PAN-OS 10.1
- PAN-OS 10.0 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 9.1 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 9.0 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 8.1 (EoL)
-
- PAN-OS 12.1
- PAN-OS 11.2
- PAN-OS 11.1
- PAN-OS 10.2
- PAN-OS 10.1
Enable NDP Monitoring
NDP uses ICMPv6 packets to discover and track the link-layer addresses and status of
neighbors on connected links.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) for IPv6 (RFC 4861) performs functions similar to ARP functions for IPv4. The
firewall by default runs NDP, which uses ICMPv6 packets to discover and track the
link-layer addresses and status of neighbors on connected links.
Use NDP to monitor IPv6 addresses, which allows you to quickly track the IPv6 address
and MAC address of a device and the associated user who has violated a security
rule. Enable NDP monitoring to view the IPv6 addresses of devices on the link local
network, their MAC address, associated username from User-ID (if the user of that
device used the directory service to log in), reachability Status of the address,
and Last Reported date and time the NDP monitor received a Router Advertisement from
this IPv6 address. The username is on a best-case basis; there can be many IPv6
devices on a network with no username, such as printers, fax machines, servers, etc.
If you want to quickly track a device and user who has violated a security rule, it
is very useful to have the IPv6 address, MAC address and username displayed all in
one place. You need the MAC address that corresponds to the IPv6 address in order to
trace the MAC address back to a physical switch or Access Point.
NDP monitoring is not guaranteed to discover all devices
because there could be other networking devices between the firewall and the client
that filter out NDP or Duplicate Address Detection (DAD) messages. The firewall can
monitor only the devices that it learns about on the interface.
NDP monitoring also monitors Duplicate Address Detection (DAD) packets from clients
and neighbors. You can also monitor IPv6 ND logs to make troubleshooting easier.
NDP monitoring is supported for Ethernet interfaces, subinterfaces, Aggregated
Ethernet interfaces, and VLAN interfaces on all PAN-OS models.
Perform this task to enable NDP monitoring for an interface.
- Enable NDP monitoring.
- Select NetworkInterfaces and Ethernet or VLAN.Select the interface you are configuring.Select IPv6.Select Address Resolution.Select Enable NDP Monitoring.After you enable or disable NDP monitoring, you must Commit before NDP monitoring can start or stop.Click OK.Commit your changes.Monitor NDP and DAD packets from clients and neighbors.
- Select NetworkInterfaces and Ethernet or VLAN.For the interface where you enabled NDP monitoring, in the Features column, hover over the NDP Monitoringicon:
![]() The NDP Monitoring summary for the interface displays the list of IPv6 Prefixes that this interface will send in the Router Advertisement (RA) if RA is enabled (they are the IPv6 prefixes of the interface itself).The summary also indicates whether DAD, Router Advertisement, and DNS Support are enabled; IP addresses of any Recursive DNS Servers configured; and any DNS suffixes configured on the DNS Search List.Click on the NDP Monitoring icon to display detailed information.
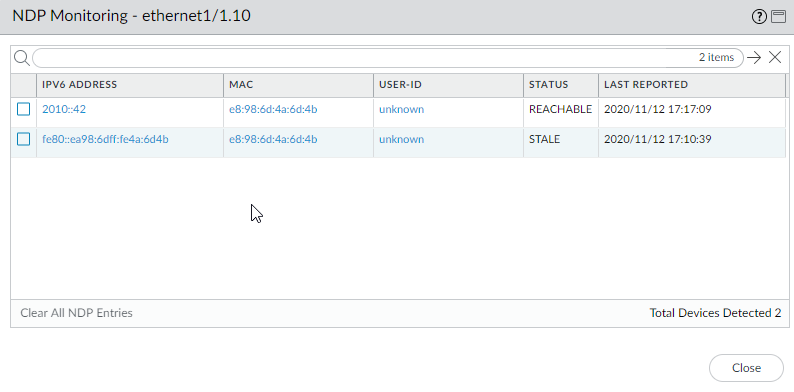
The NDP Monitoring summary for the interface displays the list of IPv6 Prefixes that this interface will send in the Router Advertisement (RA) if RA is enabled (they are the IPv6 prefixes of the interface itself).The summary also indicates whether DAD, Router Advertisement, and DNS Support are enabled; IP addresses of any Recursive DNS Servers configured; and any DNS suffixes configured on the DNS Search List.Click on the NDP Monitoring icon to display detailed information.![]() Each row of the detailed NDP Monitoring table for the interface displays the IPv6 address of a neighbor the firewall has discovered, the corresponding MAC address, corresponding User ID (on a best-case basis), reachability Status of the address, and Last Reported date and time this NDP Monitor received an RA from this IP address. A User ID will not display for printers or other non-user-based hosts. If the status of the IP address is Stale, the neighbor is not known to be reachable, per RFC 4861.At the bottom right is the count of Total Devices Detected on the link local network.
Each row of the detailed NDP Monitoring table for the interface displays the IPv6 address of a neighbor the firewall has discovered, the corresponding MAC address, corresponding User ID (on a best-case basis), reachability Status of the address, and Last Reported date and time this NDP Monitor received an RA from this IP address. A User ID will not display for printers or other non-user-based hosts. If the status of the IP address is Stale, the neighbor is not known to be reachable, per RFC 4861.At the bottom right is the count of Total Devices Detected on the link local network.- Enter an IPv6 address in the filter field to search for an address to display.
- Select the check boxes to display or not display IPv6 addresses.
- Click the numbers, the right or left arrow, or the vertical scroll bar to advance through many entries.
- Click Clear All NDP Entries to clear the entire table.
Monitor ND logs for reporting purposes.- Select MonitorLogsSystem.In the Type column, view ipv6nd logs and corresponding descriptions.For example, inconsistent router advertisementreceived indicates that the firewall received an RA different from the RA that it is going to send out.