Next-Generation Firewall
Create BGP Routing Profiles
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Next-Generation Firewall Docs
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- PAN-OS 12.1
- PAN-OS 11.2
- PAN-OS 11.1
- PAN-OS 11.0 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 10.2
- PAN-OS 10.1
- PAN-OS 10.0 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 9.1 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 9.0 (EoL)
- PAN-OS 8.1 (EoL)
-
- PAN-OS 12.1
- PAN-OS 11.2
- PAN-OS 11.1
- PAN-OS 10.2
- PAN-OS 10.1
Create BGP Routing Profiles
Use BGP routing profiles to easily configure settings and route
redistribution.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
For Strata Cloud Manager:
|
On an Advanced Routing Engine, BGP has many settings that you can easily configure in a
profile and then apply to a BGP peer group or peer or to redistribution rules. Reuse profiles to
apply them to multiple logical routers and virtual systems. Create multiple profiles of the same
type to handle different peer groups and peers differently. BGP peer groups and peers inherit
global profiles; you can also create a profile for a BGP peer group to override the global
profile, and create a profile for a BGP peer, which overrides the profile for the peer group to
which the peer belongs.
This topic describes the BGP routing profiles and how to create them.
- BGP Authentication Profiles—Specify the Secret key for MD5 authentication, which is used between BGP peers during negotiation to determine whether they can communicate with each other. Reference the profile in a BGP peer group or peer configuration.
- BGP Timer Profiles— Control various BGP timers that affect keepalive and update messages that advertise routes. Reference the profile in a BGP peer group or peer configuration.
- BGP Address Family Profiles—Determine the behavior of IPv6 or IPv4 when a BGP autonomous system uses both types of address. Reference the profile in a BGP peer group or peer configuration.
- BGP Dampening Profiles—Determine how to penalize a flapping route to suppress it from being used until it stabilizes. Reference the profile in a BGP peer group or peer configuration.
- BGP Redistribution Profiles—Redistribute static, connected, OSPF, OSPFv3, or RIP routes (that meet the criteria of the assigned route map) into BGP and apply the route map Set attributes to the redistributed routes. Reference the profile on NetworkRoutingLogical RoutersBGPRedistribution.
- BGP Filtering Profiles—Simultaneously apply multiple filters to a peer group or peer
to do the following:
- Accept routes that came from a specific AS Path (based on the AS Path access list).
- Advertise routes that have a specific AS Path (based on the AS Path access list).
- Accept routes to the local BGP RIB based on either a distribute list or prefix list (not both in the same Filtering Profile). A distribute list is based on source IP address with wildcard mask to get a prefix range. A prefix list is based on network address/prefix length.
- Advertise routes from the local BGP RIB based on a distribute list or prefix list (not both in the same Filtering Profile).
- Accept routes that meet route map attribute criteria into the local BGP RIB, and optionally set attributes.
- Advertise routes that meet route map attribute criteria, and optionally set attributes.
- Conditionally advertise routes that exist (satisfy exist criteria).
- Conditionally advertise routes other than those that meet criteria (satisfy non-exist criteria).
- Unsuppress dampened or summarized routes.
Create BGP Routing Profiles (PAN-OS)
Learn about creating BGP profiles in PAN-OS and Panorama.
- Create a BGP Authentication profile.
- Select NetworkRoutingRouting ProfilesBGP.
![]() Add a BGP Auth Profile by Name (a maximum of 63 characters) to identify the profile. The name must start with an alphanumeric character, underscore (_), hyphen (-), or dot (.) and can contain alphanumeric characters, underscores, hyphens and dots. A space is not allowed.Enter the Secret and Confirm Secret. The Secret is used as a key in MD5 authentication. The Secret can include only !@#%^_- characters and alphanumeric characters.Create a BGP Timer profile.
Add a BGP Auth Profile by Name (a maximum of 63 characters) to identify the profile. The name must start with an alphanumeric character, underscore (_), hyphen (-), or dot (.) and can contain alphanumeric characters, underscores, hyphens and dots. A space is not allowed.Enter the Secret and Confirm Secret. The Secret is used as a key in MD5 authentication. The Secret can include only !@#%^_- characters and alphanumeric characters.Create a BGP Timer profile.- Select NetworkRoutingRouting ProfilesBGP.In the BGP Timer Profiles window, select the default BGP Timer Profile to see the default profile settings:
![]() If the default BGP Timer Profile settings are not what you need, Add a BGP Timer Profile by Name (a maximum of 63 characters). The name must start with an alphanumeric character, underscore (_), hyphen (-), or dot (.) and can contain alphanumeric characters, underscores, hyphens and dots. A space is not allowed.Set the Keep Alive Interval (sec)—the interval, in seconds, at which the BGP speaker sends Keepalives to the peer (range is 0 to 1,200; default is 30). If no Keepalive is received from a peer during a Hold Time interval, the BGP peering is closed. Often, the Hold Time is three times the Keep Alive Interval to allow for three missed Keepalives before BGP peering is brought down.Set the Hold Time (sec)—the length of time, in seconds, that may elapse between successive Keepalive or Update messages from the peer before the peer connection is closed (range is 3 to 3,600; default is 90).Set the Reconnect Retry Interval—the number of seconds to wait in Idle state before retrying to connect to the peer (range is 1 to 3,600; default is 15).Set the Open Delay Time (sec)—the number of seconds of delay between opening the TCP connection to the peer and sending the first BGP Open message to establish a BGP connection (range is 0 to 240; default is 0).Set the Minimum Route Advertise Interval (sec)—the minimum amount of time, in seconds, that must elapse between an advertisement and/or withdrawal of routes to a particular destination by a BGP speaker to a peer (range is 1 to 600; default is 30).Click OK.To use MP-BGP, create a BGP Address Family Identifier (AFI) profile of shared attributes.
If the default BGP Timer Profile settings are not what you need, Add a BGP Timer Profile by Name (a maximum of 63 characters). The name must start with an alphanumeric character, underscore (_), hyphen (-), or dot (.) and can contain alphanumeric characters, underscores, hyphens and dots. A space is not allowed.Set the Keep Alive Interval (sec)—the interval, in seconds, at which the BGP speaker sends Keepalives to the peer (range is 0 to 1,200; default is 30). If no Keepalive is received from a peer during a Hold Time interval, the BGP peering is closed. Often, the Hold Time is three times the Keep Alive Interval to allow for three missed Keepalives before BGP peering is brought down.Set the Hold Time (sec)—the length of time, in seconds, that may elapse between successive Keepalive or Update messages from the peer before the peer connection is closed (range is 3 to 3,600; default is 90).Set the Reconnect Retry Interval—the number of seconds to wait in Idle state before retrying to connect to the peer (range is 1 to 3,600; default is 15).Set the Open Delay Time (sec)—the number of seconds of delay between opening the TCP connection to the peer and sending the first BGP Open message to establish a BGP connection (range is 0 to 240; default is 0).Set the Minimum Route Advertise Interval (sec)—the minimum amount of time, in seconds, that must elapse between an advertisement and/or withdrawal of routes to a particular destination by a BGP speaker to a peer (range is 1 to 600; default is 30).Click OK.To use MP-BGP, create a BGP Address Family Identifier (AFI) profile of shared attributes.- Select NetworkRoutingRouting ProfilesBGP.Add a BGP Address Family Profile by Name (a maximum of 63 characters). The name must start with an alphanumeric character, underscore (_), hyphen (-), or dot (.) and can contain alphanumeric characters, underscores, hyphens and dots. A space is not allowed.
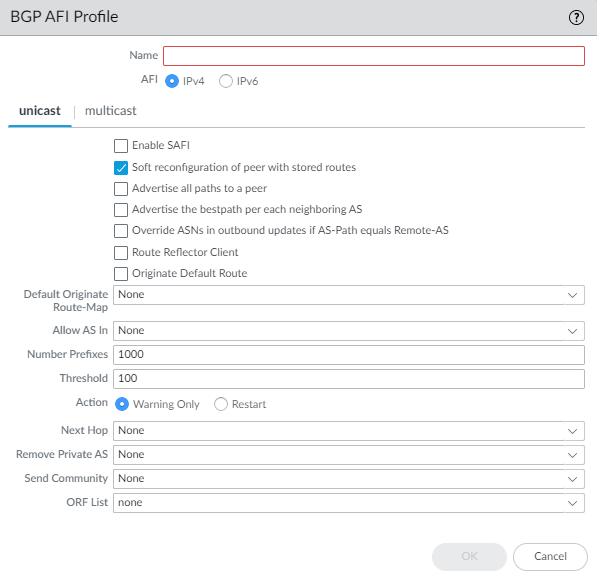
![]() Select IPv4 or IPv6 AFI to specify the type of profile.Select unicast or multicast.Multicast is supported only for an IPv4 AFI profile.On the unicast tab, Enable SAFI to enable the unicast SAFI for the profile. On the multicast tab, Enable SAFI to enable the multicast SAFI for the profile. If Enable SAFI is checked for both unicast and multicast, both SAFI are enabled. At least one SAFI must be enabled for the BGP profile to be valid.Select Soft reconfiguration of peer with stored routes to cause the firewall to perform a soft reset of itself after settings of any of its BGP peers are updated. (Enabled by default.)Advertise all paths to peers— to have BGP advertise all known paths to neighbor in order to preserve multipath capabilities inside a network.Advertise the bestpath for each neighboring AS to have BGP advertise the best known paths to neighbors in order to preserve multipath capabilities inside a network. Disable this if you want to advertise the same path to all autonomous systems.Override ASNs in outbound updates if AS-Path equals Remote-AS—This setting is helpful if you have multiple sites belonging to the same AS number (AS 64512, for example) and there is another AS between them. A router between the two sites receives an Update advertising a route that can access AS 64512. To avoid the second site dropping the Update because it is also in AS 64512, the intermediate router replaces AS 64512 with its own AS number (ASN), AS 64522, for example.Enable Route Reflector Client to make the BGP peer a Route Reflector client in an IBGP network.Originate Default Route—Select to generate a default route and place it in the local BGP RIB.Default Originate Route-Map—Select or create a route map to control the attributes of the default route.Allow AS in:
Select IPv4 or IPv6 AFI to specify the type of profile.Select unicast or multicast.Multicast is supported only for an IPv4 AFI profile.On the unicast tab, Enable SAFI to enable the unicast SAFI for the profile. On the multicast tab, Enable SAFI to enable the multicast SAFI for the profile. If Enable SAFI is checked for both unicast and multicast, both SAFI are enabled. At least one SAFI must be enabled for the BGP profile to be valid.Select Soft reconfiguration of peer with stored routes to cause the firewall to perform a soft reset of itself after settings of any of its BGP peers are updated. (Enabled by default.)Advertise all paths to peers— to have BGP advertise all known paths to neighbor in order to preserve multipath capabilities inside a network.Advertise the bestpath for each neighboring AS to have BGP advertise the best known paths to neighbors in order to preserve multipath capabilities inside a network. Disable this if you want to advertise the same path to all autonomous systems.Override ASNs in outbound updates if AS-Path equals Remote-AS—This setting is helpful if you have multiple sites belonging to the same AS number (AS 64512, for example) and there is another AS between them. A router between the two sites receives an Update advertising a route that can access AS 64512. To avoid the second site dropping the Update because it is also in AS 64512, the intermediate router replaces AS 64512 with its own AS number (ASN), AS 64522, for example.Enable Route Reflector Client to make the BGP peer a Route Reflector client in an IBGP network.Originate Default Route—Select to generate a default route and place it in the local BGP RIB.Default Originate Route-Map—Select or create a route map to control the attributes of the default route.Allow AS in:- Origin—Accept routes even if the firewall’s own AS is present in the AS_PATH.
- Occurrence—Number of times the firewall’s own AS can be in the AS_PATH.
- None—(default setting) No action taken.
Number Prefixes—Maximum number of prefixes to accept (learn) from the peer. Range is 1 to 4,294,967,295; default is 1,000.Threshold—Percentage of the maximum number of prefixes. The prefixes are added to the BGP local RIB. If the peer advertises more than the threshold, the firewall takes the specified action (Warning Only or Restart). Range is 1 to 100; default is 100.Action—Warning Only message in system logs or Restart the BGP peer connection after the maximum number of prefixes is exceeded.Select the Next Hop:- Self—Causes the firewall to change the Next Hop address (in Updates it receives) to its own IP address in the Update before sending it on. This is helpful when the firewall is communicating with an EBGP router (in another AS) and with an IBGP router (in its own AS). For example, suppose the Next Hop address in a BGP Update that arrives at AS 64512 is the IP address of the egress interface of Router 2 where the Update egressed AS 64518. The Update indicates that to reach networks that Router 2 is advertising, use the Next Hop address of Router 2. However, if the firewall sends that Update to an iBGP neighbor in AS 64512, the unchanged Next Hop of Router 2 is outside AS 64512 and the iBGP neighbor does not have a route to it. When you select Self, the firewall changes the Next Hop to its own IP address so that an iBGP neighbor can use that Next Hop to reach the firewall, which in turn can reach the eBGP router.
- Self Force—Force set the next hop to self for the reflected routes.
- None—(default setting) Keep the original Next Hop in the attribute.
To have BGP remove private AS numbers from the AS_PATH attribute in Updates that the firewall sends to a peer in another AS, in Remove Private AS, select one of the following:- All—Remove all private AS numbers.
- Replace AS—Replace all private AS numbers with the firewall’s AS number.
- None—(default setting) No action taken.
For Send Community, select the type of BGP community attribute to send in outbound Update packets:For ORF List—Advertise the ability of the peer group or peer to send a prefix list and/or receive a prefix list to implement outbound route filtering (ORF) at the source, and thereby minimize sending or receiving unwanted prefixes in Updates. Select an ORF capability setting:- none—(default setting) The peer group or peer (where this AFI profile is applied) has no ORF capability.
- both—Advertise that the peer group or peer (where this AFI profile is applied) can send a prefix list and receive a prefix list to implement ORF.
- receive—Advertise that the peer group or peer (where this AFI profile is applied) can receive a prefix list to implement ORF. The local peer receives the remote peer’s ORF capability and prefix list, which it implements as an outbound route filter.
- send—Advertise that the peer group or peer (where this AFI profile is applied) can send a prefix list to implement ORF. The remote peer (with receive capability) receives the ORF capability and implements the prefix list it received as an outbound route filter when advertising routes to the sender.
ORF is a solution to two potential problems: a) wasting bandwidth by advertising unwanted routes and b) filtering route prefixes that perhaps the receiving peer wants. Implement ORF by doing the following:- Specify ORF capability in the Address Family profile.
- For a peer group or peer that is a sender (send or both capability), create a prefix list containing the set of prefixes the peer group/peer wants to receive.
- Create a BGP Filtering profile and in the Inbound Prefix List, select the prefix list you created.
- For the BGP peer group, select the Address Family profile you created to apply it to the peer group. In the case of the sender, also select the Filtering Profile you created (which indicates the prefix list). If the peer group or peer is an ORF receiver only, it does not need the Filtering Profile; it needs only the Address Family profile to indicate ORF receive capability.
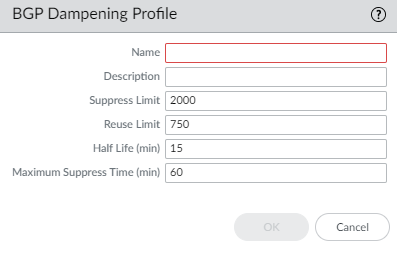
Click OK.Create a BGP Dampening Profile.- Select NetworkRoutingRouting ProfilesBGP.Add a BGP Dampening Profile by Name. The name must start with an alphanumeric character, underscore (_), hyphen (-), or dot (.) and can contain alphanumeric characters, underscores, hyphens and dots. A space is not allowed.Enter a helpful Description.Suppress Limit— Enter the suppress value (cumulative value of the penalties for flapping), at which point all the routes coming from a peer are dampened. Range is 1 to 20,000; default is 2,000.Reuse Limit—Enter the value that controls when a route can be reused based on the procedure described for Half Life. Range is 1 to 20,000; default is 750.Half Life (min)—Enter the number of minutes for the half life time to control the stability metric (penalty) applied to a flapping route. Range is 1 to 45; default is 15. The stability metric starts at 1,000. After a penalized route stabilizes, the half life timer counts down until it expires, at which point the next stability metric applied to the route is only half of the previous value (500). Successive cuts continue until the stability metric is less than half of the Reuse Limit, and then the stability metric is removed from the route.Maximum Suppress Time (min)—Enter the maximum number of minutes a route can be suppressed, regardless of how unstable it has been. Range is 1 to 255; default is 60.
![]() Click OK.Create a BGP Redistribution Profile to redistribute static, connected, and OSPF routes (that match the corresponding route map) to BGP.
Click OK.Create a BGP Redistribution Profile to redistribute static, connected, and OSPF routes (that match the corresponding route map) to BGP.- Select NetworkRoutingRouting ProfilesBGP.Add a BGP Redistribution Profile by Name (a maximum of 63 characters). The name must start with an alphanumeric character, underscore (_), hyphen (-), or dot (.) and can contain alphanumeric characters, underscores, hyphens and dots. A space is not allowed.Select the AFI of routes to redistribute: IPv4 or IPv6.
![]() Select Static to configure static route redistribution.Enable redistribution of IPv4 or IPv6 static routes (based on the AFI you selected).Configure the Metric to apply to the static routes being redistributed into BGP (range is 1 to 65,535).Select a Route-Map to specify the match criteria that determine which static routes to redistribute. Default is None. If the route map Set configuration includes a Metric Action along with a specified Metric Value, that value will be applied to the redistributed route. If no Metric Value is defined within the route map, the firewall will use default metric values. This means that routes redistributed via BGP will retain the same metric value that they had on the originating device. For example, if a static route is configured with a metric value of 10 and then redistributed into BGP, the metric value will remain 10.Select Connected to configure connected route redistribution.Enable redistribution of locally connected IPv4 or IPv6 routes (based on the AFI you selected).Configure the Metric to apply to the connected routes being redistributed into BGP (range is 1 to 65,535).Select a Route Map to specify the match criteria that determine which connected routes to redistribute. Default is None. If the route map Set configuration includes a Metric Action along with a specified Metric Value, that value will be applied to the redistributed route. If no Metric Value is defined within the route map, the firewall will use default metric values. This means that routes redistributed via BGP will retain the same metric value that they had on the originating device.(IPv4 AFI only) Select OSPFv2 to configure OSPFv2 route redistribution.Enable redistribution of OSPFv2 routes.Configure the Metric to apply to the OSPF routes being redistributed into BGP (range is 1 to 65,535).Select a Route-Map to specify the match criteria that determine which OSPF routes to redistribute. Default is None. If the route map Set configuration includes a Metric Action along with a specified Metric Value, that value will be applied to the redistributed route. If no Metric Value is defined within the route map, the firewall will use default metric values. This means that routes redistributed via BGP will retain the same metric value that they had on the originating device. For example, if an OSPF route is configured with a metric value of 2 and then redistributed into BGP, the metric value will remain 2.(IPv4 AFI only) Select RIPv2 to configure RIPv2 route redistribution.Enable redistribution of RIPv2 routes.Configure the Metric to apply to the RIP routes being redistributed into BGP (range is 1 to 65,535).Select a Route-Map to specify the match criteria that determine which RIP routes to redistribute. Default is None. If the route map Set configuration includes a Metric Action along with a specified Metric Value, that value will be applied to the redistributed route. If no Metric Value is defined within the route map, the firewall will use default metric values. This means that routes redistributed via BGP will retain the same metric value that they had on the originating device. For example, if a RIPv2 route is configured with a metric value of 10 and then redistributed into BGP, the metric value will remain 10.(IPv6 AFI only) Select OSPFv3 to configure OSPFv3 route redistribution.Enable redistribution of OSPFv3 routes.Configure the Metric to apply to the OSPFv3 routes being redistributed into BGP (range is 1 to 65,535).Select a Route-Map to specify the match criteria that determine which OSPFv3 routes to redistribute. Default is None. If the route map Set configuration includes a Metric Action along with a specified Metric Value, that value will be applied to the redistributed route. If no Metric Value is defined within the route map, the firewall will use default metric values. This means that routes redistributed via BGP will retain the same metric value that they had on the originating device. For example, if an OSPFv3 route is configured with a metric value of 2 and then redistributed into BGP, the metric value will remain 2.Click OK.Create a BGP Filtering Profile.
Select Static to configure static route redistribution.Enable redistribution of IPv4 or IPv6 static routes (based on the AFI you selected).Configure the Metric to apply to the static routes being redistributed into BGP (range is 1 to 65,535).Select a Route-Map to specify the match criteria that determine which static routes to redistribute. Default is None. If the route map Set configuration includes a Metric Action along with a specified Metric Value, that value will be applied to the redistributed route. If no Metric Value is defined within the route map, the firewall will use default metric values. This means that routes redistributed via BGP will retain the same metric value that they had on the originating device. For example, if a static route is configured with a metric value of 10 and then redistributed into BGP, the metric value will remain 10.Select Connected to configure connected route redistribution.Enable redistribution of locally connected IPv4 or IPv6 routes (based on the AFI you selected).Configure the Metric to apply to the connected routes being redistributed into BGP (range is 1 to 65,535).Select a Route Map to specify the match criteria that determine which connected routes to redistribute. Default is None. If the route map Set configuration includes a Metric Action along with a specified Metric Value, that value will be applied to the redistributed route. If no Metric Value is defined within the route map, the firewall will use default metric values. This means that routes redistributed via BGP will retain the same metric value that they had on the originating device.(IPv4 AFI only) Select OSPFv2 to configure OSPFv2 route redistribution.Enable redistribution of OSPFv2 routes.Configure the Metric to apply to the OSPF routes being redistributed into BGP (range is 1 to 65,535).Select a Route-Map to specify the match criteria that determine which OSPF routes to redistribute. Default is None. If the route map Set configuration includes a Metric Action along with a specified Metric Value, that value will be applied to the redistributed route. If no Metric Value is defined within the route map, the firewall will use default metric values. This means that routes redistributed via BGP will retain the same metric value that they had on the originating device. For example, if an OSPF route is configured with a metric value of 2 and then redistributed into BGP, the metric value will remain 2.(IPv4 AFI only) Select RIPv2 to configure RIPv2 route redistribution.Enable redistribution of RIPv2 routes.Configure the Metric to apply to the RIP routes being redistributed into BGP (range is 1 to 65,535).Select a Route-Map to specify the match criteria that determine which RIP routes to redistribute. Default is None. If the route map Set configuration includes a Metric Action along with a specified Metric Value, that value will be applied to the redistributed route. If no Metric Value is defined within the route map, the firewall will use default metric values. This means that routes redistributed via BGP will retain the same metric value that they had on the originating device. For example, if a RIPv2 route is configured with a metric value of 10 and then redistributed into BGP, the metric value will remain 10.(IPv6 AFI only) Select OSPFv3 to configure OSPFv3 route redistribution.Enable redistribution of OSPFv3 routes.Configure the Metric to apply to the OSPFv3 routes being redistributed into BGP (range is 1 to 65,535).Select a Route-Map to specify the match criteria that determine which OSPFv3 routes to redistribute. Default is None. If the route map Set configuration includes a Metric Action along with a specified Metric Value, that value will be applied to the redistributed route. If no Metric Value is defined within the route map, the firewall will use default metric values. This means that routes redistributed via BGP will retain the same metric value that they had on the originating device. For example, if an OSPFv3 route is configured with a metric value of 2 and then redistributed into BGP, the metric value will remain 2.Click OK.Create a BGP Filtering Profile.- Select NetworkRoutingRouting ProfilesBGP.Add a BGP Filtering Profile by Name (a maximum of 63 characters). The name must start with an alphanumeric character, underscore (_), hyphen (-), or dot (.) and can contain alphanumeric characters, underscores, hyphens and dots. A space is not allowed.Enter a helpful Description.Select IPv4 or IPv6 Address Family Identifier (AFI) to indicate the type of route to filter.
![]() Select Unicast or Multicast Subsequent Address Family Identifier (SAFI).For Unicast, Inbound Filter List —Select an AS Path access list or create a new AS Path access list to specify that, when receiving routes from peers, only routes with the same AS Path are imported from the peer group or peer, meaning added to the local BGP RIB.In the Network Filter area, Inbound—Distribute List—Use an access list (Source Address only; not Destination Address) to filter BGP routing information that BGP receives. Mutually exclusive with Inbound Prefix List in a single Filtering Profile.Prefix List—Use a prefix list to filter BGP routing information that BGP receives, based on a network prefix. Mutually exclusive with Inbound Distribute List in a single Filtering Profile.Inbound Route Map—Use a route map to have even more control over which routes are allowed into the local BGP RIB (Match criteria) and to set attributes for the routes (Set options). For example, you can control route preference by prepending an AS to the AS Path of a route.If an Inbound Route Map is configured with an Inbound Distribute List or Prefix List, the conditions of both the route map and list must be met (logical AND).Outbound Filter List—Select an AS Path access list or create a new AS Path access list to specify that only routes with the same AS Path are advertised to a peer router (peer group or peer where this filter is applied).Outbound—Distribute List—Use an access list to filter BGP routing information that BGP advertises, based on the IP address of the destination. Mutually exclusive with Outbound Prefix List in a single Filtering Profile.Prefix List—Use a prefix list to filter BGP routing information that BGP advertises, based on a network prefix. Mutually exclusive with Outbound Distribute List in a single Filtering Profile.Outbound Route Map—Use a route map to have even more control over which routes BGP advertises (Match criteria) and to set attributes for advertised routes.If an Outbound Route Map is configured with an Outbound Distribute List or Prefix List, the conditions of both the route map and list must be met (logical AND).Configure conditional advertisements, which allow you to control what route to advertise in the event that a different route exists or does not exist in the local BGP RIB. A route not existing in the local BGP RIB can indicate a peering or reachability failure. Conditional advertisements are useful in cases where you want to try to force routes to one AS over another, such as when you have links to the internet through multiple ISPs and you want traffic to be routed to one provider instead of another, except when there is a loss of connectivity to the preferred provider. In the Conditional Advertisement Exist area:
Select Unicast or Multicast Subsequent Address Family Identifier (SAFI).For Unicast, Inbound Filter List —Select an AS Path access list or create a new AS Path access list to specify that, when receiving routes from peers, only routes with the same AS Path are imported from the peer group or peer, meaning added to the local BGP RIB.In the Network Filter area, Inbound—Distribute List—Use an access list (Source Address only; not Destination Address) to filter BGP routing information that BGP receives. Mutually exclusive with Inbound Prefix List in a single Filtering Profile.Prefix List—Use a prefix list to filter BGP routing information that BGP receives, based on a network prefix. Mutually exclusive with Inbound Distribute List in a single Filtering Profile.Inbound Route Map—Use a route map to have even more control over which routes are allowed into the local BGP RIB (Match criteria) and to set attributes for the routes (Set options). For example, you can control route preference by prepending an AS to the AS Path of a route.If an Inbound Route Map is configured with an Inbound Distribute List or Prefix List, the conditions of both the route map and list must be met (logical AND).Outbound Filter List—Select an AS Path access list or create a new AS Path access list to specify that only routes with the same AS Path are advertised to a peer router (peer group or peer where this filter is applied).Outbound—Distribute List—Use an access list to filter BGP routing information that BGP advertises, based on the IP address of the destination. Mutually exclusive with Outbound Prefix List in a single Filtering Profile.Prefix List—Use a prefix list to filter BGP routing information that BGP advertises, based on a network prefix. Mutually exclusive with Outbound Distribute List in a single Filtering Profile.Outbound Route Map—Use a route map to have even more control over which routes BGP advertises (Match criteria) and to set attributes for advertised routes.If an Outbound Route Map is configured with an Outbound Distribute List or Prefix List, the conditions of both the route map and list must be met (logical AND).Configure conditional advertisements, which allow you to control what route to advertise in the event that a different route exists or does not exist in the local BGP RIB. A route not existing in the local BGP RIB can indicate a peering or reachability failure. Conditional advertisements are useful in cases where you want to try to force routes to one AS over another, such as when you have links to the internet through multiple ISPs and you want traffic to be routed to one provider instead of another, except when there is a loss of connectivity to the preferred provider. In the Conditional Advertisement Exist area:- Select or create a route map in the Exist Map field to specify the match criteria for the conditional advertisement. Only the Match portion of the route map in this field is considered; the Set portion is ignored.
- Advertise Map—Select or create a route map to specify the routes to advertise in the event that the condition is met (routes from the Exist Map exist in the local BGP RIB). Only the Match portion of the route map in this field is considered; the Set portion is ignored.
In the Conditional Advertisement Non-Exist area:- Select or create a route map in the Non-Exist Map field to specify the match criteria for which routes do not exist in the local BGP RIB in order to conditionally advertise. Only the Match portion of the route map in this field is considered; the Set portion is ignored.
- Advertise Map—Select or create a route map to specify routes to advertise when the routes in the Non-Exist Map are not in the local BGP RIB. Only the Match portion of the route map in this field is considered; the Set portion is ignored.
Unsuppress Map—Select or create a route map of routes that you want to unsuppress, perhaps because they were summarized and therefore suppressed, or they were suppressed because they met dampening criteria, but you want specific routes to be advertised (unsuppressed).(IPv4 AFI only) Select Multicast to filter MP-BGP Multicast routes. Select Inherit from Unicast if you want all filtering from the Unicast SAFI to also apply to the Multicast SAFI. Otherwise, continue to configure the following filtering fields.For Multicast, Inbound Filter List —Specify an AS Path access list or create a new AS Path access list to specify that, when receiving routes from peers, only routes with the same AS Path are imported from the peer group or peer, meaning added to the local BGP RIB.In the Network Filter area, Inbound—Distribute List—Use an access list (Source Address only; not Destination Address) to filter BGP routing information that BGP receives. Mutually exclusive with Inbound Prefix List in a single Filtering Profile.Prefix List—Use a prefix list to filter BGP routing information that BGP receives, based on a network prefix. Mutually exclusive with Inbound Distribute List in a single Filtering Profile.Inbound Route Map—Use a route map to have even more control over which routes are allowed into the local BGP RIB (Match criteria) and to set attributes for the routes (Set options). For example, you can control route preference by prepending an AS to the AS Path of a route.If an Inbound Route Map is configured with an Inbound Distribute List or Prefix List, the conditions of both the route map and list must be met (logical AND).Outbound Filter List—Select an AS Path access list or create a new AS Path access list to specify that only routes with the same AS Path are advertised to a peer router (peer group or peer where this filter is applied).Outbound—Distribute List—Use an access list to filter BGP routing information that BGP advertises, based on the IP address of the destination. Mutually exclusive with Outbound Prefix List in a single Filtering Profile.Prefix List—Use a prefix list to filter BGP routing information that BGP advertises, based on a network prefix. Mutually exclusive with Outbound Distribute List in a single Filtering Profile.Outbound Route Map—Use a route map to have even more control over which routes BGP advertises (Match criteria) and to set attributes for advertised routes.If an Outbound Route Map is configured with an Outbound Distribute List or Prefix List, the conditions of both the route map and list must be met (logical AND).Configure conditional advertisements, which allow you to control what route to advertise in the event that a different route exists or does not exist in the local BGP RIB. A route not existing in the local BGP RIB can indicate a peering or reachability failure. Conditional advertisements are useful in cases where you want to try to force routes to one AS over another, such as when you have links to the internet through multiple ISPs and you want traffic to be routed to one provider instead of another, except when there is a loss of connectivity to the preferred provider. In the Conditional Advertisement Exist area:- Select or create a route map in the Exist Map field to specify the match criteria for the conditional advertisement. Only the Match portion of the route map in this field is considered; the Set portion is ignored.
- Advertise Map—Select or create a route map to specify the routes to advertise in the event that the condition is met (routes from the Exist Map exist in the local BGP RIB). Only the Match portion of the route map in this field is considered; the Set portion is ignored.
In the Conditional Advertisement Non-Exist area:- Select or create a route map in the Non-Exist Map field to specify the match criteria for which routes do not exist in the local BGP RIB in order to conditionally advertise. Only the Match portion of the route map in this field is considered; the Set portion is ignored.
- Advertise Map—Select or create a route map to specify routes to advertise when the routes in the Non-Exist Map are not in the local BGP RIB. Only the Match portion of the route map in this field is considered; the Set portion is ignored.
Unsuppress Map—Select or create a route map of routes that you want to unsuppress, perhaps because they were summarized and therefore suppressed, or they were suppressed because they met dampening criteria, but you want specific routes to be advertised (unsuppressed).Click OK.Create BGP Routing Profiles (SCM)
Learn about how to configure BGP routing profiles in Strata Cloud Manager.- Log in to Strata Cloud Manager.Select ManageConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessDevice SettingsRoutingProfilesBGPConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessDevice SettingsRoutingProfilesBGP and select the Configuration Scope where you want to configure a profile for a BGP configuration.You can select a folder or firewall from your Folders or select Snippets to configure a profile for a BGP configuration in a snippet.For Address Family Profiles, Add Profile.
- Enter a Name for the profile.The name must start with an alphanumeric character, underscore (_), or hyphen (-), and can contain a combination of alphanumeric characters, underscore, or hyphen. No dot (.) or space is supported.Select Unicast or Multicast and Enable.Both Unicast and Multicast can be enabled.Enable Soft reconfiguration of peer stored with routes to cause the firewall to perform a soft reset after the settings of any of its BGP peers are updated.This setting is enabled by default.Enable Advertise all paths to peer to have BGP advertise all known paths to its neighbor in order to preserve multipath capabilities inside a network.Enable Advertise the best path per each neighboring AS to have BGP advertise the best known paths to neighbors in order to preserve multipath capabilities inside a network.Disable this if you want to advertise the same path to all autonomous systems.Enable Override ASNs in outbound updates if AS-Path equals Remote-AS.This setting is helpful if you have multiple sites belonging to the same AS number (AS 64512, for example) and there’s another AS between them. A router between the two sites receives an Update advertising a route that can access AS 64512. To avoid the second site dropping the Update because it’s also in AS 64512, the intermediate router replaces AS 64512 with its own AS number (ASN), AS 64522, for example.Enable Route Reflector Client to make the BGP peer a route reflector in an iBGP network.Select the Default Originate Route Map used in the default originate configuration.Allow AS In:
- Origin—Accept routes even if the firewall’s own AS is present in the AS_PATH.
- Occurrence—Number of times the firewall’s own AS can be in the AS_PATH.
- None (default)—No action taken.
Enter the maximum Number Prefix to accept (learn) from the peer.Range is 1-4,294,9677,295. Default is 1,000.Enter the Threshold (percentage) of the maximum number of prefixes added to the BGP local RIB.If the peer advertises more than the threshold, the firewall takes the specified