Prisma AIRS
GCP
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma AIRS Docs
GCP
Prisma AIRS AI Runtime Firewall post-deployment configurations
in Strata Cloud Manager and GCP to protect VM workloads and Kubernetes
clusters.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
- Log in to Strata Cloud Manager.Configure Prisma AIRS AI Runtime Firewall interfaces:
- Navigate to Configuration → NGFW and Prisma Access.Select Device Settings → Interfaces.Set the Configuration Scope to your AI Runtime Security folder.In the Ethernet tab:Configure a Layer 3 Interface for eth1/1 and eth1/2:
- Interfaces: eth1/1 and eth1/2
- Location: Specify location if applicable
- Interface Type: Layer3
- IP Address: Dynamic (DHCP Client)
Select the Loopback tab to configure the Loopback interface:- In IPv4s, enter the ILB (Internal Load Balancer) private IP address
- Set Security Zone to trust for eth1/2 and untrust for eth1/1
- Ensure VR (Virtual Router) is set to default or the same as eth1/2
Create zones. Select Manage→ Configuration → NGFW and Prisma Access → Device Settings → Zones.Configure a Logical Router:- Create a Logical Router and add the Layer 3 interfaces (eth1/1 and eth1/2).
- Configure a Static Route with the ILB static IP addresses for routing. Use the trust interface gateway IP address.
Add a security policy (Configuration → NGFW and Prisma Access → Security Services → Security Policy → Add Rule).Set the action to Allow.Ensure the policy allows health checks from the GCP Load Balancer (LB) pool to the internal LB IP from Strata Cloud Manager. Check session IDs to ensure the firewall responds correctly on the designated interfaces.Configurations to Secure VM Workloads
- Configure Static Routes for VPC endpoints.
- Log in to Strata Cloud Manager.Navigate to Manage→ Configuration → NGFW and Prisma Access → Device Settings → Routing → Logical Routers.For VPC Subnet:
- Edit the IPv4 Static Routes and add VPC IPv4 range CIDR subnets route.
- Set the Next Hop as eth1/2.
- Set the Destination as the trust subnet gateway IP from Strata Cloud Manager.
- Update the static route.
Save the Logical Router.Log in to Strata Cloud Manager.Select Configuration → Push Config and push the policy configurations to Prisma AIRS AI Runtime Firewall.Configurations to Secure Kubernetes Clusters
- Add pod and service IP Subnets to Prisma AIRS AI Runtime Firewall trust firewall rules:
- Get the IP addresses for pod and service subnets:
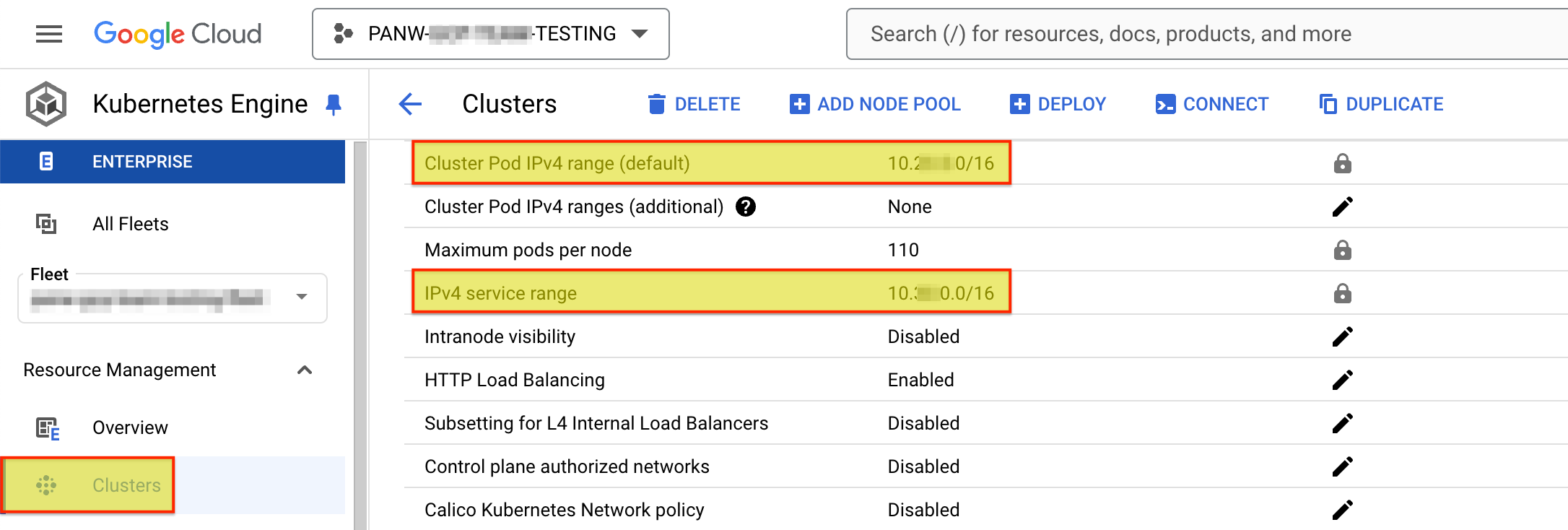
- Go to Kubernetes Engine -> Clusters.Select a Cluster and copy the Cluster Pod IPv4 and IPv4 Service range IP addresses.
![]() Follow the AI network intercept deployment in GCP to save and download the Terraform template.Edit the Terraform template to allow the following IP addresses in your VPC network firewall rules:
Follow the AI network intercept deployment in GCP to save and download the Terraform template.Edit the Terraform template to allow the following IP addresses in your VPC network firewall rules:- Navigate to the `<unzipped-folder>/architecture/security_project` directory.
- Edit the `terraform.tfvars` file to add the copied IP addresses list
to your `source_ranges`.firewall_rules = { allow-trust-ingress = { name = "allow-trust-vpc" source_ranges = ["35.xxx.0.0/16", "130.xxx.0.0/22", "192.xxx.0.0/16", "10.xxx.0.0/14", "10.xx.208.0/20"] # 1st 2 IPs are for health check packets. Add APP VPC/Pod/Service CIDRs priority = "1000" allowed_protocol = "all" allowed_ports = [] } }
- Apply Terraform:terraform init terraform plan terraform applyAdd static routes on the logical router for Kubernetes workloads:
- Log in to Strata Cloud Manager.Select Configuration → NGFW and Prisma Access → Device Settings → Routing → Logical Routers.Configure Static Routes for the pod and service subnets for the Kubernetes workloads:Pod Subnet:
- Edit the IPv4 Static Routes and add a route with the Pod IPv4 range CIDR.
- Set the Next Hop as eth1/2 (trust interface).
- Set the Destination as the trust subnet gateway IP from Strata Cloud Manager.
Service Subnet:- Edit the IPv4 Static Routes add a route with the IPv4 Service range CIDR.
- Set the Next Hop as eth1/2 (trust interface).
- Set the Destination as the trust subnet gateway IP from Strata Cloud Manager.
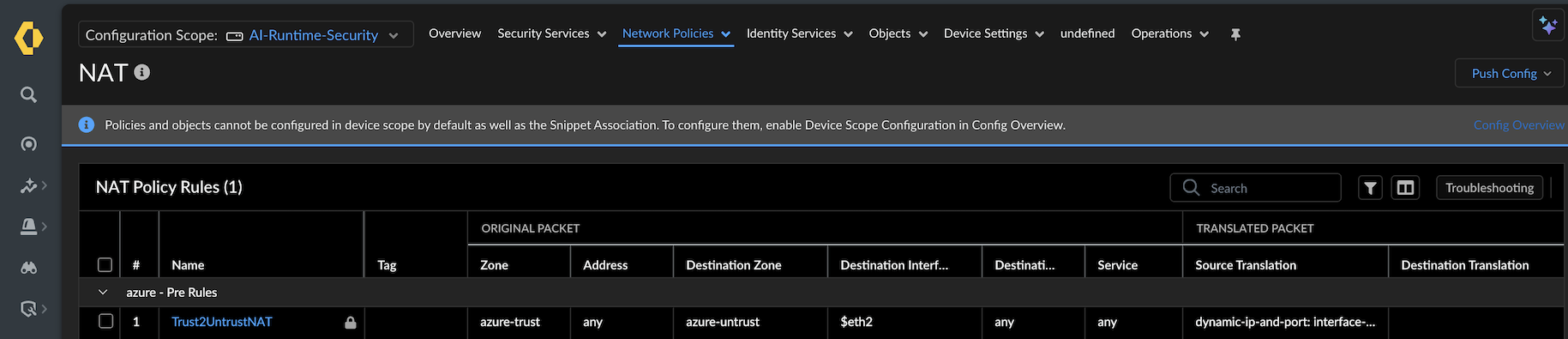
Add source NAT Policy for Outbound Traffic:- Log in to Strata Cloud Manager.Select Configuration → NGFW and Prisma Access → Network Policies → NAT.
![]() Create or modify a source NAT Policy:
Create or modify a source NAT Policy:- Source Zone: Trust
- Destination Zone: Untrust (eth1/1)
- Policy Name: trust2untrust or similar.
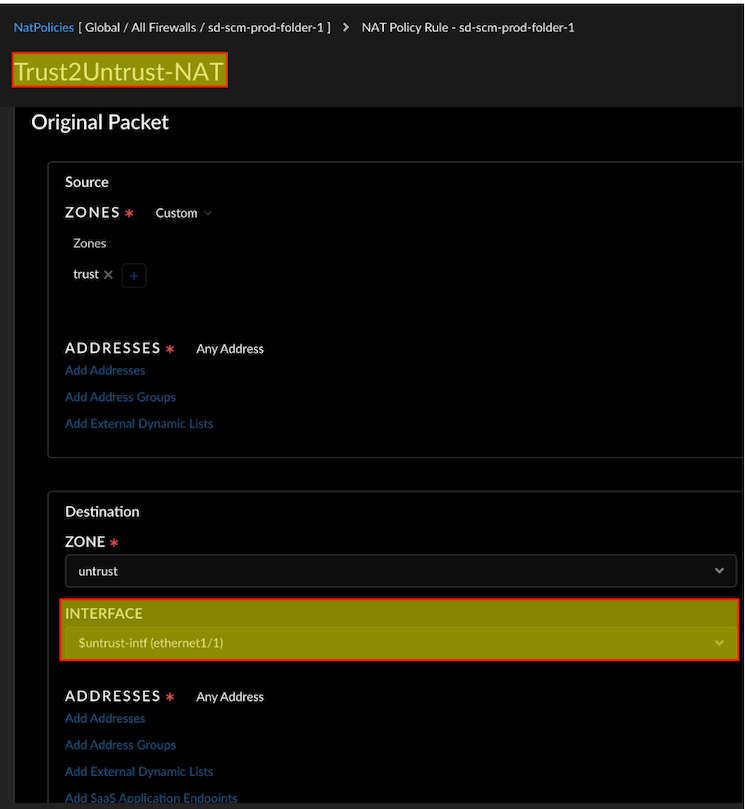
![]() Configure NAT settings:Interface Address Section:
Configure NAT settings:Interface Address Section:- Set the Interface to eth1/1. (The translation happens at
eth1/1).If needed, create a complementary rule for the reverse direction (for example, untrust2trust).
Log in to Strata Cloud Manager.Select Configuration → Push Config and push the policy configurations to Prisma AIRS AI Runtime Firewall.If you have a Kubernetes cluster running, follow the section to install a Kubernetes application with Helm.Secure a Kubernetes Application with Helm
This section covers how to install and configure the Helm chart to secure your Kubernetes applications based on the protection level you selected during deployment. The Helm chart installation process and directory structure vary depending on whether you selected VPC-level protection or namespace-level protection with traffic steering inspection. VPC-level protection secures all applications within the VPC, while namespace-level protection with traffic inspection provides granular control over specific application traffic flows and CIDR-based inspection rules.Your deployment configuration determines the specific Helm chart structure and commands required for your environment.- Navigate to the downloaded tar file and extract the contents:tar -xvzf <your-terraform-download.tar.gz>Navigate to the appropriate Helm directory based on your deployment configuration:
- For VPC-level
security:cd <unzipped-folder>/architecture/helm
- For namespace-level security with traffic steering inspection:
cd <unzipped-folder>/architecture/helm-<complete-app-name-path>- Navigate to each Helm application folder. When you configure traffic steering inspection, separate Helm charts are generated for each protected namespace, allowing granular security policies per application.
- GKE Autopilot clusters do not support Helm deployments due to restrictions on modifying the kube-system namespace.
Install the Helm chart using the appropriate command:- For VPC-level
security:helm install ai-runtime-security helm --namespace kube-system --values helm/values.yaml
- For namespace-level security with traffic steering inspection:
Repeat this command for each namespace-specific Helm chart generated during the deployment process.helm install ai-runtime-security helm-<complete-app-name-path> --namespace kube-system --values helm-<complete-app-name-path>/values.yamlThis creates a container network interface (CNI), but doesn’t protect the container traffic until you annotate the application `yaml` or `namespace`.Verify the Helm installation:#List all Helm releases helm list -A #Ensure the output shows your installation with details such as: NAME NAMESPACE REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION ai-runtime-security kube-system 1 2024-08-13 07:00 PDT deployed ai-runtime-security-0.1.0 11.2.2Check the pod status:kubectl get pods -A #Verify that the pods with names similar to `pan-cni-*****` are present.Check the endpoint slices:kubectl get endpointslice -n kube-system #Confirm that the output shows an ILB IP address: NAME ADDRESSTYPE PORTS ENDPOINTS AGE my-endpointslice IPv4 80/TCP 10.2xx.0.1,10.2xx.0.2 12hVerify the Kubernetes resources were created properly:a. Check the service accounts kubectl get serviceaccounts -n kube-system | grep pan b. Check the secrets kubectl get secrets -n kube-system | grep pan c. Check the services: `kubectl get svc -n kube-system | grep pan`You should see resources like pan-cni-sa (service accounts), pan-plugin-user-secret (secrets), and pan-ngfw-svc (service).Annotate at the pod level in your application yaml so that the traffic from the pod is redirected to the Prisma AIRS AI Runtime Firewall for inspection.Annotate the pod using the below command:- For VPC-level
security:kubectl annotate namespace <namespace-to-be-annotated> paloaltonetworks.com/firewall=pan-fw
- For namespace-level security with traffic steering inspection:
Ensure every pod has this annotation to be moved to the ‘protected’ state across all cloud environments.kubectl annotate pods --all paloaltonetworks.com/subnetfirewall=ns-secure/bypassfirewallRestart the existing application pods after applying Helm and annotating the pods for all changes to take effect. This enables the firewall to inspect the pod traffic and secure the containers. - For namespace-level security with traffic steering inspection:
- For namespace-level security with traffic steering inspection:
- For namespace-level security with traffic steering inspection: