Prisma SD-WAN
Secure Group Tags (SGT) Propagation
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma SD-WAN Docs
-
-
- Prisma SD-WAN Controller
-
- CloudBlade Integrations
- CloudBlades Integration with Prisma Access
-
-
-
-
- 6.5
- 6.4
- 6.3
- 6.1
- 5.6
- Prisma SD-WAN Controller
- Prisma SD-WAN On-Premises Controller
- Prisma SD-WAN CloudBlades
- Prisma Access CloudBlade Cloud Managed
- Prisma Access CloudBlade Panorama Managed
Secure Group Tags (SGT) Propagation
Secure Group Tags (SGTs) in Prisma SD-WAN which integrates with third-party
identity-based security systems to ensure tag-based policy rules across the Prisma SD-WAN
fabric.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
Secure Group Tags (SGTs) in Prisma SD-WAN integrate with third-party identity-based
security systems, such as Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE), to ensure tag-based
policy rules across the Prisma SD-WAN fabric. SGTs preserve information across the
Prisma SD-WAN fabric, enabling granular access control. SGT propagation works over
both public and private VPN overlays and supports various site types, including
Branch, Data Center (DC), and Branch Gateway configurations.
When enabled at the site level, SGT allows the ION device to parse Cisco
metadata headers, extract Security Group Information (SGI) values, and preserve them
across the Prisma SD-WAN fabric. This ensures consistent tagging throughout the
network, including LAN to LAN propagation on the same device. You can configure
static tag values for ION initiated traffic
such as NTP, DHCP, App Probes, and enable or disable SGT settings at the interface
level. Static SGT tagging ensures effective routing and consistent propagation
across the network, regardless of topology.
The diagram shows how SGTs move through network layers. It begins at the Cisco SGT
Router, where SGTs are added to packets, then it travels through the distribution
switch, firewall, and the ION device where SGT information is preserved across the
Prisma SD-WAN fabric as they travel. The goal is for the SGT to reach the data
center, enabling enforcement of security and networking policies based on these tags
across the network thus reserving SGT information from end to end in the network for
security policy enforcement.

Strata Cloud Manager supports multiple SGT propagation scenarios, including Branch to
Branch Gateway, Branch to Data Center, LAN to LAN, and both private and public
direct connections. SGT information can be accessed through the Flow Browser
and Device Toolkit commands, allowing for enhanced troubleshooting and
monitoring capabilities.
Cisco TrustSec uses tags, known
as Security Group Tags (SGTs), to represent logical group privileges
in access policies. Cisco switches, routers, and firewalls recognize and enforce
traffic based on these SGTs. Tagging ION initiated traffic with a static SGT
ensures effective routing and comprehensive SGT propagation across the network.
Prisma SD-WAN offers two levels for static tag configuration:
- Site-Level Static Tag ConfigurationAt the site level, the controller assigns a static tag and pushes this configuration to all devices associated with that site. Any packet originating from the ION device will include metadata headers generated from the static tag, ensuring each packet carries the designated tag.
- Port-Level Static Tag ConfigurationThis configuration provides control over tag usage on each individual port. You can enable or disable the static tag at the interface level. However, you can't override the static tag for specific device-generated traffic on particular ports. This allows static tags to be disabled when needed, enabling the traffic to be sent without additional metadata.
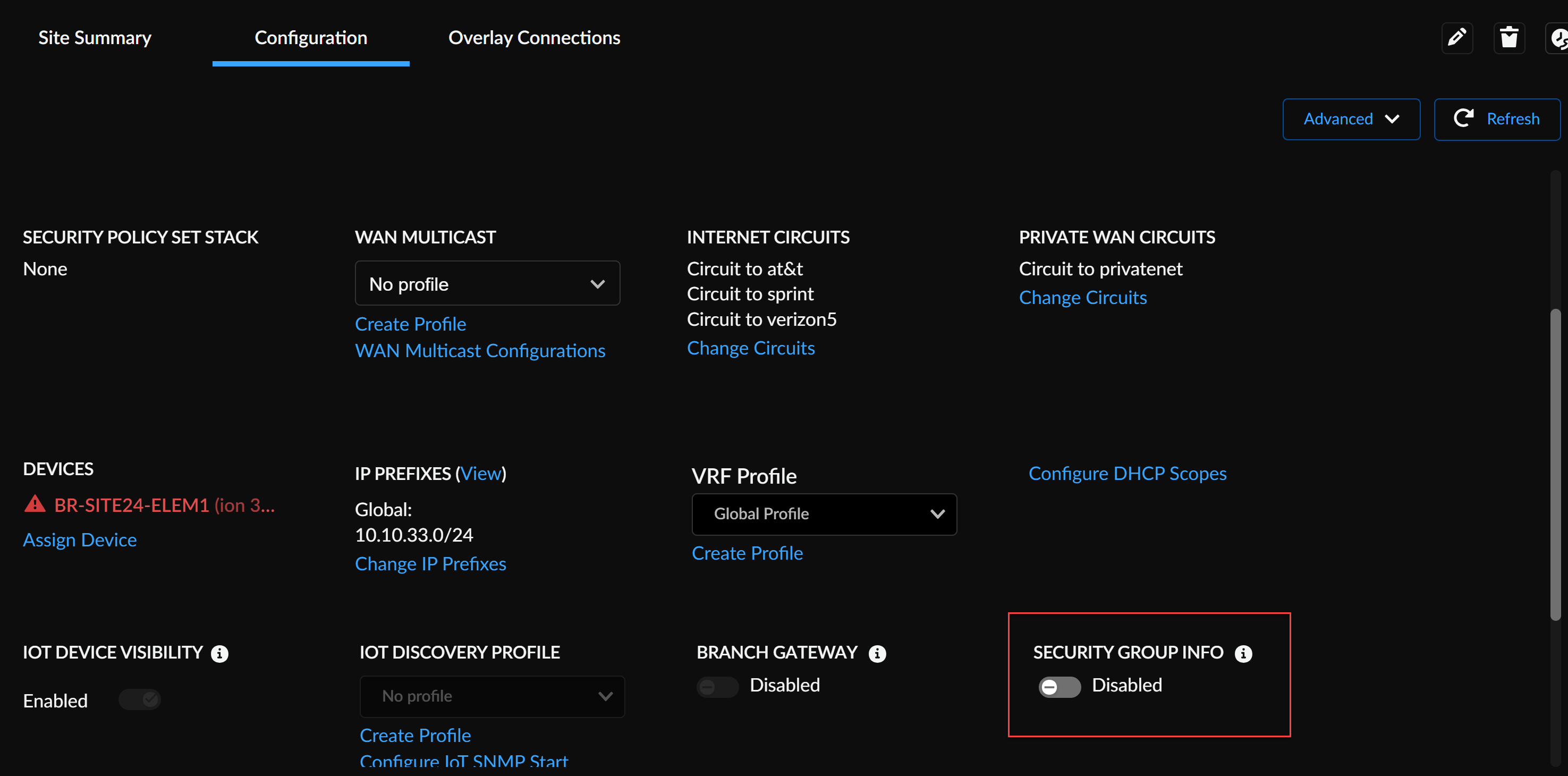
- In Strata Cloud Manager, go to ConfigurationPrisma SD-WAN Branch/Data CenterSites.Select the site name and go to the Configurationtab.Enable the Security Group Info (SGI) option.
![]() Specify a static SGI value between 1-65533 for ION-generated traffic and align it with Cisco ISE security policies. Prisma SD-WAN ION devices support values only within this range.
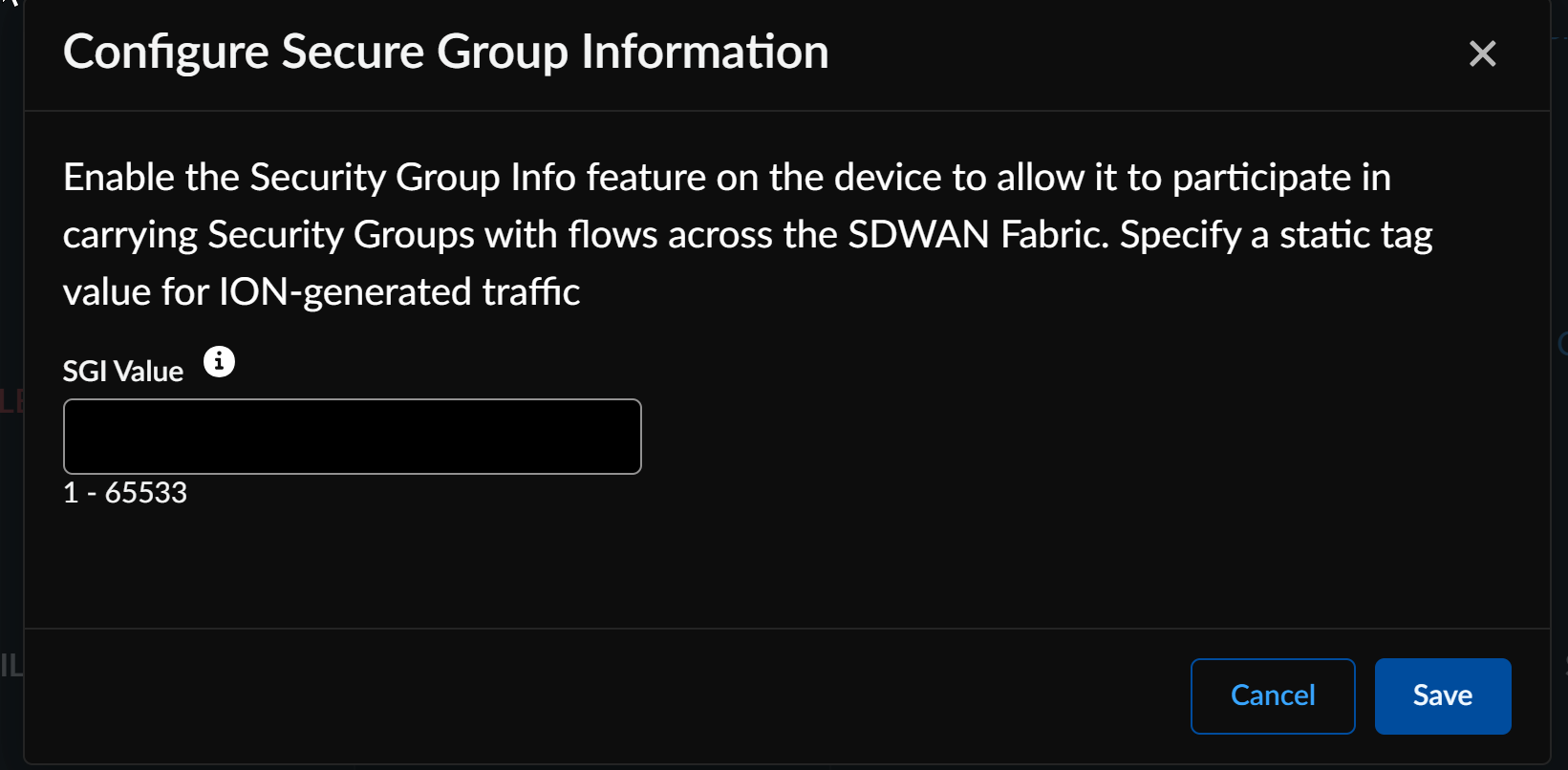
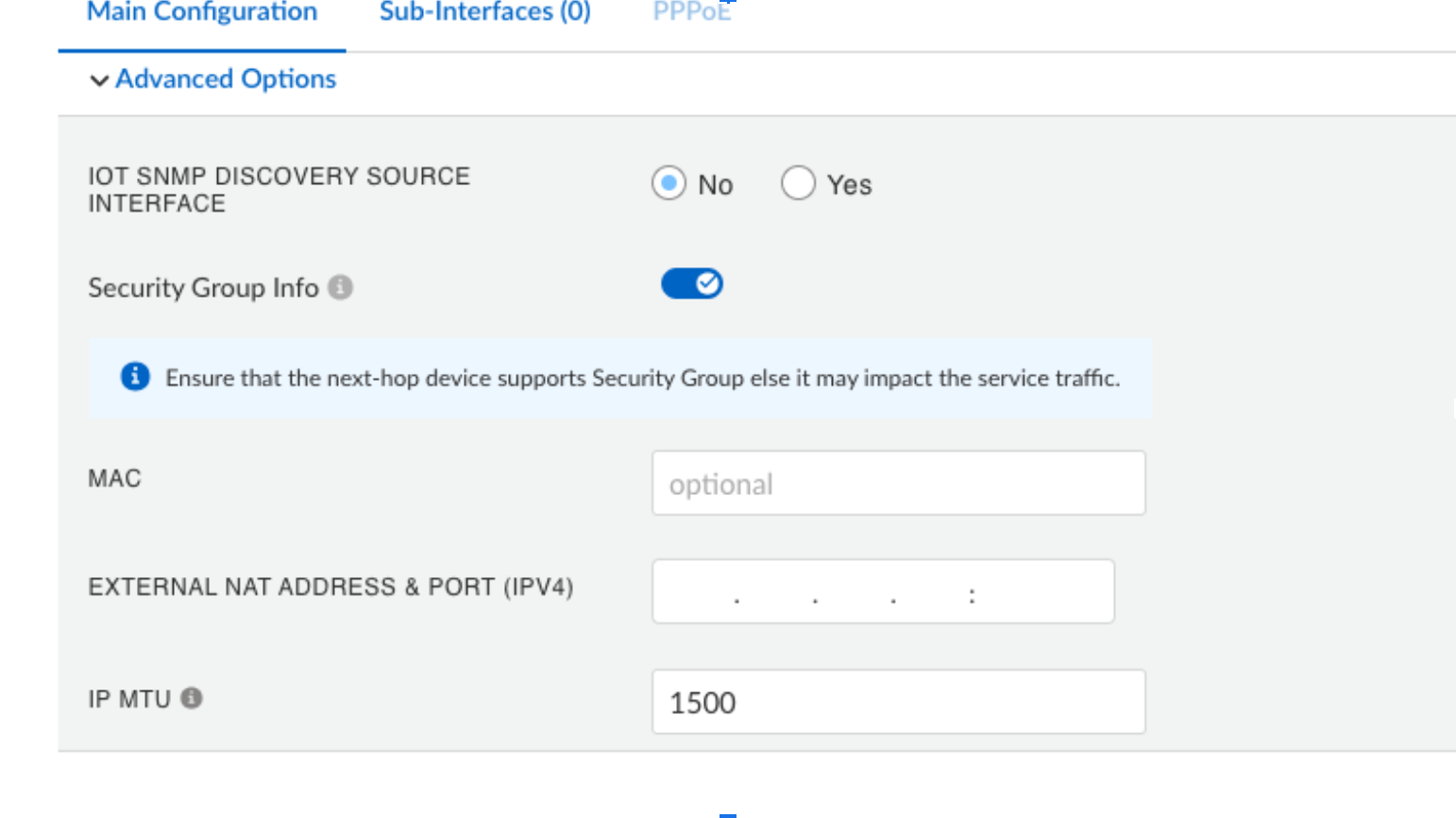
Specify a static SGI value between 1-65533 for ION-generated traffic and align it with Cisco ISE security policies. Prisma SD-WAN ION devices support values only within this range.![]() After enabling SGI at the site level, navigate to ConfigurationPrisma SD-WANION DevicesInterfacesAdvanced Options and enable Security Group Info.
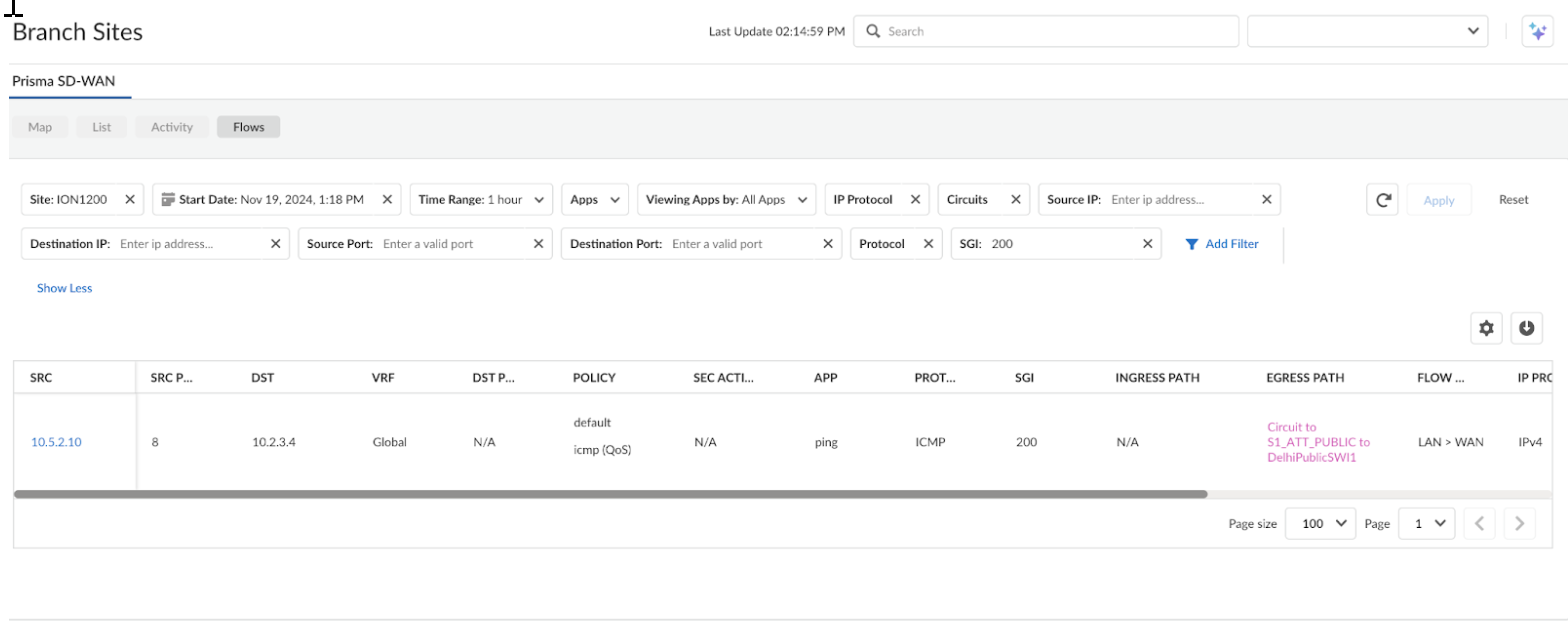
After enabling SGI at the site level, navigate to ConfigurationPrisma SD-WANION DevicesInterfacesAdvanced Options and enable Security Group Info.![]() This setting appears only when you enable SGI at the site level as it applies the site-level value directly to the device. This configuration supports static tagging for ION-generated traffic only.To view the SGI information for a flow, go to ConfigurationPrisma SD-WAN Branch SitesFlows.If SGI is enabled, the system includes the value in the flow attributes.
This setting appears only when you enable SGI at the site level as it applies the site-level value directly to the device. This configuration supports static tagging for ION-generated traffic only.To view the SGI information for a flow, go to ConfigurationPrisma SD-WAN Branch SitesFlows.If SGI is enabled, the system includes the value in the flow attributes.![]()
Use Case: Configure Static SGT for Site-Level Cisco Metadata Tagging
In a typical setup, a network administrator configures a static SGT value at the site level to tag ION-initiated traffic with Cisco metadata headers. This tagging mechanism is essential for enabling efficient policy enforcement and security classification across the network.This approach proves useful in scenarios where site-specific services like DHCP, syslog, or other management traffic must route through a Cisco router supporting the SGT tagging feature. By tagging this traffic with an SGT, the network enforces policy-based or role-based access control (PBAC or RBAC) at the edge or core level, ensuring that only authorized users or devices access sensitive resources.![]() In the example topology above, traffic originating from the ION toward the DHCP server carries the configured SGT value (100). The system forwards this tagged traffic to the downstream Cisco switch or router, which applies SGT based RBAC policies to ensure that only authorized users or devices access the resource.
In the example topology above, traffic originating from the ION toward the DHCP server carries the configured SGT value (100). The system forwards this tagged traffic to the downstream Cisco switch or router, which applies SGT based RBAC policies to ensure that only authorized users or devices access the resource.Related CLIs