Service Provider Interconnects
Table of Contents
Expand all | Collapse all
- Strata Multitenant Cloud Manager
- First Time Setup
-
- Monitoring Summary Across All Tenants
- SASE Summary Dashboard
- Prisma Access Summary Dashboard
- Prisma Browser Summary Dashboard
- Prisma SD-WAN Summary Dashboard
- Monitor Tenant Applications
- Monitor Tenant Branches
- Monitor Tenant Devices
- Monitor Tenant Licenses
- Monitor Tenant Upgrades
- Monitor Using Prisma Access Insights
- Switch Tenants
-
- Monitor Status of Services through the ASC Support View
- Monitor Performance of Tunnel Status through the ASC Support View
- Monitor Performance of Auto Scaling through the ASC Support View
- Monitor Performance of Throughput through the ASC Support View
- Monitor Performance of the System through the ASC Support View
- View Licenses through the ASC Partner Portal
- View Status of Upgrades through the ASC Support View
- Manage Multitenant Reports
Service Provider Interconnects
Overview about what are interconnects and types of interconnects
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
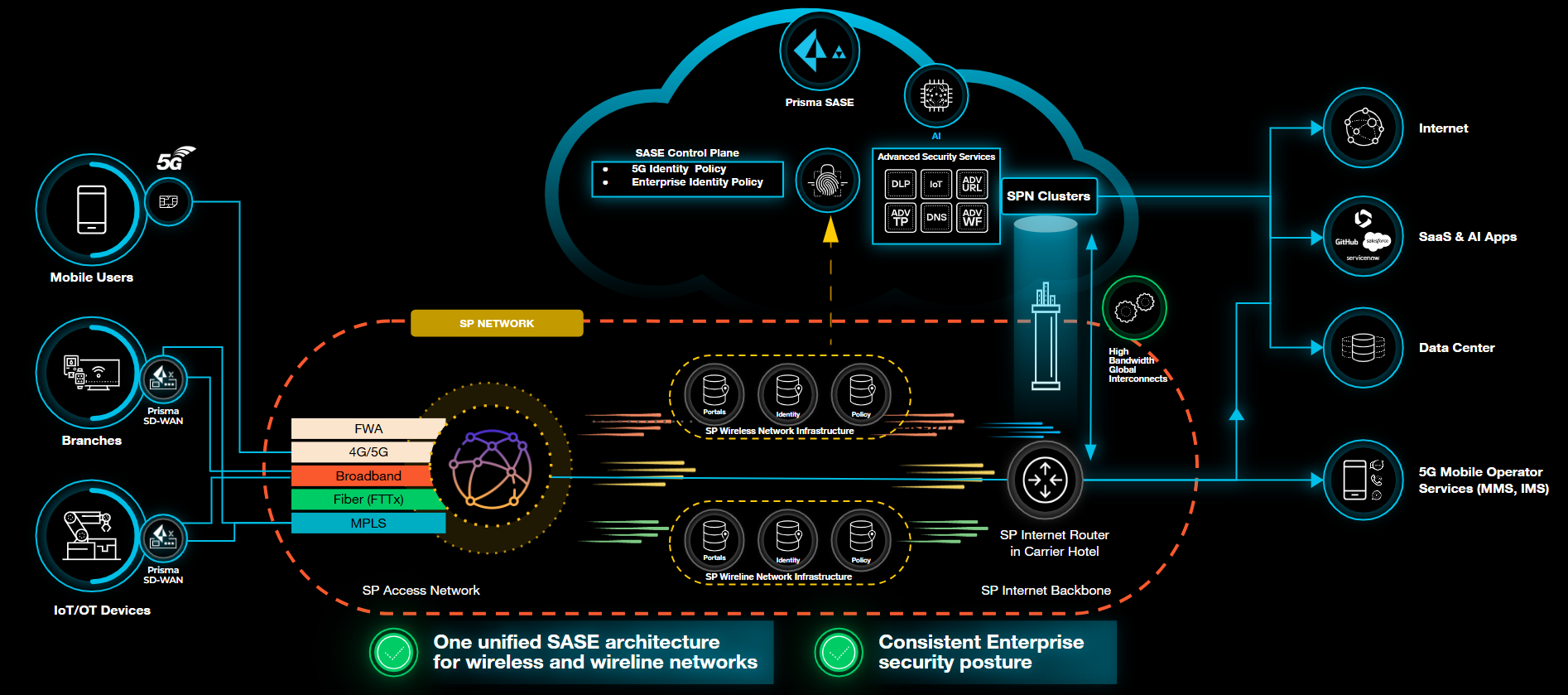
Service Provider Interconnects (SPI) describe how Service Providers (SPs)
connect their customer or tenant networks to Prisma Access™. Prisma Access offers two
interconnect models that define how data moves securely between customer environments
and the Prisma Access infrastructure:
Both models enable secure, non-IPsec connectivity between SP and Prisma Access, with
different design approaches for traffic handling and egress management.
Service Provider Interconnect with Non-IPsec
Understand what is Service Provider Interconnect, how does it work and how to
configure
Service Provider Interconnect offers a non-IPsec on-ramp (Native IP ingress) that enables
Service Providers (SPs) to deliver enterprise customer traffic directly to Prisma
Access™ without relying on IPsec tunnels.By utilizing native IP forwarding, SPI
minimizes tunnel overhead, enables high-bandwidth connectivity, and maintains end-to-end
control on the SP backbone. The design ensures zero operational touchpoints on SP or
branch networks, simplifying integration while preserving network SLAs. Traffic is
routed through SP networks and Partner Interconnects with cloud providers such as GCP
and AWS into the Prisma Access compute environment, enabling unified security and
optimized performance.
SPI supports multi-tenant isolation, granular policy control, and full integration with
Prisma Access services. You can configure SPI with either Service Provider Egress or
Prisma Access Egress, depending on how you want to route outbound traffic.
SPI with Service Provider Egress
In this configuration, customer traffic enters Prisma Access through the SPI,
security controls are applied, and then sent back to the Service Provider’s network
for egress. This deployment gives the SP control over routing and policy
enforcement, allowing them to apply their own compliance and logging mechanisms
before internet breakout.
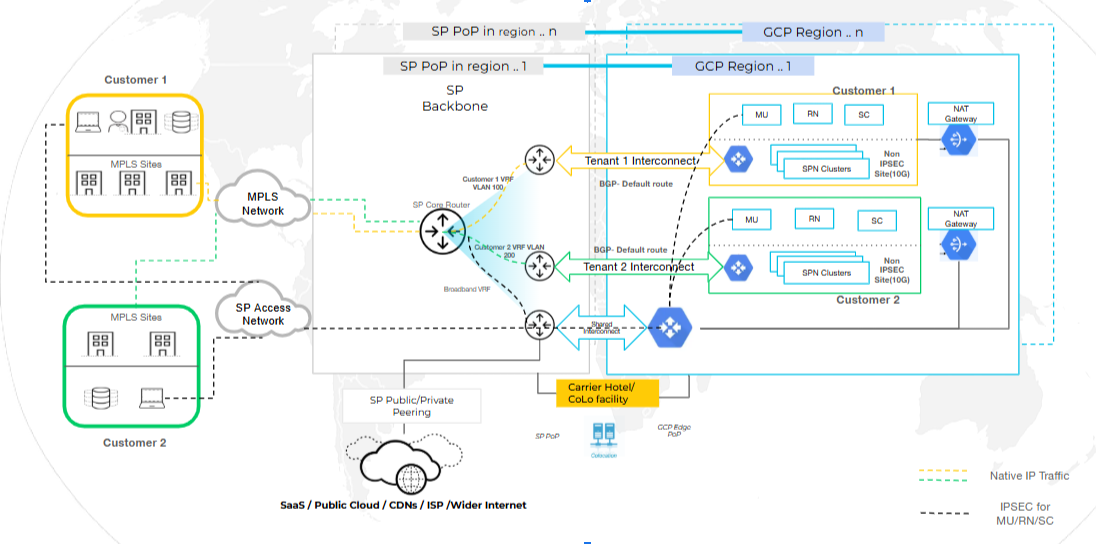
Suitable for Service Providers that want to maintain centralized control of egress
routing and security policies.
To configure SPI with Service Provider Egress, perform the following:
- Select the Egress path as Egress back to the service provider network.
- Set up Shared Interconnect on the root tenant. This interconnect will be used to egress the traffic back to the Service Provider.
- Set up Per-tenant Interconnect for each child tenant. This is used to ingress traffic from the Service provider.
- (optional) Set up VLAN Attachments for HA and redundancy.
- (optional) Set up IP Pools if not configured during shared interconnect setup.
- Copy the VLAN attachment pairing key and use it when configuring the interconnect in colocation providers such as Equinix.
- Onboard Remote Network and select PA Connect as the traffic type and select the required region.
- Continue with Prisma Access feature configurations.
SPI with Prisma Access Egress
In this configuration, customer traffic enters Prisma Access via SPI and exits
through Prisma Access-managed egress points. This setup simplifies operations and
leverages Prisma Access capabilities for advanced security, threat prevention, and
data protection.
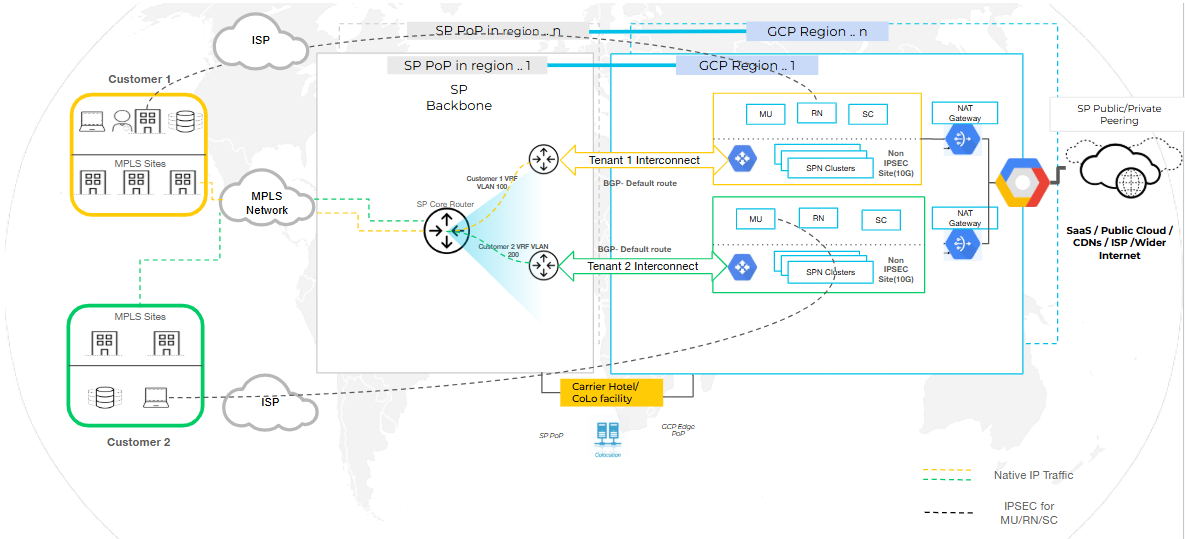
Suitable for Service Providers or customers who prefer a fully cloud-delivered model
without managing egress routing.
To configure SPI with Prisma Access Egress, perform the following:
- Select the Egress path as Egress back to the service provider network.
- Set up Per-tenant Interconnect for each tenant. This is used to ingress traffic from the Service provider.
- Set up VLAN Attachments for HA and redundancy.
- Copy the VLAN attachment pairing key and use it when configuring the interconnect in colocation providers such as Equinix.
- Onboard Remote Network and select PA Connect as the traffic type and select the required region.
- Continue with Prisma Access feature configurations.
Service Provider Interconnect with IPsec
Understand what is Service Provider Interconnect with IPsec, how does it work and how
to configure
The Service Provider Interconnect with IPsec (Cleanpipe) feature enables
Service Providers (SPs) to securely deliver enterprise traffic to Prisma Access™ using
IPsec tunnels. It leverages VLAN-based forwarding per tenant to provide simple,
scalable, and secure connectivity for internet-bound traffic.
In this configuration, customer traffic enters Prisma Access via Cleanpipe and
exits through the Service Provider’s egress network. This setup allows SPs to manage
egress routing, traffic policies, and compliance while delivering secure connectivity to
tenants.
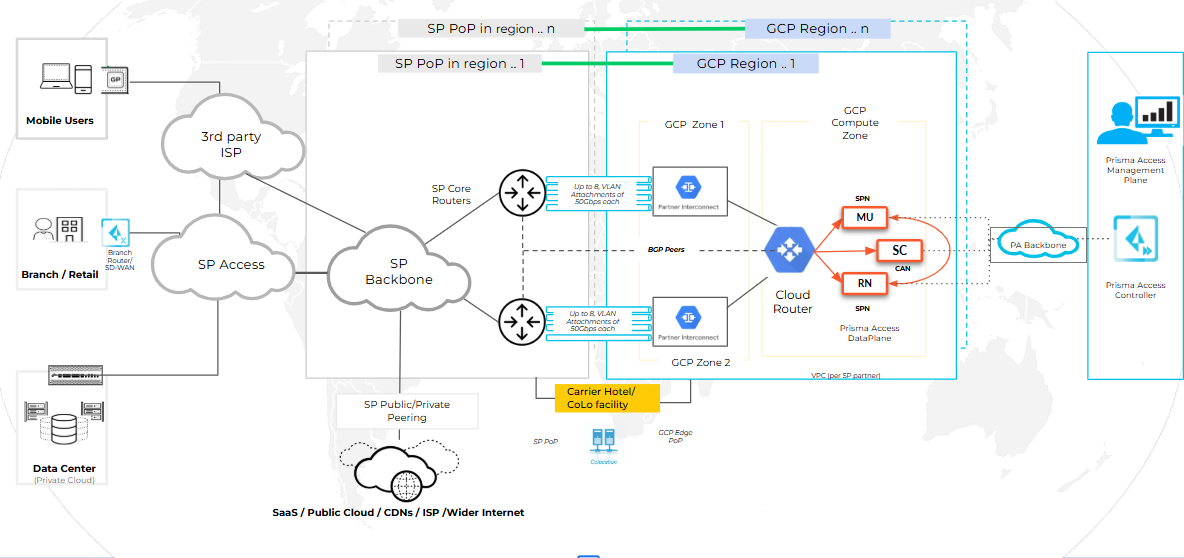
To configure SPI with Service Provider Egress, perform the following:
- Select the Egress path as Egress back to the service provider network.
- Set up Shared Interconnect which will be used for both the egress and ingress traffic.
- Copy the VLAN attachment pairing key and use it when configuring the interconnect in colocation providers such as Equinix.
- Continue with Prisma Access feature configurations.
- Onboard Remote Network and select PA Connect as the traffic type and select the required region.
Use Case: High Bandwidth Native IP Branch Site Configuration
In this use case, we are going to configure non-IPsec (native IP) Remote Networks to
onboard large campuses and branch sites with high bandwidth up to 20 Gbps per region per
customer. The traffic must be routed back to the Service Provider for security policy
enforcement. The deployment supports IPv4 with overlapping IPs across child tenants. The
customer wants to have hybrid deployments with both IPsec and non-IPsec RNs across
regions.
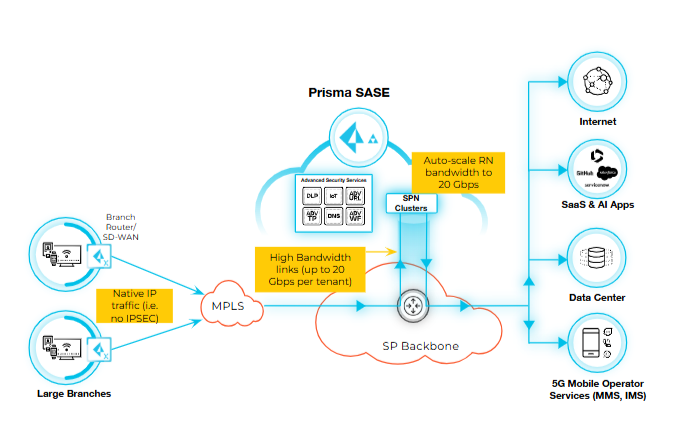
- Configure the Egress path as Egress back to the service provider network.
- Create a shared interconnect on the SP host project for traffic egress.
- Configure SP IP Pool using Bring Your Own IP configuration.
- Configure additional VLAN Attachments for each region and also for HA.
- Create per-tenant interconnect for all the child customer projects for traffic ingress.
- Onboard Remote Network and select PA Connect as the traffic type and select the required region.
