Network Security
Create a Security Policy Rule (Strata Cloud Manager)
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Network Security Docs
Create a Security Policy Rule (Strata Cloud Manager)
Learn how to create a security rule.
To ensure that end users authenticate when they try to access your network
resources, authentication is evaluated before Security policy. For details, see
Authentication.
- Add a rule.
- Select ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessSecurity ServicesSecurity PolicyAdd RuleSecurity Rule and build your rule by configuring the following rulecomponents. Components marked with an asterisk(*) are mandatory.In the General tab, enter a descriptive Name for the rule.Give a Description for your rule's intent.Add Tag to your rules to group them using keywords or phrases.Limit a security rule to specific times using a Schedule.Define the matching criteria for the source fields in the packet.
- In the Source tab, select a Source Zone.Specify a Source IP Address or leave the value set to ny.You can search for specific Usersor User Groups to enforce policy for individual users or a group of users. Specify the match criteria that define which users and user groups.
- Sub string or partial string search is not supported for performance reasons.
- Entire string search is possible when delimiters such as space and hyphen is present.
- When number of users is more than 500 then string search use quotes with exact string
If you're using GlobalProtect™ with host information profile (HIP) enabled, you can also base the policy on information collected by GlobalProtect. For example, the user access level can be determined from the HIP that informs your environment about the user's local configuration. The HIP information can be used for granular access control based on the security programs that are running on the host, registry values, and many other checks such as whether the host has antivirus software installed.If you decide to Negate a region as a source address, ensure that all regions that contain private IP addresses are added to the source address to avoid connectivity loss between those private IP addresses.Define the matching criteria for the destination fields in the packet.- In the Destination tab, set the Zone.Specify a Destination IP Address or leave the value set to any.If you decide to Negate a region as the Destination Address, ensure that all regions that contain private IP addresses are added to the Destination Address to avoid connectivity loss between those private IP addresses.As a best practice, use address objects as the Destination Address to enable access to only specific servers or specific groups of servers especially for commonly exploited services, such as DNS and SMTP. By restricting users to specific destination server addresses, you can prevent data exfiltration and command-and-control traffic from establishing communication through techniques such as DNS tunneling.Specify the Application/Service that the rule will allow or block.As a best practice, always use application-based security rules instead of port-based rules and always set the Service to application-default unless you're using a more restrictive list of ports than the standard ports for an application.
- Under Application, Select any Applications, Application Groups, or Application Filters you want to safely enable. You can select multiple applications or you can use application groups or application filters. Certain applications may possess application dependency (also shown as Depends on when viewing application details), which you will need to consider for inclusion into the security rule.To view application dependency from the security rule:
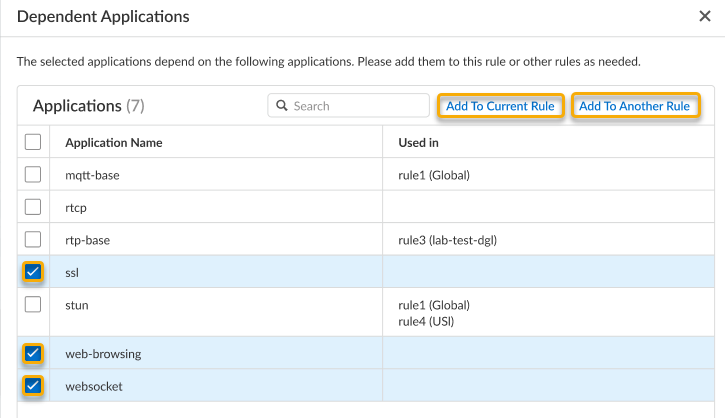
- Select an application and then click Dependent Applications to display all associated dependent applications and the rules they are used in.
![]()
- Additionally, for certain applications, you can select these dependent applications and either Add To Current Rule or Add to Another Rule.
![]()
Under Service, keep the service set to Application Default to ensure that any applications that the rule allows are allowed only on their standard ports. You can also select Any or Select specific Services or Services Groups, as necessary.As a best practice, always use application-based Security policy rules instead of port-based rules and always set the Service to application-default unless you're using a more restrictive list of ports than the standard ports for an application.(Optional) Specify a URL category as match criteria for the rule.Select URL Category or Tenant Restriction to specify a specific TCP and/or UDP port number, a URL category, a tenant restriction as match criteria in the security rule. If you select a URL category, only web traffic will match the rule and only if the traffic is destined for that specified category.Define what action you want the firewall to take for traffic that matches the rule.Configure the log settings.- By default, the rule is set to Log at Session End. You can disable this setting if you don’t want any logs generated when traffic matches this rule or you can select Log at Session Start for more detailed logging.
- Select a Log Forwarding profile.
As a best practice, don't select the check box to Disable Server Response Inspection (DSRI). Selecting this option prevents the inspection of packets from the server to the client. For the best security posture, both the client-to-server flows and the server-to-client flows must be inspected to detect and prevent threats.Attach security profiles to scan all allowed traffic for threats.Make sure you create best practice security profiles that help protect your network from both known and unknown threats.In ActionsProfile Group, select a Profile Group from the drop-down to attach to the rule.Select Save to save the security rule, then Push Config to your devices.When you save the security rule, the rule is validated against the configured security checks. If a security check fails, you can either Override and Save the rule or Close and Fix the issue. You can override and save only if your role includes the Override Security Check Block Action permission.Monitor the security rule usage status and determine the effectiveness of the security rule, and optimize if needed.