VM-Series Auto Scaling Templates for AWS Version 2.1
Table of Contents
9.1 (EoL)
Expand all | Collapse all
-
- VM-Series Deployments
- VM-Series in High Availability
- Enable Jumbo Frames on the VM-Series Firewall
- Hypervisor Assigned MAC Addresses
- Custom PAN-OS Metrics Published for Monitoring
- Interface Used for Accessing External Services on the VM-Series Firewall
- PacketMMAP and DPDK Driver Support
-
- VM-Series Firewall Licensing
- Create a Support Account
- Serial Number and CPU ID Format for the VM-Series Firewall
-
- Activate Credits
- Transfer Credits
- Create a Deployment Profile
- Manage a Deployment Profile
- Provision Panorama
- Migrate Panorama to a Software NGFW License
- Renew Your Software NGFW Credits
- Amend and Extend a Credit Pool
- Deactivate License (Software NGFW Credits)
- Delicense Ungracefully Terminated Firewalls
- Create and Apply a Subscription-Only Auth Code
- Migrate to a Flexible VM-Series License
-
- Generate Your OAuth Client Credentials
- Manage Deployment Profiles Using the Licensing API
- Create a Deployment Profile Using the Licensing API
- Update a Deployment Profile Using the Licensing API
- Get Serial Numbers Associated with an Authcode Using the API
- Deactivate a VM-Series Firewall Using the API
- Use Panorama-Based Software Firewall License Management
- What Happens When Licenses Expire?
- Install a Device Certificate on the VM-Series Firewall
-
- Supported Deployments on VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi)
-
- Plan the Interfaces for the VM-Series for ESXi
- Provision the VM-Series Firewall on an ESXi Server
- Perform Initial Configuration on the VM-Series on ESXi
- Add Additional Disk Space to the VM-Series Firewall
- Use VMware Tools on the VM-Series Firewall on ESXi and vCloud Air
- Use vMotion to Move the VM-Series Firewall Between Hosts
- Use the VM-Series CLI to Swap the Management Interface on ESXi
-
-
- VM-Series Firewall for NSX-V Deployment Checklist
- Install the VMware NSX Plugin
- Apply Security Policies to the VM-Series Firewall
- Steer Traffic from Guests that are not Running VMware Tools
- Add a New Host to Your NSX-V Deployment
- Dynamically Quarantine Infected Guests
- Migrate Operations-Centric Configuration to Security-Centric Configuration
- Use Case: Shared Compute Infrastructure and Shared Security Policies
- Use Case: Shared Security Policies on Dedicated Compute Infrastructure
- Dynamic Address Groups—Information Relay from NSX-V Manager to Panorama
-
- Supported Deployments of the VM-Series Firewall on VMware NSX-T (North-South)
- Components of the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (North-South)
-
- Install the Panorama Plugin for VMware NSX
- Enable Communication Between NSX-T Manager and Panorama
- Create Template Stacks and Device Groups on Panorama
- Configure the Service Definition on Panorama
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall
- Direct Traffic to the VM-Series Firewall
- Apply Security Policy to the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T
- Use vMotion to Move the VM-Series Firewall Between Hosts
- Extend Security Policy from NSX-V to NSX-T
-
- Components of the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (East-West)
- VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (East-West) Integration
- Supported Deployments of the VM-Series Firewall on VMware NSX-T (East-West)
-
- Install the Panorama Plugin for VMware NSX
- Enable Communication Between NSX-T Manager and Panorama
- Create Template Stacks and Device Groups on Panorama
- Configure the Service Definition on Panorama
- Launch the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (East-West)
- Add a Service Chain
- Direct Traffic to the VM-Series Firewall
- Apply Security Policies to the VM-Series Firewall on NSX-T (East-West)
- Use vMotion to Move the VM-Series Firewall Between Hosts
- Extend Security Policy from NSX-V to NSX-T
- Use Migration Coordinator to Move Your VM-Series from NSX-V to NSX-T
-
-
- Deployments Supported on AWS
-
- Planning Worksheet for the VM-Series in the AWS VPC
- Launch the VM-Series Firewall on AWS
- Launch the VM-Series Firewall on AWS Outpost
- Create a Custom Amazon Machine Image (AMI)
- Encrypt EBS Volume for the VM-Series Firewall on AWS
- Use the VM-Series Firewall CLI to Swap the Management Interface
- Enable CloudWatch Monitoring on the VM-Series Firewall
- VM-Series Firewall Startup and Health Logs on AWS
- Use Case: Secure the EC2 Instances in the AWS Cloud
- Use Case: Use Dynamic Address Groups to Secure New EC2 Instances within the VPC
-
-
- What Components Does the VM-Series Auto Scaling Template for AWS (v2.0) Leverage?
- How Does the VM-Series Auto Scaling Template for AWS (v2.0 and v2.1) Enable Dynamic Scaling?
- Plan the VM-Series Auto Scaling Template for AWS (v2.0 and v2.1)
- Customize the Firewall Template Before Launch (v2.0 and v2.1)
- Launch the VM-Series Auto Scaling Template for AWS (v2.0)
- SQS Messaging Between the Application Template and Firewall Template
- Stack Update with VM-Series Auto Scaling Template for AWS (v2.0)
- Modify Administrative Account and Update Stack (v2.0)
-
- Launch the Firewall Template (v2.1)
- Launch the Application Template (v2.1)
- Create a Custom Amazon Machine Image (v2.1)
- VM-Series Auto Scaling Template Cleanup (v2.1)
- SQS Messaging Between the Application Template and Firewall Template (v2.1)
- Stack Update with VM-Series Auto Scaling Template for AWS (v2.1)
- Modify Administrative Account (v2.1)
- Change Scaling Parameters and CloudWatch Metrics (v2.1)
-
-
- Enable the Use of a SCSI Controller
- Verify PCI-ID for Ordering of Network Interfaces on the VM-Series Firewall
-
- Deployments Supported on Azure
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall from the Azure Marketplace (Solution Template)
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall from the Azure China Marketplace (Solution Template)
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall on Azure Stack
- Enable Azure Application Insights on the VM-Series Firewall
- Set up Active/Passive HA on Azure
- Use the ARM Template to Deploy the VM-Series Firewall
-
- About the VM-Series Firewall on Google Cloud Platform
- Supported Deployments on Google Cloud Platform
- Create a Custom VM-Series Firewall Image for Google Cloud Platform
- Prepare to Set Up VM-Series Firewalls on Google Public Cloud
-
- Deploy the VM-Series Firewall from Google Cloud Platform Marketplace
- Management Interface Swap for Google Cloud Platform Load Balancing
- Use the VM-Series Firewall CLI to Swap the Management Interface
- Enable Google Stackdriver Monitoring on the VM Series Firewall
- Enable VM Monitoring to Track VM Changes on GCP
- Use Dynamic Address Groups to Secure Instances Within the VPC
- Locate VM-Series Firewall Images in the GCP Marketplace
-
- Prepare Your ACI Environment for Integration
-
-
- Create a Virtual Router and Security Zone
- Configure the Network Interfaces
- Configure a Static Default Route
- Create Address Objects for the EPGs
- Create Security Policy Rules
- Create a VLAN Pool and Domain
- Configure an Interface Policy for LLDP and LACP for East-West Traffic
- Establish the Connection Between the Firewall and ACI Fabric
- Create a VRF and Bridge Domain
- Create an L4-L7 Device
- Create a Policy-Based Redirect
- Create and Apply a Service Graph Template
-
- Create a VLAN Pool and External Routed Domain
- Configure an Interface Policy for LLDP and LACP for North-South Traffic
- Create an External Routed Network
- Configure Subnets to Advertise to the External Firewall
- Create an Outbound Contract
- Create an Inbound Web Contract
- Apply Outbound and Inbound Contracts to the EPGs
- Create a Virtual Router and Security Zone for North-South Traffic
- Configure the Network Interfaces
- Configure Route Redistribution and OSPF
- Configure NAT for External Connections
-
-
- Choose a Bootstrap Method
- VM-Series Firewall Bootstrap Workflow
- Bootstrap Package
- Bootstrap Configuration Files
- Generate the VM Auth Key on Panorama
- Create the bootstrap.xml File
- Prepare the Licenses for Bootstrapping
- Prepare the Bootstrap Package
- Bootstrap the VM-Series Firewall on AWS
- Bootstrap the VM-Series Firewall on Azure
- Bootstrap the VM-Series Firewall on Google Cloud Platform
- Verify Bootstrap Completion
- Bootstrap Errors
End-of-Life (EoL)
VM-Series Auto Scaling Templates for AWS Version 2.1
Learn how VM-Series Auto Scaling templates help with
centralized security and connectivity for AWS deployments.
The VM-Series Auto Scaling templates
enable you to deploy a single auto scaling group (ASG) of VM-Series
firewalls to secure inbound traffic from the internet to your application
workloads on AWS. You can deploy the VM-Series firewall ASG and
the application workloads within a single VPC as shown below.
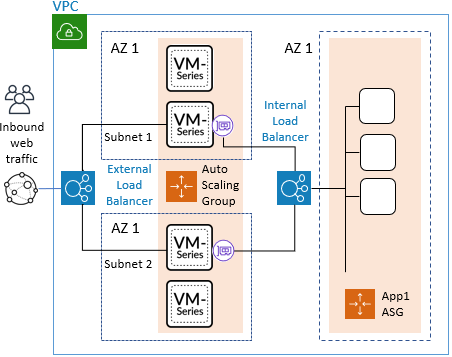
You can also deploy the firewall ASG in a centralized VPC and
your application workloads in separate VPCs within the same region,
forming a hub and spoke architecture, as shown below.
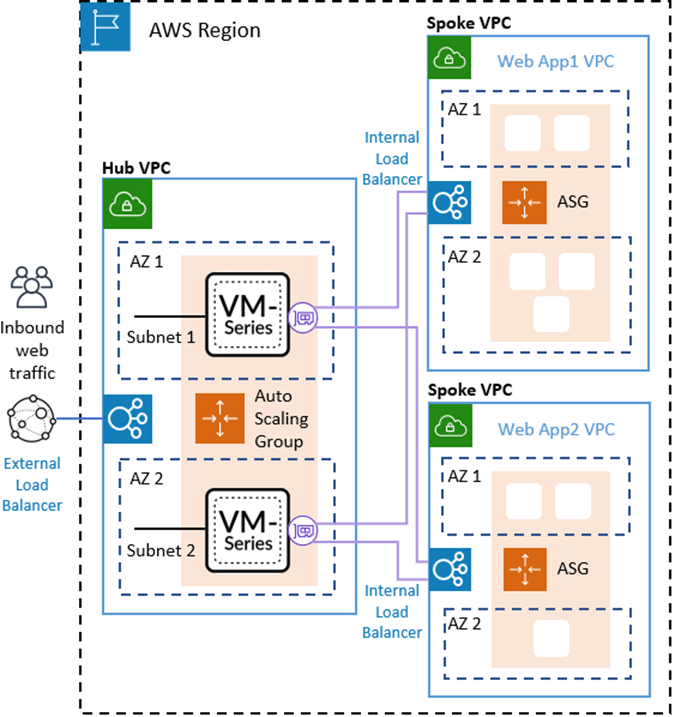
With the hub and spoke architecture you can streamline the delivery
of centralized security and connectivity for AWS deployments with
many applications, VPCs, or accounts. This architecture can increase
agility. Your network security administrators manage the firewall
VPC, and DevOps administrators or application developers can manage
the application VPCs.
Ensure that the application VPCs connected
to the firewall VPC, do not have an Internet Gateway (IGW), and
use a continuous monitoring and security compliance service such
as Prisma Public Cloud.
You can use a single AWS account or multiple AWS accounts to
monitor and secure traffic between VPCs and the internet. Centralizing
firewalls in a single VPC can reduce costs for deployments with
multiple VPCs and/or multiple accounts.
To provide flexibility with securing your application workloads,
version 2.1 allows you to deploy an application load balancer or
a network load balancer for both the external load balancer that
fronts your VM-Series firewall ASG, and the internal load balancer
(ILB) that fronts your application workloads.
When an application load balancer fronts the application workloads,
you can connect the firewall VPC to the application VPC using VPC
peering. When an NLB fronts the application workloads you can use
VPC Peering or an AWS Private Link to connect the firewall and application
VPCs, as summarized below:
| Firewall VPC LB(External) | Application VPC LB (Internal) | Connection Method |
|---|---|---|
| ALB | NLB | AWS Private Link |
| NLB | NLB | AWS Private Link |
| NLB | ALB | VPC Peering |
| ALB | ALB | VPC Peering |
If you deploy in a single VPC you can use all the load balancing
combinations in the previous table.
You can deploy the templates in both and greenfield (new VPC
and applications) and brownfield (existing VPC and applications)
use cases.
| Template | New | Existing |
|---|---|---|
| Firewall | firewall-new-vpc-v2.1.template panw-aws-same-vpc-v2.1.template | firewall-existing-vpc-v2.1.template panw-aws-same-vpc-v2.1.template |
| Application | panw-aws-nlb-new-vpc-v2.1.template panw-aws-alb-new-vpc-v2.1.template | panw-aws-alb-existing-vpc-v2.1.template panw-aws-nlb-existing-vpc-v2.1.template |
What Components Do the VM-Series Auto Scaling Template for AWS (v2.1) Leverage?
The VM-Series Auto Scaling template for AWS includes
the following building blocks.
VM-Series Firewall Templates
The firewall templates deploy an internet-facing external
load balancer and VM-Series firewalls within an auto scaling group
that spans a minimum of two Availability Zones (AZs). The external
load balancer distributes incoming VPC traffic across the pool of
VM-Series firewalls. It can be an application load balancer (ALB)
or a network load balancer (NLB). The VM-Series firewalls automatically
publish custom PAN-OS metrics that enable auto scaling.
| Template | Description |
|---|---|
| firewall-new-vpc-v2.1.template | Deploys a firewall stack with two to four availability zones in a new VPC. |
| firewall-existing-vpc-v2.1.template | Deploys a firewall stack with two to four
availability zones in an existing VPC. To deploy in an existing
VPC you must enter:
|
See Customize the Firewall Template Before Launch (v2.0 and v2.1) for more
on these parameters.
Application Templates
The application template deploys an internal load balancer
(ILB) and one auto scaling group with a web server in each availability
zone (AZ).
| Template | Description |
|---|---|
| panw-aws-same-vpc-v2.1.template | Deploy application in same VPC as the firewall VPC. You can choose a network or application load balancer. |
panw-aws-alb-new-vpc-v2.1.template | Deploy application in a new VPC, using ALB
as the internal load balancer, and using VPC Peering between the
firewall VPC and application VPC. Supports both same account and
cross-account deployments. You must supply the following parameters:
|
| panw-aws-nlb-new-vpc-v2.1.template | Deploy application in a new VPC, using NLB
as the internal load balancer, and using NLB Endpoint Services/Interfaces
to communicate between the firewall VPC and application VPC. You
must supply these parameters.
|
| panw-aws-alb-existing-vpc-v2.1.template | Deploy ALB in an existing Application VPC.
You must supply the VPC ID for your application, and an existing
Subnet ID. This template deploys the load balancer in the application
VPC and establishes the lambda resources. You must detach your target
workload from any existing load balancer, and connect it to the
new load balancer. |
| panw-aws-nlb-existing-vpc-v2.1.template | Deploy NLB in an existing Application VPC.
Deploy application in a new VPC, using NLB as the internal load
balancer, and using NLB Endpoint Services/Interfaces to communicate
between the firewall VPC and application VPC. |
Lambda Functions
AWS Lambda provides robust, event-driven automation
without the need for complex orchestration software. AWS Lambda
monitors a Simple Queue Service (SQS) to learn about load balancers
(ALBs or NLBs) that publish to the queue. When the Lambda function
detects a new load balancer, it creates a new NAT policy rule and
applies it to the VM-Series firewalls within the ASG. The firewalls
have a NAT policy rule for each application, and the firewalls use
the NAT policy rule (that maps the port to the load balancer IP
address) to forward traffic to the load balancer in front of the
application web servers.
The Lambda functions also delete all the configuration items
that Lambda added to the device group and template stack in Panorama.
This includes the NAT rule, Address Object, and Static Routes that
were pushed to the VM-Series firewall. The Lambda function handles
delicensing as well.
To learn more about the Lambda functions, refer to the Palo Alto Networks AWS AutoScale Documentation.
Panorama
You must have Panorama management server in Panorama
mode to configure Auto Scaling v2.1.
The Panorama management server provides centralized monitoring
and management of multiple Palo Alto Networks next-generation firewalls
from a single location. Panorama allows you to oversee all applications,
users, and content traversing your network, and use this knowledge
to create application enablement policies that protect and control
the network. If you are not familiar with Panorama please see the Panorama Administrator’s Guide.
Managed firewalls are bootstrapped with an init-config.txt file.
A sample file is included in the GitHub repository so that you can
copy the configuration from the template stack and device group
when you create them in your existing Panorama.
The untrust and trust zones created in Panorama must be
all lower case.
In Panorama you must configure your network interfaces using
DHCP.
- Only eth1/1 should automatically create default route trust and untrust zones.
- The Security Policy zones are named untrust and trust.All zone names must be lower case
- The templates configure an Administrator account named pandemo and the password demopassword.
- Create a virtual router with the naming convention VR-<TemplateStackName>. On the virtual router ECMP tab, enable ECMP.
- To set the DNS server address on Panorama, select DeviceSetupServices. Set the Primary DNS Server to 169.254.169.253, the Secondary DNS Server to 8.8.8.8, and the FQDN Refresh Time (sec) to 60. Panorama requires the AWS DNS server IP address to resolve the FQDN of the internal load balancer on AWS. The FQDN refresh time is the interval at which Panorama commits newly detected internal load balancers.
After the application template has launched, Lambda populates
the following in Panorama:
- NAT policy
- Address object for LB in Application Template
- Static routes in the virtual router
- Tcp81 service object
The v2.1 firewall template includes an AWS NAT gateway that the
firewalls use to initiate outbound requests for retrieving updates,
connecting to Panorama, and publishing metrics to AWS CloudWatch.
The NAT Gateways also have Elastic IP addresses attached to them
for each zone.
You need the following Panorama resources to work with the Auto
Scale templates for AWS.
| Panorama API Key | You need a Panorama API key to authenticate the API. Lambda uses your API key to autoconfigure template and device group options. To generate the API key, see Get Your API Key. |
| Panorama License Deactivation Key | The template requires a license deactivation API key and the “Verify Update Server Identity” to be enabled to deactivate the license keys from Panorama. The license deactivation key should be obtained from Palo Alto Customer Support Portal as described in Install a License Deactivation API Key. |
| Panorama VM-Auth-Key | You need a vm-auth-key to enable bootstrapped
firewalls to connect to Panorama and receive their bootstrap configuration.
See Generate the VM Auth Key on Panorama. |
| Panorama Management Interface Access |
|
Bootstrap Files
The GitHub auto scaling repository includes an init-cfg.txt file
so that the VM-Series firewall has the basic configuration to:
- Perform interface swap so the VM-Series firewall untrust traffic uses AWS ENI for eth0.
- Communicate to Panorama for device group and template configuration.
The auto scaling GitHub repository has the basic configuration
to get started. This auto scaling solution requires swapping the
dataplane and management interfaces to enable the load balancer
to forward web traffic to the VM-Series firewall auto scaling tier.
For details on management interface mapping with the Amazon ELB as
shown in Management Interface Mapping for Use with Amazon ELB.
Plan to Deploy VM-Series Auto Scaling Templates for AWS (v2.1)
Before starting the deployment, review the following
resources.
- See Auto Scaling VM-Series Firewalls with the Amazon ELB Service for an overview of template features, and account planning.
- Customize the Firewall Template Before Launch (v2.0 and v2.1). The basic parameters in this topic apply to all template versions.
- These concepts apply to all template versions.