Next-Generation Firewall
Configure the Management Interface Settings
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Next-Generation Firewall Docs
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- PAN-OS 12.1
- PAN-OS 11.2
- PAN-OS 11.1
- PAN-OS 11.0 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 10.2
- PAN-OS 10.1
- PAN-OS 10.0 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 9.1 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 9.0 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 8.1 (EoL)
-
- PAN-OS 12.1
- PAN-OS 11.2
- PAN-OS 11.1
- PAN-OS 10.2
- PAN-OS 10.1
Configure the Management Interface Settings
Configure the connection settings, allowed services, and administrative access
settings for the management interface.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
| One of these licenses:
|
Configure the management interfaces settings to establish the connection settings,
allowed services, and administrative access settings permitted over the management
interface.
- Log in to Strata Cloud Manager.Select ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessDevice SettingsDevice SetupManagement and select the Configuration Scope where you want to configure the management interface settings.You can select a folder or firewall from your Folders or select Snippets to configure the management interface settings in a snippet.Click the cog wheel to edit the Management Interface Settings and Customize.Configure the management interface settings.
- Set the Speed to auto-negotiate.Specify the MTU in bytes for packets sent on this interface.Configure the address settings for the MGT interface using one of the following methods:
- To configure static IP address settings for the MGT interface, set the IP Type to Static and enter the IP Address, Netmask, and Default Gateway.
- To dynamically configure the MGT interface address settings, set the IP Type to DHCP Client.
To prevent unauthorized access to the management interface, it is a an administrative best practice to Add the Permitted IP Addresses from which an administrator can access the MGT interface.Select which Administrative Management Services that you want to enable on the interface in order to access the firewall web interface and CLI.HTTP and HTTPS are the supported protocols to access the firewall web interface.Telnet and SSH are supported protocols to access the firewall CLI.Palo Alto Networks recommends enabling HTTPS and SSH for management traffic on the interface rather than HTTP and Telnet. HTTP and Telnet both use plaintext, which isn’t as secure as HTTPS and SSH.Select the Network Services that you want to enable on the interface.- HTTP OCSP—Configure the firewall as an Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) responder.
- Ping—Test connectivity with external services. For example, you can ping the interface to verify it can receive PAN-OS software and content updates from the Palo Alto Networks Update Server.In a high availability (HA) deployment, HA peers use ping to exchange heartbeat backup information.
- SNMP—Process firewall statistics queries from an SNMP manager.
- User-ID—Enable data redistribution of user mappings among firewalls.
- User-ID Syslog Listener-SSL—Enable the PAN-OS integrated User-ID™ agent to collect syslog messages over SSL.
- User-ID Syslog Listener-UDP—Enable the PAN-OS integrated User-ID agent to collect syslog messages over UDP.
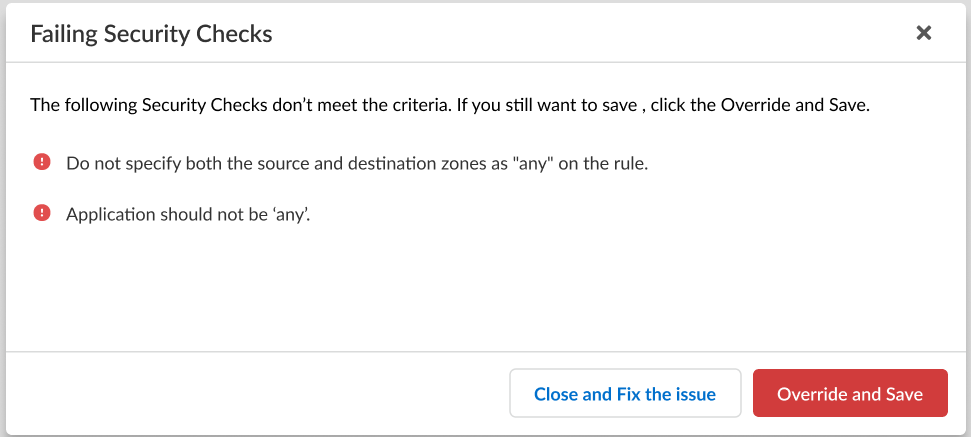
Add Permitted IP Addresses from which administrators can access the firewall through the interface.The list is empty by default. An empty Permitted IP Address list specifies that access is available from an IP address.To prevent unauthorized access, Palo Alto Networks recommends specifying IP addresses that are allowed to access the firewall through the management interface rather than leaving the Permitted IP Addresses empty.Save.If the configuration you're trying to save doesn't meet the criteria to pass the compliance check, you'll have the option to remediate the issue or override the warning and save the configuration anyway.![]() Push Config to push your configuration changes.
Push Config to push your configuration changes.