Identity
Set Up an Entra ID Directory
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Identity Docs
Set Up an Entra ID Directory
Learn how to set up an Entra ID directory in the Cloud Identity Engine.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
| The Cloud Identity Engine service is free; however, the enforcement points utilizing directory data may require specific licenses. Click here for more information. |
Configure an Entra ID directory in the Cloud Identity Engine to allow the
Cloud Identity Engine to collect data from your Entra ID directory for policy rule
enforcement and user visibility.
To configure an Entra ID in the Cloud Identity Engine, you
must have at least the following role privileges in Entra ID:
- Application Administrator
- Cloud Application Administrator
For more information about roles in Azure AD, refer to the following link.
If you Configure Entra ID Using the CIE Enterprise App, the account you use must have the Global
Administrator Role to set up Azure. However, the app itself uses the Cloud
Application Administrator Role, not the Global Administrator Role.
To further reduce sync time and minimize the amount of
data collected by the Cloud Identity Engine, you can configure the Cloud Identity
Engine to sync only specific groups from your directory by filtering the groups.
Because SCIM is most suitable for small and frequent data requests, directory update
intervals are restricted by Microsoft to once every 40 minutes. If you choose to
filter the groups instead, directory updates can be as often as every 5 minutes.
Choose the best option for your deployment based on your organizational and
regulatory requirements.
For an Azure Active Directory (AD), the Cloud
Identity Engine retrieves updates from the directory using the following
schedule:
- Users, Groups, and Devices—When the Cloud Identity Engine syncs changes.
- Apps—Every x hours (where x is either a maximum of 3 hours or the duration necessary to complete the previous apps sync).
- Role Assignments—Every x hours (where x is either a maximum of 24 hours or the duration necessary to complete the previous role assignment sync).
When you configure an Azure
AD for the Cloud Identity Engine, log in, and grant the necessary permissions,
Microsoft automatically onboards the Cloud Identity Engine Enterprise App into your
Azure AD.
Select one of the two
methods for the Cloud Identity Engine to connect to your Azure AD:
- The CIE Enterprise App, which requires you to log in to make changes to the directory configuration in the Cloud Identity Engine
- The Client Credential Flow, which initially requires additional permissions but does not require you to log in to change the directory configuration in the Cloud Identity Engine.
Configure Entra ID Using the CIE Enterprise App
Learn how to configure Entra ID in the Cloud Identity Engine using the CIE Enterprise
app.
- Copy the directory ID for your Azure directory.
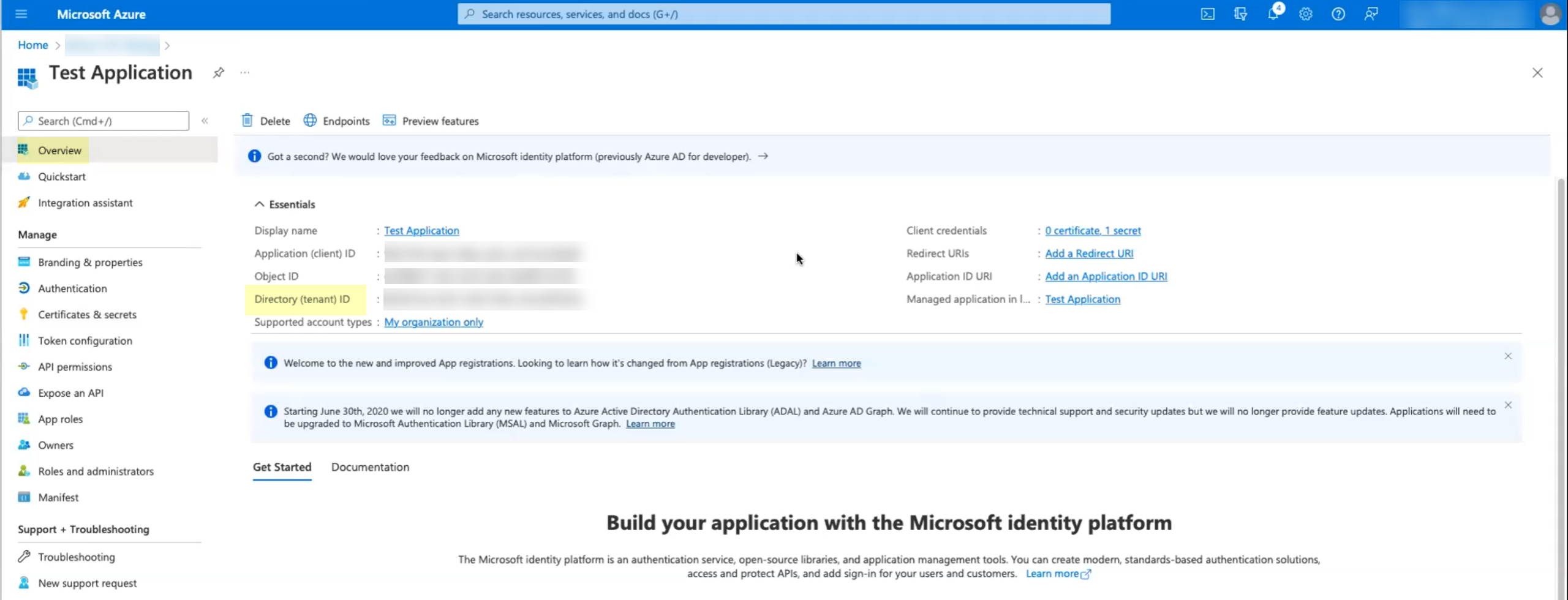
- Log in to the Azure administrator portal using the credentials of the account you want to use to connect to the Cloud Identity Engine (for example, a service account) and select Overview.Copy the Directory (tenant) ID and store it in a secure location.
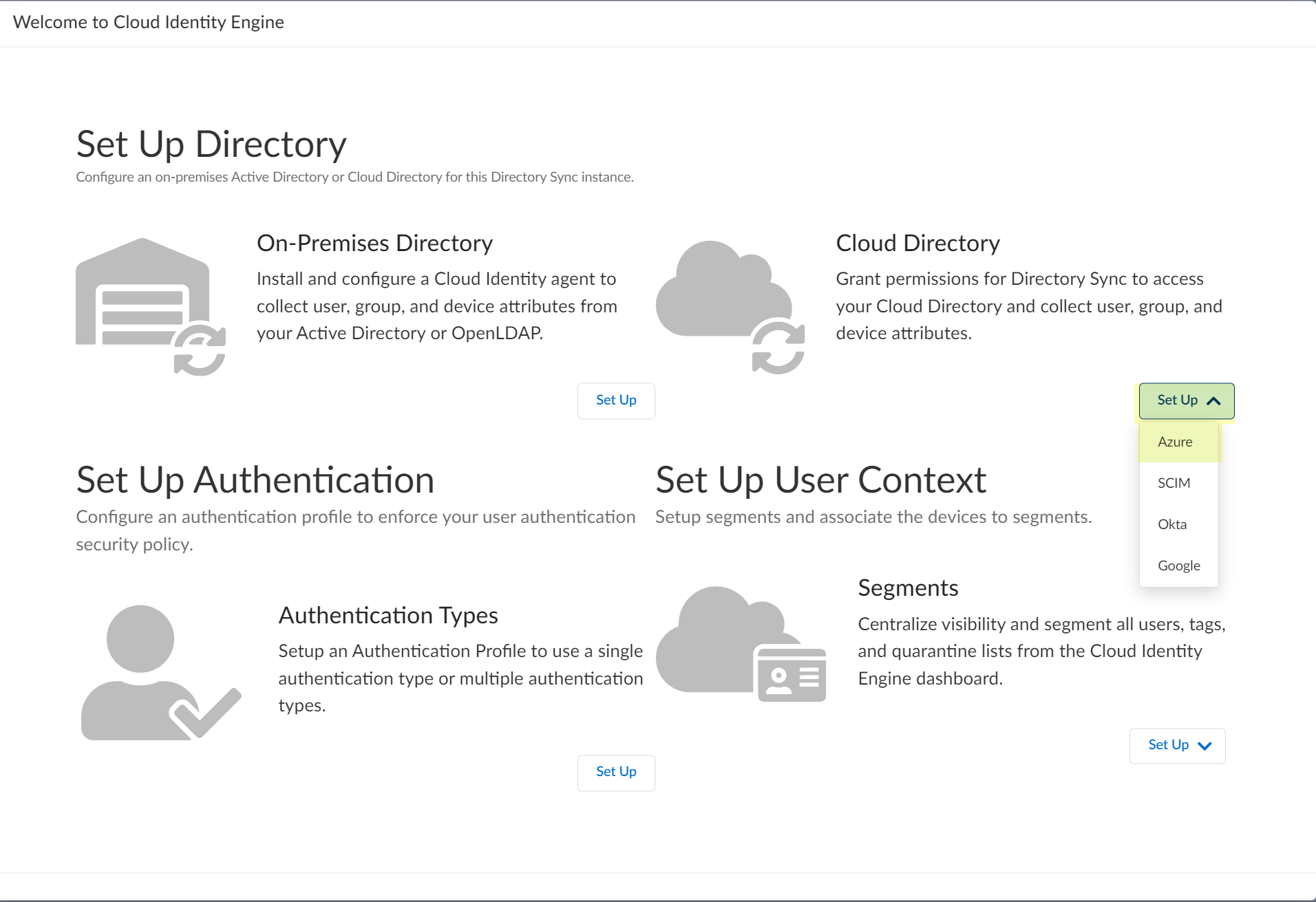
![]() Set up your Azure directory in the Cloud Identity Engine.
Set up your Azure directory in the Cloud Identity Engine.- In the Cloud Identity Engine app, select Directories then click Add New Directory.Set Up an Azure directory.
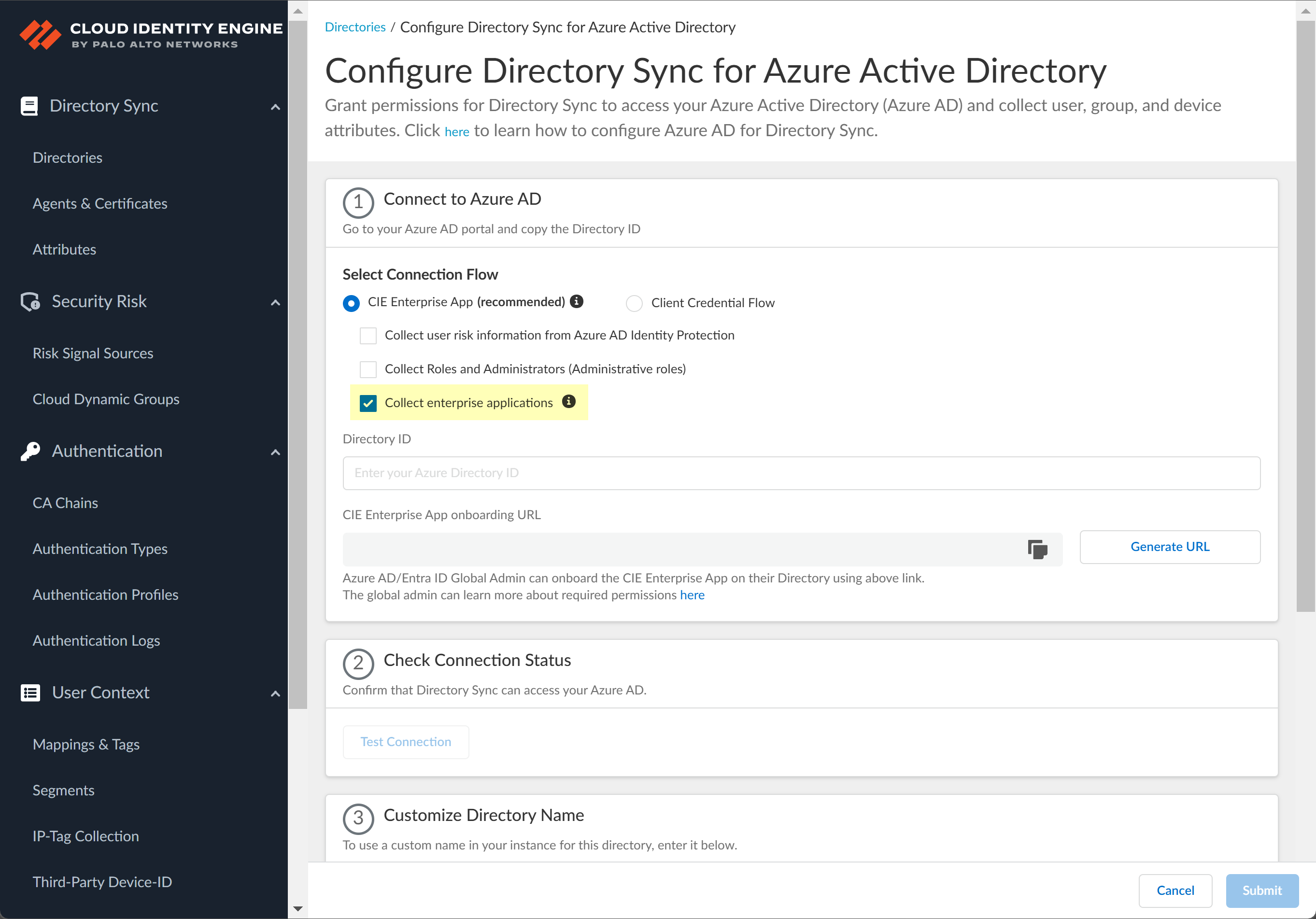
![]() (Optional) Select additional information types to collect from your Azure directory.The CIE Enterprise app automatically requests the privileges necessary to retrieve the directory information, including for any options you have selected. If you enable an option that requires additional privileges, you must reconnect the directory. For configurations that use the CIE Enterprise app, use the CIE Enterprise App onboarding URL in step 4.2 to ensure you grant the necessary privileges.After onboarding the app into the directory, you can revoke privileges if they are not necessary for your configuration. Do not revoke privileges for options that you have selected for your configuration. If you revoke a privilege that is necessary for an option you have select or that is required for the Cloud Identity Engine by default, the sync cannot complete successfully.To enable permissions that have been revoked, edit the directory configuration and complete steps 4.1 through 4.5.The following list provides the permissions for each additional information type.
(Optional) Select additional information types to collect from your Azure directory.The CIE Enterprise app automatically requests the privileges necessary to retrieve the directory information, including for any options you have selected. If you enable an option that requires additional privileges, you must reconnect the directory. For configurations that use the CIE Enterprise app, use the CIE Enterprise App onboarding URL in step 4.2 to ensure you grant the necessary privileges.After onboarding the app into the directory, you can revoke privileges if they are not necessary for your configuration. Do not revoke privileges for options that you have selected for your configuration. If you revoke a privilege that is necessary for an option you have select or that is required for the Cloud Identity Engine by default, the sync cannot complete successfully.To enable permissions that have been revoked, edit the directory configuration and complete steps 4.1 through 4.5.The following list provides the permissions for each additional information type.- Collect user risk information from Azure AD Identity
Protection:
- IdentityRiskyUser.Read.All
- IdentityRiskEvent.Read.All
- Collect Roles and Administrators (Administrative roles): Directory.Read.All or RoleManagement.Read.Directory.
- Collect enterprise applications: Application.Read.All
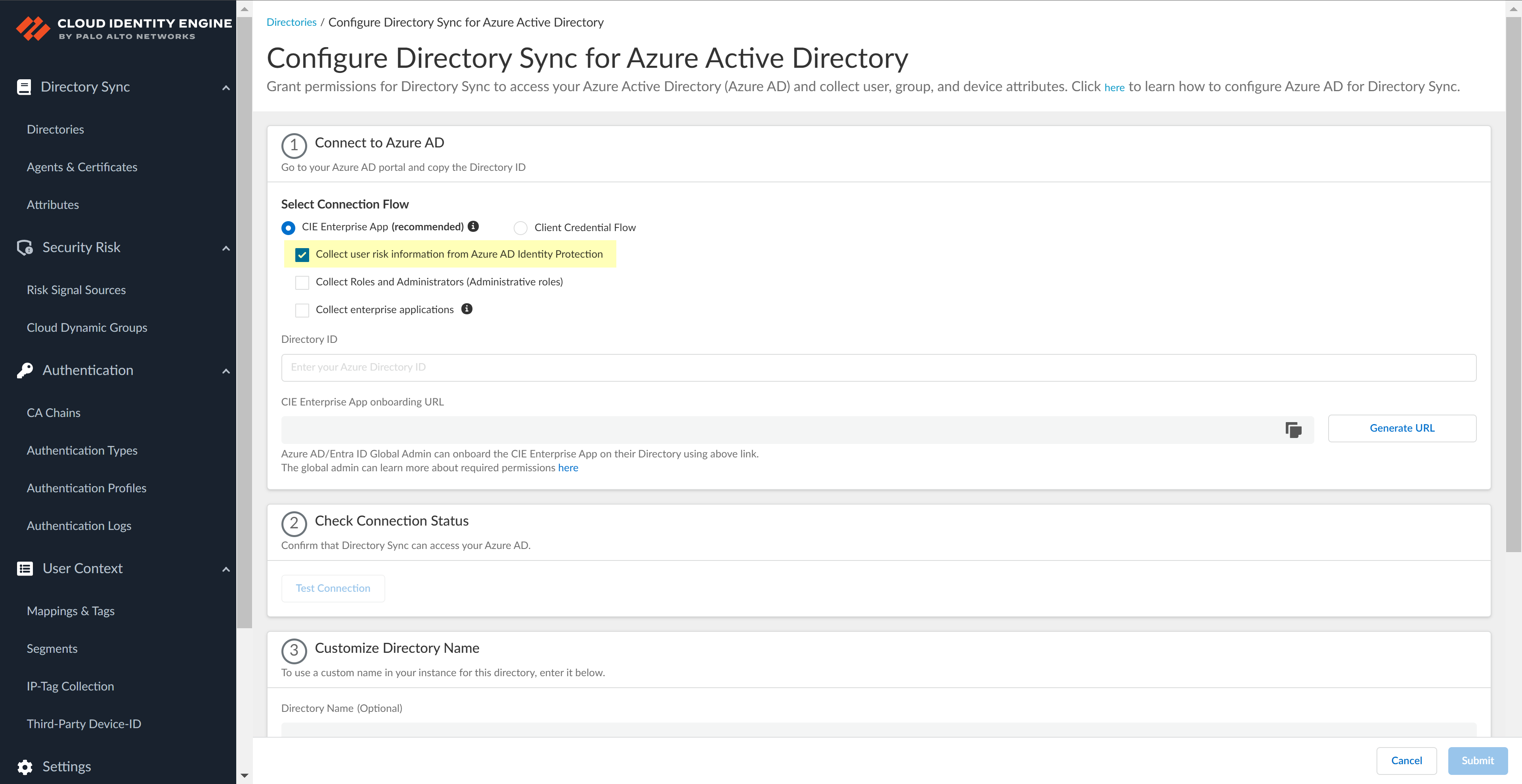
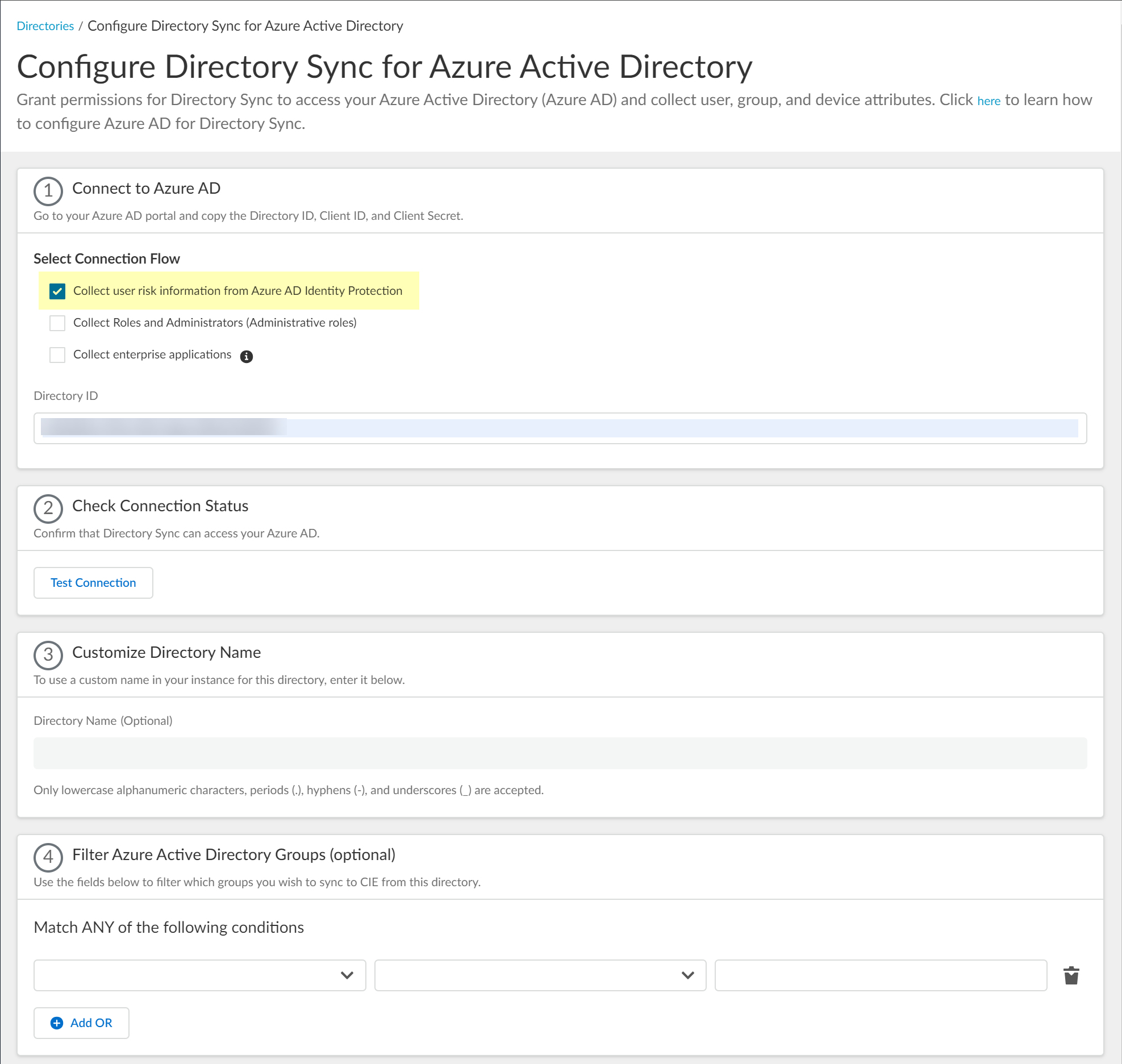
- Select whether you want to Collect user risk information from Azure AD Identity Protection to use in attribute-based Cloud Dynamic User Groups.
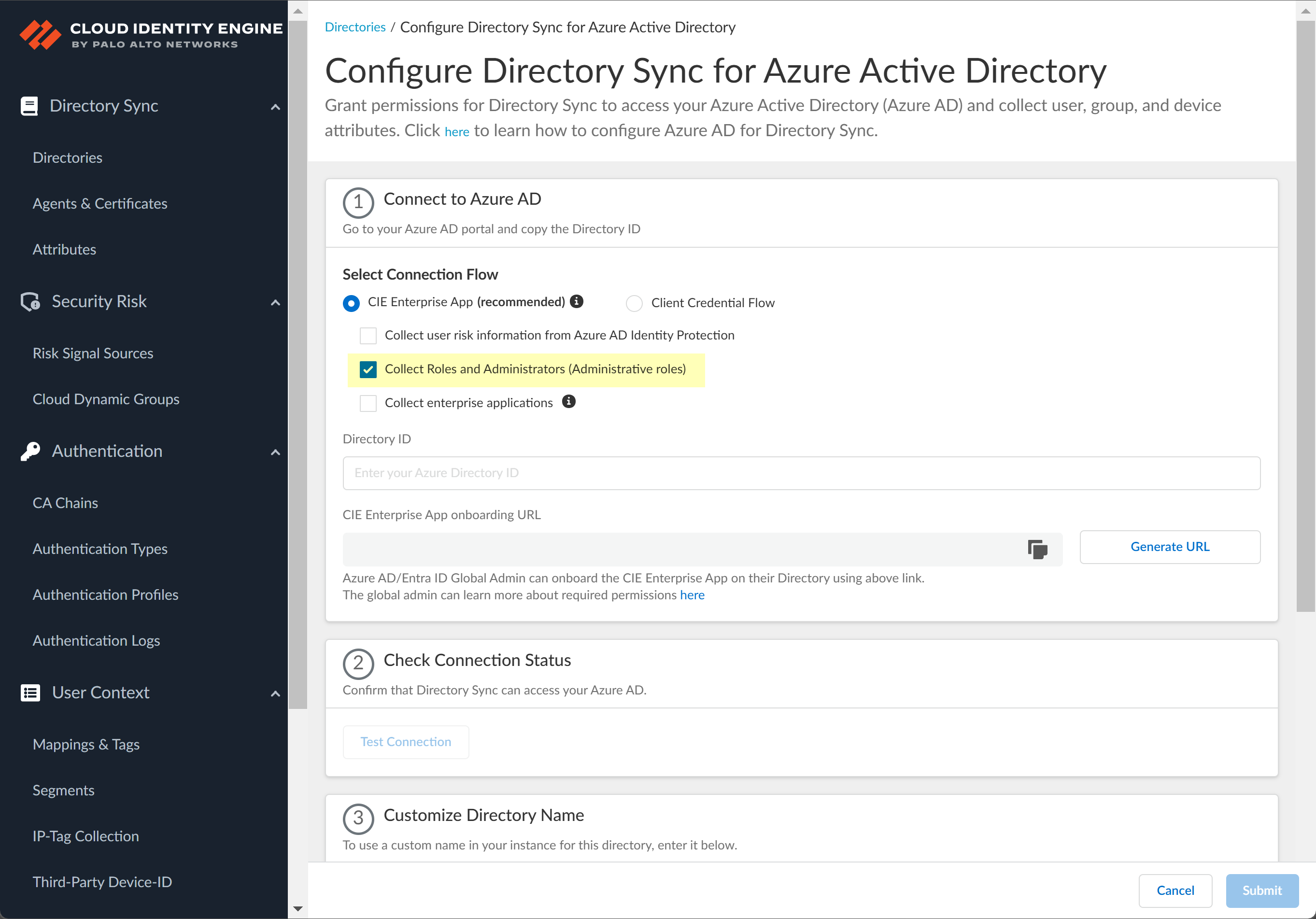
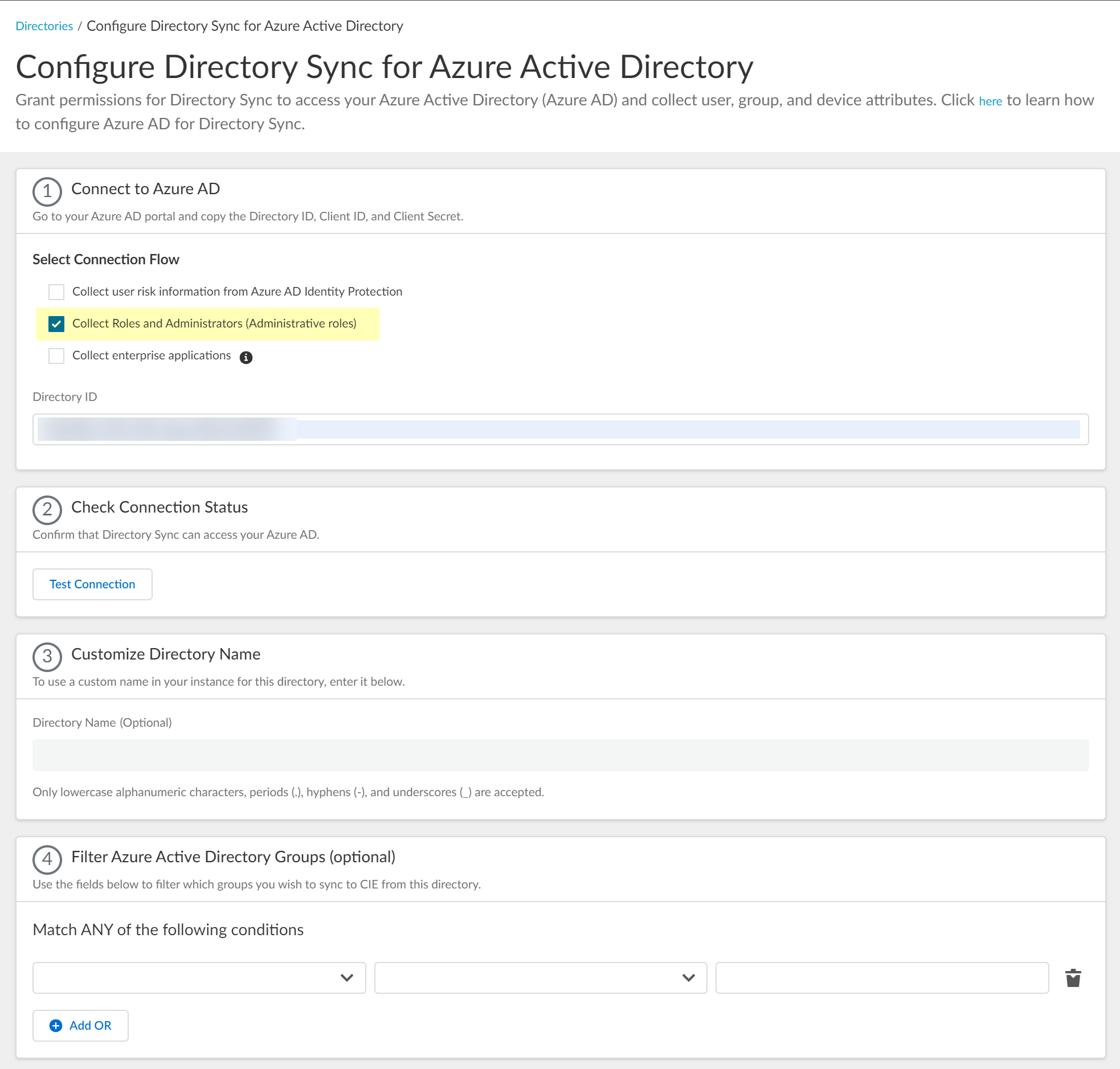
![]() Select whether you want to Collect Roles and Administrators (Administrative roles) to retrieve roleAssignments attribute information for users and groups. Allowing the Cloud Identity Engine to include this information for analysis helps to prevent role-based malicious attacks.By default, the Cloud Identity Engine enables this option for tenants who are associated with Cortex XDR.
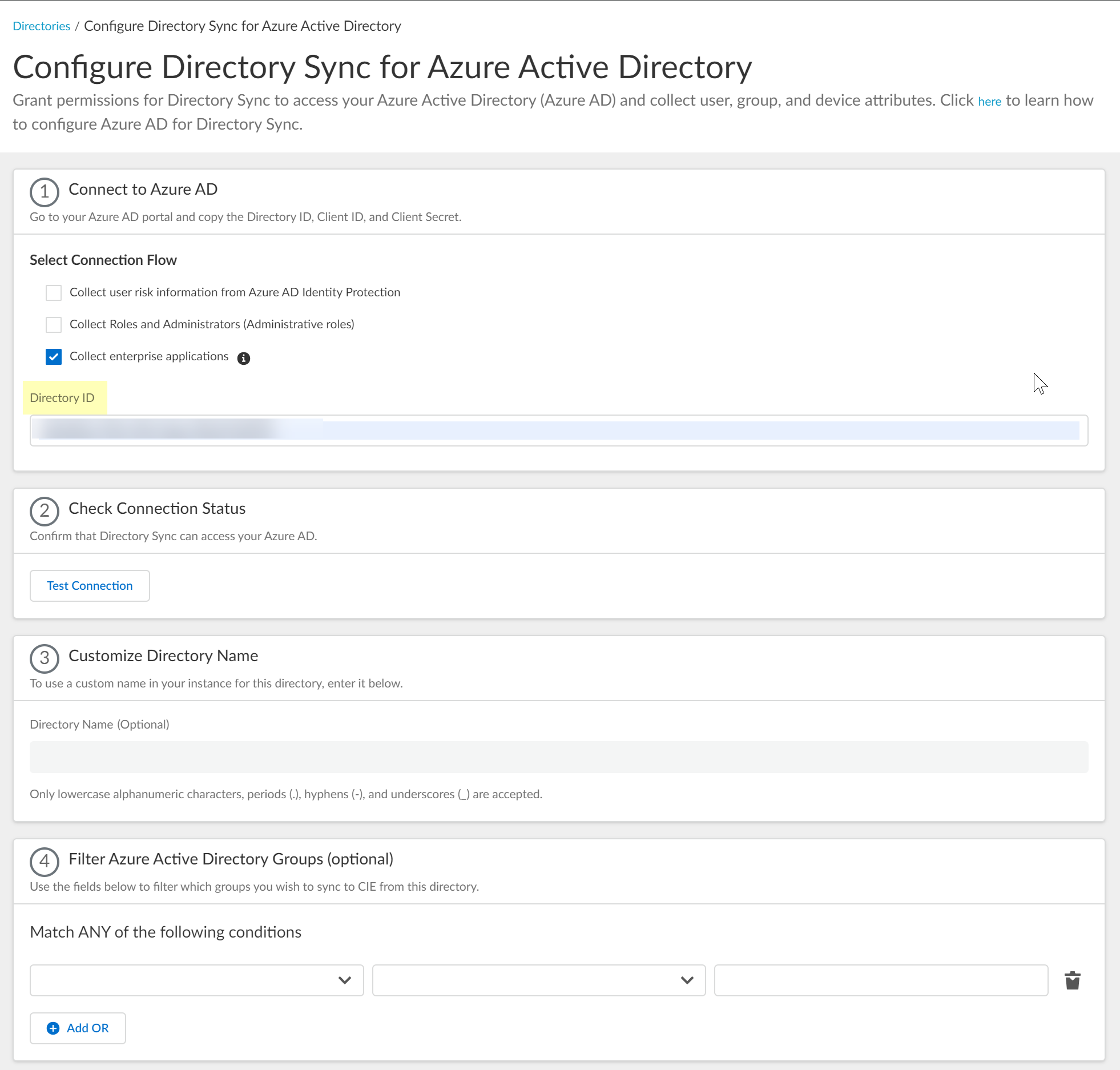
Select whether you want to Collect Roles and Administrators (Administrative roles) to retrieve roleAssignments attribute information for users and groups. Allowing the Cloud Identity Engine to include this information for analysis helps to prevent role-based malicious attacks.By default, the Cloud Identity Engine enables this option for tenants who are associated with Cortex XDR.![]() Select whether you want to Collect enterprise applications data so that it displays when you View Directory Data. If you don't want to collect the application data or you don't use application data in your Security policy, deselect the check box to decrease the sync time.
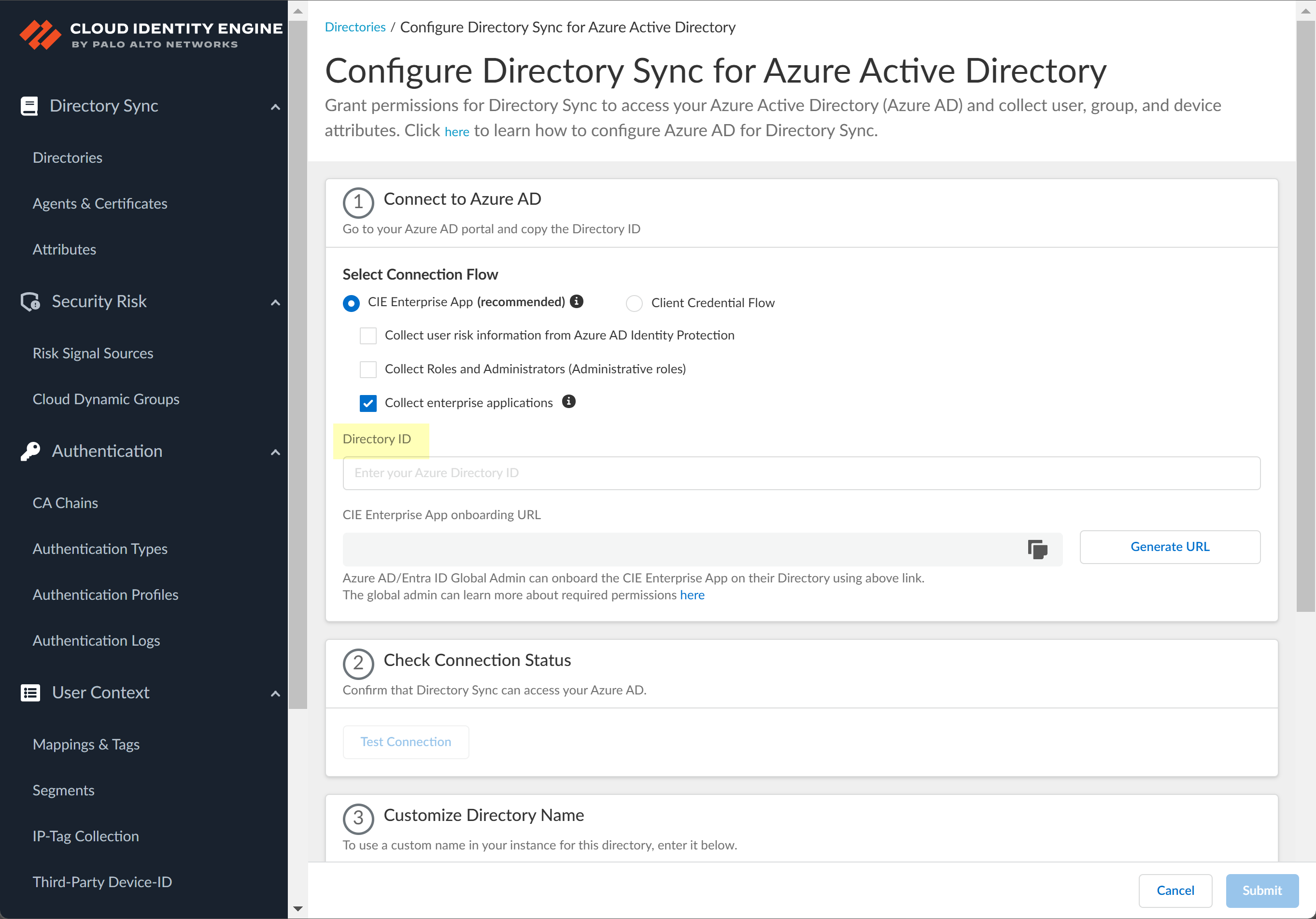
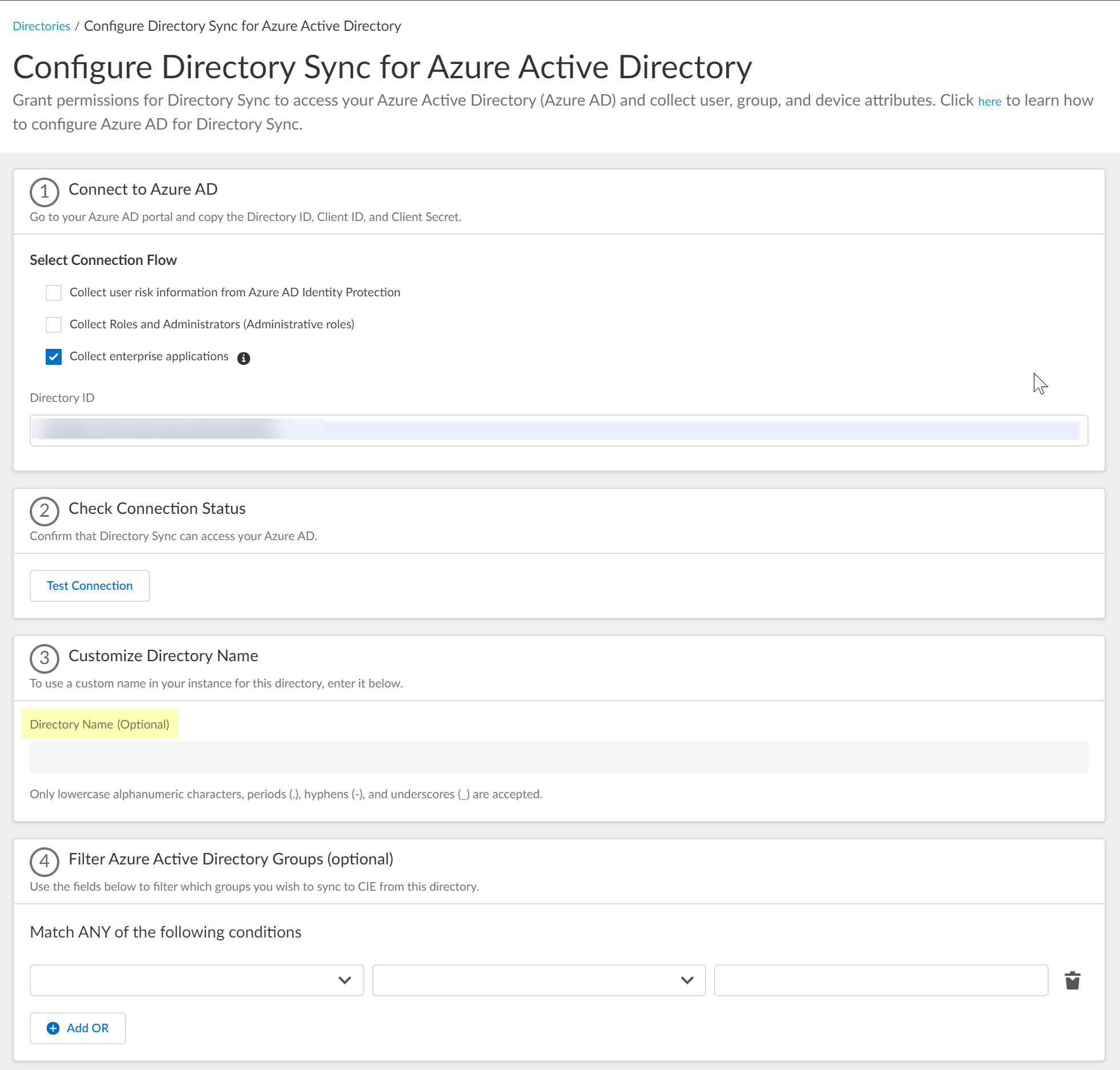
Select whether you want to Collect enterprise applications data so that it displays when you View Directory Data. If you don't want to collect the application data or you don't use application data in your Security policy, deselect the check box to decrease the sync time.![]() Configure your Azure directory information in the Cloud Identity Engine.
Configure your Azure directory information in the Cloud Identity Engine.- Enter the directory ID you copied in step 1.2 as the Directory ID.
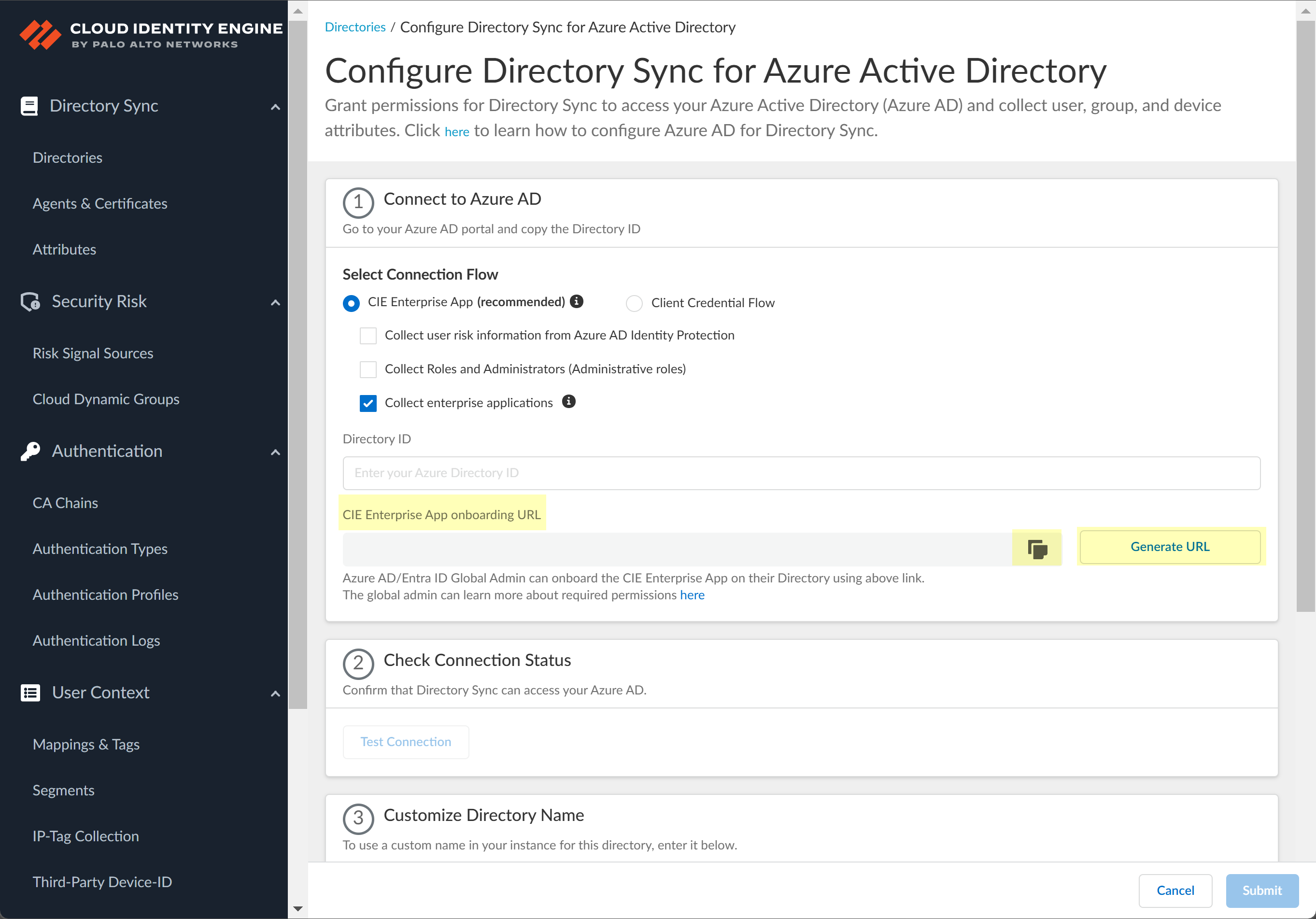
![]() To obtain the CIE Enterprise App onboarding URL, click Generate URL then Copy the URL and open it in a new tab or window.
To obtain the CIE Enterprise App onboarding URL, click Generate URL then Copy the URL and open it in a new tab or window.![]() Enter the email address or phone number for the Global Administrator Role account you use to connect to the Cloud Identity Engine then click Next.
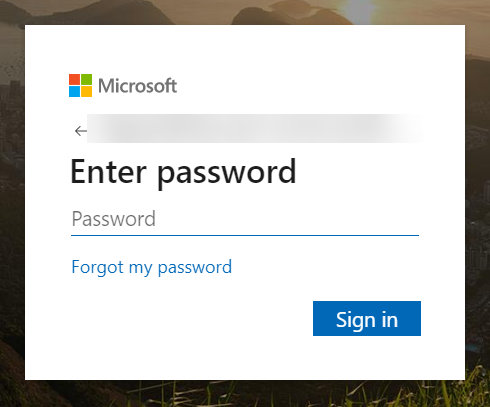
Enter the email address or phone number for the Global Administrator Role account you use to connect to the Cloud Identity Engine then click Next.![]() Enter your password and Sign in.
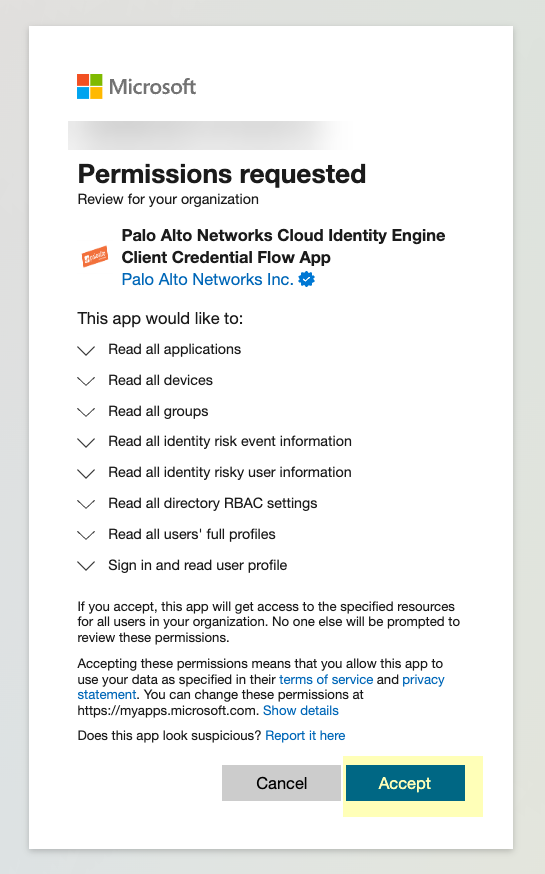
Enter your password and Sign in.![]() Click Accept to grant the necessary permissions for your Azure directory.When you accept, Azure automatically enables the following required permissions, as well as the additional information type permissions listed in step 3:
Click Accept to grant the necessary permissions for your Azure directory.When you accept, Azure automatically enables the following required permissions, as well as the additional information type permissions listed in step 3:- Device.Read.All—Application, Read all devices
- Group.Read.All—Application, Read all groups
- User.Read.All—Application, Read all users' full profiles
- User.Read—Delegated, Sign in and read user profile
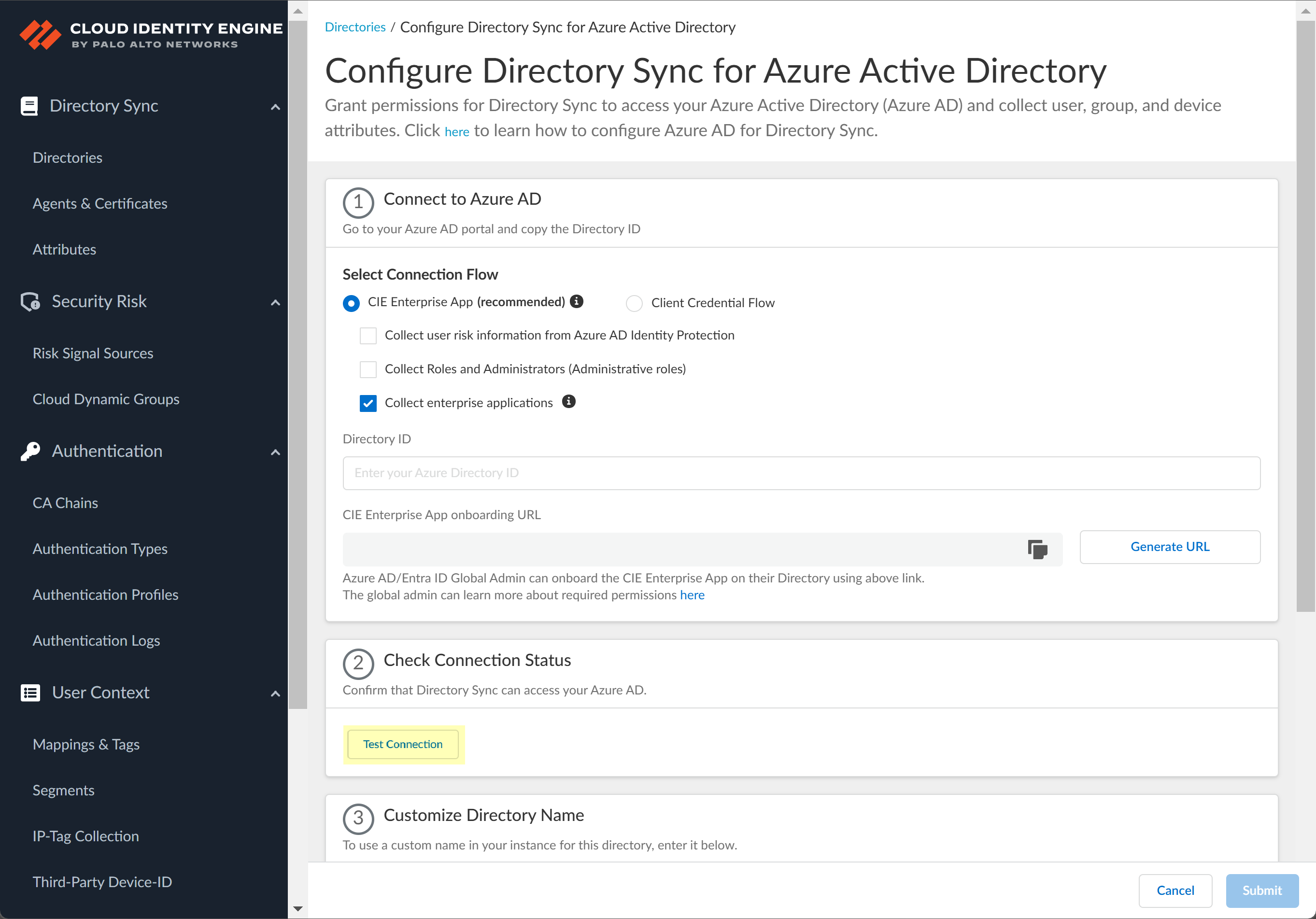
![]() Click Test Connection to confirm that the Cloud Identity Engine can successfully connect to your Azure AD tenant.
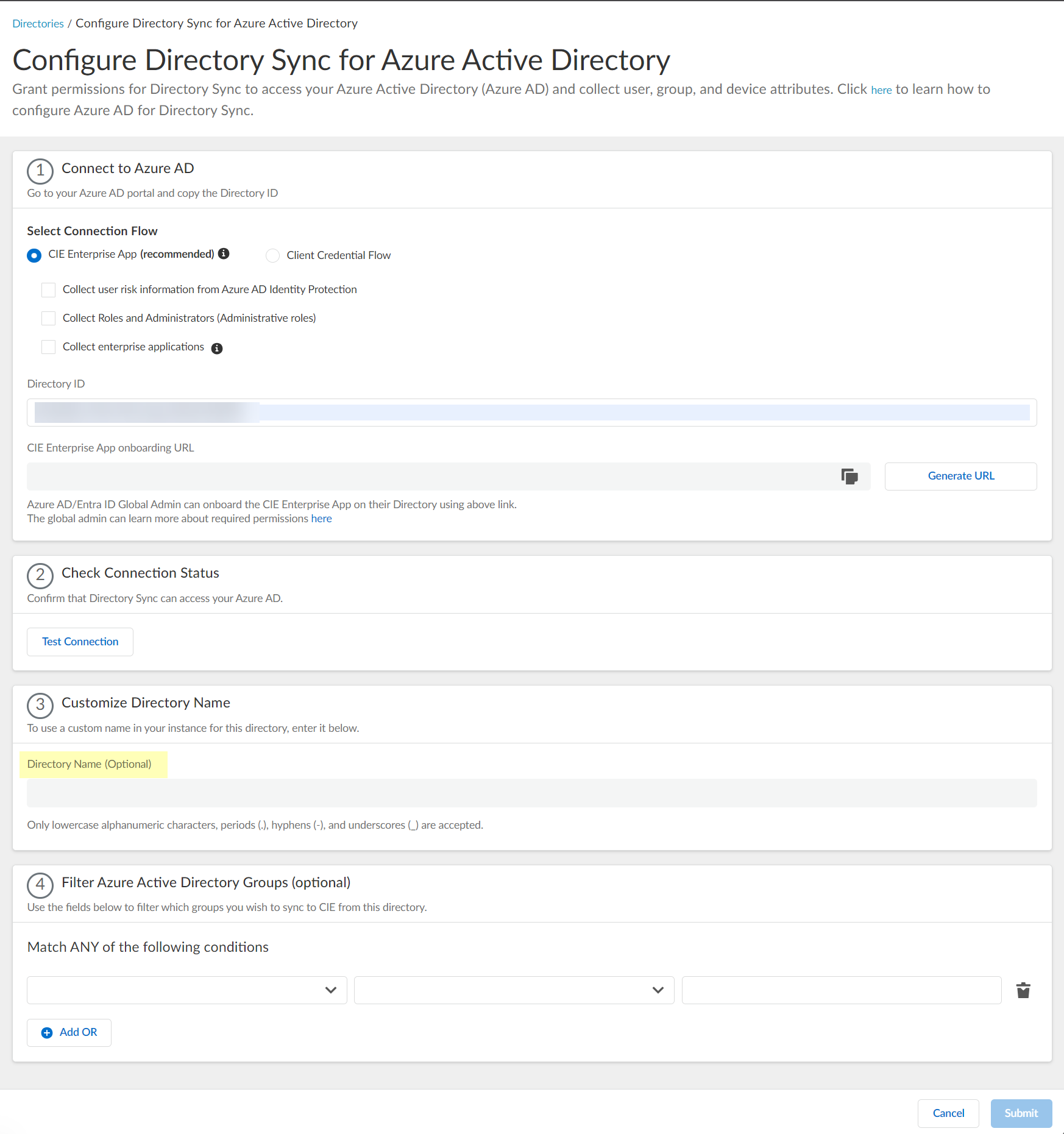
Click Test Connection to confirm that the Cloud Identity Engine can successfully connect to your Azure AD tenant.![]() (Optional) Enter a custom Directory Name (Optional) to use in the Cloud Identity Engine.
(Optional) Enter a custom Directory Name (Optional) to use in the Cloud Identity Engine.![]() (Optional) Upload a .CSV file to use as a filter for groups.
(Optional) Upload a .CSV file to use as a filter for groups.- Click Upload CSV to upload a comma-separated value (CSV) file to use as a filter.
![]() Drag and drop the .CSV file or click Browse files to select the .CSV file you want to use as a filter.
Drag and drop the .CSV file or click Browse files to select the .CSV file you want to use as a filter.![]() Select the Upload Type for the filter.
Select the Upload Type for the filter.- Update Filters—Update the existing filters with the .CSV data.
- Replace Existing Filters—Replace the existing filters with the .CSV data.
![]() Select the Attribute Name you want to use for the filter (Name or Unique Identifier).Click Apply to confirm the changes.
Select the Attribute Name you want to use for the filter (Name or Unique Identifier).Click Apply to confirm the changes.![]() (Optional) Select whether you want to Filter Azure Active Directory Groups.
(Optional) Select whether you want to Filter Azure Active Directory Groups.- Select the group attribute you want to use as a filter.
- Name—Filter the groups based on the group name.
- Unique Identifier—Filter the groups based on the unique identifier for the group.
![]() Select how you want to filter the groups.
Select how you want to filter the groups.- (for Name attribute only)
begins with—Filter the groups based on a
partial match for the text you enter. The filter supports spaces in the search query.
- is equal to—Filter the groups based on an exact match for the text you enter.
![]() Enter the search query you want to use to filter the groups (either alphanumeric characters for a name or numeric characters for a unique identifier).
Enter the search query you want to use to filter the groups (either alphanumeric characters for a name or numeric characters for a unique identifier).![]() (Optional) Configure an additional filter by clicking Add ORAdd Filter and repeating the previous three steps for each filter you want to include.If you select additional attributes as match conditions, the Cloud Identity Engine initially attempts to find a match for the first condition, then continues to match based on the additional conditions you specify.
(Optional) Configure an additional filter by clicking Add ORAdd Filter and repeating the previous three steps for each filter you want to include.If you select additional attributes as match conditions, the Cloud Identity Engine initially attempts to find a match for the first condition, then continues to match based on the additional conditions you specify.![]() Submit your changes and verify your directory information when the Directories page displays.
Submit your changes and verify your directory information when the Directories page displays.Configure Azure Using the Client Credential Flow
The Client Credential Flow option for Azure Active Directory (AD) in the Cloud Identity Engine allows you to use a service account to log in to your Azure AD in the Cloud Identity Engine. Using a service account is strongly recommended, as this is a more secure method for directory access and does not require the account to be associated with a specific user.If this is the first time you have created a Cloud Identity Engine tenant, the Cloud Identity Engine app is not available in the Azure app gallery, so you must create a custom app.If you already have an existing Azure AD configuration in the Cloud Identity Engine, you can easily migrate the existing configuration to use the client credential flow option by reconnecting your Azure AD to the Cloud Identity Engine, selecting the Client Credential Flow option, and testing the connection to verify the configuration.- If you have not already done so, activate your Cloud Identity Engine tenant.Grant the required read-only permissions in the Azure Portal.
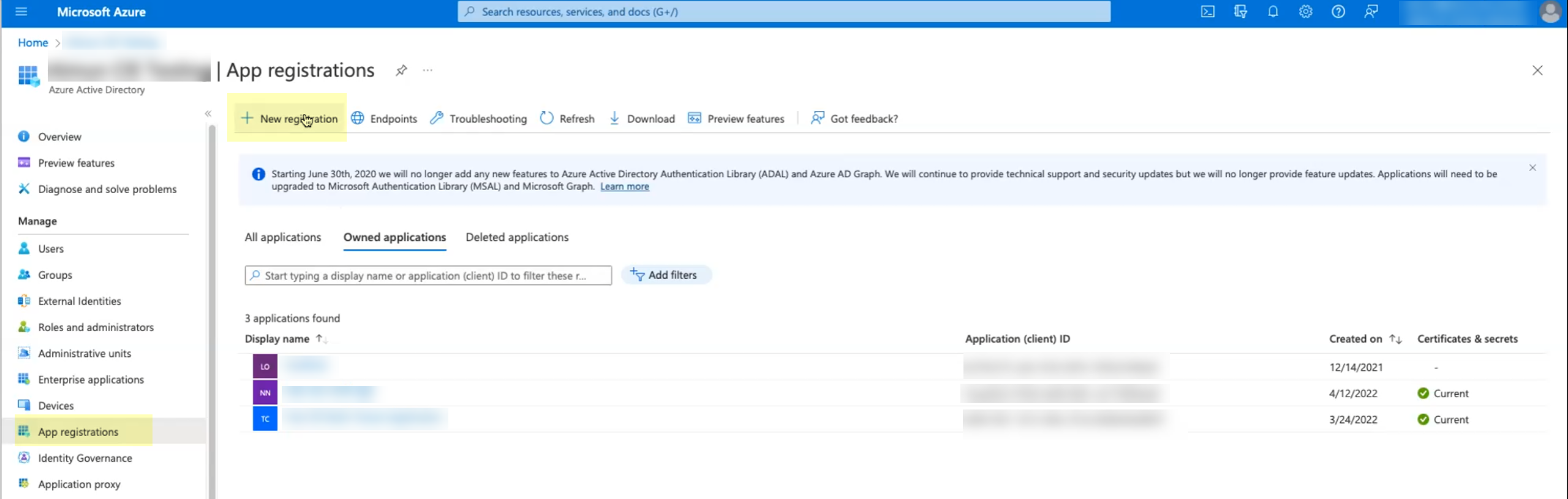
- In the Azure Portal, select HomeAzure Active DirectoryApp Registrations.Click New registration.
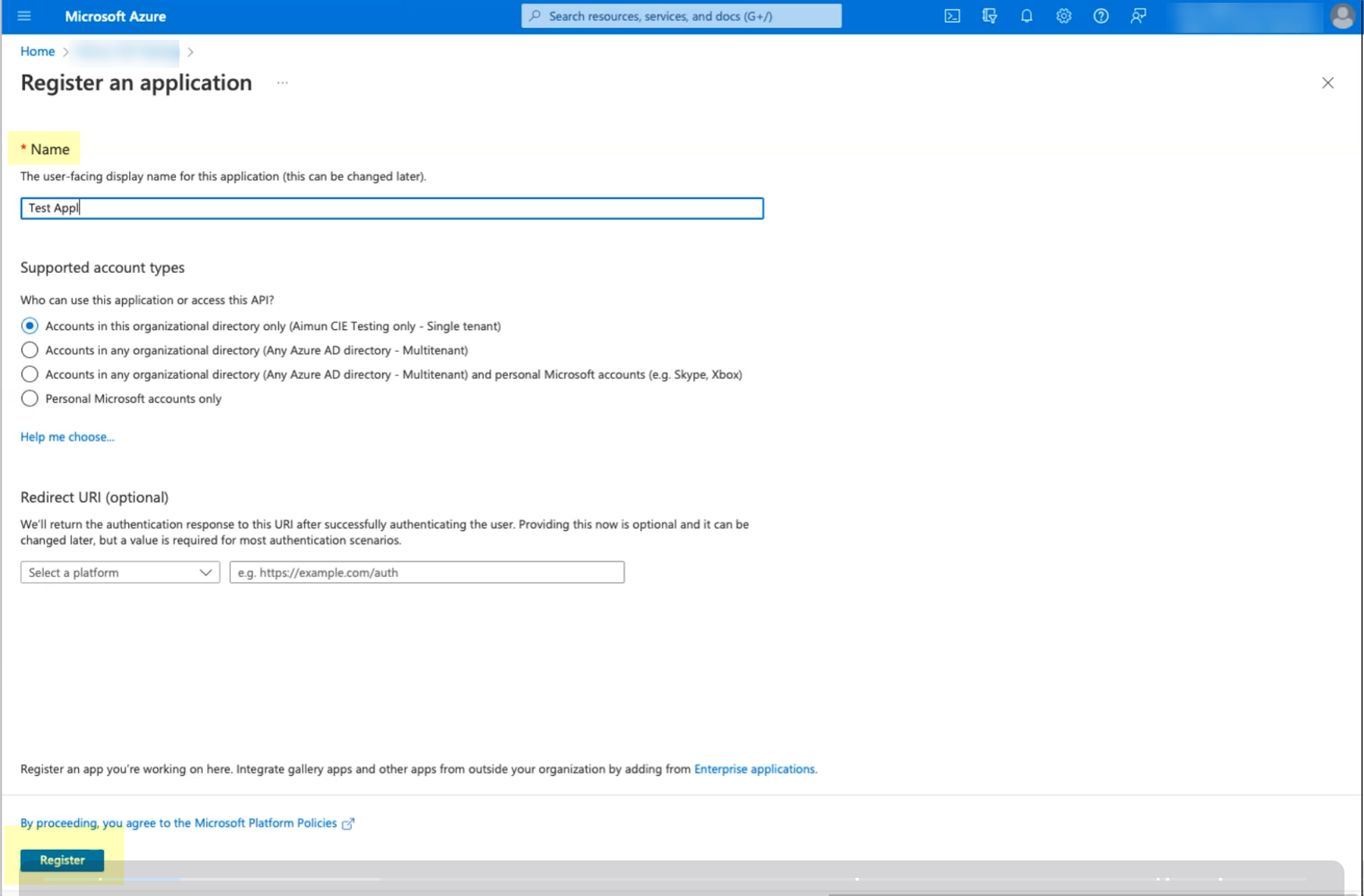
![]() Enter a Name then click Register.
Enter a Name then click Register.![]() Select API permissions then click Add a permission.
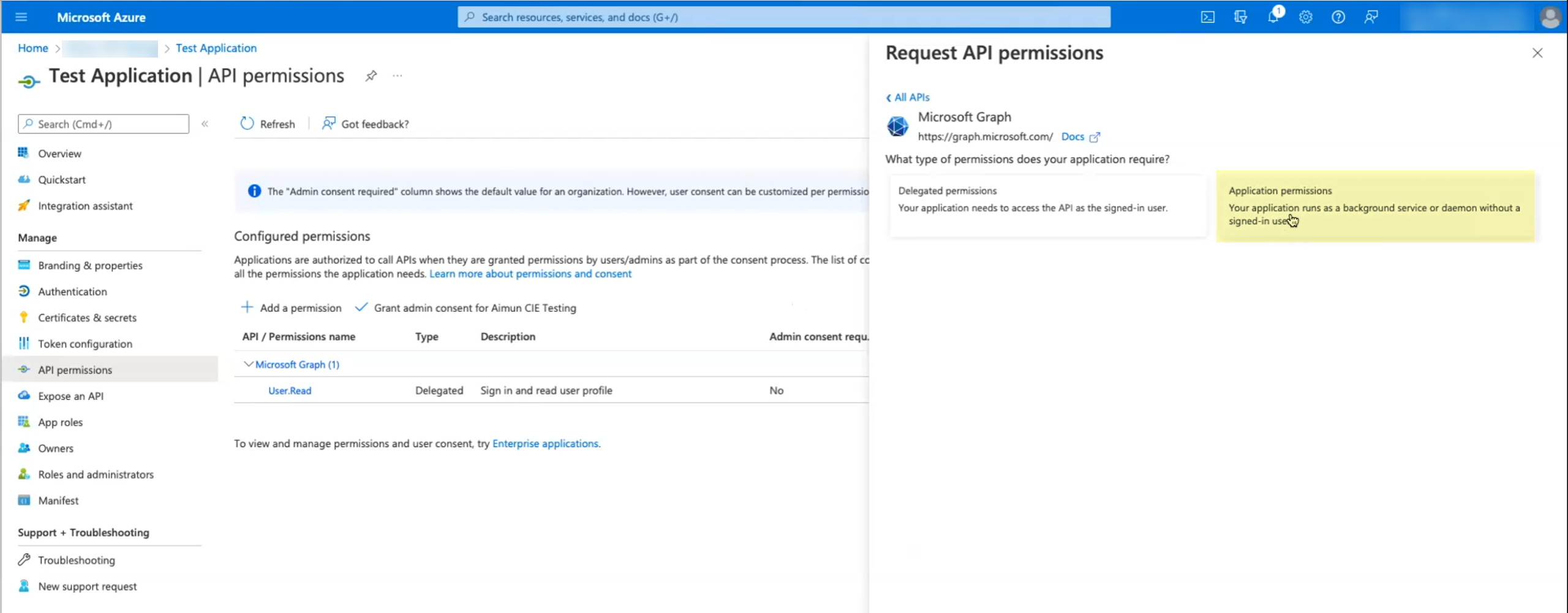
Select API permissions then click Add a permission.![]() Click Microsoft Graph then select Application permissions.
Click Microsoft Graph then select Application permissions.![]() Select the following permissions then click Add permissions:
Select the following permissions then click Add permissions:- Device.Read.All—Application, Read all devices
- GroupMember.Read.All—Application, Read all groups
- User.Read.All—Application, Read all users' full profiles
- User.Read—Delegated, Sign in and read user profile
The permissions listed above represent the minimum required permissions that use least privilege access. If you prefer a less granular scope that is simpler to implement, you can use these permissions instead:- Directory.Read.All
- Organization.Read.All
- If you want to use user risk information in attribute-based Cloud Dynamic User Groups, you must grant additional permissions. For more information, refer to the documentation on how to Create a Cloud Dynamic User Group.
- If you want to collect information on roles and administrators, if you have already granted the Directory.Read.All scope, no further permissions are required. If you are using the scopes listed above, you must also grant the RoleManagement.Read.Directory scope to collect role and administrator information. For more information, refer to step 6.
- If you want to collect enterprise application data, you must also grant the Application.Read.All scope. For more information, refer to step 7.
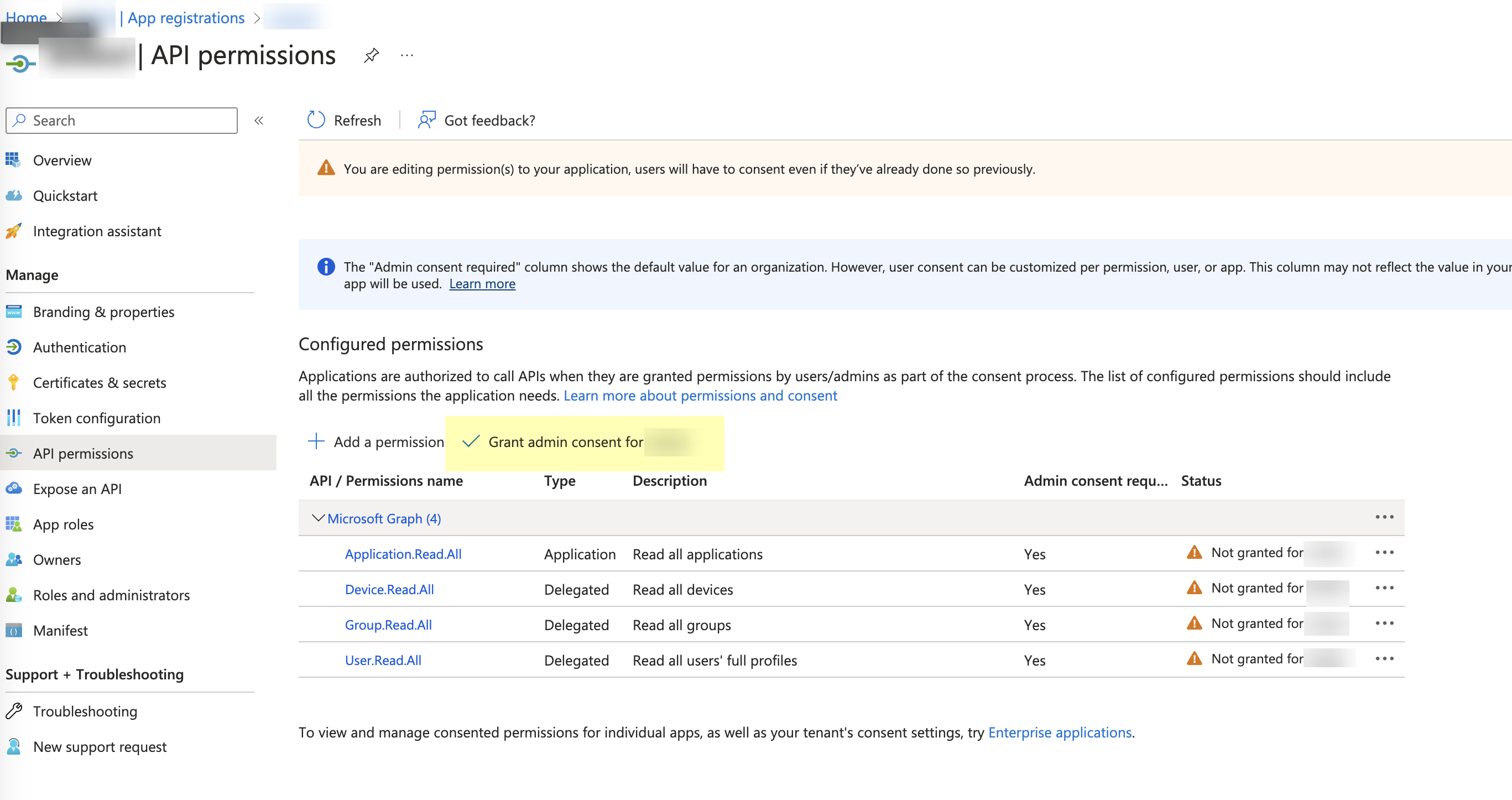
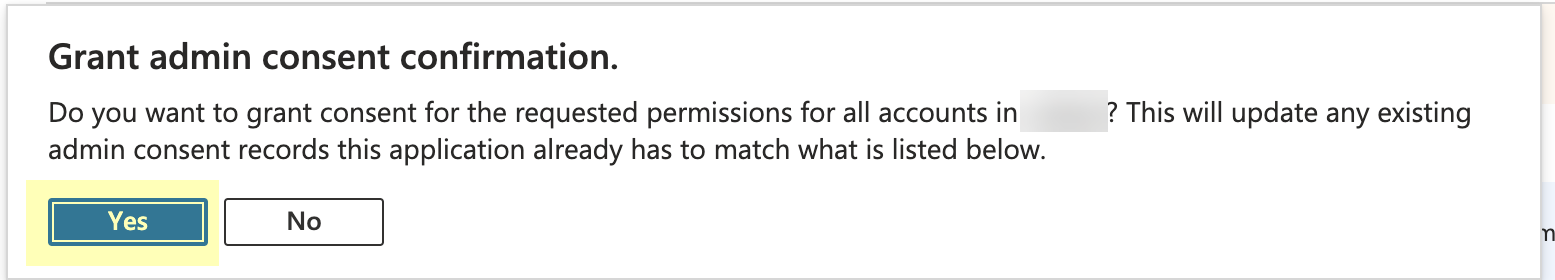
Click Grant admin consent for DirectoryName (where DirectoryName represents the name of your Azure AD).![]() Click Yes to confirm.
Click Yes to confirm.![]() Collect the necessary configuration information from the Azure Portal.
Collect the necessary configuration information from the Azure Portal.- In the Azure dashboard, select your Azure AD, then select App Registrations and select the app you created.Select Certificates & secrets then click New client secret.
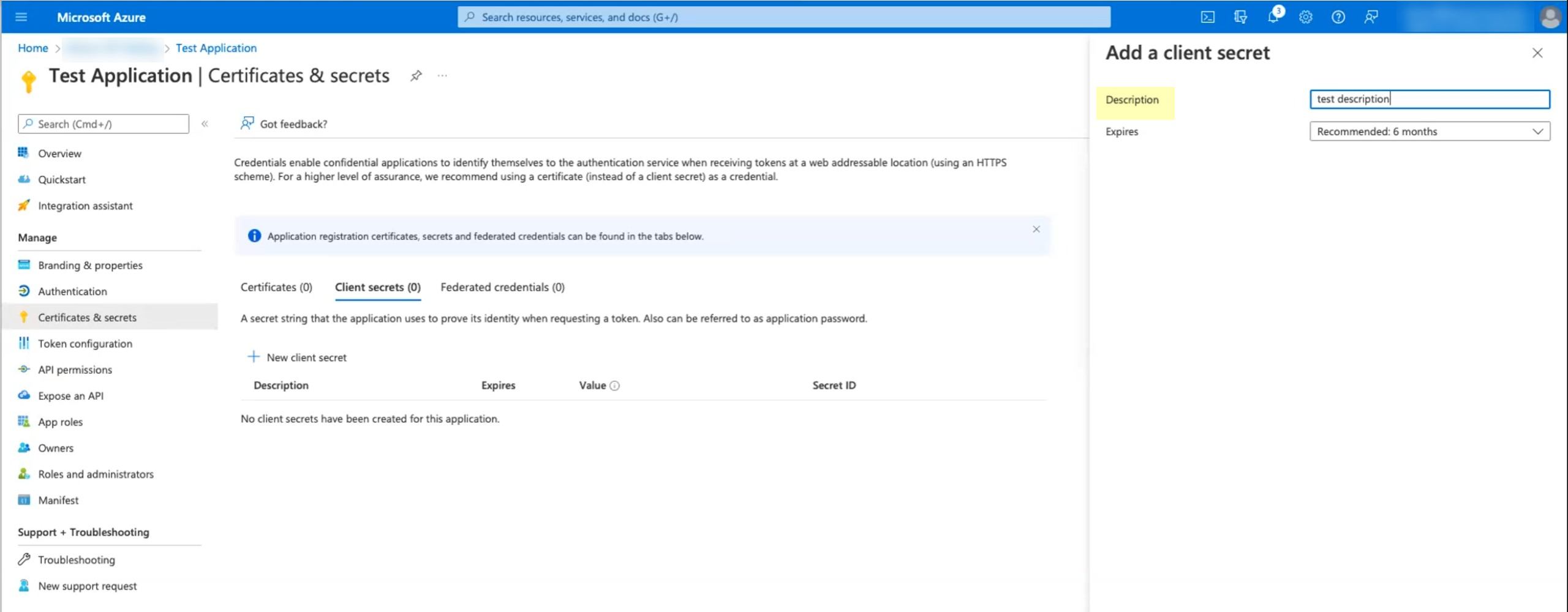
![]() Enter a Description and Add the secret.When you add the secret, make sure to keep track of when the secret Expires. When the secret expires, you must configure the new secret in the Azure Portal and update the configuration in the Cloud Identity Engine app to replace the expired secret. Keep this in mind when selecting the expiry value for the secret. If you prioritize ease of configuration, select a longer expiration for the secret (the maximum value is 2 years). If security is of greater concern, select a shorter value for the secret’s expiration (the default is 6 months).
Enter a Description and Add the secret.When you add the secret, make sure to keep track of when the secret Expires. When the secret expires, you must configure the new secret in the Azure Portal and update the configuration in the Cloud Identity Engine app to replace the expired secret. Keep this in mind when selecting the expiry value for the secret. If you prioritize ease of configuration, select a longer expiration for the secret (the maximum value is 2 years). If security is of greater concern, select a shorter value for the secret’s expiration (the default is 6 months).![]() Copy the Value of the secret and store it in a secure location.
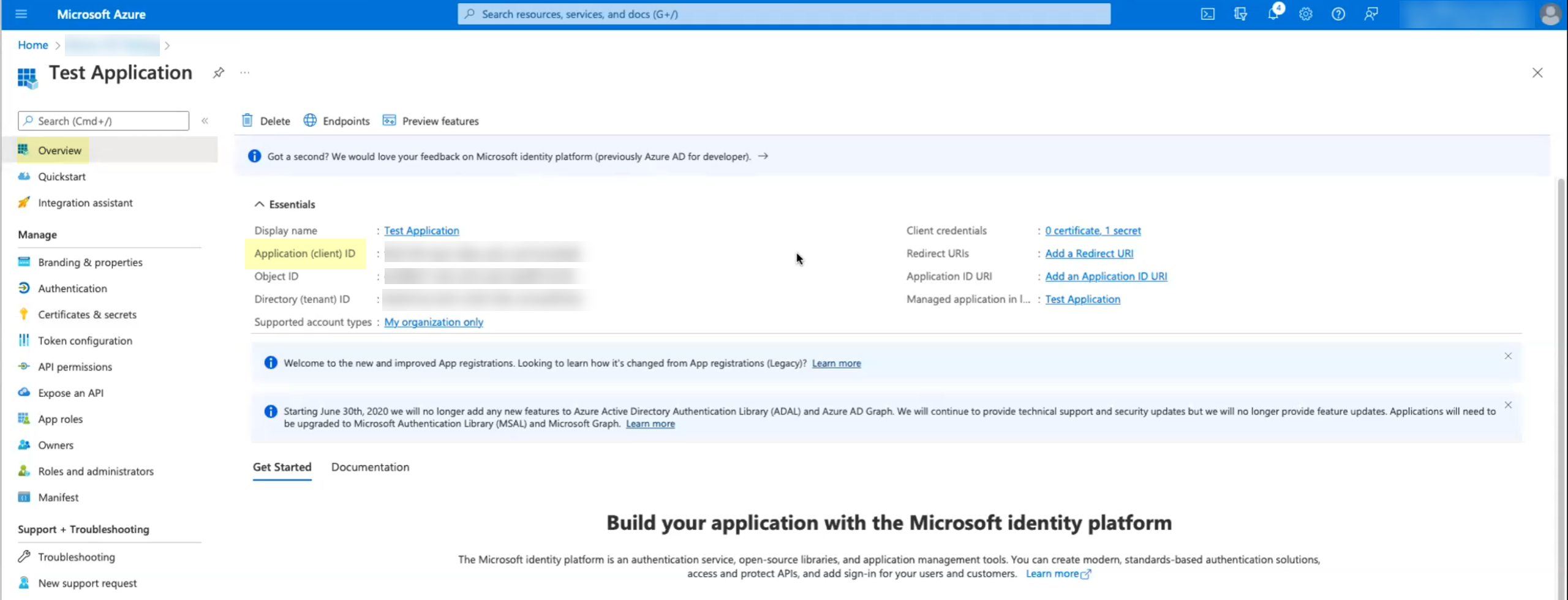
Copy the Value of the secret and store it in a secure location.![]() Click Overview then copy the Application (client) ID and store it in a secure location.
Click Overview then copy the Application (client) ID and store it in a secure location.![]() Copy the Directory (tenant) ID and store it in a secure location.
Copy the Directory (tenant) ID and store it in a secure location.![]() Add your Azure AD directory in the Cloud Identity Engine.(Required for migration) If you are migrating an existing Azure AD configuration, select ActionsReconnect on the Directories page for the Azure AD you want to migrate. The Cloud Identity Engine automatically populates the necessary information so you can continue to step 9 (testing the connection).
Add your Azure AD directory in the Cloud Identity Engine.(Required for migration) If you are migrating an existing Azure AD configuration, select ActionsReconnect on the Directories page for the Azure AD you want to migrate. The Cloud Identity Engine automatically populates the necessary information so you can continue to step 9 (testing the connection).- In the Cloud Identity Engine app, select Directories then click Add New Directory.Set Up an Azure directory.
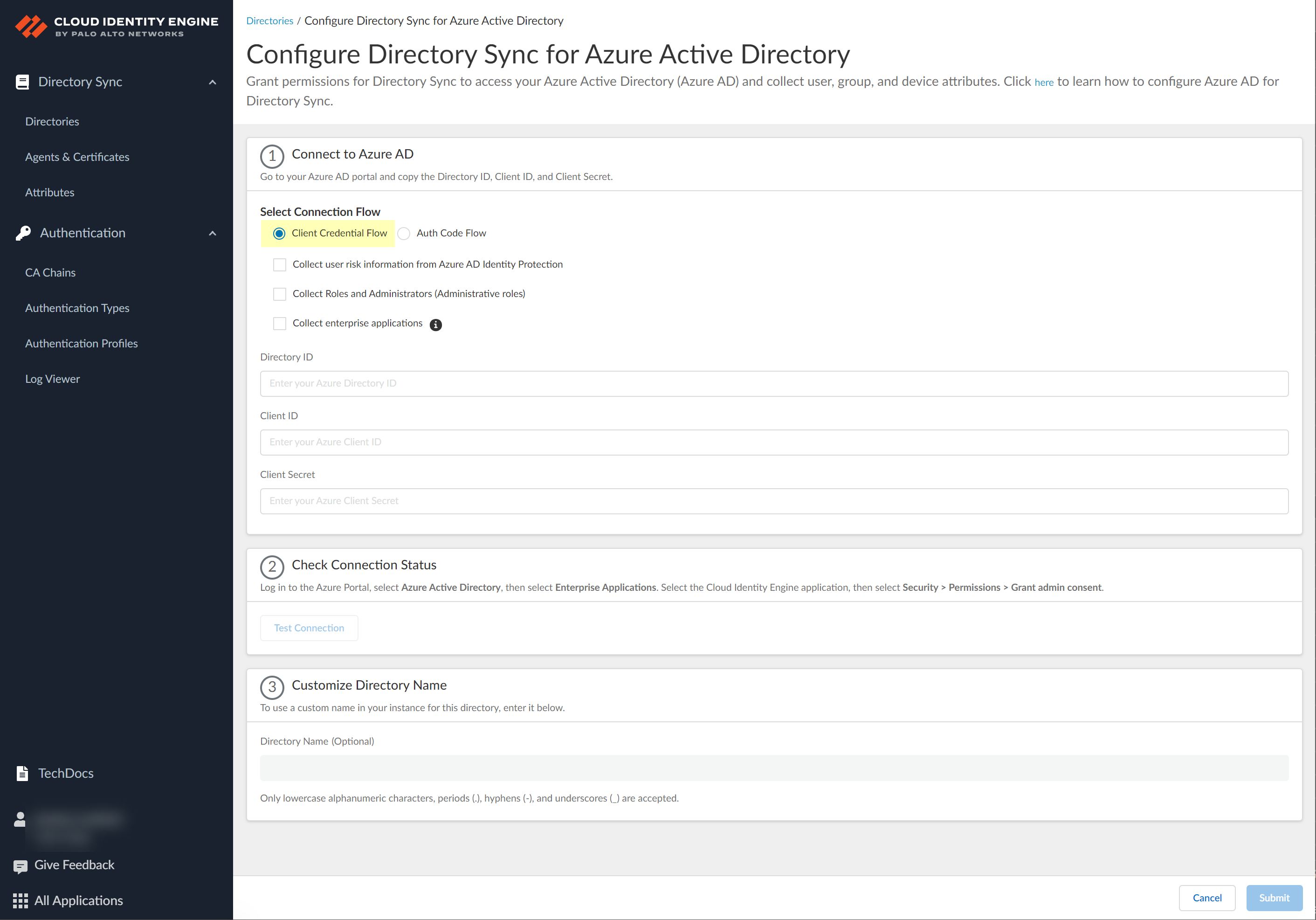
![]() Select Client Credential Flow as the method you want to use to Connect to Azure AD.
Select Client Credential Flow as the method you want to use to Connect to Azure AD.![]() Select whether you want to Collect user risk information from Azure AD Identity Protection to use in attribute-based Cloud Dynamic User Groups.If you select this option, you must grant additional permissions for the Cloud Identity Engine in the Azure AD Portal. For more information, refer to the documentation for Cloud Dynamic User Groups.
Select whether you want to Collect user risk information from Azure AD Identity Protection to use in attribute-based Cloud Dynamic User Groups.If you select this option, you must grant additional permissions for the Cloud Identity Engine in the Azure AD Portal. For more information, refer to the documentation for Cloud Dynamic User Groups.![]() Select whether you want to Collect Roles and Administrators (Administrative roles) to retrieve roleAssignments attribute information for users and groups. Allowing the Cloud Identity Engine to include this information for analysis helps to prevent role-based malicious attacks.By default, the Cloud Identity Engine enables this option for tenants that are associated with Cortex XDR.
Select whether you want to Collect Roles and Administrators (Administrative roles) to retrieve roleAssignments attribute information for users and groups. Allowing the Cloud Identity Engine to include this information for analysis helps to prevent role-based malicious attacks.By default, the Cloud Identity Engine enables this option for tenants that are associated with Cortex XDR.![]() If you do not see the Collect Roles and Administrators (Administrative roles) option, reconnect your directory to select the option.Select whether you want to Collect enterprise applications data so that it displays when you View Directory Data. If you don't want to collect the application data or you don't use application data in your security policy, deselect the checkbox to decrease the sync time. If you select this option, you must enable additional permissions for the Cloud Identity Engine (see step 2.6).For beta users of this feature, the Cloud Identity Engine continues collecting enterprise application data for any directories configured in your tenant during the beta and no further configuration is required. If you configure a new directory, you must select whether you want to collect enterprise application data from the new directory.
If you do not see the Collect Roles and Administrators (Administrative roles) option, reconnect your directory to select the option.Select whether you want to Collect enterprise applications data so that it displays when you View Directory Data. If you don't want to collect the application data or you don't use application data in your security policy, deselect the checkbox to decrease the sync time. If you select this option, you must enable additional permissions for the Cloud Identity Engine (see step 2.6).For beta users of this feature, the Cloud Identity Engine continues collecting enterprise application data for any directories configured in your tenant during the beta and no further configuration is required. If you configure a new directory, you must select whether you want to collect enterprise application data from the new directory.![]() Enter your directory information as indicated, using the information you copied from the Azure Portal in steps 3.4, 3.5, and 3.6:During migration of an existing Azure AD configuration to the client credential flow, the Cloud Identity Engine automatically populates the Directory ID.
Enter your directory information as indicated, using the information you copied from the Azure Portal in steps 3.4, 3.5, and 3.6:During migration of an existing Azure AD configuration to the client credential flow, the Cloud Identity Engine automatically populates the Directory ID.Copy from Azure Portal Enter in Cloud Identity Engine Directory (tenant) ID Directory ID Application (client) ID Client ID Value Client Secret ![]() (Required) Confirm the Cloud Identity Engine app can successfully communicate with your directory.
(Required) Confirm the Cloud Identity Engine app can successfully communicate with your directory.- In the Cloud Identity Engine, click Test Connection to confirm that the Cloud Identity Engine can successfully connect to your Azure AD.
![]() (Optional) Enter a new name to Customize Directory Name in the Cloud Identity Engine.
(Optional) Enter a new name to Customize Directory Name in the Cloud Identity Engine.![]() (Optional) Select whether you want to Filter Azure Active Directory Groups.To reduce sync time and minimize the amount of data collected by the Cloud Identity Engine, you can configure the Cloud Identity Engine to sync only specific groups from your directory. To do this, you can Configure SCIM Connector for the Cloud Identity Engine or you can filter the groups. Because SCIM is most suitable for small and frequent data requests, directory update intervals are restricted to once every 40 minutes. If you choose to filter the groups instead, directory updates can be as often as every 5 minutes. Choose the best option for your deployment based on your organizational and regulatory requirements.
(Optional) Select whether you want to Filter Azure Active Directory Groups.To reduce sync time and minimize the amount of data collected by the Cloud Identity Engine, you can configure the Cloud Identity Engine to sync only specific groups from your directory. To do this, you can Configure SCIM Connector for the Cloud Identity Engine or you can filter the groups. Because SCIM is most suitable for small and frequent data requests, directory update intervals are restricted to once every 40 minutes. If you choose to filter the groups instead, directory updates can be as often as every 5 minutes. Choose the best option for your deployment based on your organizational and regulatory requirements.- Select the group attribute you want to use as a filter.
- Name—Filter the groups based on the group name.
- Unique Identifier—Filter the groups based on the unique identifier for the group.
![]() Select how you want to filter the groups.
Select how you want to filter the groups.- (for Name attribute only)begins with—Filter the groups based on a partial match for the text you enter.
- is equal to—Filter the groups based on an exact match for text you enter.
![]() Enter the text you want to use to filter the groups.
Enter the text you want to use to filter the groups.![]() (Optional) Configure an additional filter by clicking Add OR and repeating the previous three steps for each filter you want to include.When you configure additional attributes, the Cloud Identity Engine initially attempts to find a match for the first criteria in the configuration, then continues to attempt to match based on the additional criteria you specify.
(Optional) Configure an additional filter by clicking Add OR and repeating the previous three steps for each filter you want to include.When you configure additional attributes, the Cloud Identity Engine initially attempts to find a match for the first criteria in the configuration, then continues to attempt to match based on the additional criteria you specify.![]() Submit your changes and verify your directory information when the Directories page displays.You can now use your Azure AD to enforce group-based policy with the Cloud Identity Engine.
Submit your changes and verify your directory information when the Directories page displays.You can now use your Azure AD to enforce group-based policy with the Cloud Identity Engine.