Identity
Cloud Identity Engine User Context
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Identity Docs
Cloud Identity Engine User Context
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
| The Cloud Identity Engine service is free; however, the enforcement points utilizing directory data may require specific licenses. Click here for more information. |
As large enterprise networks continue to become increasingly distributed across
cities, regions, and countries, enforcing least-privilege user access becomes
increasingly challenging, especially as scale increases. User Context for the Cloud
Identity Engine provides simplified granular control over the data that is shared
across your security devices. It provides administrators with the flexibility to
specify the data types (such as mappings and quarantine lists) each device sends and
receives.
The simplified deployment of User Context for information such as user mappings and
tags minimizes time to enforcement. Centralizing visibility for users, tags, and
mappings makes it easier to segment the data types based on user access needs. This
method also increases scalability for Virtual Desktop users (VDI) using the Terminal
Server agent.
To enforce policy, User Context provides IP address-to-usernamemappings, IP port to username mappings,
user tags IP address tags, Host IDs, and
quarantine list information to other NGFWs and devices in your network through
segments, which consist of firewalls that you specify. A segment can
collect information as well as share information. A publishing segment
sends the data from the firewalls and devices in that segment to the firewalls in
the subscribed segment, which contains the firewalls that receive the
data from the publishing segments.
NGFWs and Panorama can share multiple data types to one segment. On a firewall or
Panorama, each data type can only be shared in one segment. Each Firewall or
Panorama can receive data from up to 100 segments.
By selecting the data that is collected by a segment and where that data is shared,
you have full control in ensuring that the information required to enforce
least-privilege access is available on each enforcement device.
If you associate a firewall that you configure as a User-ID hub with a segment,
the Cloud Identity Engine provides the data types based on the firewall that is
subscribed or publishing the segment, not based on the virtual system. To ensure
that both locally learned data and data that the User Context Cloud Service provides
are available to all virtual systems, configure the User-ID hub firewall as a
subscriber in the segment.
Cloud Identity User Context (PAN-OS)
Learn about user context for PAN-OS & Panorama with CIE.
To control data shared over your network with User Context:
- Onboard your Cloud Identity Engine instance.
- Obtain the serial number for the firewall you want to onboard, and Register the firewall with the Palo Alto Networks Customer Support Portal (CSP).Click the magic link provided by Palo Alto Networks to begin onboarding your Cloud Identity Engine tenant.The magic link is provided by Palo Alto Networks by email.Click MSP Cloud Management.
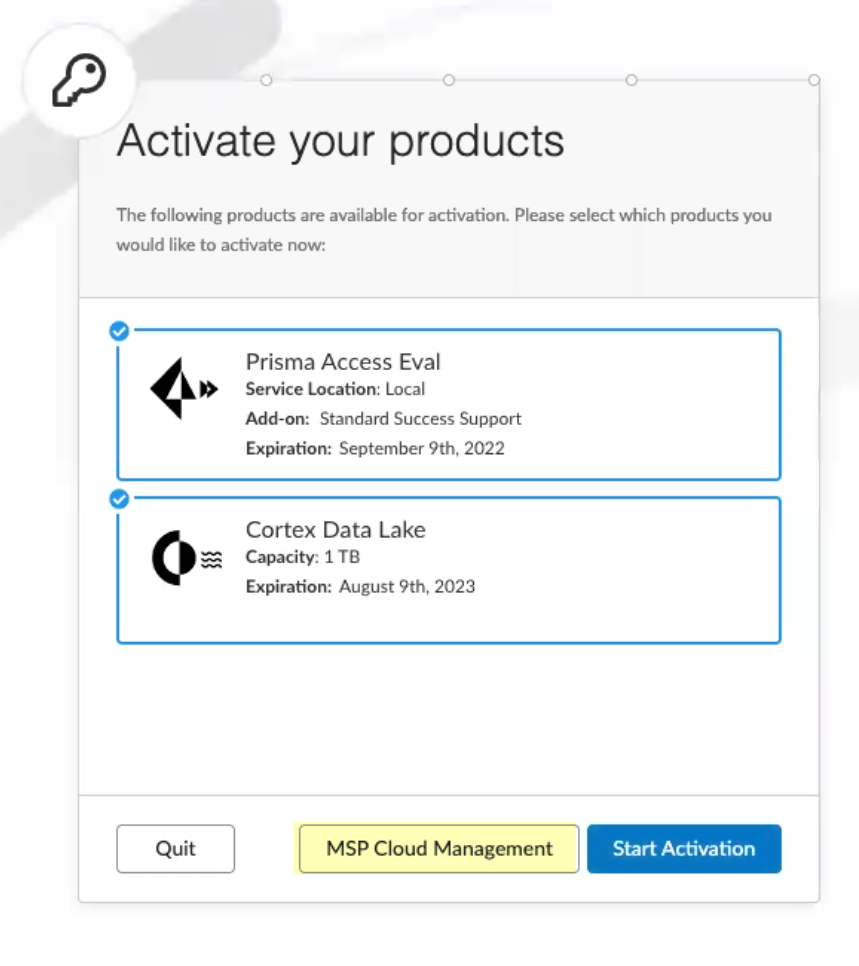
![]() Continue the onboarding process.
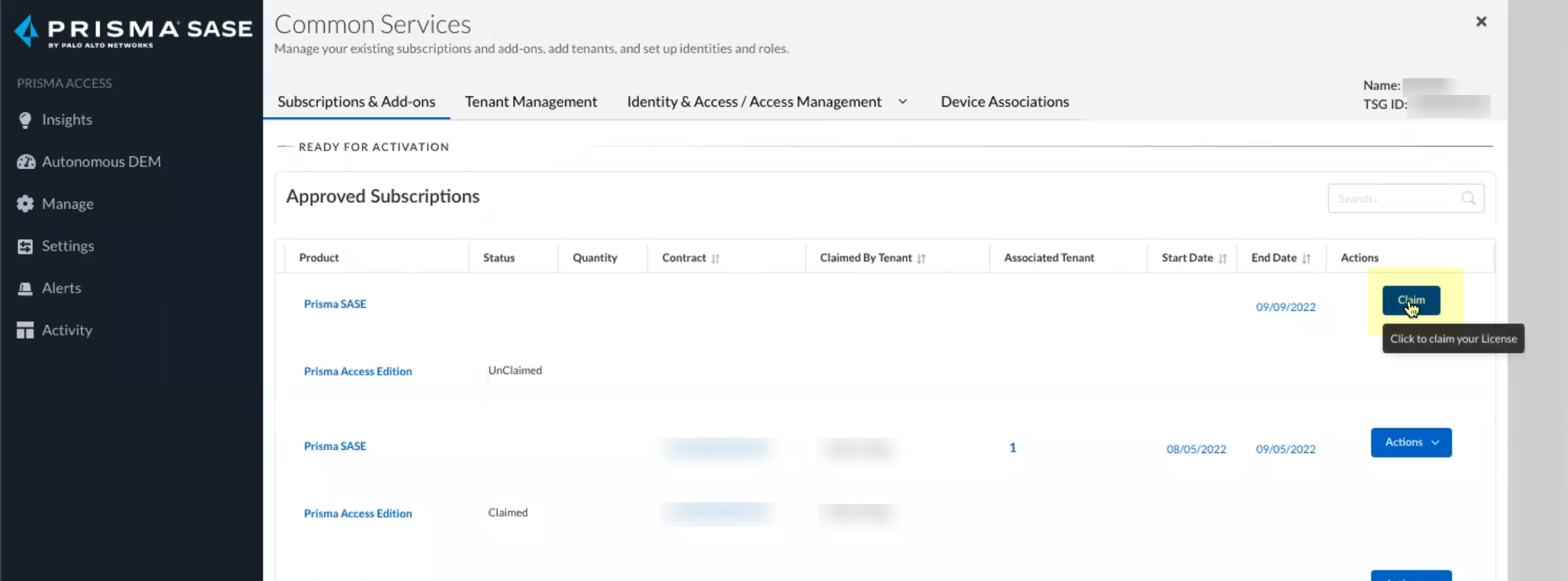
Continue the onboarding process.![]() Claim the license for the tenant you want to onboard.
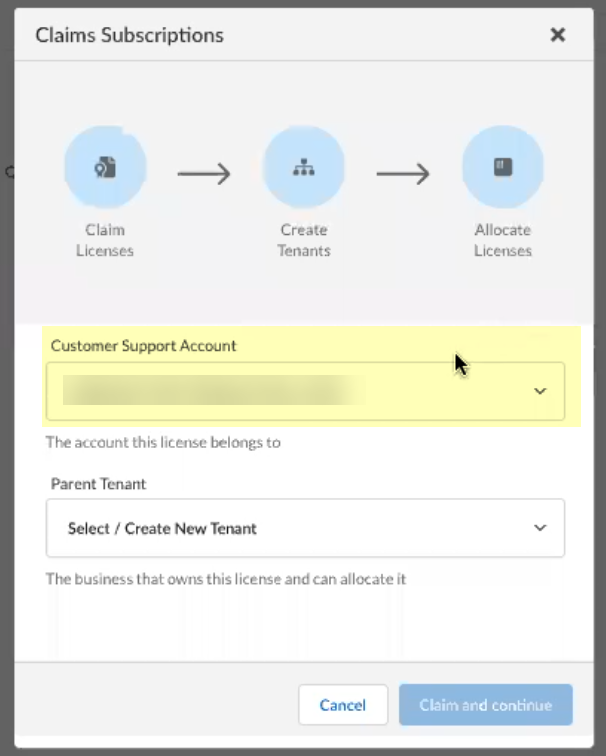
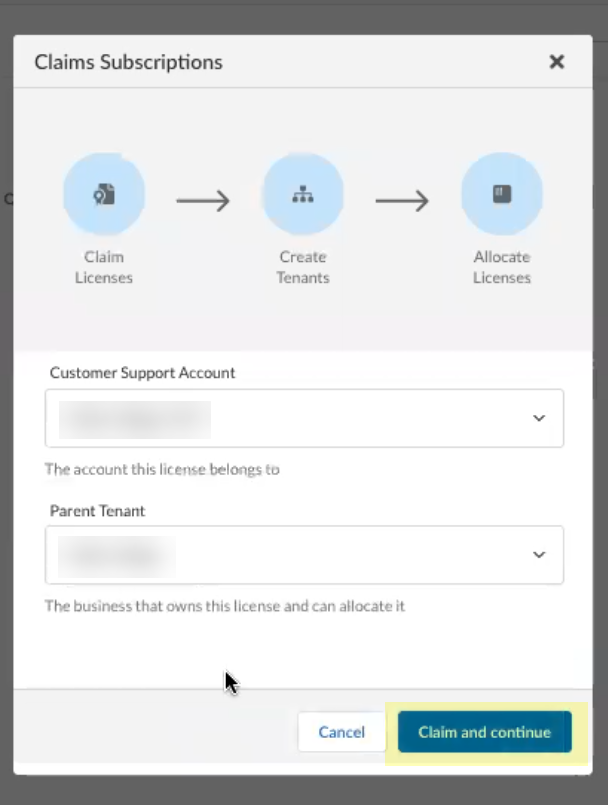
Claim the license for the tenant you want to onboard.![]() Select the Customer Support Account you want to use.
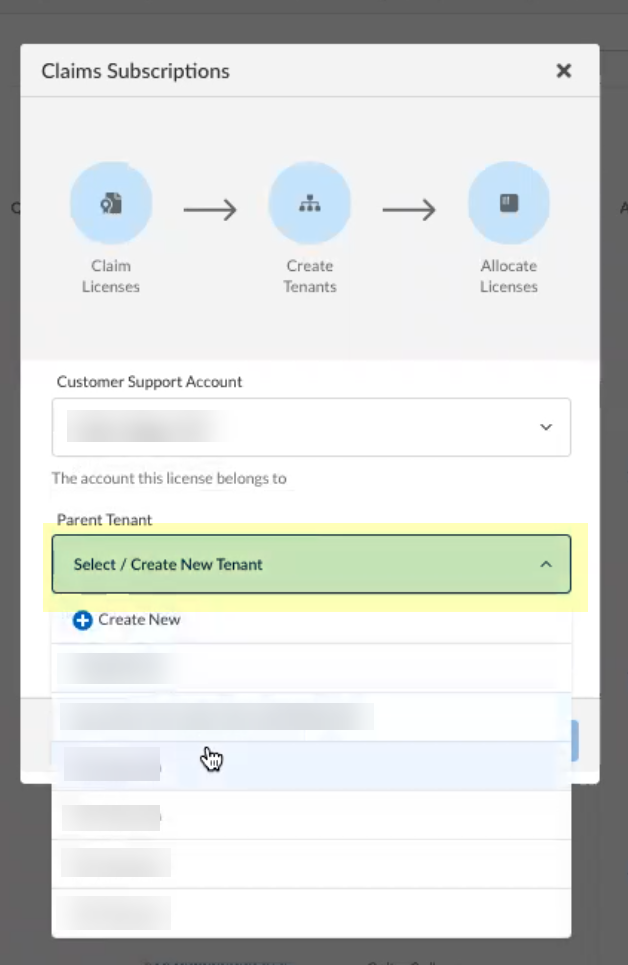
Select the Customer Support Account you want to use.![]() Select the Parent Tenant you want to use or click Create New to create a new tenant.
Select the Parent Tenant you want to use or click Create New to create a new tenant.![]() Click Claim and continue to continue the onboarding process.
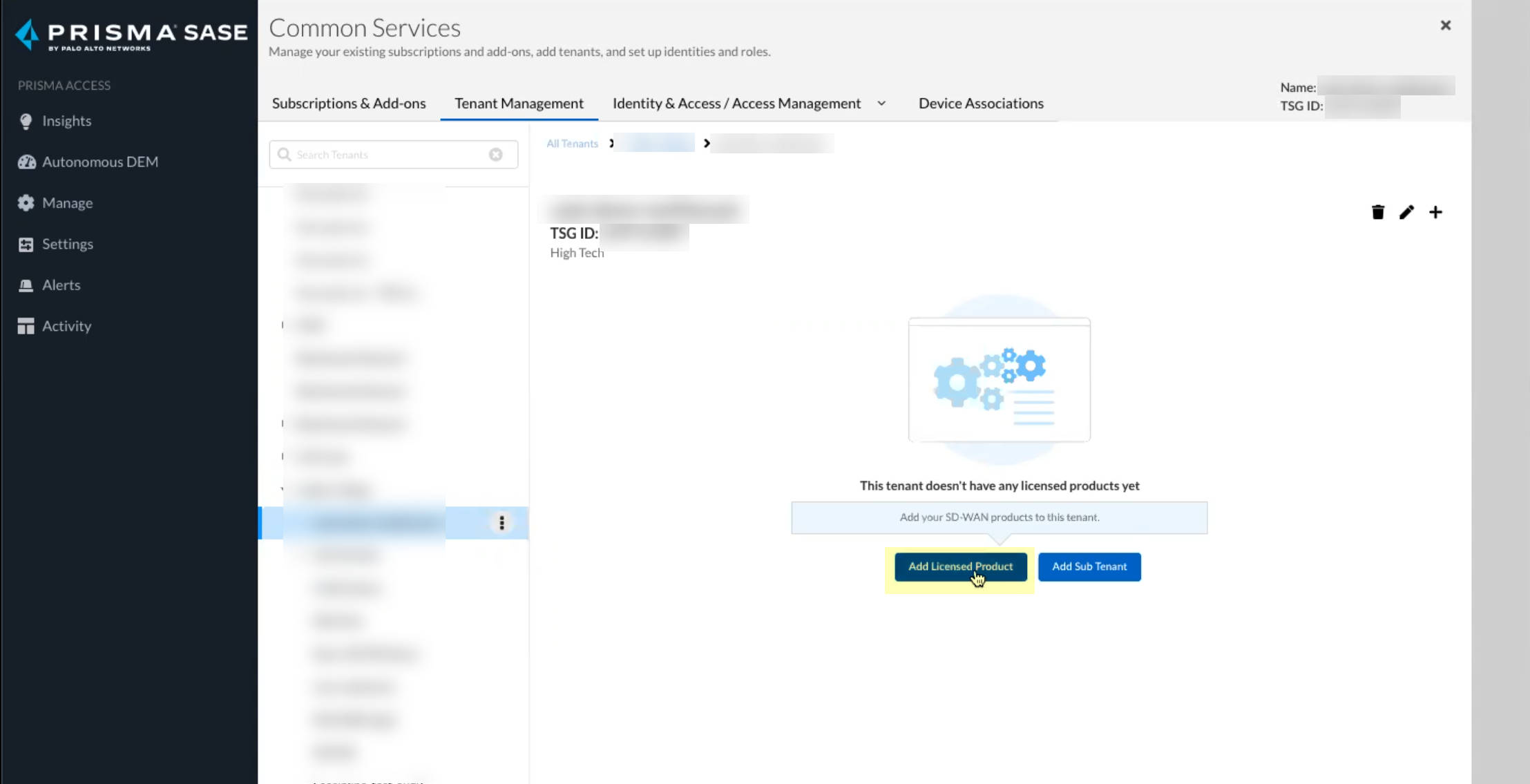
Click Claim and continue to continue the onboarding process.![]() Click Add Licensed Product to continue the onboarding process.
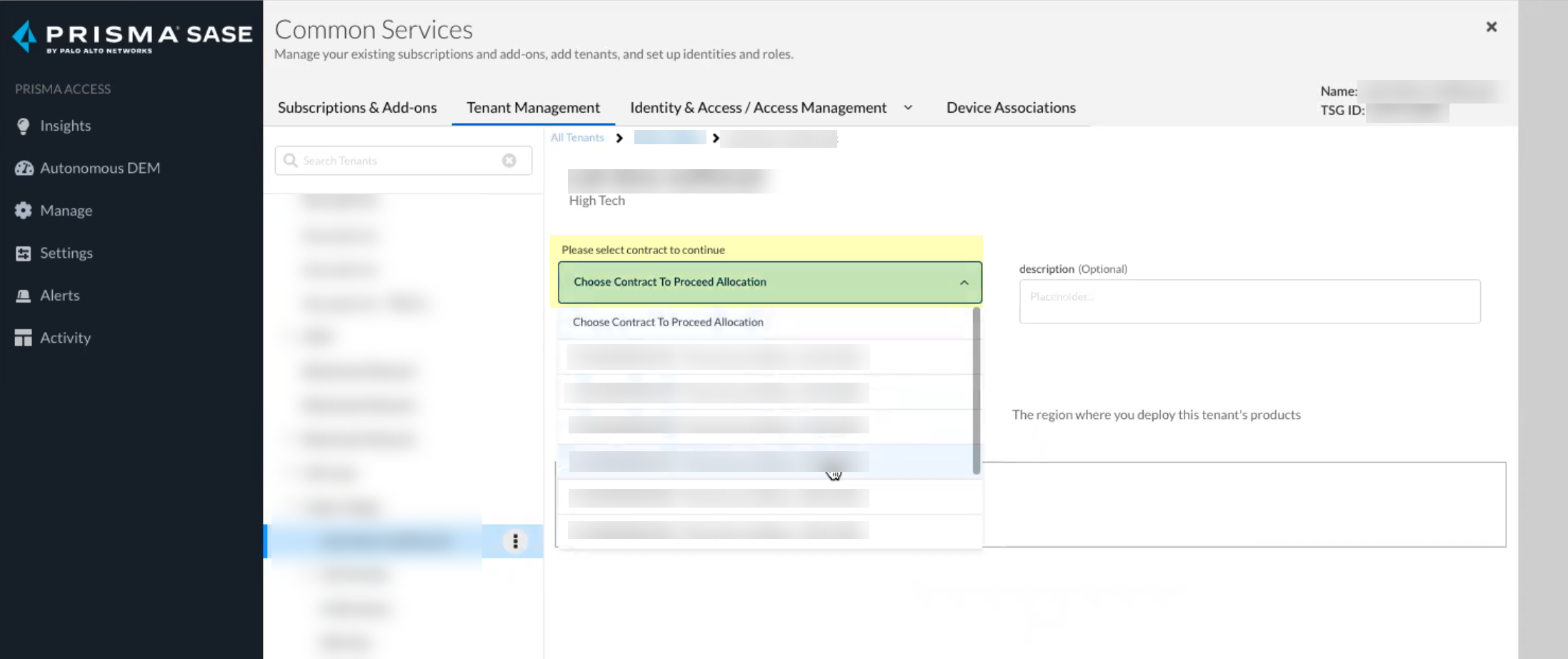
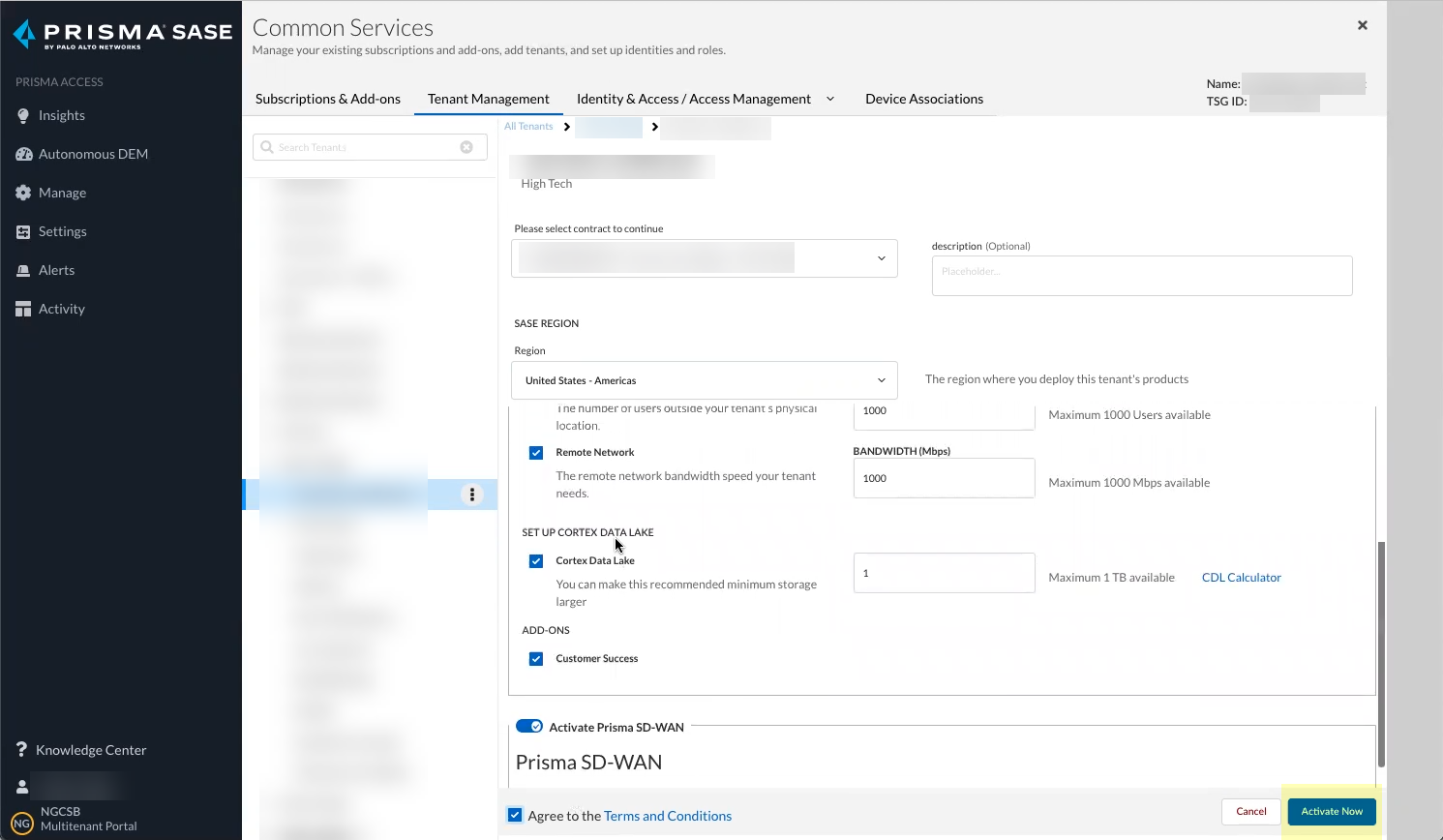
Click Add Licensed Product to continue the onboarding process.![]() Select the contract you want to use.
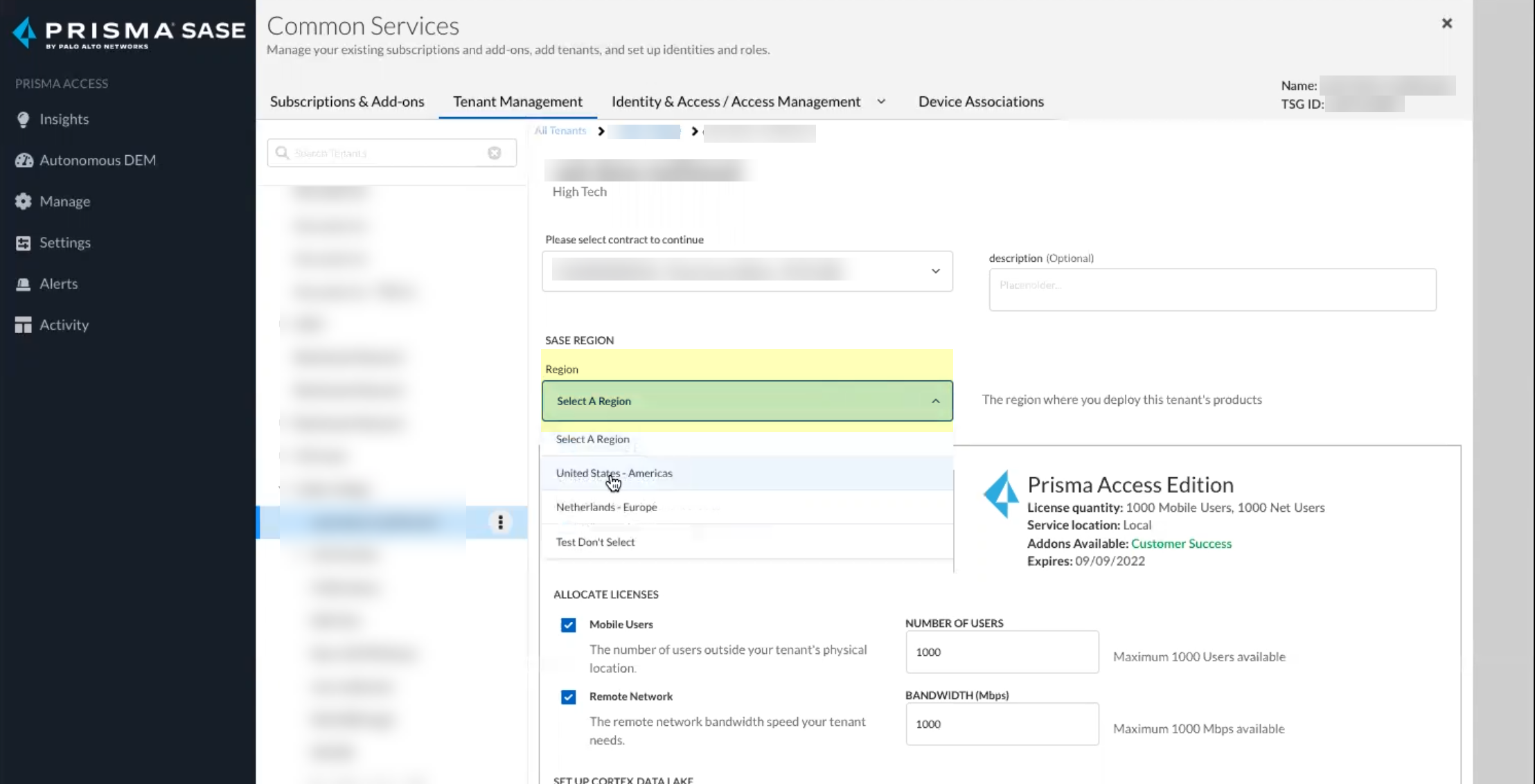
Select the contract you want to use.![]() Select the Region for your Cloud Identity Engine instance.
Select the Region for your Cloud Identity Engine instance.![]() Click Activate Now to complete the onboarding process.
Click Activate Now to complete the onboarding process.![]() Confirm that the Status for the Cloud Identity Engine is Complete.You can access your Cloud Identity Engine instance by selecting Cloud Identity Engine.
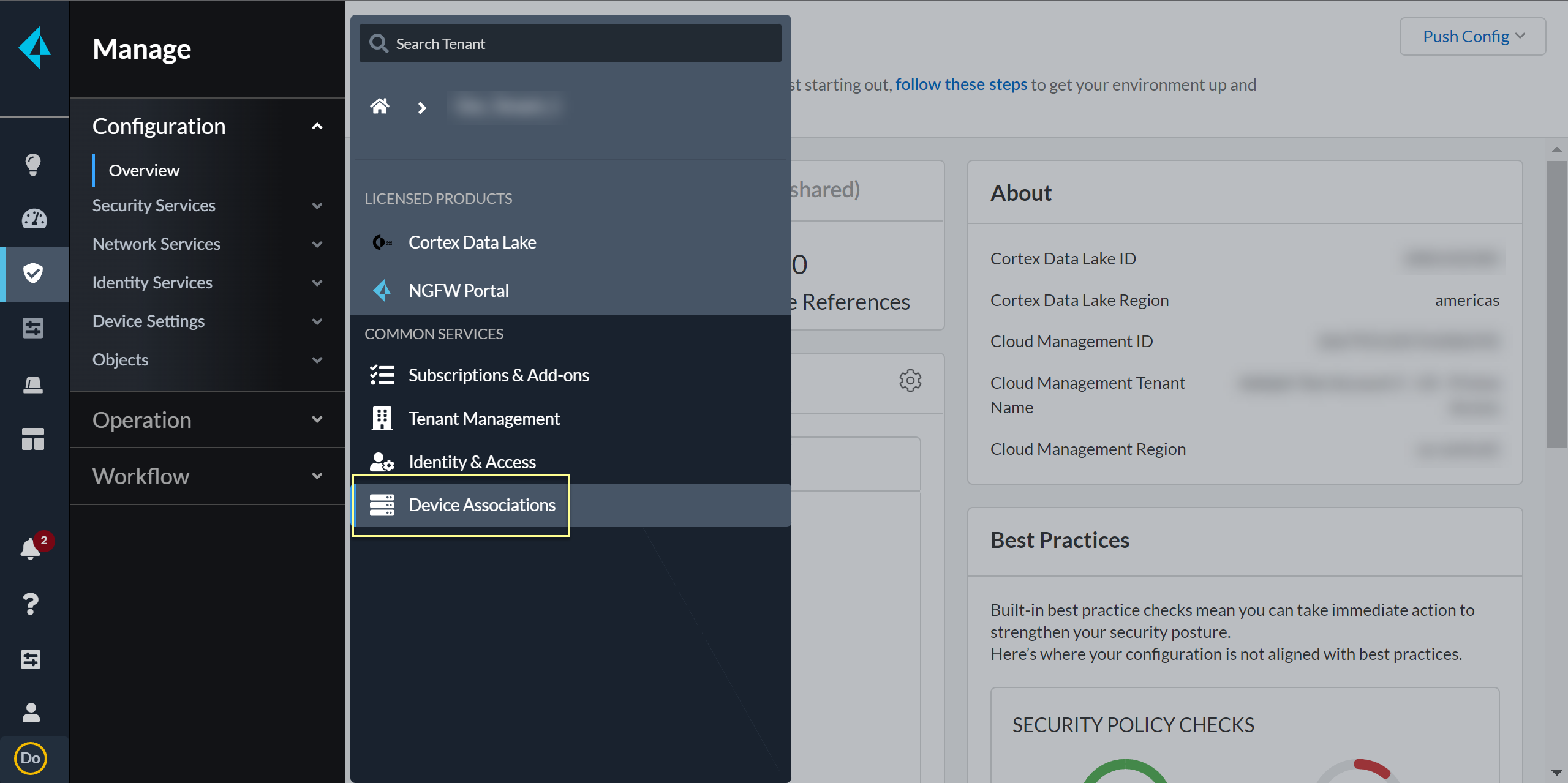
Confirm that the Status for the Cloud Identity Engine is Complete.You can access your Cloud Identity Engine instance by selecting Cloud Identity Engine.![]() In the bottom left of the window, select the icon for your tenant and select Device Associations.
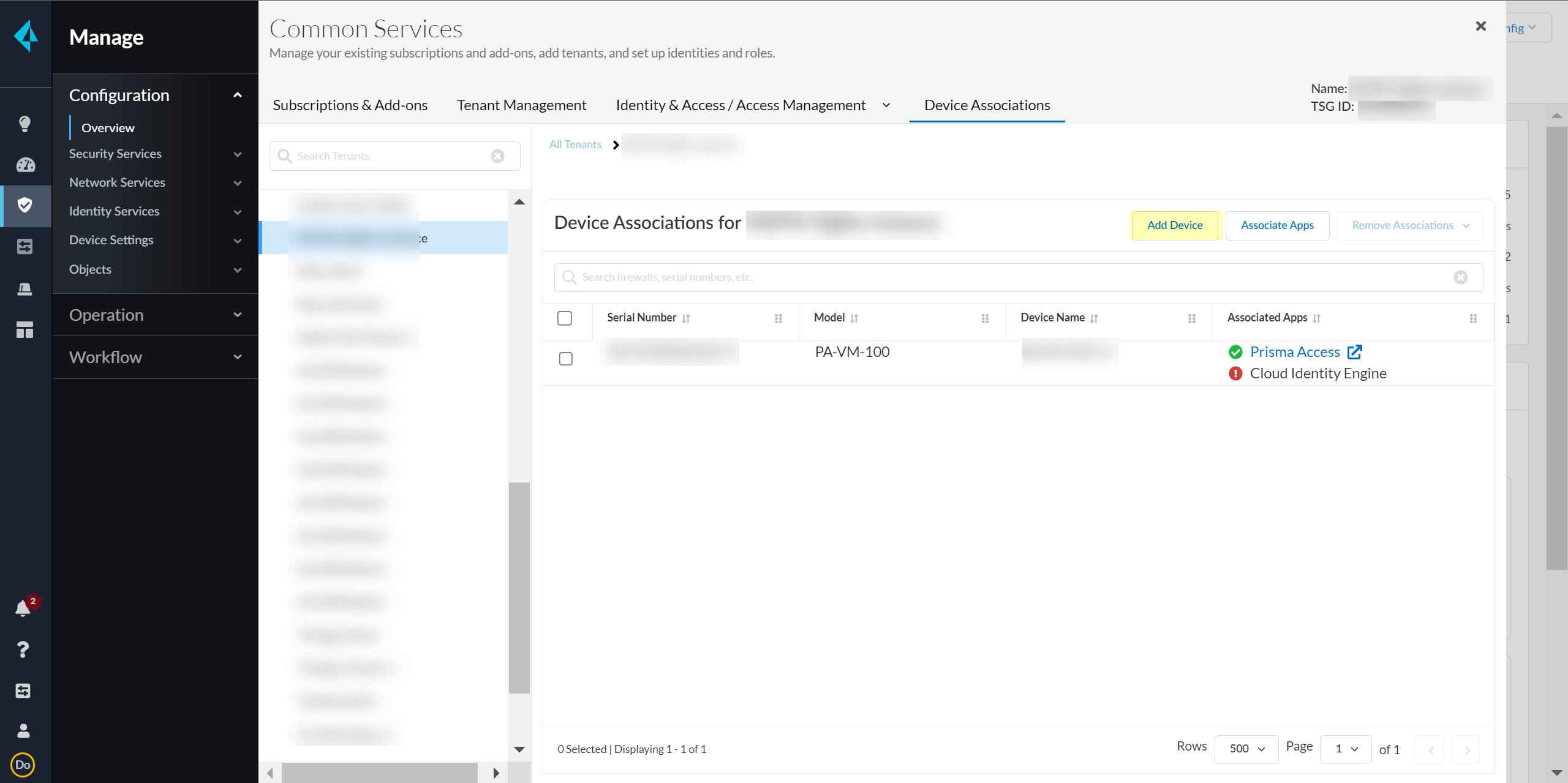
In the bottom left of the window, select the icon for your tenant and select Device Associations.![]() Select Add Device.
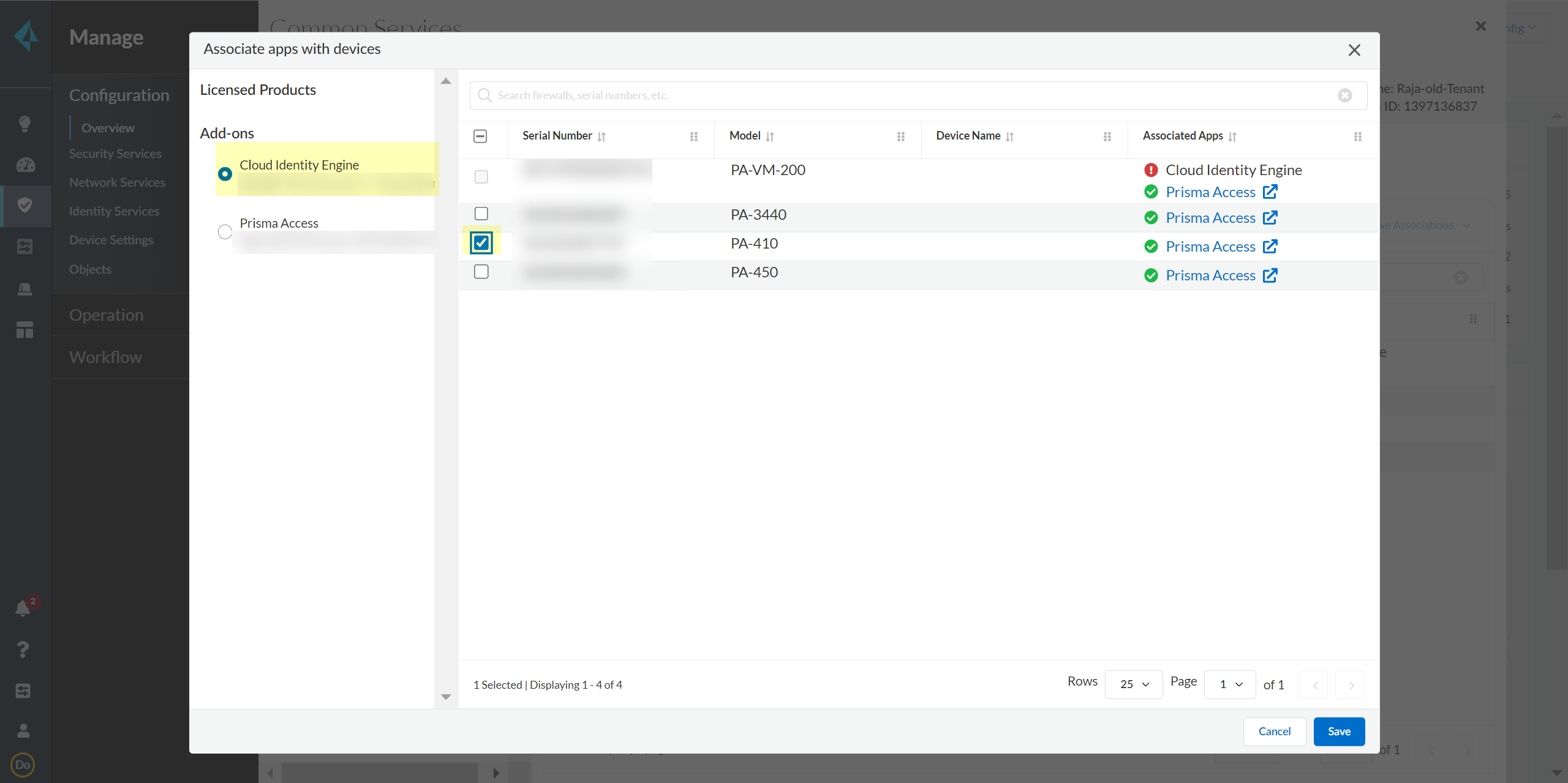
Select Add Device.![]() Select your Customer Support Account and enter your firewall serial number.Select the firewall Save your changes.Select Associate Apps.Select the firewall, select the Cloud Identity Engine, and Save your selections.
Select your Customer Support Account and enter your firewall serial number.Select the firewall Save your changes.Select Associate Apps.Select the firewall, select the Cloud Identity Engine, and Save your selections.![]() In the Cloud Identity Engine, activate sharing for mappings.
In the Cloud Identity Engine, activate sharing for mappings.- Log in to the Cloud Identity Engine app and select User ContextSegmentsActivate sharing for mappings.
![]() Configure the default segment as a publishing segment.
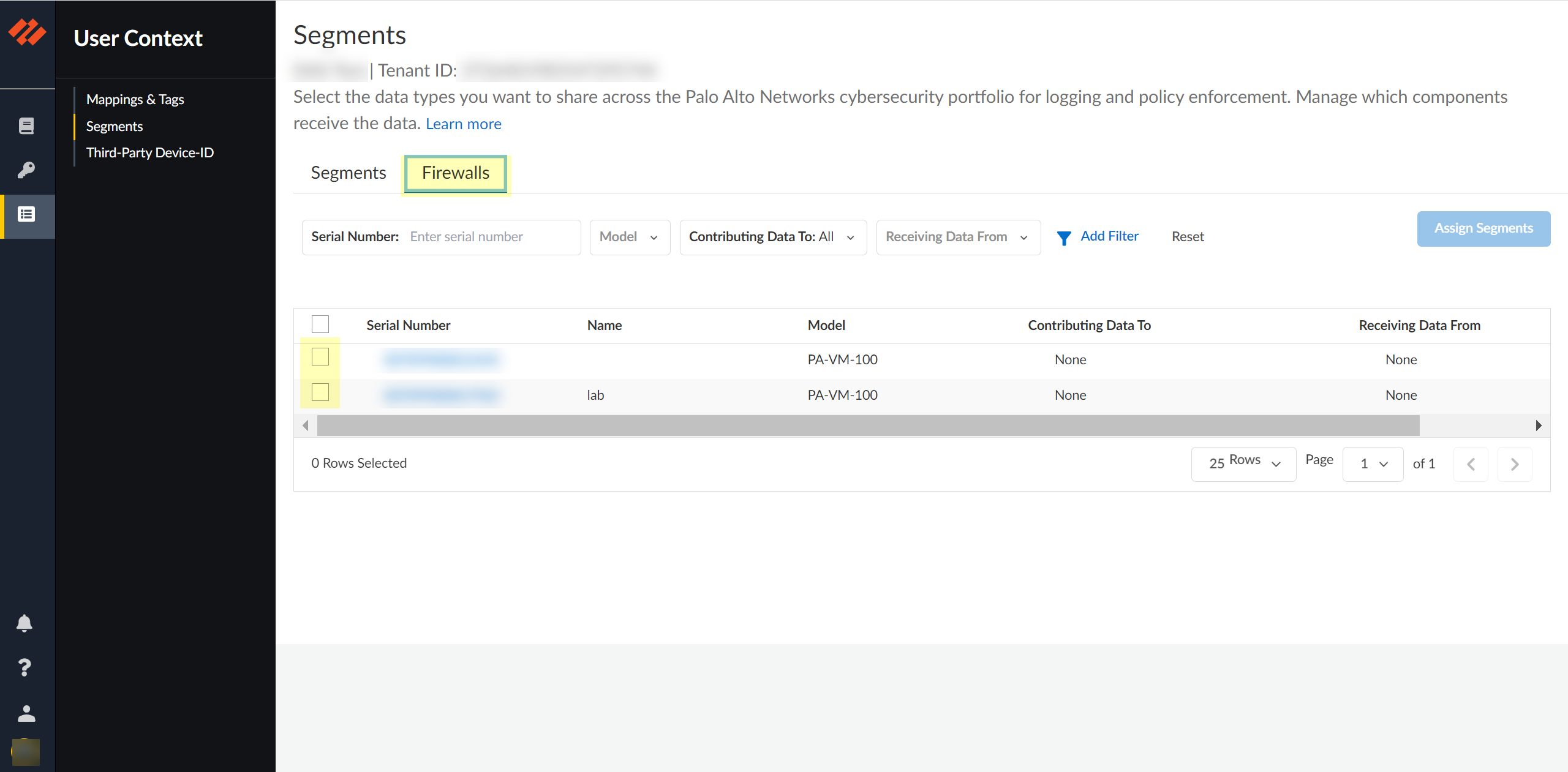
Configure the default segment as a publishing segment.- Select the Firewalls tab and select one or more firewalls.
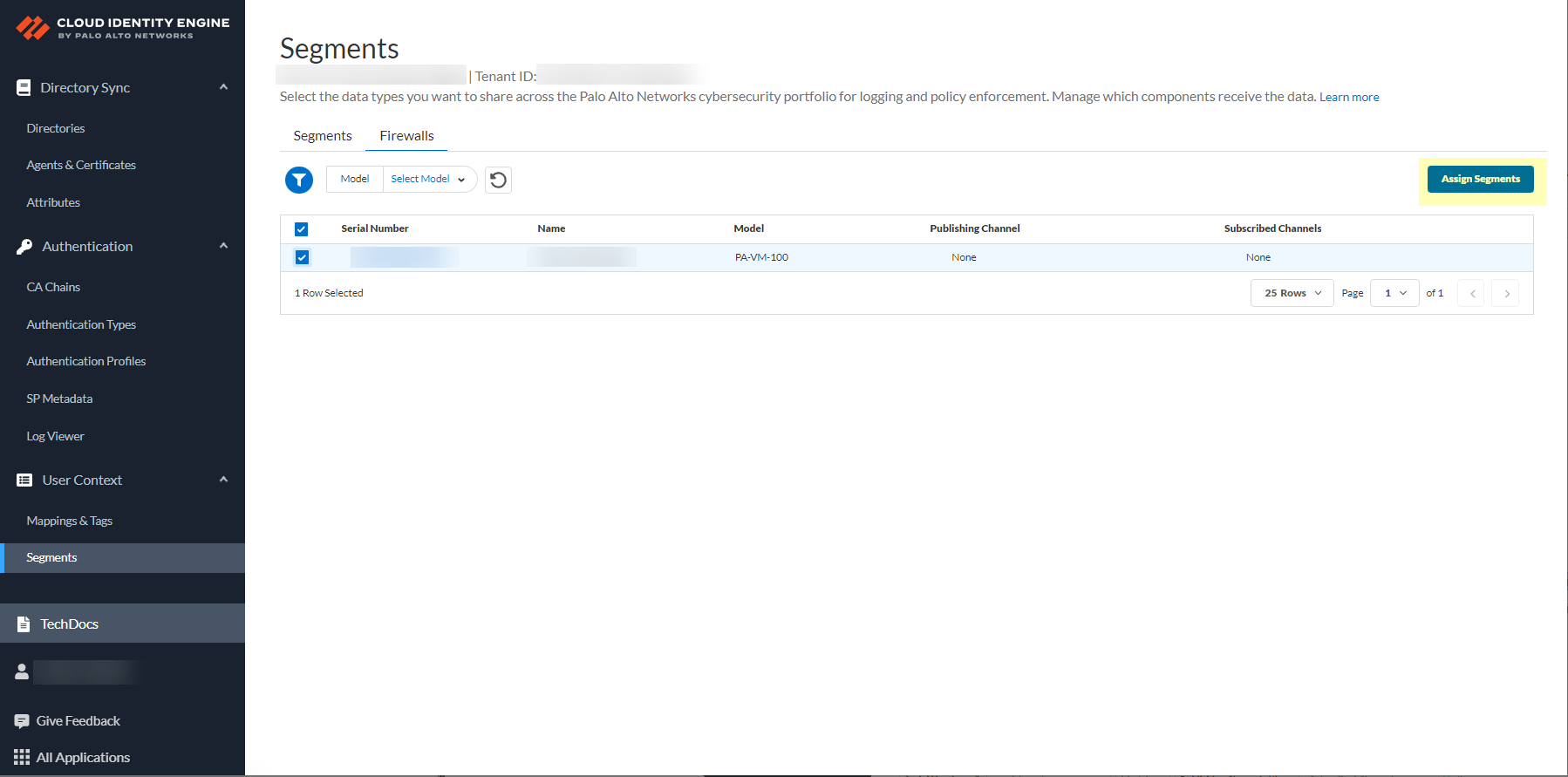
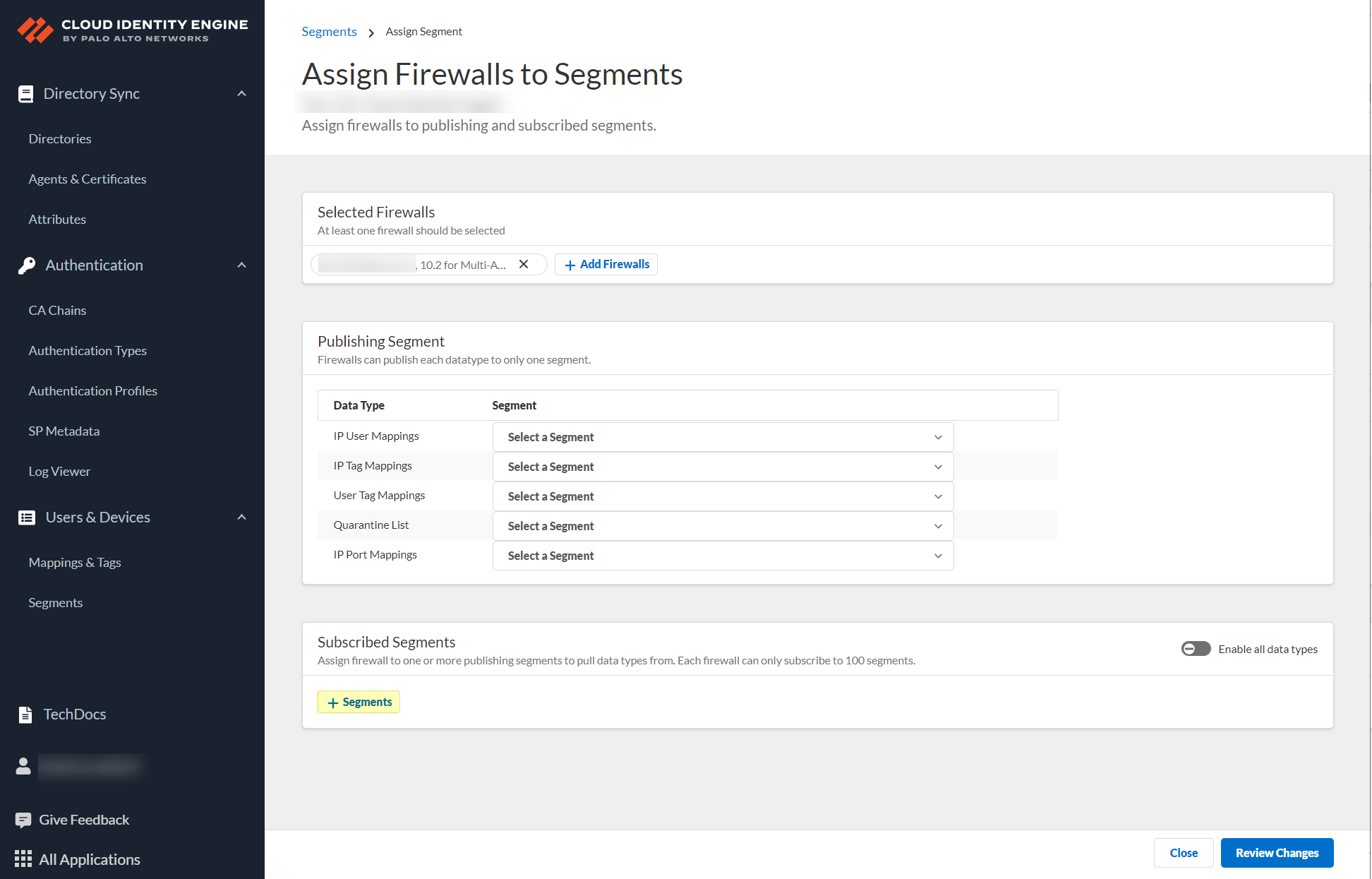
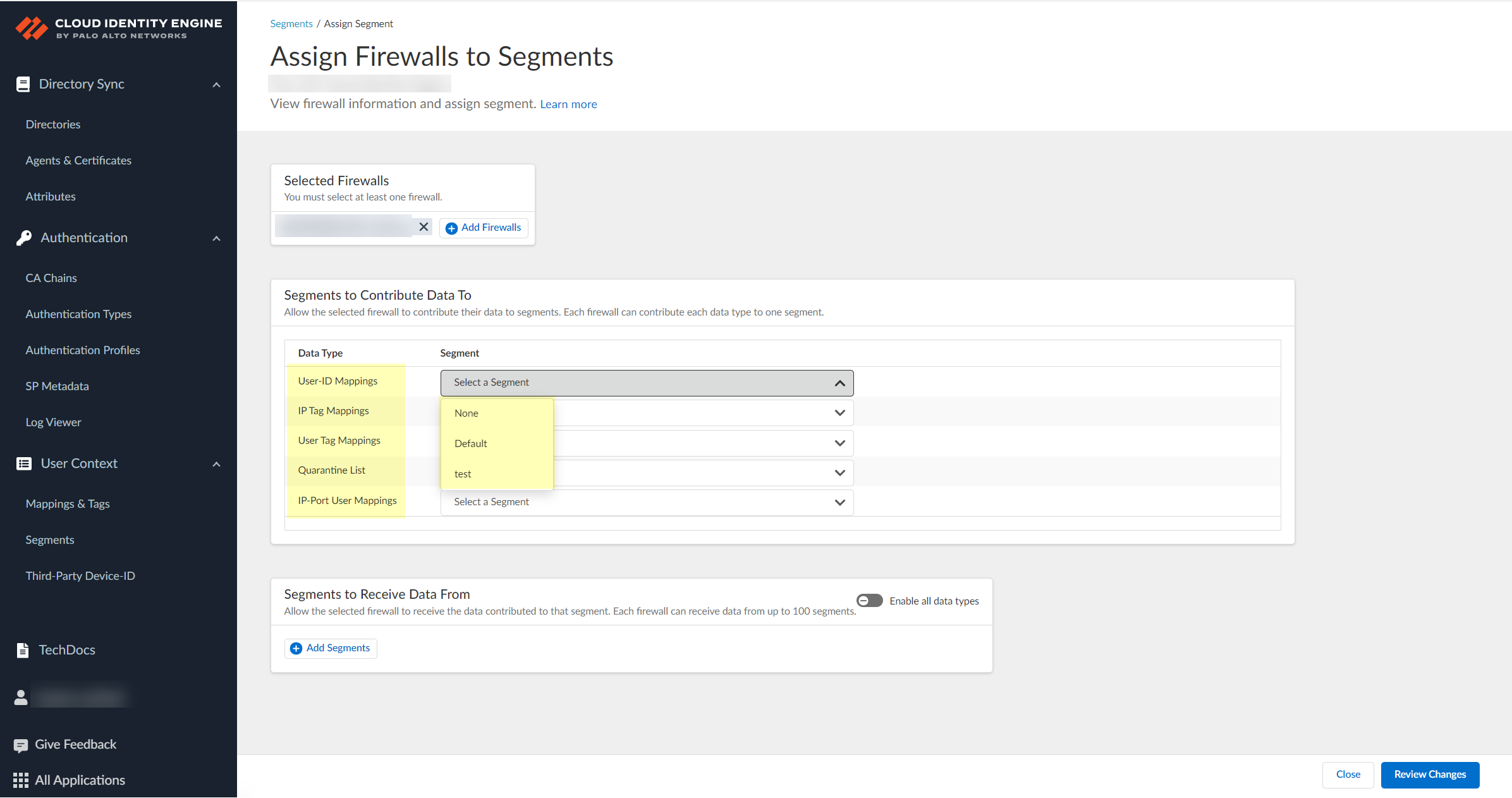
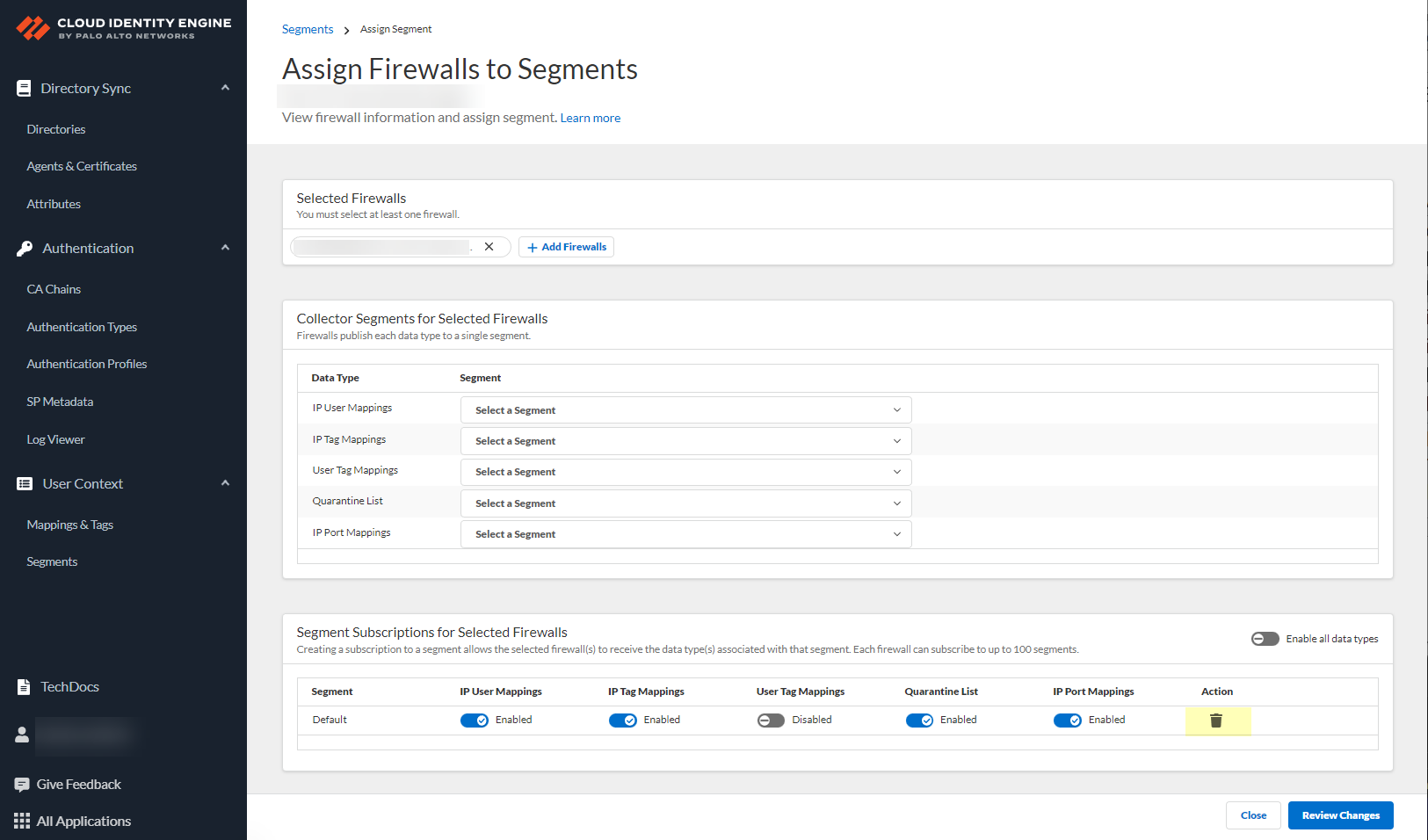
![]() After selecting the firewalls that you want to include in this segment, Assign Segments to the selected firewalls.Assigning a segment to a firewall allows you to define which data the Cloud Identity Engine receives from or provides to that firewall. You can only assign segments to a firewall that uses PAN-OS 11.0; User Context does not support other source types.
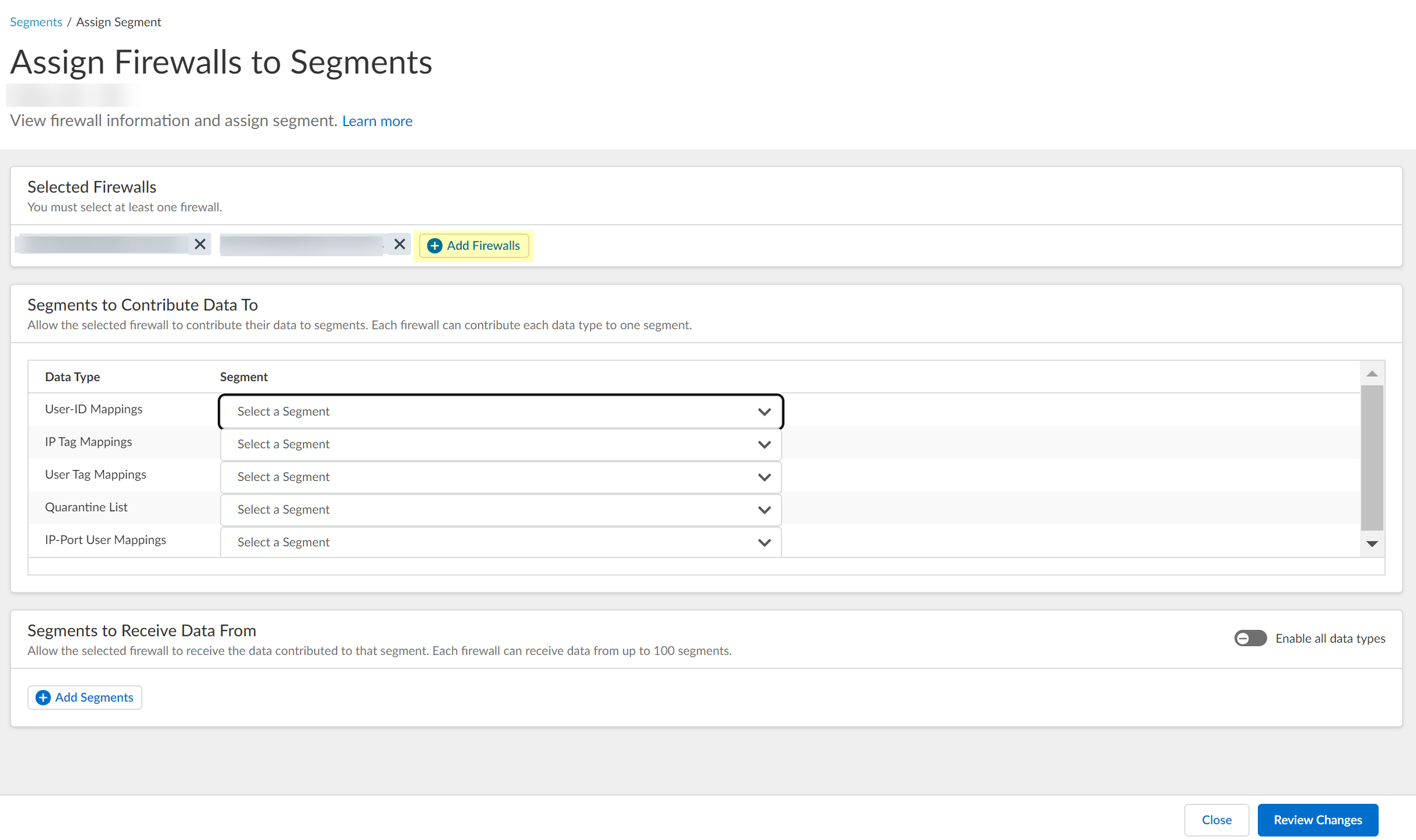
After selecting the firewalls that you want to include in this segment, Assign Segments to the selected firewalls.Assigning a segment to a firewall allows you to define which data the Cloud Identity Engine receives from or provides to that firewall. You can only assign segments to a firewall that uses PAN-OS 11.0; User Context does not support other source types.![]() (Optional) If you want to include additional firewalls in the segment, Add Firewalls to the segment to specify the firewalls you want to include.
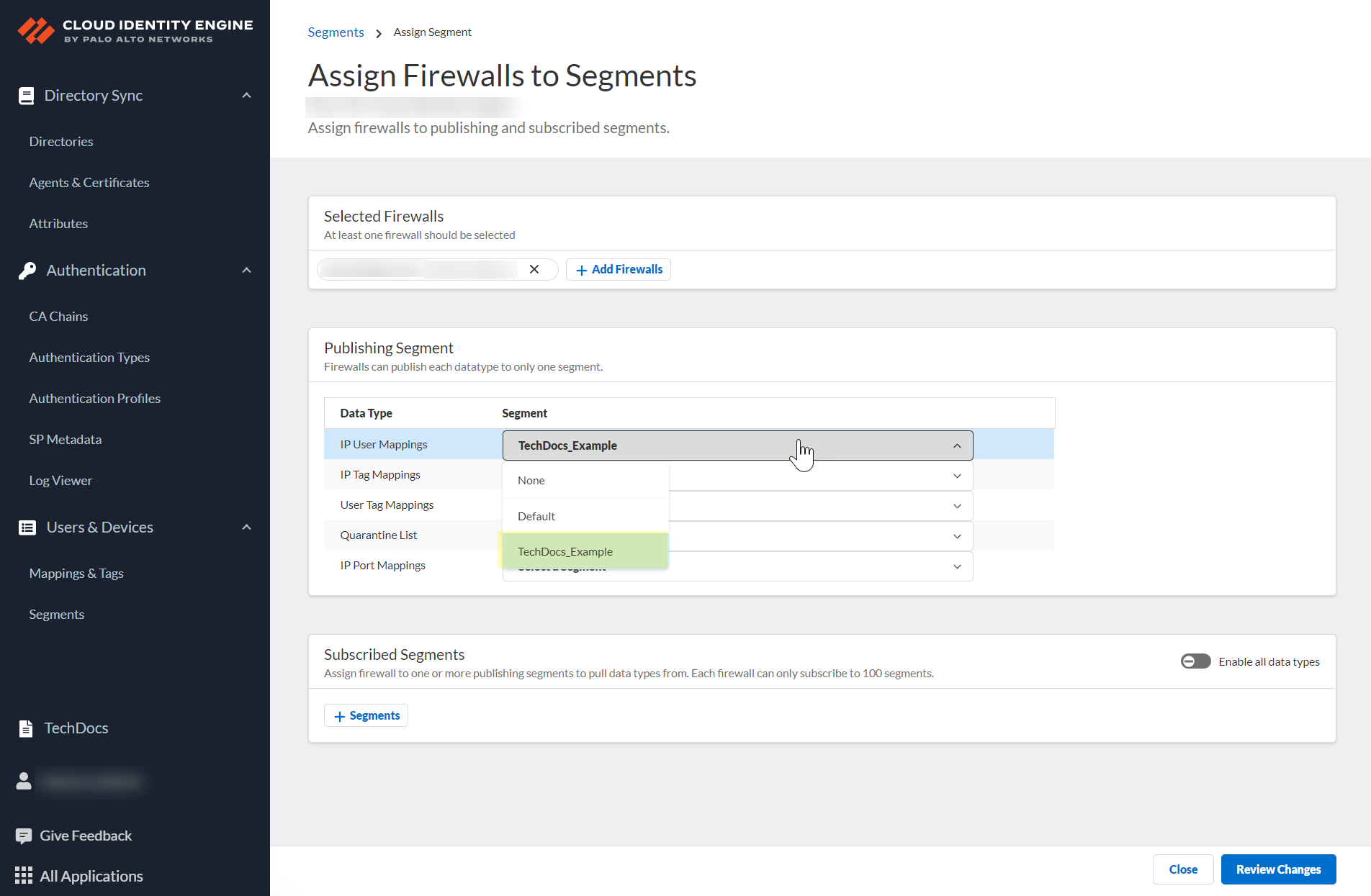
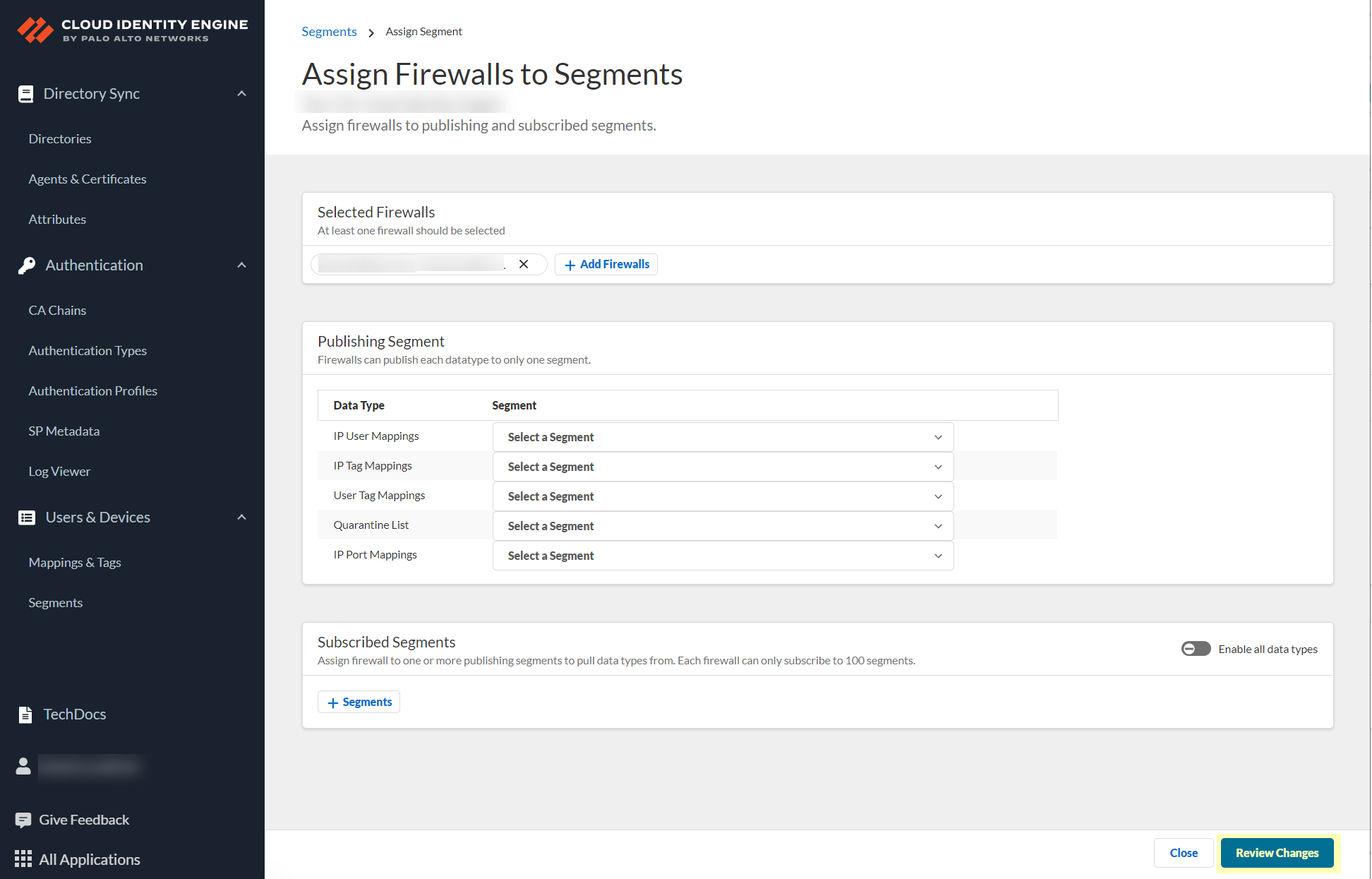
(Optional) If you want to include additional firewalls in the segment, Add Firewalls to the segment to specify the firewalls you want to include.![]() For each Data Type that you want to share, select the Segment where you want to publish the data type.Firewalls publish each data type to one segment. To share data between firewalls, you will need to configure a segment for each data type you want share.You can select the following data types:
For each Data Type that you want to share, select the Segment where you want to publish the data type.Firewalls publish each data type to one segment. To share data between firewalls, you will need to configure a segment for each data type you want share.You can select the following data types:- IP User Mappings—(GlobalProtect, Authentication Portal, XFF Headers, Username Header Insertion, XML APIs, Syslog, Server Monitoring, Panorama TrustSec plugin) Maps the IP address to a username.
- IP Tag Mappings—(Dynamic Address Group only) Maps the IP address to a tag.
- User Tag Mappings—(Dynamic User Group only) Maps the tag to a user.
- Quarantine List—(GlobalProtect only) Lists the firewalls that GlobalProtect has in quarantine.
- IP Port Mappings—(Terminal Server agent only) Maps the IP address to the port range allocated to a Windows-based terminal server user.
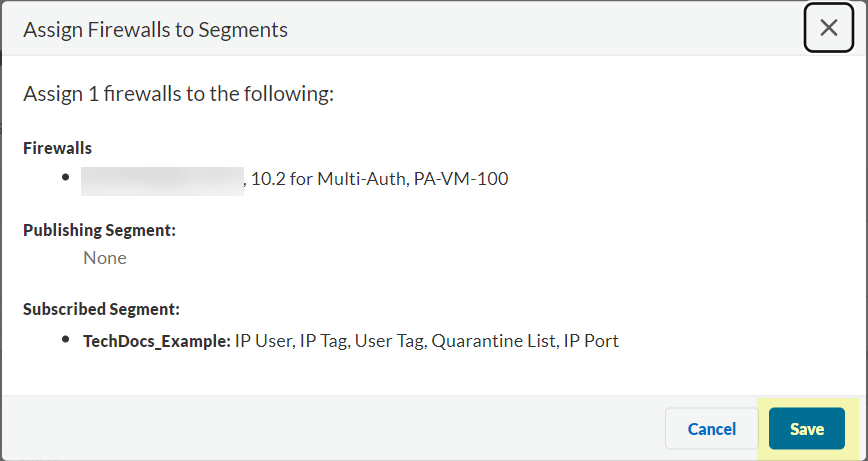
![]() Click Review Changes to review your configuration before submitting the changes.
Click Review Changes to review your configuration before submitting the changes.![]() Save the changes to confirm the configuration.
Save the changes to confirm the configuration.![]() Create a segment to subscribe to the publishing segment you created in the previous step.Publishing segments provide the specified data type that the Cloud Identity Engine collects from other firewalls to the segment containing the firewalls that you select.You can subscribe up to 100 segments per firewall.
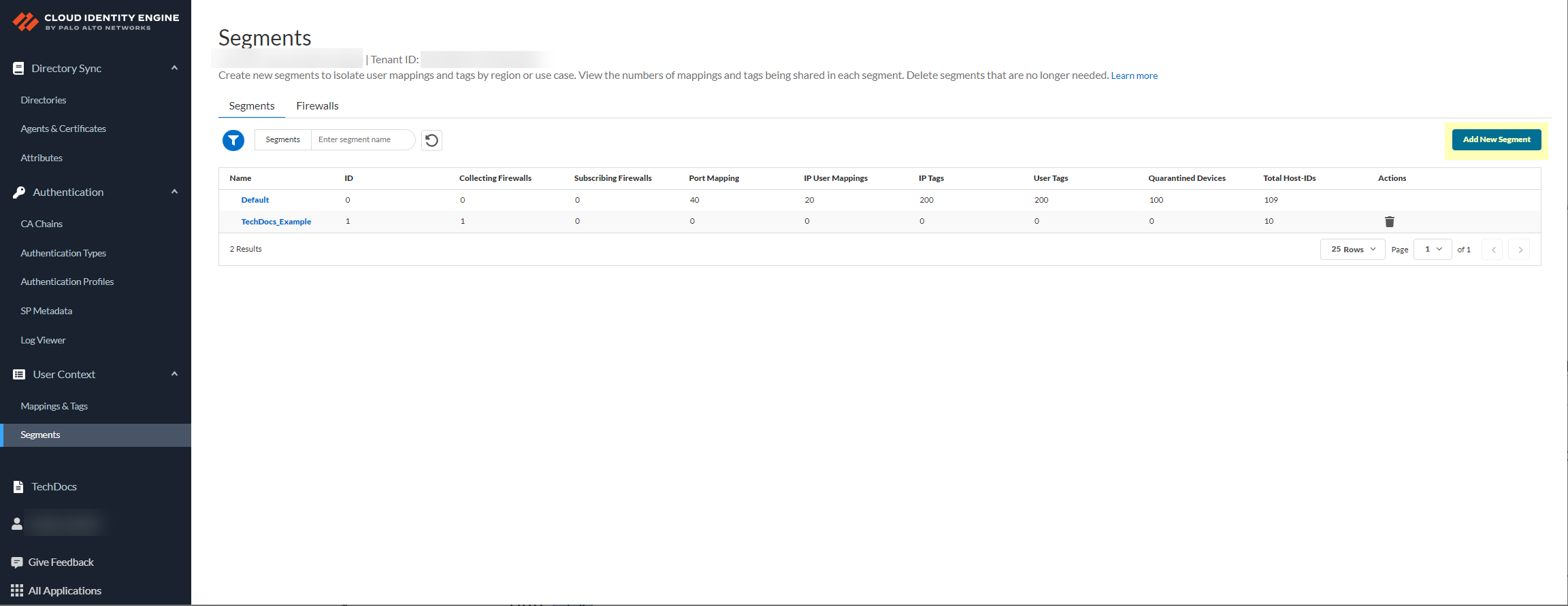
Create a segment to subscribe to the publishing segment you created in the previous step.Publishing segments provide the specified data type that the Cloud Identity Engine collects from other firewalls to the segment containing the firewalls that you select.You can subscribe up to 100 segments per firewall.- Select User ContextSegments and click Add New Segment.
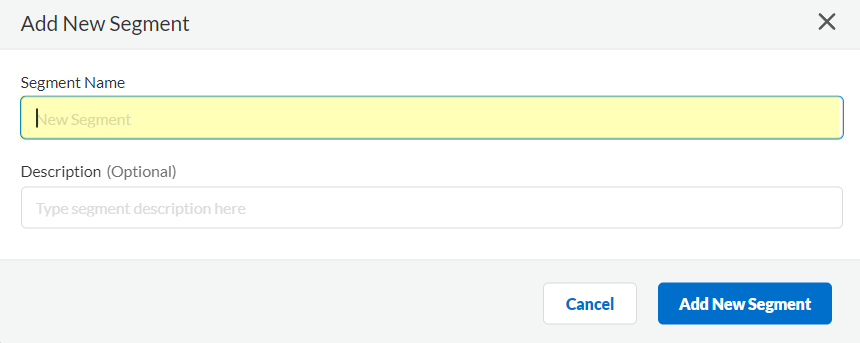
![]() Enter a unique Segment Name and optionally a Description for the segment.
Enter a unique Segment Name and optionally a Description for the segment.![]() Click Add New Segment to save the changes.Click Segments to add the segments you want to receive data.
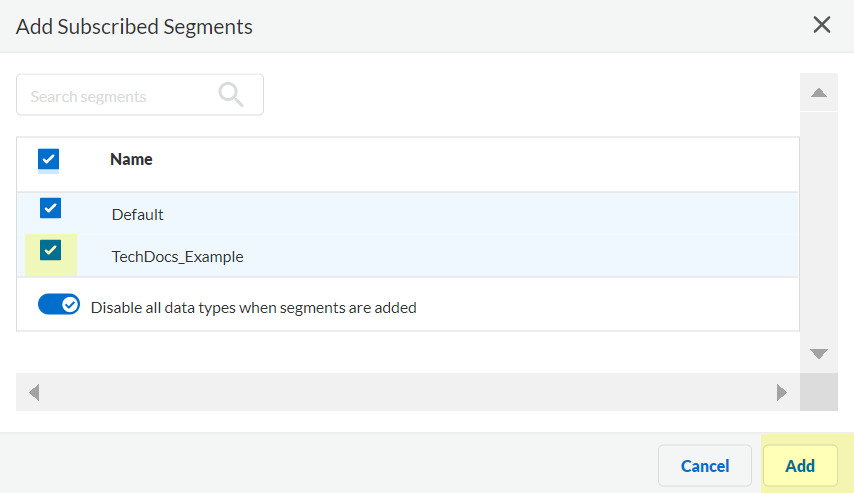
Click Add New Segment to save the changes.Click Segments to add the segments you want to receive data.![]() Select the segments that you want to include and Add the segments.
Select the segments that you want to include and Add the segments.![]() (Optional) Edit segments as needed to customize how the Cloud Identity Engine provides mappings to the firewalls.
(Optional) Edit segments as needed to customize how the Cloud Identity Engine provides mappings to the firewalls.- If sharing for data type is Enabled and you do not want to share this data type in this segment, select it to change the setting to Disabled.
![]() If you no longer need a segment, delete it from the configuration.
If you no longer need a segment, delete it from the configuration.![]() When your configuration is complete, Review Changes and Save the configuration.On your firewall, enable the service that the Cloud Identity Engine uses to communicate with your firewall.
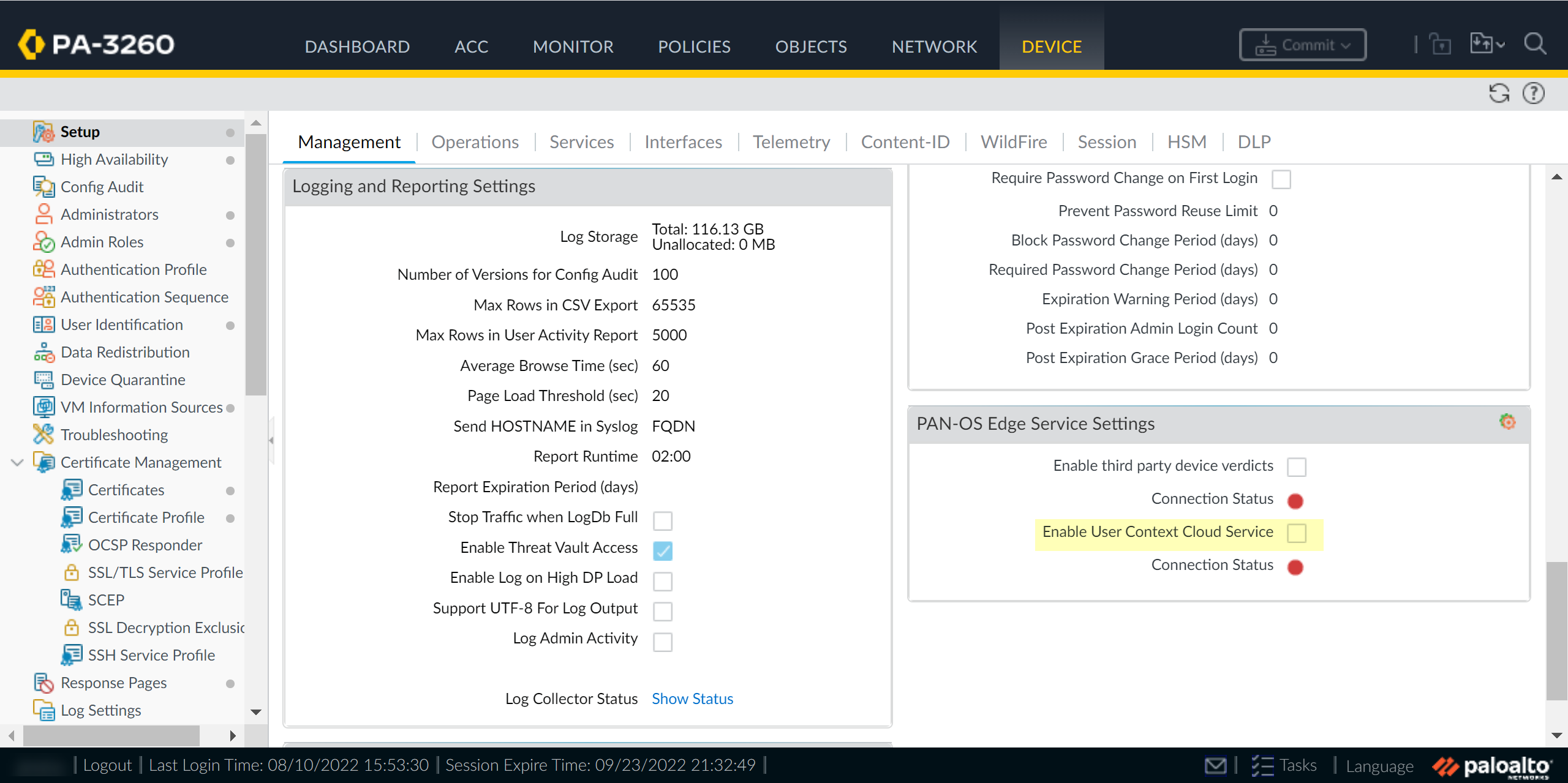
When your configuration is complete, Review Changes and Save the configuration.On your firewall, enable the service that the Cloud Identity Engine uses to communicate with your firewall.- Ensure that you have configured a device certificate.Log in to the firewall and Edit the PAN-OS Edge Service Settings (DeviceManagementSetupPAN-OS Edge Service Settings).
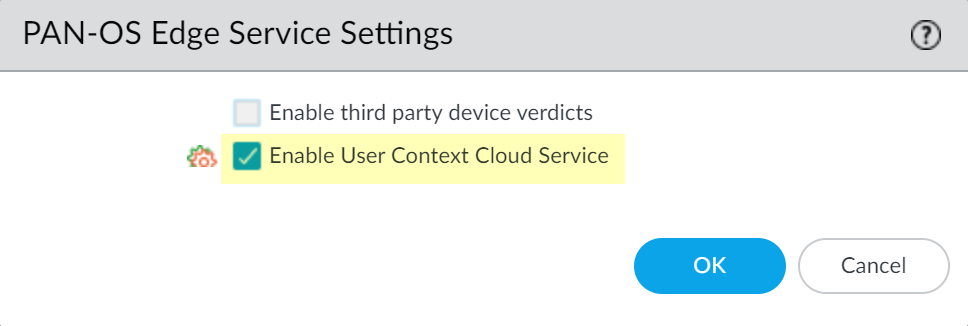
![]() Enable User Context Cloud Service and click OK to confirm the changes.If the firewall traffic uses a management interface, create security policy rules to allow connectivity between the firewall and the User Context Cloud Service.
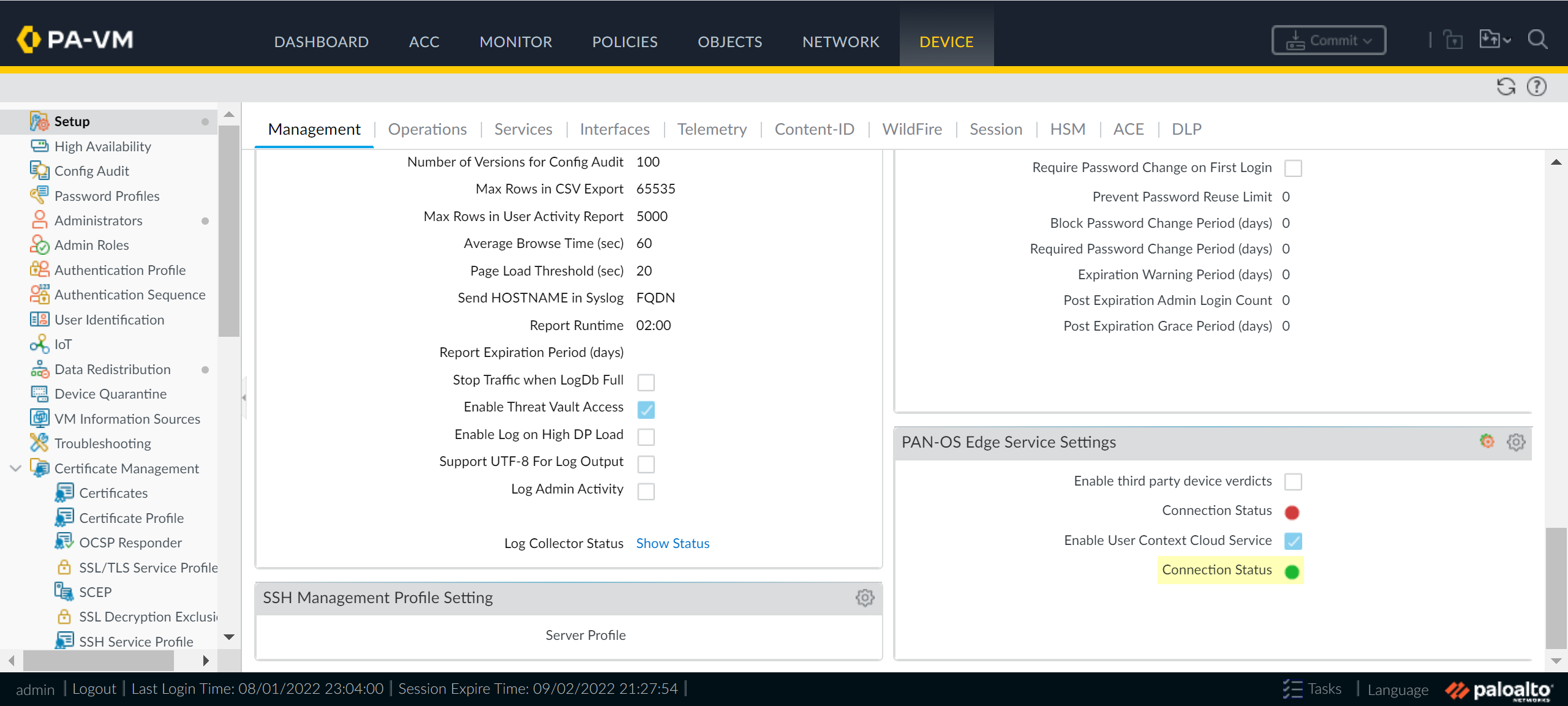
Enable User Context Cloud Service and click OK to confirm the changes.If the firewall traffic uses a management interface, create security policy rules to allow connectivity between the firewall and the User Context Cloud Service.![]() Commit your changes on the firewall.Verify the User Context configuration is successful and view the mappings and tags that the Cloud Identity Engine collects from the firewall.
Commit your changes on the firewall.Verify the User Context configuration is successful and view the mappings and tags that the Cloud Identity Engine collects from the firewall.- On the firewall, verify the User Context Cloud Service Connection Status is active.
![]() In the Cloud Identity Engine app, select User ContextMappings & Tags to review the information for the data types.You can review the following data types:
In the Cloud Identity Engine app, select User ContextMappings & Tags to review the information for the data types.You can review the following data types:- User-ID—Search User-ID mappings by Username or IP address.
- User Tags—Search Dynamic User Group tags by Username or by Tag.
- IP Tags—Search Dynamic Address Group tags by IP address or by Tag.
- IP-Port User—(Terminal Server agent only) Search Terminal Server agent mappings by IP address.
- Host IDs—(GlobalProtect only) Search devices (both quarantined and not quarantined) by Host ID.
![]() Now that you’ve configured segments, you can use them to enable user- and group-based policy, authentication profiles and sequences, and other firewall-based tasks.
Now that you’ve configured segments, you can use them to enable user- and group-based policy, authentication profiles and sequences, and other firewall-based tasks.
Cloud Identity User Context (SCM)
Learn about User Context with Strata Cloud Manager and CIE.Details coming soon.