SaaS Security
Assess Identity Security
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
SaaS Security Docs
Assess Identity Security
Use the Identity Security component of SaaS Security Posture Management to identify
misconfigurations in your identity posture.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
Or any of the following licenses that include the Data Security license:
|
SaaS Security Posture Management includes an
Identity component for identifying threats to your identity posture. You can
navigate to the Identity page in SSPM to examine these threats. The Identity page
provides an overview of identity-related threats across SaaS apps used in your
organization. From here, you have a unified view of human and non-human identities
in your organization and the threats related to those identities. By giving you
visibility into these threats, the Identity page enables to you to address areas of
concern and close security gaps.
To display information on the Identity page, SSPM
first runs identity scans of the SaaS apps. SSPM supports identity scans only for
certain SaaS apps. You can identify the supported SaaS apps from the Add Application
page (Posture SecurityApplicationsAdd Application). On the Add Application page, the onboarding tiles for the supported
SaaS apps have an Identity label.
From the information that SSPM collects from the
identity scan, SSPM then applies a series of detectors to identify common identity
threats such as overpriviledged accounts, dormant accounts, and accounts with
unrotated credentials.
Additional detectors are available if you integrate
your identity provider with the Identity component. You can integrate either the
Okta or Microsoft Azure identity provider with the Identity component. To integrate
the Okta identity provider, complete the onboarding instructions for Okta. To integrate the Microsoft Azure identity provider, complete the
onboarding instructions for Microsoft 365. With access to
your identity provider, SSPM can apply a detector for multi-factor authentication
(MFA) threats to identify users with no MFA or weak MFA. By comparing account
information from the SaaS app instance with information from the identity provider,
SSPM can also apply a detector for identifying local accounts, which are accounts
that weren’t created through your identity provider.
To navigate to the Identity page, select ConfigurationSaaS SecurityPosture SecurityIdentity.
View Identity Threats for SaaS Apps
Navigate to the Identity page in SSPM to view threats by individual SaaS app
accounts.
The Identity page provides an overview of identity-related threats across SaaS apps
used in your organization. Details about the threats are listed in tables on the
following tabs:
- The Identity Threats tab, which provides details for each individual threat that SSPM detected. Each entry in this tab's table is a separate threat detected for a single SaaS application account.
- The Unique Identities tab. On this tab, SSPM attempts to resolve a user's various identities across SaaS apps into a single unified identity. The best results are realized if you have onboarded an instance of either the Microsoft Azure or the Okta identity provider. In this case, SSPM can determine the various SaaS apps that you're accessing through single sign-on (SSO). If you have not onboarded an identity provider, then SSPM uses email login addresses to determine unique identities across SaaS apps. If multiple SaaS app accounts are using the same email address for login, SSPM consolidates those accounts into a unique identity.
- To navigate to the Identity page, select ConfigurationSaaS SecurityPosture SecurityIdentity.
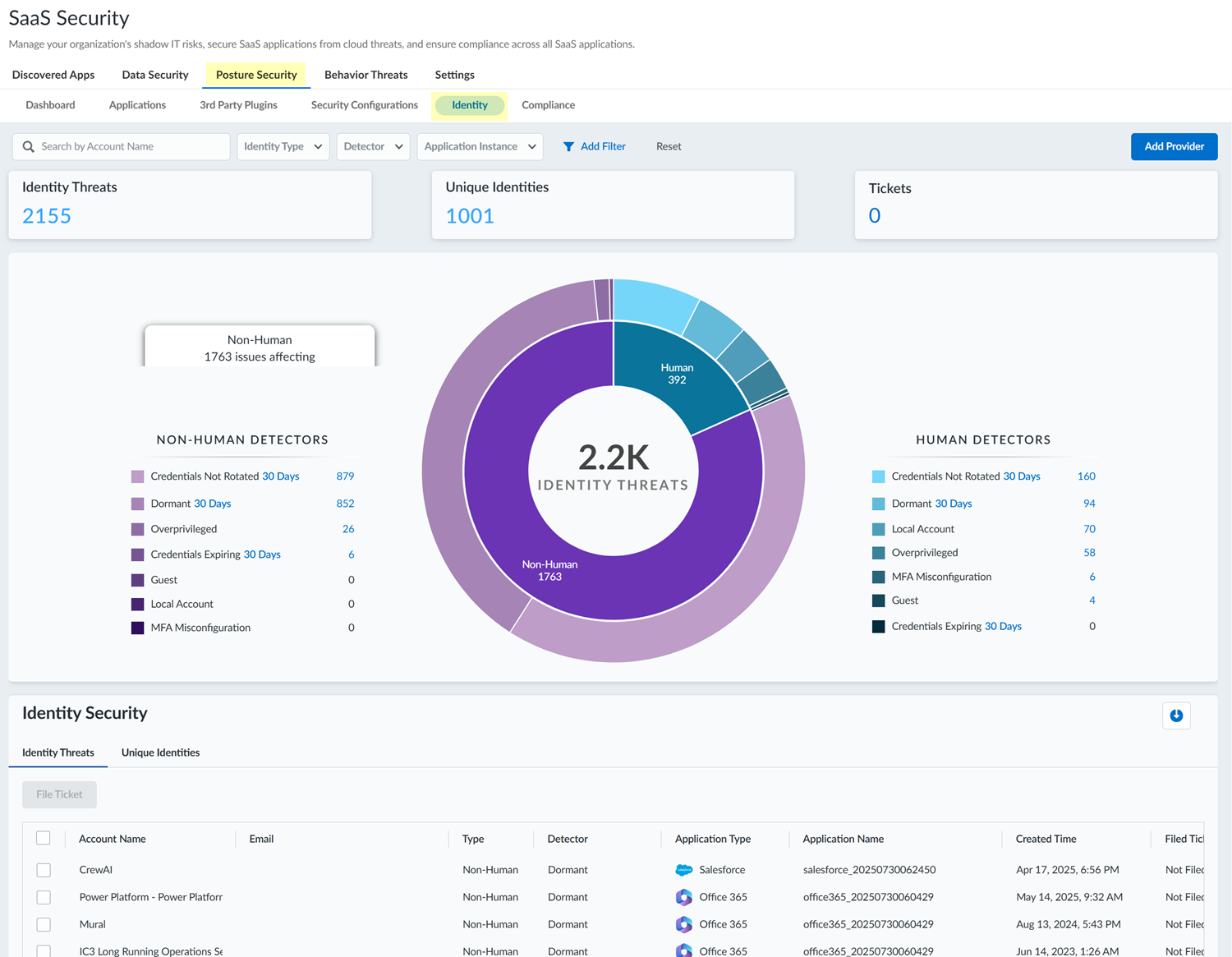
![]() SSPM supports identity scans for certain SaaS apps. If one or more of those SaaS apps were scanned, SSPM displays identity threats for those SaaS app instances. You can view a list of the SaaS app instances in the Application Instance filter list. To view a list of the SaaS apps that SSPM supports for identity scans, and to onboard instances of those apps, Add Provider.In the upper section of the Identity page, examine the overview of the identity threats that SSPM detected across all instances of the supported SaaS apps.This overview divides the threats into the threats detected for non-human identities (such as services that authenticate to an API by using a token or an API key) and human identities (accounts tied to individual people). For the non-human and human identities, the threats are further categorized by the types of threats (as indicated by the threats discovered by the different threat detectors).A donut chart represents all the detected identity threats, with slices of the chart representing threats for non-human and human identities relative to the whole. Additional slices of the donut chart show the percentage of different threat types detected relative to the whole. You can hover over the slices in the donut chart to display more details.In the lower section of the Identity page, view the information shown in the Identity Threats table, which lists the individual threats that SSPM detected.The table lists each threat that was detected for SaaS accounts. The table shows information about the account where the threat was detected. The account information shows the type of account (human or non-human) and the application. The Detector column shows the type of threat, as indicated by the detector name. Each entry in the table is a single threat, even if multiple threats were detected for the account. To view all the threats for a particular account, use the Search by Account Name filter in the upper-left corner of the Identity page.
SSPM supports identity scans for certain SaaS apps. If one or more of those SaaS apps were scanned, SSPM displays identity threats for those SaaS app instances. You can view a list of the SaaS app instances in the Application Instance filter list. To view a list of the SaaS apps that SSPM supports for identity scans, and to onboard instances of those apps, Add Provider.In the upper section of the Identity page, examine the overview of the identity threats that SSPM detected across all instances of the supported SaaS apps.This overview divides the threats into the threats detected for non-human identities (such as services that authenticate to an API by using a token or an API key) and human identities (accounts tied to individual people). For the non-human and human identities, the threats are further categorized by the types of threats (as indicated by the threats discovered by the different threat detectors).A donut chart represents all the detected identity threats, with slices of the chart representing threats for non-human and human identities relative to the whole. Additional slices of the donut chart show the percentage of different threat types detected relative to the whole. You can hover over the slices in the donut chart to display more details.In the lower section of the Identity page, view the information shown in the Identity Threats table, which lists the individual threats that SSPM detected.The table lists each threat that was detected for SaaS accounts. The table shows information about the account where the threat was detected. The account information shows the type of account (human or non-human) and the application. The Detector column shows the type of threat, as indicated by the detector name. Each entry in the table is a single threat, even if multiple threats were detected for the account. To view all the threats for a particular account, use the Search by Account Name filter in the upper-left corner of the Identity page.- To investigate a threat in more detail, click the View More link for the threat.If the Account Name in the table appears as a hyperlink, click the link to open an access graph, which shows the different SaaS apps that the identity can access. The access graph shows information, such as the SaaS apps that the user accesses through the identity provider versus direct login to local accounts. The access graph also shows SaaS apps that are accessed through non-human accounts that the unique identity created.In the lower section of the Identity page, view the information shown in the Unique Identities table.The table lists each unique identity that SSPM was able to discern from your identity provider or other sources. The Detector column shows the types of threats that SSPM detected for the unique identity across SaaS apps that the identity can access.When viewing either the Identity Threats or the Unique Identities tab, you can click the download icon to export a CSV file that contains the table information.Optionally, filter the information on the Identity page to show only the information that you're interested in.For example, you can filter the information by identity type (human or non-human), detector, or application instance. You can apply these filters using the Add Filter control, or by clicking on the relevant slices in the donut chart. To return to the full unfiltered view, Reset the filters.Investigate the accounts further and take action to resolve threats.For example, you might investigate dormant accounts to determine if you can delete them, or you might investigate guest accounts to ensure that their access to your resources is properly restricted. If SSPM is linked to an issue tracking system, you can create a ticket to resolve account threats. To do this, select one or more accounts names in the table and File Ticket.
Identity Threat Detectors
The Identity Security component has a variety of detectors for discovering specific types of identity threats, such as dormant accounts or accounts with unrotated credentials.The Identity Security component has a variety of detectors for discovering specific types of identity threats, as described in the following table. SSPM displays the detected threats on the Identity page.Detector Description DormantDetects accounts that have not been accessed for a specified period. Because the account owner isn’t logging in, they will be less likely to notice if the account is compromised. They will also not have received password expiration notifications or prompts to change their password. As a result, the account might have an old password that predates newer requirements for password length and complexity.By default, the threshold SSPM uses for detecting dormant accounts is 30 days. In the upper section of the Identity page, you can click on the current threshold value to reset it.For GitHub Enterprise accounts, SSPM determines how long an account has been dormant based on the last time the user performed certain Git repository activities. These activities include creating or deleting a repository, cloning a repository, pushing changes to a remote repository, or fetching changes from a remote repository.Credentials ExpiringDetects accounts whose credentials will expire within a set number of days. By default, the threshold SSPM uses for detecting expiring credentials is 30 days. In the upper section of the Identity page, you can click on the current threshold value to reset it.Credentials Not RotatedDetects accounts that have not had their credentials rotated within a set number of days. Account credentials include user ID and password combinations, as well as credentials for accessing APIs, such as API keys and OAuth tokens. Failure to rotate these account credentials can represent a significant risk to your organization.Passwords that are not rotated are more vulnerable to brute-force attacks, especially if the password predates enforced requirements for password length, complexity, and reuse. API keys that are not rotated increase the window of opportunity for bad actors to exploit leaked or compromised keys. Similarly, if the client secret of an OAuth app isn’t rotated, a compromised refresh token will enable a bad actor to continue to obtain valid access tokens.By default, the threshold SSPM uses for detecting non-rotated credentials is 30 days. In the upper section of the Identity page, you can click on the current threshold value to reset it.GuestA guest account is an account designed to provide external users, such as a partner or contractor, limited or temporary access to the SaaS application. Guest accounts enable you to collaborate with people who are outside of your organization. Although guest accounts are designed to give outside users access to your resources for legitimate purposes, they can represent a risk if their access isn’t properly restricted. For example, an external collaboration setting in Azure Active Directory might grant guest users the same access as members. Another Azure Active Directory setting might allow anyone in the organization to invite guest users, including guests and non-administrators.Local AccountLocal accounts are accounts that weren’t created through your identity provider. Local accounts are a security risk because the identity provider isn’t managing access for them. Because they have bypassed the identity provider, it's difficult to enforce security policy rules for them.The Identity component identifies these risky local accounts by comparing account information from the SaaS app instance with account information from the identity provider. For this reason, the Identity component displays local account information only if you have onboarded an instance of either the Microsoft Azure or the Okta identity provider. If the Identity component isn’t displaying this local account information, you can Add Provider and follow the steps to onboard Okta or Microsoft 365.In the upper section of the Identity page, the Identity Provider field shows the identity provider that the Identity component uses to detect local accounts. If more than one identity provider was onboarded, you can select a different one from this list. Selecting a different identity provider does not immediately refresh the information displayed on the Identity pages. The displayed information will be refreshed after the next identity scan completes.MFA MisconfigurationMulti-factor authentication (MFA) misconfigurations are users with no MFA or with weak MFA.If MFA enforcement policies are not configured for the identify provider, a user can access SaaS apps through the identity provider by using only one factor. If those credentials are compromised, there is no additional layer of security to prevent unauthorized access to their account. These users should enroll in a strong second factor for MFA.Weak MFA refers to users who are enrolled in one or more additional factors for MFA, but whose factors are not resistant to phishing, social engineering, or interception attacks. The weak MFA factors include factors such as email verification and short message service (SMS) verification.Weak second factors offer less protection than stronger factors, such as biometric login or a hardware key. If MFA enforcement policy rules on the identity provider are not configured to prevent sign-ins using only weak factors, then the account can be more easily compromised. These users should enroll in a strong second factor for MFA.OverprivilegedOverprivileged accounts are accounts that have elevated, administrator-level access to the SaaS app. For some administrators, this level of access might be legitimate. However, for other accounts, the elevated privileges are not needed for the human or non-human entity to complete their tasks. To follow the principle of least privilege, you should investigate accounts with elevated permissions to verify that they have only the permissions necessary to complete their work.