Network Security
Create an Internet Access Rule (Strata Cloud Manager)
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Network Security Docs
Create an Internet Access Rule (Strata Cloud Manager)
Learn how to create an Internet Access rule in Strata Cloud Manager
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
- To create an Internet Access rule in Strata Cloud Manager:
- Go to ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessSecurity ServicesSecurity PolicyAdd RuleInternet Access Rule.Configure these components:
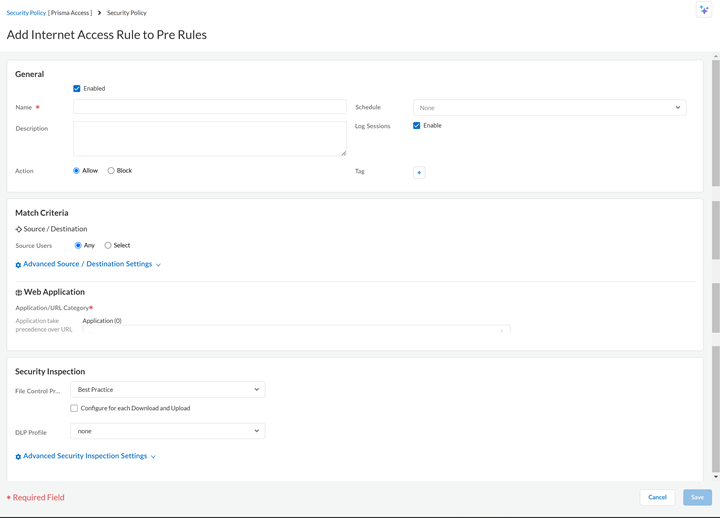
![]() Name your policy. You can use up to 63 characters.Add an optional Description. You can use up to 1,024 characters.Set Schedules to manage policy rules that need enforcement at regular intervals.Add Tags to your rules for easy filtering. This helps when you have defined many rules and wish to review tags with specific keywords.Configure Log at Sessions. This is enabled by default. You can disable this setting if you don’t want to generate logs when traffic matches this rule.Choose to Allow or Block web application and URLs.Define match criteria.
Name your policy. You can use up to 63 characters.Add an optional Description. You can use up to 1,024 characters.Set Schedules to manage policy rules that need enforcement at regular intervals.Add Tags to your rules for easy filtering. This helps when you have defined many rules and wish to review tags with specific keywords.Configure Log at Sessions. This is enabled by default. You can disable this setting if you don’t want to generate logs when traffic matches this rule.Choose to Allow or Block web application and URLs.Define match criteria.![]()
- Specify Source Users including users, user groups, or IP addresses as source.
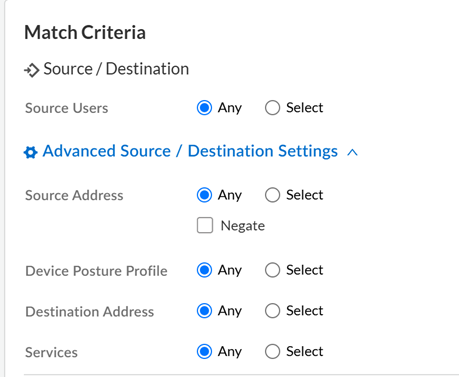
- Use Advanced Source and Destination settings to
manage source or destination IP addresses, service ports, or device
posture.
- In Source selection, define traffic enforcement based on source. Set the Source Address or leave as Any.
- Select Address, Address Groups, or
Regions.If you decide to Negate a region as source address, add all regions with private IP addresses to avoid connectivity loss.
- Add Device Posture profile to use device state information for policy enforcement.
- Define destination address or leave as
Any.If you decide to Negate a region as destination address, add all regions with private IP addresses to avoid connectivity loss.
- Specify application Services to allow or block. Add the application you want to safely enable. You can select multiple applications or use the application groups or application filters.
Use the Web Application section to configure controls for web applications and URLs.![]()
- Select Applications to restrict access to
specific features within allowed applications. Add sanctioned
applications to explicitly allow or block for enterprise use.Use Advanced Application Settings to capture additional functional controls for web applications.You can restrict access to specific features within allowed applications. For example, you might want to allow Gmail, but block chat or calls within Gmail. File controls enable the selection of actions for incoming files through allowed applications. These actions vary on a per-application basis. Custom profiles allow preconfiguration of file control rules. Internet Access rules then incorporate these custom profiles. This approach grants fine-grained control over application features and file handling in the network.
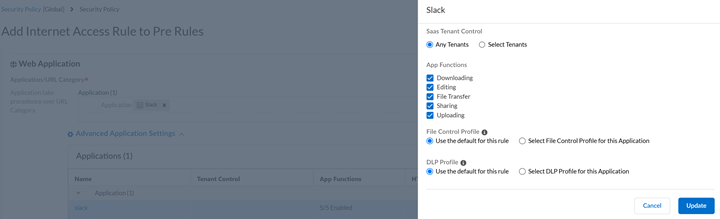
- Tenant control manages access across different SaaS application tenants.
It allows for differentiated policy rules within the same application.
You can tailor the functional controls specifically to SaaS application
tenants allowing for granular control. The default setting applies to
all tenants unless specified otherwise. This provides control over
application usage on a per tenant basis.In the Applications section, select the application to restrict specific functions for particular tenants.
![]()
- Specify URL Category as a match criteria for your rule. When you select a URL Category or Tenant Restriction, you can specify TCP and UDP port numbers, URL categories, or tenant restrictions in security rules. Selecting a URL category ensures that the rule matches only web traffic destined for that specified category.Use Advanced URL Category Settings to capture controls for URLs such as decryption, credential leak detection, and user notification applications. You can also override data inspection profiles as needed.
Use the Security Inspection options to bulk edit Applications and URL Categories.- Select the File Control Profile to change for all web applications.
- Select the DLP Profile for all web applications.
- Use the Advanced Security Inspection setting to disable specific security inspection for the policy.
Save policy rule, then Push Config to your devices.