Prisma SD-WAN
Add and Configure Port Channel Interface
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma SD-WAN Docs
-
-
- Prisma SD-WAN Controller
-
- CloudBlade Integrations
- CloudBlades Integration with Prisma Access
-
-
-
-
- 6.5
- 6.4
- 6.3
- 6.1
- 5.6
- Prisma SD-WAN Controller
- Prisma SD-WAN On-Premises Controller
- Prisma SD-WAN CloudBlades
- Prisma Access CloudBlade Cloud Managed
- Prisma Access CloudBlade Panorama Managed
Add and Configure Port Channel Interface
Prisma SD-WAN now supports the Link Aggregation Group (LAG) and Link Aggregation
Control Protocol (LACP), commonly called port-channel.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
The LAG (Link Aggregation Group) and LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol),
commonly called port-channel, on Layer 3 ports on the LAN side. LAG and LACP support
enhances your network infrastructure by allowing you to combine multiple physical
interfaces into a single logical interface.
This feature provides increased bandwidth, improved reliability, and enhanced
load-balancing capabilities for your Prisma SD-WAN deployment. Implementing LAG and
LACP can effectively aggregate multiple links between your ION devices and upstream
switches or routers, resulting in a more robust and efficient network architecture.
LAG and LACP support aligns with industry standards, allowing seamless integration
with your existing network equipment.
By leveraging this capability, you can enhance your network performance, simplify
management, and improve overall user experience across your distributed enterprise
environments.
Device Compatibility: The LAG and LACP functionalities are supported on the
following devices:
- ION 3200 (Layer 3 mode only)
- ION 5200
- ION 9200
LAG/LACP is now supported on WAN. This enables you to configure port channels for
Internet and Private WAN circuits to facilitate automated Fabric Overlays
(VPNs).
Configure port channel on Layer 3 ports to combine physical interfaces into a single
logical interface.
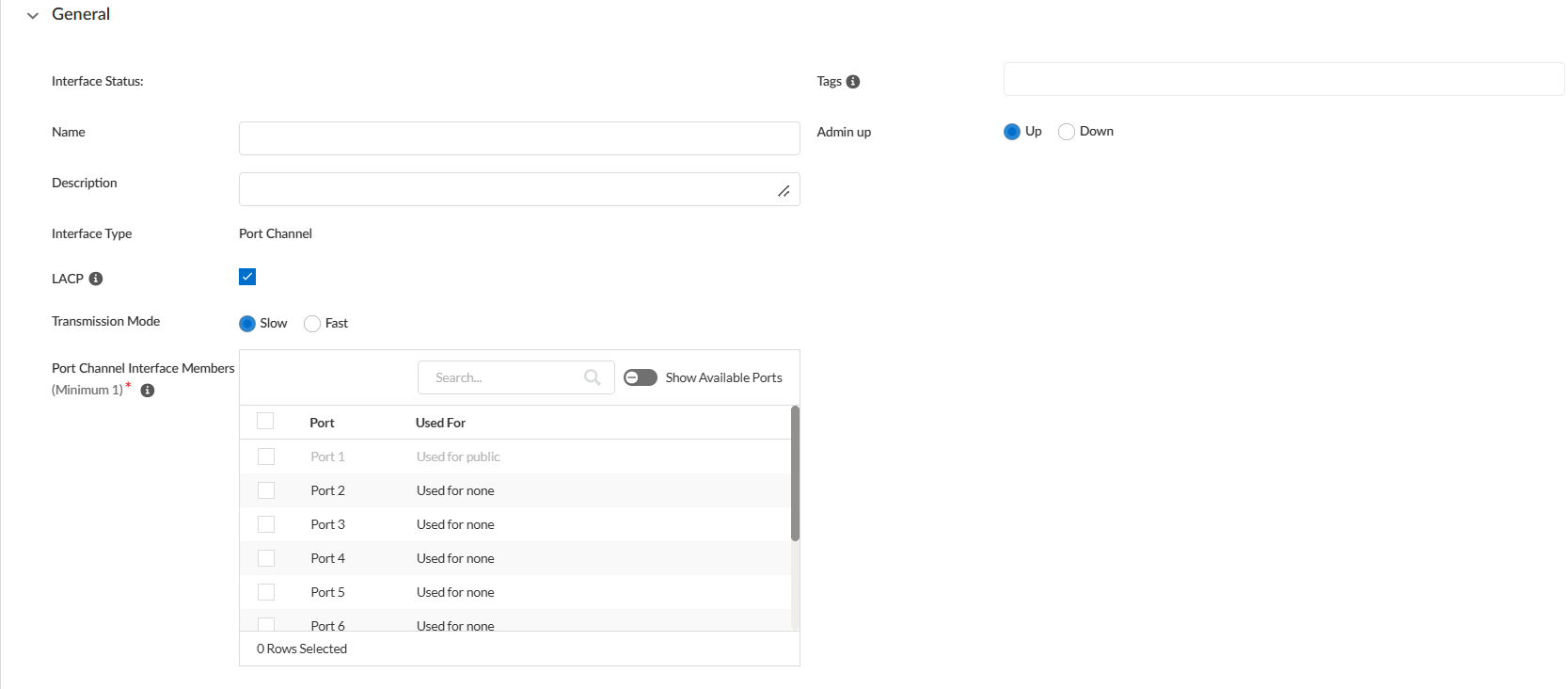
- Select ConfigurationPrisma SD-WANION DevicesClaimed, select the device you want to configure.On the device's interface configuration page, select the Interfaces+ Add Interface to add a port channel interface.In the General section,
- Enter a Name and (Optional) Description, and add Tags for the port channel interface.For Admin Up, select Up.Enable LACP on the Main Configurations tab. When the LACP option is enabled, the LACP protocol is set between the two devices running port channels. When the LACP option is disabled, the interface will be set to static Port-Channel mode.For Transmission Mode, select Slow or Fast. Set the Transmission Mode for LACP query and response exchanges to Slow (every 30 seconds—the default) or Fast (every second). Base your selection on how much LACP processing your network supports and how quickly LACP peers must detect and resolve interface failures. By default, Slow is selected.You can select the port-channel interface members from the Port Channel Interface Members list or search for the Ports.Ensure that the ports selected as Port Channel interface members are not members or parents of another interface or link (Sub-interface, PPPoE, Standard VPN, Virtual Interface). Also, ensure that no other feature, such as SNMP Trap, Syslog Server, AAA, or DNS Service, uses the selected ports.Toggle to Show Available Ports Only to see all the available ports.You can toggle the admin state of port channel and individual member ports as well.
![]() Click Save to complete the configuration.The MAC address of the port channel is assigned based on the lowest interface number of its members, providing a flexible approach. For example, if port-channel members are interface 2,4,7, the port-channel's mac address will be the MAC address of interface 2. If you remove interface 2 from the port channel, then the MAC address of the port channel changes to the MAC address of interface 4. If you add interface 1 to the port channel, the MAC address changes to the MAC address of interface 1. This flexibility ensures that the MAC address can adapt to your network's changing needs.In the Network Setting section,
Click Save to complete the configuration.The MAC address of the port channel is assigned based on the lowest interface number of its members, providing a flexible approach. For example, if port-channel members are interface 2,4,7, the port-channel's mac address will be the MAC address of interface 2. If you remove interface 2 from the port channel, then the MAC address of the port channel changes to the MAC address of interface 4. If you add interface 1 to the port channel, the MAC address changes to the MAC address of interface 1. This flexibility ensures that the MAC address can adapt to your network's changing needs.In the Network Setting section,- Select Use this Port Channel Interface for Internet, Private WAN, LAN, HA, or None from the list. Select Peer with the Network or None for data center sites.Toggle Scope as Global or Local.For IPv4 Configuration, select None, DHCP, or Static.
- If the IP address dynamically assigned, select DHCP.
- If the IP address is fixed and specified manually, select Static. If you select Static, specify the IP Address/Mask, Default Gateway, and DNS server(s).
Select Enable IPv6 On This Interface to configure IPv6.Fabric Overlay (VPN) automation does not support IPv6. Use IPv4 to establish automated fabric links over a WAN Port Channel.For VRF, select Global or any other custom VRF that is available and associated with the VRF profile. VRF Global is enabled only when the associated device supports VRF.In the NAT Configuration section, configure the NAT Zone (Zones must be bound to interfaces for NAT to be effective) and NAT Pools (Pools can be attached or bound to individual interfaces at the device-level, which contains range of IP addresses with mandatory start and end addresses) from the available list. You may also click on the Add New to create a NAT Zone or Nat Pool on your own.In the Advanced Settings section, specify IoT SNMP Discovery Source Interface as Enable or Disable, IP MTU, and Physical from the available range.IP MTU value should be at least 1280 for IPv6. If it is less than 1280, IPv6 cannot be enabled.Click Save to complete the configuration.Related CLIs
- config interface
- ping
- ping6
- debug bounce interface
- debug bw test src interface
- ssh Interface
- tcp dump
- tcp ping
- trace route
- inspect interface stats
- inspect wan paths
- dump cgnx infra status
- dump cgnx infra status live
- dump cgnx infra status store
- dump interface config
- dump interface status
- dump interface status interface details
- dump interface status interface module
- dump wan interface config
- dump wan interface summary