Network Security
Troubleshoot Pinned Certificates
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Network Security Docs
Troubleshoot Pinned Certificates
Find sites that have pinned certificates so you can decide whether to allow the
traffic by excluding it from decryption.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
No separate license required for decryption when using NGFWs or
Prisma Access.
Note: The features and capabilities available to you in
Strata Cloud Manager depend on your active license(s).
|
Certificate pinning forces the client application to validate the server’s
certificate against a known copy to ensure that certificate really comes from the
server. The intent of pinned certificates is to protect against man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks where a device between
the client and the server replaces the server certificate with another certificate.
Although this prevents malicious actors from intercepting and manipulating connections, it also
prevents forward proxy decryption
because the NGFW creates an impersonation certificate instead of the server
certificate to present to the client. Instead of one session that connects the
client and server directly, forward proxy creates two sessions, one between the
client and the NGFW and another between the NGFW and the server. This establishes
trust with the client so that the NGFW can decrypt and inspect the traffic.
However, when a certificate is pinned, the NGFW cannot decrypt the traffic because the client
does not accept the NGFW’s impersonation certificate—the client only accepts the
certificate that is pinned to the application.
Troubleshoot Pinned Certificates (Strata Cloud Manager)
- Filter the decryption logs for pinned certificates.
- Select Log ViewerFirewall/Decryption.
- Use the query Error Message LIKE ‘Unknown CA’.
The application generates a TLS error code (Alert) when it fails to verify the server’s certificate. Different applications may use different error codes to indicate a pinned certificate. The most common error indicators for pinned certificates are UnknownCA and BadCertificate. After running the Error Message LIKE ‘Unknown CA’ query, run the query Error Message LIKE ‘Unknown CA’ ‘Bad Certificate’ to catch more pinned certificate errors.You can use Wireshark or other packet analyzers to double-check the error. Look for the client breaking the connection immediately after the TLS handshake to confirm that it is a pinned certificate issue.Decide what to do about pinned certificates.If you don’t need access for business purposes, you can let the NGFW continue to block access. If you need access, then you can exclude the server from decryption by adding it to the SSL Decryption Exclusion List. The NGFW bypasses decryption for sites on the SSL Decryption Exclusion List. The NGFW cannot inspect the traffic, but the traffic is allowed.
Troubleshoot Pinned Certificates (PAN-OS)
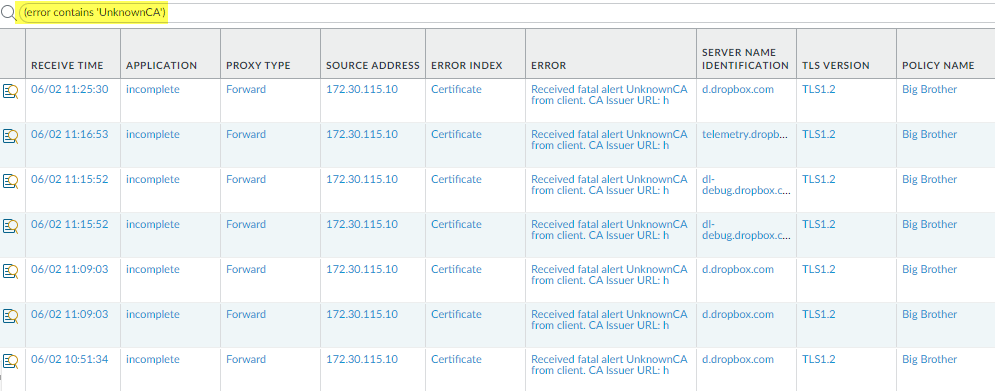
- Filter the Decryption log (MonitorLogsDecryption) to find pinned certificates using the query (error contains ‘UnknownCA’).
![]() The application generates a TLS error code (Alert) when it fails to verify the server’s certificate. Different applications may use different error codes to indicate a pinned certificate. The most common error indicators for pinned certificates are UnknownCA and BadCertificate. After running the (error contains ‘UnknownCA’) query, run the query (error contains ‘BadCertificate’) to catch more pinned certificate errors.You can use Wireshark or other packet analyzers to double-check the error. Look for the client breaking the connection immediately after the TLS handshake to confirm that it is a pinned certificate issue.Decide what to do about pinned certificates.If you don’t need access for business purposes, you can let the NGFW continue to block access. If you need access, you can exclude the server from decryption by adding it to the SSL Decryption Exclusion List (DeviceCertificate ManagementSSL Decryption Exclusion.The NGFW bypasses decryption for sites on the SSL Decryption Exclusion List. The NGFW cannot inspect the traffic, but the traffic is allowed.
The application generates a TLS error code (Alert) when it fails to verify the server’s certificate. Different applications may use different error codes to indicate a pinned certificate. The most common error indicators for pinned certificates are UnknownCA and BadCertificate. After running the (error contains ‘UnknownCA’) query, run the query (error contains ‘BadCertificate’) to catch more pinned certificate errors.You can use Wireshark or other packet analyzers to double-check the error. Look for the client breaking the connection immediately after the TLS handshake to confirm that it is a pinned certificate issue.Decide what to do about pinned certificates.If you don’t need access for business purposes, you can let the NGFW continue to block access. If you need access, you can exclude the server from decryption by adding it to the SSL Decryption Exclusion List (DeviceCertificate ManagementSSL Decryption Exclusion.The NGFW bypasses decryption for sites on the SSL Decryption Exclusion List. The NGFW cannot inspect the traffic, but the traffic is allowed.